⊹ 9998. CCIE SGT ⊹
CCIE SGT
SGT BRKSEC-3690 – PDF
SGT BRKSEC-3690 – Notes
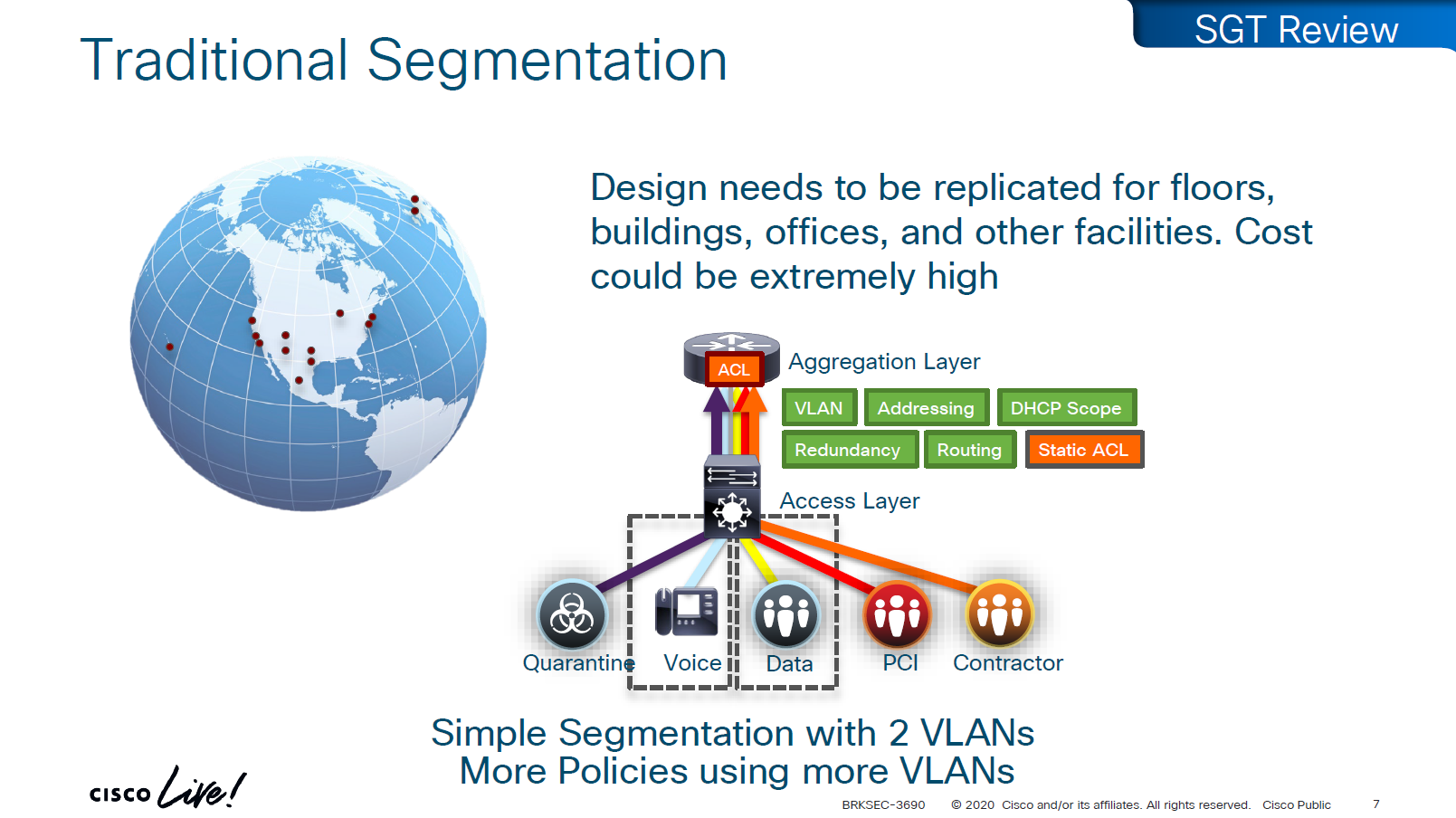
A Security Group Tag is a 16-bit label attached to traffic to identify the security group or role of the source (e.g., Employees, Guests, IoT Devices).
SGTs are used in Cisco TrustSec / SD-Access environments to create role-based access control policies that don’t rely on IP addresses.
SGT is not just used for SGACL or filtering only, because it is a tag on IP packet, this is also being used Policy based routing and also QoS – QoS based on SGT
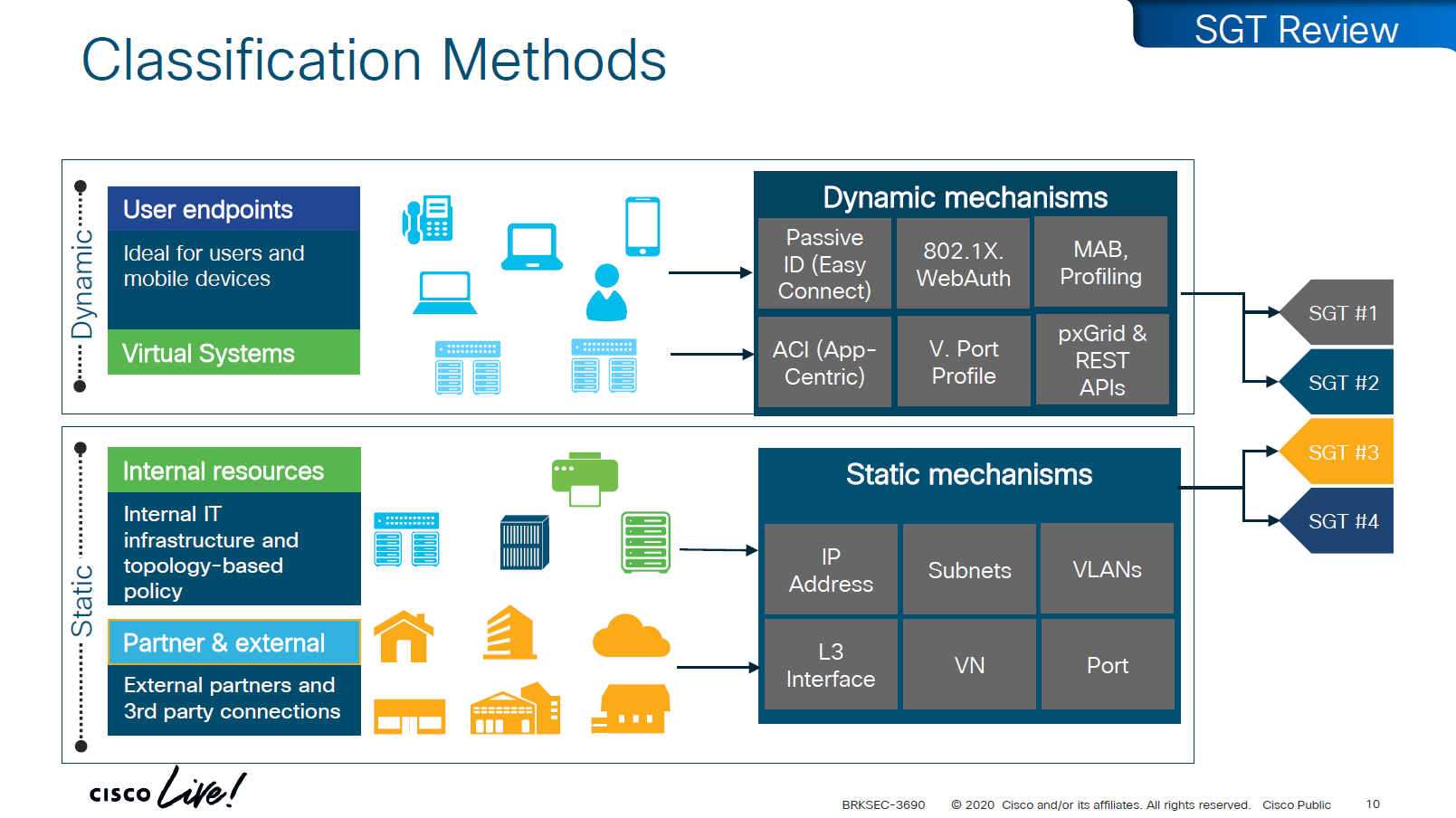
There are 2 ways of classifying the devices in an SGT group
- Dynamic
- ISE
- 802.1x
- MAB, profiling
- pxGrid, Rest API
- ACI
- ISE
- Static
- IP address
- Subnets
- VLANs
- L3 interface
- VN
- Port
Traffic or packets are classified and tagged on ingress into the network which is access layer and filter on the egress of the network
Because classification and tagging on ingress of the network and filtering on egress of the network, it is very important to have tags pushed or transport the tags to all devices on the network
There are 2 ways to do that,
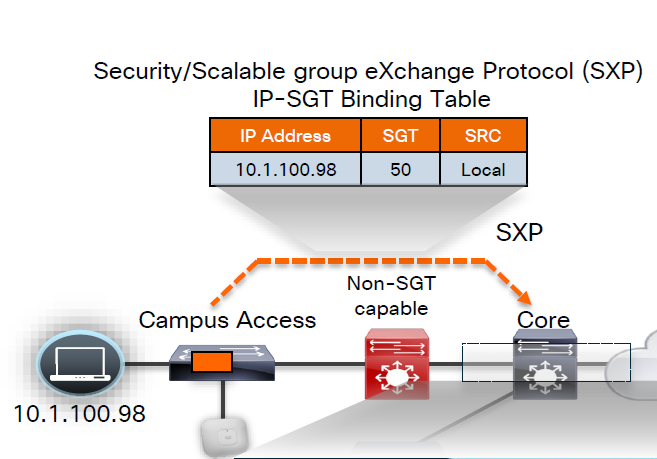
No packet tagging, but use control plane, using SXP (Scalable Group Exchange) protocol to teach foreign devices about the IP to SGT over TCP control plane
This way frame or packet has not been modified or tag is not added in the IP header, and target device also understood the tag that applies to that traffic.
SXP can be activated on a headend only that makes drop or allow policy decisions, it does not have to be applied on all intermediate nodes in the topology hop by hop unlike QoS that requires every hop to do QoS enforcement.
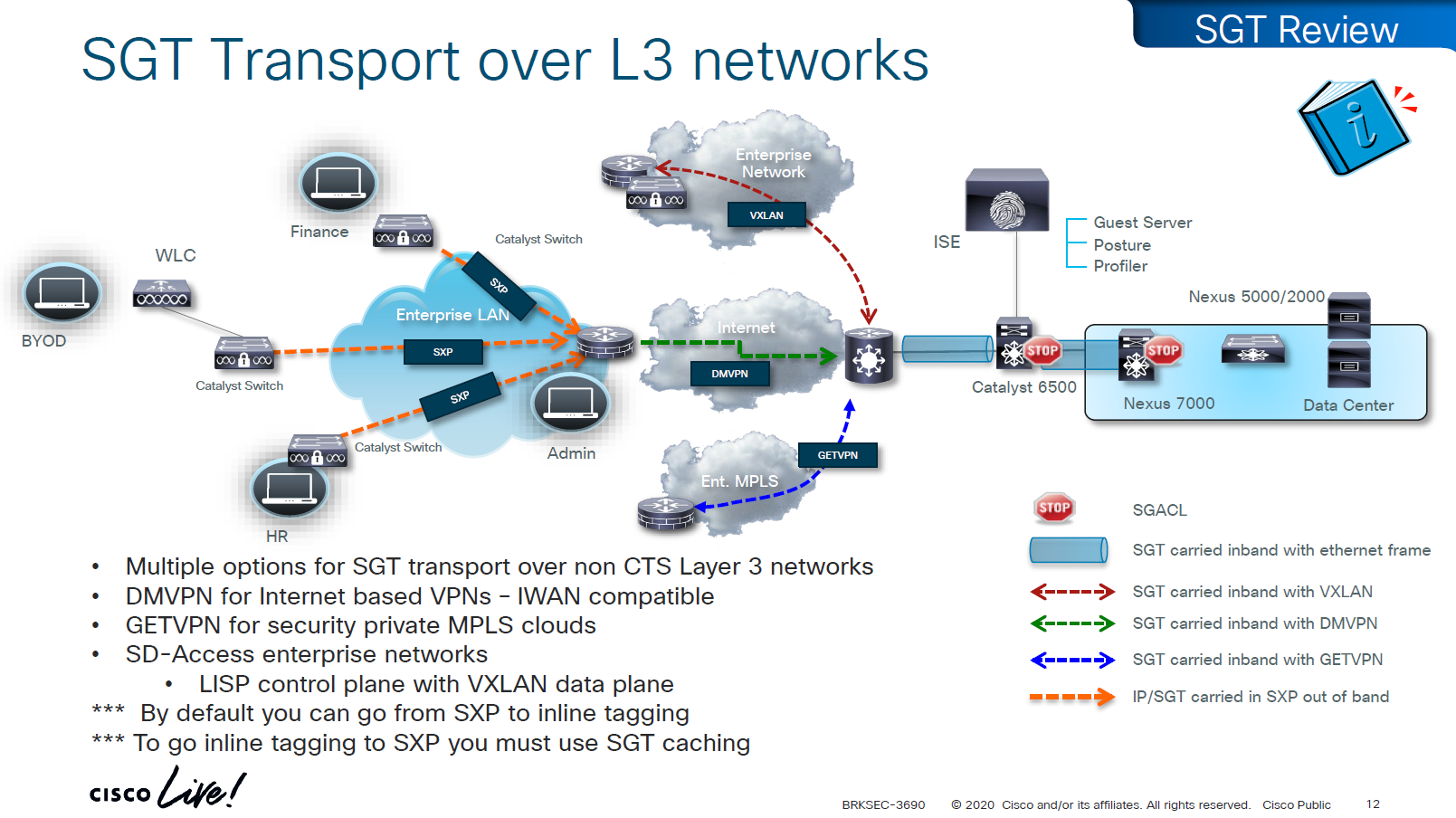
other one is inline tagging
with inline tagging we also have some encryption options such as IPSec or MACsec to prevent people from messing with tags
By default you can go from SXP to inline tagging
to go from inline tagging to SXP you must enable SGT caching
All firewall vendors like Firepower, Checkpoint, Fortigate and Palo Alto, do support pxGrid based implementation for SXP, pxGrid is a publisher and subscriber model where publisher can push information down to subscribers for different topics and one topic can be SXP protocol that has a table that contains IP address to SGT tag mapping

SXP can be activated on a headend only that makes drop or allow policy decisions, it does not have to be applied on all intermediate nodes in the topology hop by hop unlike QoS that requires every hop to do QoS enforcement.
End to end SGT work flow
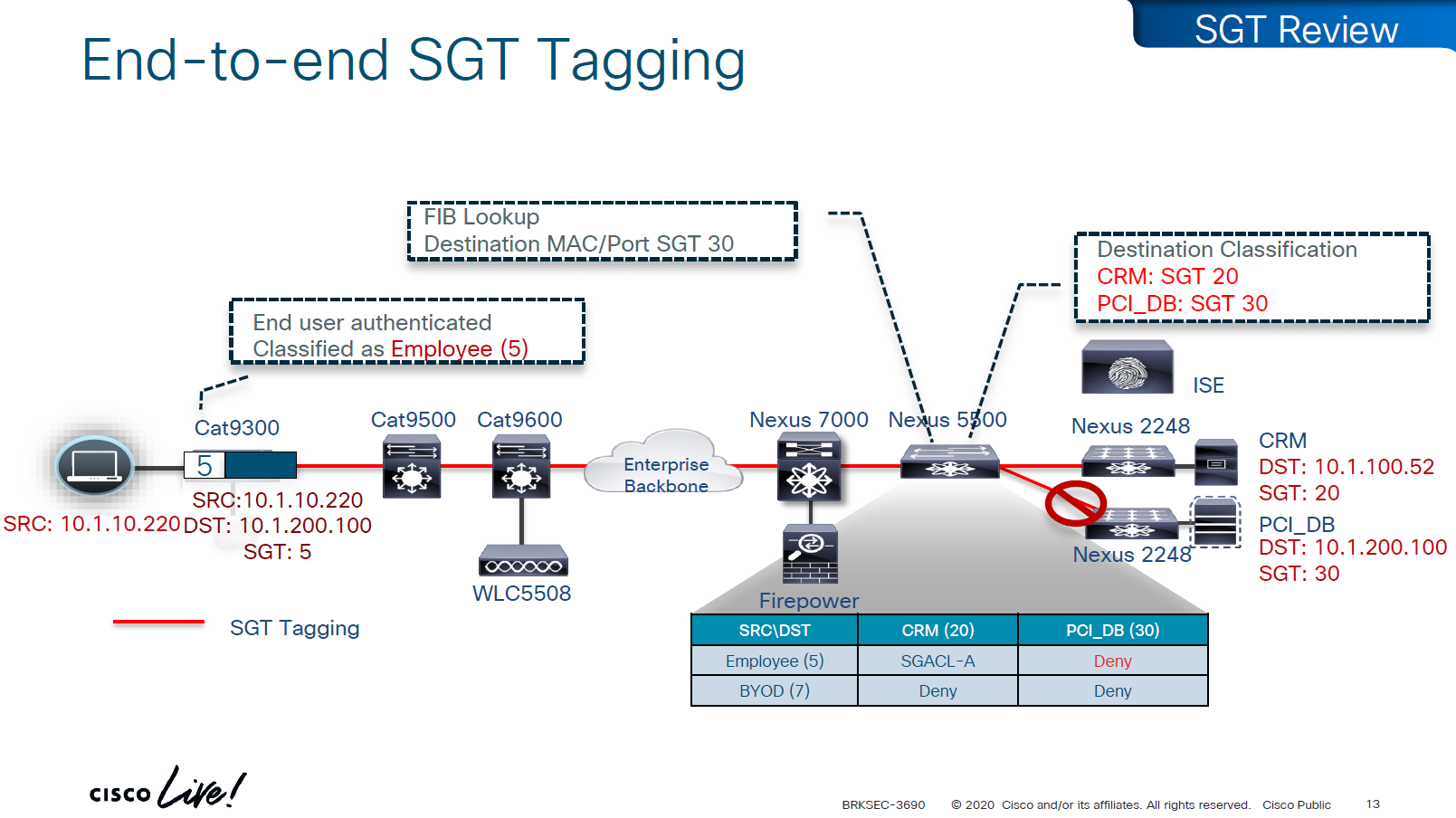
Filtering with SGTs is always done on egress or last switch where destination is connected,
this is because we do not want to overload our access layer switches with all policies and track of all devices connected on the network ahead of it
This optimizes and keeps memory size smaller for small devices,
Access or ingress will only add tag to the traffic and send,
it is the destination switch after it has received the packet,
checks the SGT on the packet – if not on packet, derive SGT from the SXP learned IP to SGT table.
Find out the mac / destination port + the SGT assigned to host on that port – if not assigned on port derive from SXP learned IP to SGT table for that IP
then egress switch will take a policy decision and drop or allow based on policy,
Switches in aggregation or core can be set to look at the destination IP and determine the SGT from SXP learned IP to SGT tag before sending packet out towards destination, this is to drop traffic in core rather than egress
on destination egress or core a log is generated for all deny or drops, if all switches in network point to central logging server, these logs can tell us about the dropped traffic

This shows the policy matrix and how switches that have hosts with certain SGT only pull “columns” from matrix for those hosts only, as soon as a host is connected that has a new SGT, policy column for that SGT is downloaded on the switch, this is very on demand like fashion where switch does not have to download all the policies of the policy matrix and be light weight
Be careful of platform support for SGT when implementing to make sure that platform does support trustsec for all actions such as Classification, Propagation and Enforcement

on 3850 as a client we are setting SXP peer (almost like a routing peer) to send it the IP to SGT mappings (local mode)
9K is SXP receiver only using “mode local listener” instead of a speaker
show cts role-based sgt-map all details
! check mappings on 3850 switch
show cts sxp connections brief
! check peersin above “show cts role-based sgt-map all details” – we can see the one attached host got SGT tag of 6:Full_Access and source is “LOCAL”
similarly not shown here but WLC also a client that got SGT of 3:BYOD and at the bottom we run “show cts role-based sgt-map all details” command on core C9K and we can see both tags learned from SXP (3850 and WLC). Aggregation layer is building table automatically as devices are learned from Access layer devices
Enabling SGT/SGACL Enforcement
Before SGT/SGACL can be enabled on Cisco devices, make sure that SGT tag for network devices TrustSec_Devices is assigned by default to the network device and make a policy that always allows TrustSec_Devices is always allowed to speak to ISE and infrastructure, why is that needed? because there is a default rule in policy, if it is set to deny then all control plane traffic from device to ISE will be dropped
There was a case once when 2000 switches disappeared from the network, that customer did not have network device SGT like TrustSec_Devices above, they also did not have policy against it to make devices from TrustSec_Devices speak to infrastructure servers SGT, third thing is that they turned on default deny rule in policy
Do not turn on that default deny unless you are really sure that every protocol and everything has been taken care off as it will start dropping the Unknown / untagged SGT traffic as well
Unknown SGT refers to the default tag used when a packet, user, or device does not have a valid SGT assigned. In Cisco TrustSec, this value is typically SGT = 0 and is considered unclassified or unauthenticated traffic. Whenever Unknown SGT of 0 is seen on traffic or host, it means following:
-The client is not authenticated via 802.1X/MAB/web-auth
-Even if authenticated from ISE, there was no SGT in Auth Z results from ISE
-The TrustSec policy mapping isn’t configured
Most TrustSec deployments deny or restrict traffic with Unknown SGT:
- Best practice: Block or isolate Unknown to → Protected traffic in policy matrix
- Allow Unknown to → Internet (e.g., guest networks) in policy matrix
Assign TrustSec_Device to network devices

SGT CTS “peer authentication” between ISE and Device is done through EAP-FAST as PAC file is downloaded on the Network device, PAC which is used in case you want password less certificate like authentication without having certificates. This is called PAC bootstrapping, this is used to download policies, SGACLs and SGT tags then later SXP is used to send or download the SGT to IP mapping separately.

look at send from ISE PSN and test connection button
If there are large number of policy changes, having CLI access from ISE is much faster and better at times, for example there was a customer with 200 x 200 policy matric, it took almost 4 hours to finish the update, it was changed to CLI for all devices and all updates completed in 30 mins, if it is small incremental updates, RADIUS CoA is fine
This device ID is the hostname of the device and password corresponds to command
cts credential id DEVICE-ID password PASSWORD! this is done in non config , enable mode
device>cts credentials id <DEVICE-ID> password <PASSWORD>
show cts credentials
show cts environment-data
show cts role-based permissionsSetting long timers make sure policy is refreshed on devices annually and also only when there is an explicit change in policy

Why the pac key appears under the radius-server host command?
Even though the PAC is used for TrustSec (CTS/NDAC) and not for normal RADIUS authentication, the PAC is delivered through RADIUS using cisco’ vendor attribute, PAC exchange is not a standard RADIUS authentication — it is a special RADIUS message (Cisco-vendor attribute) used only for TrustSec device bootstrapping that is why it is configured under RADIUS server configuration block along with RADIUS shared secret.
cts authorization list <AUTHZ_List_Name> is the list of ISE RADIUS nodes that are running TrustSec
Why Cisco did it this way
Cisco chose to reuse the RADIUS channel rather than invent a new protocol:
- RADIUS is already required for 802.1X authentications
- Switches already have reachability to ISE
- The PAC exchange can ride over the same transport (UDP 1812/1645)
So the PAC bootstrap process piggybacks on RADIUS → therefore, the PAC key configuration lives inside the radius-server settings.
Full configuration of ISE RADIUS Servers with PAC
! Enable AAA
aaa new-model
! Define ISE as a RADIUS server (auth/acct) and include the PAC bootstrap secret
radius server ISE1
address ipv4 10.10.10.10 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
key RADIUS_SHARED_SECRET
pac key RADIUS_PAC_SECRET
!
! send vsa or vendor attributes in RADIUS authentication request
radius-server vsa send authentication
! (Optional) put servers into a group and set a source interface
aaa group server radius ISE-GRP
server name ISE1
ip radius source-interface Vlan10
! CTS/NDAC: define the authorization list used for policy download only (not tags - tags are pulled before SGACL or policy is pulled) - as clients connect with new SGT , more policy columns are pulled
cts authorization list CTS-AUTHZ
! 802.1X + CTS use the RADIUS group
aaa authentication dot1x default group ISE-GRP
aaa authorization network CTS-AUTHZ group ISE-GRP
! aaa authorization network command is usually used to allow on network or authorize audience or entity authenticated through network ports and this config says that authorized list of server (which are allowed to make CLI or COA changes) will be downloaded from ISE-GRP
! which makes it look like this
aaa authorization network ( CTS-AUTHZ ) group ISE-GRP
aaa authorization network ( cts authorization list ) group ISE-GRP
! Define credentials for EAP-FAST I-ID, these are configured under enable mode and not in config mode
cts credential id DEVICE-ID password PASSWORD
! enable 802.1x on system level
dot1x system-auth-control
! enable CTS enforcement
cts role-based enforcementSXP does not carry SGACL policies.
SXP only carries IP-to-SGT mappings
SGACL policy travels via DTLS tunnel established using PAC.
Policy matrix is translated or converted into bunch of SGACLs and then sent out to devices
Sequence and use of PAC:
1. Authenticate the switch to ISE for TrustSec
2. Receive the PAC credential
3. Establish a secure, encrypted control channel DTLS for SGACL policy download
It is sent through the PAC → NDAC → Secure DTLS Trust Tunnel that is established after the PAC is provisioned
Switch proves identity to ISE to download PAC -> RADIUS
Policy download (SGACLs and SGT tags – “TrustSec Bootstrapping”) -> PAC established DTLS (UDP)
IP-to-SGT sharing between devices -> SXP (TCP)


First thing to notice in this output is the Local Device SGT that is assigned to network device, any control plane communication from this device will be assigned SGT
Then coming below we can see 3 TrustSec ISE servers are set as servers for downloading SGT tags and SGACL policy (but not SGT to IP mappings which are downloaded over SXP)

We define more tags in ISE, in above picture we can see ACI EPGs (contracts) defined as tags and this is through automation , automatically created through API
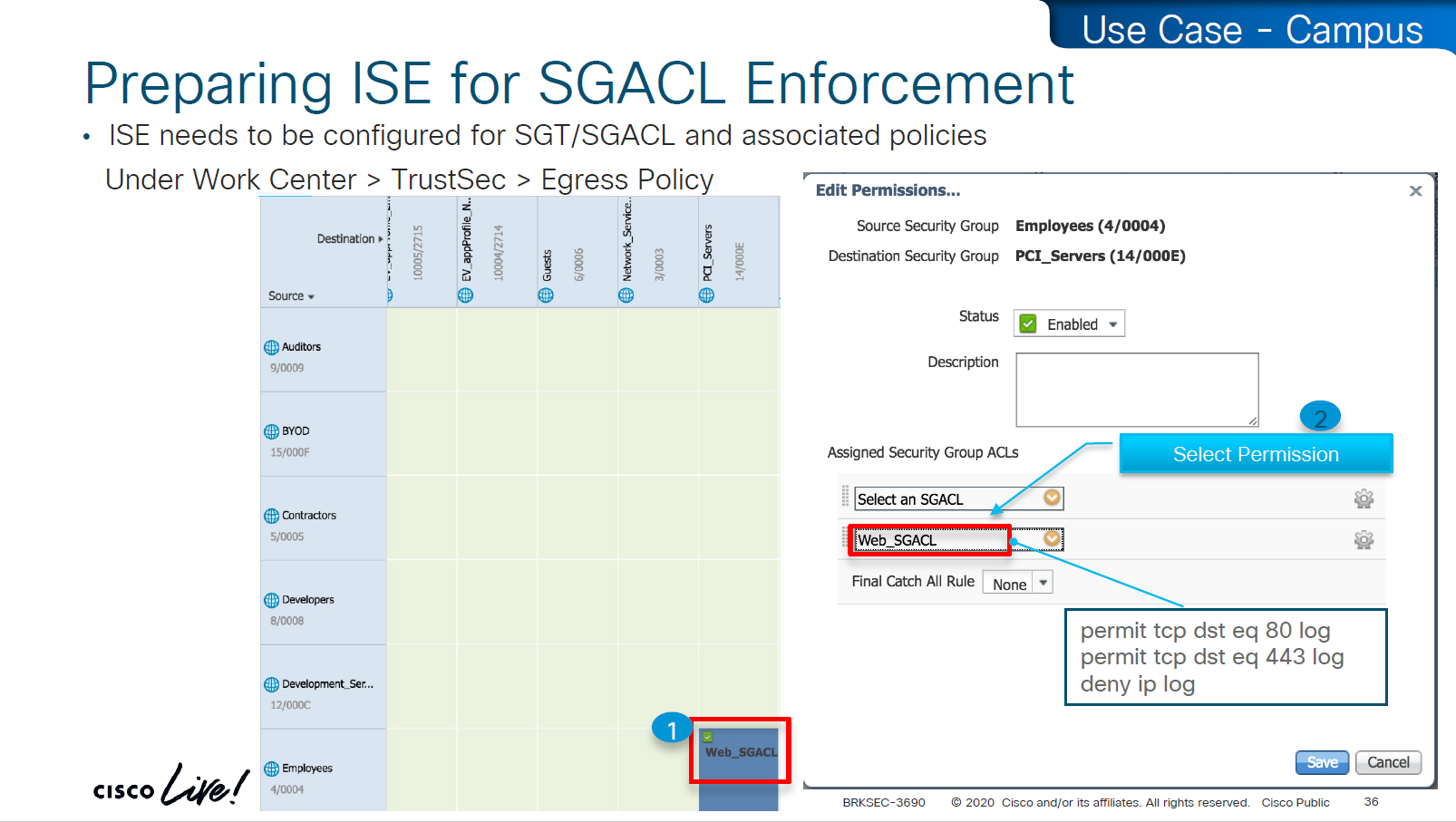
These are stateless ACLs unlike firewalls, this is exact filtering as described ACEs
but best thing about these ACEs is there are no IP addresses
One thing to notice in above screenshot is ability to define multiple ACLs in a single cell of the policy matrix but this is turned off by default as it is not supported by all devices yet because WLCs and Nexus only support single ACL for an SGT and DGT filtering
Only IOS XE switches are supporting multiple ACL per cell

above we can see manual IP to SGT map, which can also be pushed from ISE via CLI or from ISE via SXP
Even if switch has policy matrix table downloaded, and switch also has all the SGT tags, switch will not enforce on traffic unless command is “cts role-based enforcement” is defined
Second command allows us to enable on per VLAN, this is very significant because we can enable SGT enforcement incrementally on VLANs

environment data is SGT tags
policy is the policy matrix

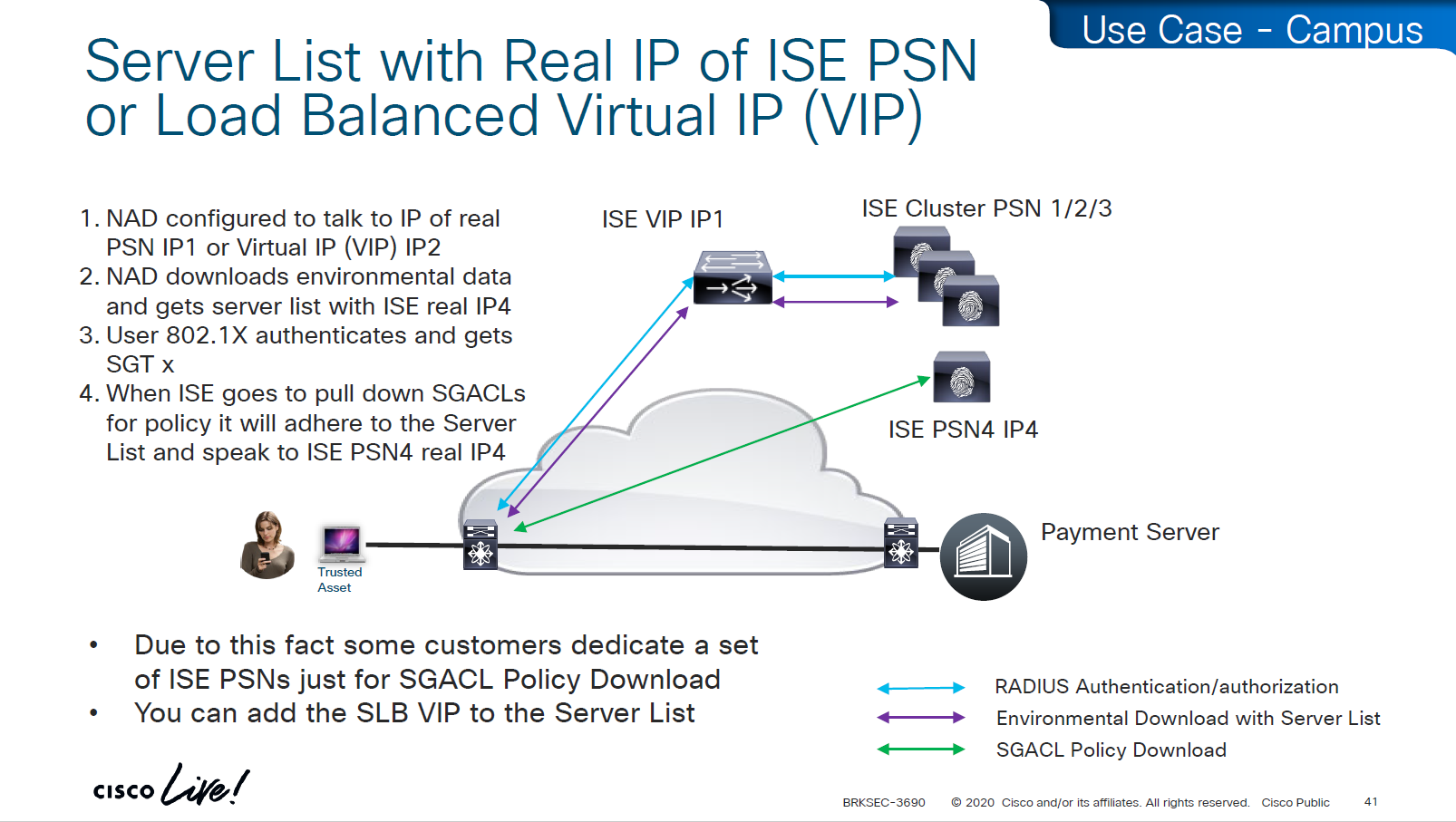
As we can see that RADIUS flow is different
“Environmental Data download + Server list” is different flow before SGACL policy is downloaded
SGACL policy download is from the server list, server list was fetched with environment data

This was done because in peak times when RADIUS servers are busy it can be too much load to download the SGACL policy over same ISE PSN nodes and it is better to download over dedicated ISE TrustSec PSN nodes

in above screen shots dynamic author (RADIUS servers allowed to do CoA) are defined
-PAN should be defined for SGT related flows
-PSNs should be configured for 802.1x / MAB
In older versions of ISE, clicking on Deploy is not enough, there is a confirmation icon on top that needs to be click and confirm, only then ISE notifies all switches that there is a change and download the new policy

There is a policy validation button that runs this command “show cts role-based permissions” and validates that ISE has same policy as devices and if there is anu mismatch or issue then an Alarm is generated from ISE


SGACL denies will show as log, and you will see that logging hits are shown as well which means that if there are a lot of logs then number of hits accumulated will be reported under logging_interval_hits and log will be generated, but in some cases auditor will come in and say that they need to see a log for every drop and allow, and at that point we need to understand that this is a switch and not the firewall, with SGACL enforcement it is not possible to get log for every hit

show cts role-based counters
! shows * to * default rule
! also shows from and to columns
! SGACL is done in hardware, unless needs punting
! for example TCAM or hardware is full, log in the end of ACE , makes SW counter increment otherwise concentrate on HW-Denied and HW-Permitted columnsSoftware denies and software permits are for to the box traffic or traffic destined for the switch, including the DHCP and ARP permits will also increment the Software counters, SGACL enforcement is in hardware
One of the examples of confusion with ping is that people test access control by pinging the switch SVI and say why is the hardware counter not increasing, it will be denied in software SW-Denied, the thing with SVI ping is that it is going up through software control plane to the CPU and then responding (punted to CPU)

Wireless APs do “enforcement” with SGACLs

TrustSec implementation in wireless does follow the same principal of tagging on ingress and filtering on egress (APs)
APs do the filtering also on egress in wireless to wireless communication, that confuses people as they see SGACL download on WLC but they do not see permit or deny logs in WLC CLI, it makes sense to check the WLC but enforcement for wireless to wireless traffic is being done on AP for scaling reasons otherwise WLC will be overwhelmed as WLC can do enforcement for wireless to wired communication
Ingress AP will tag the packet and send it across the WLC over CAPWAP due to central switching and egress AP will do the lookup for SGT of the destination client using client table and perform policy enforcement based on that
Skipped Nexus 7000 SGT Considerations

Common issues


SGT trustsec relies on IP device tracking
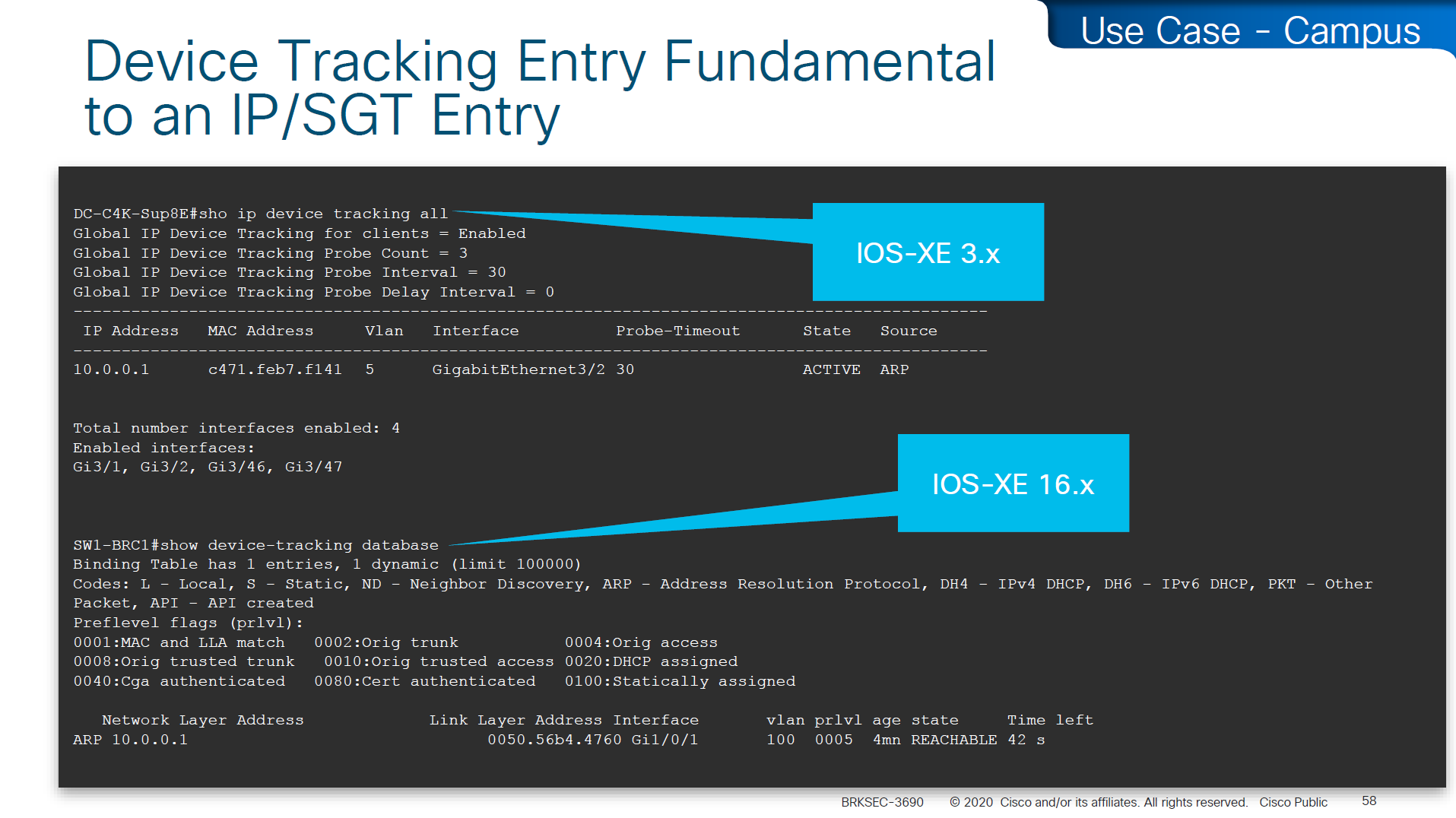
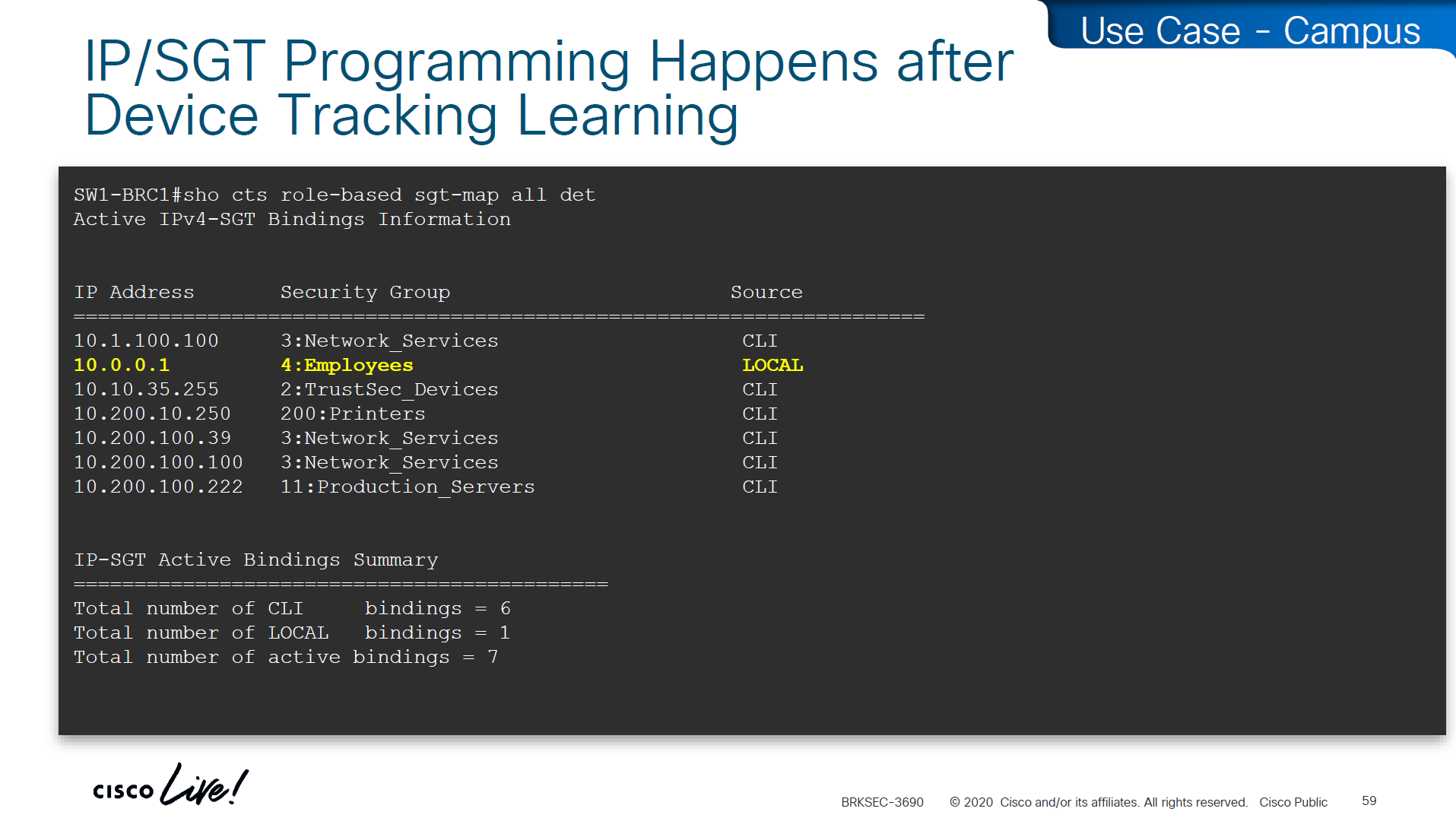
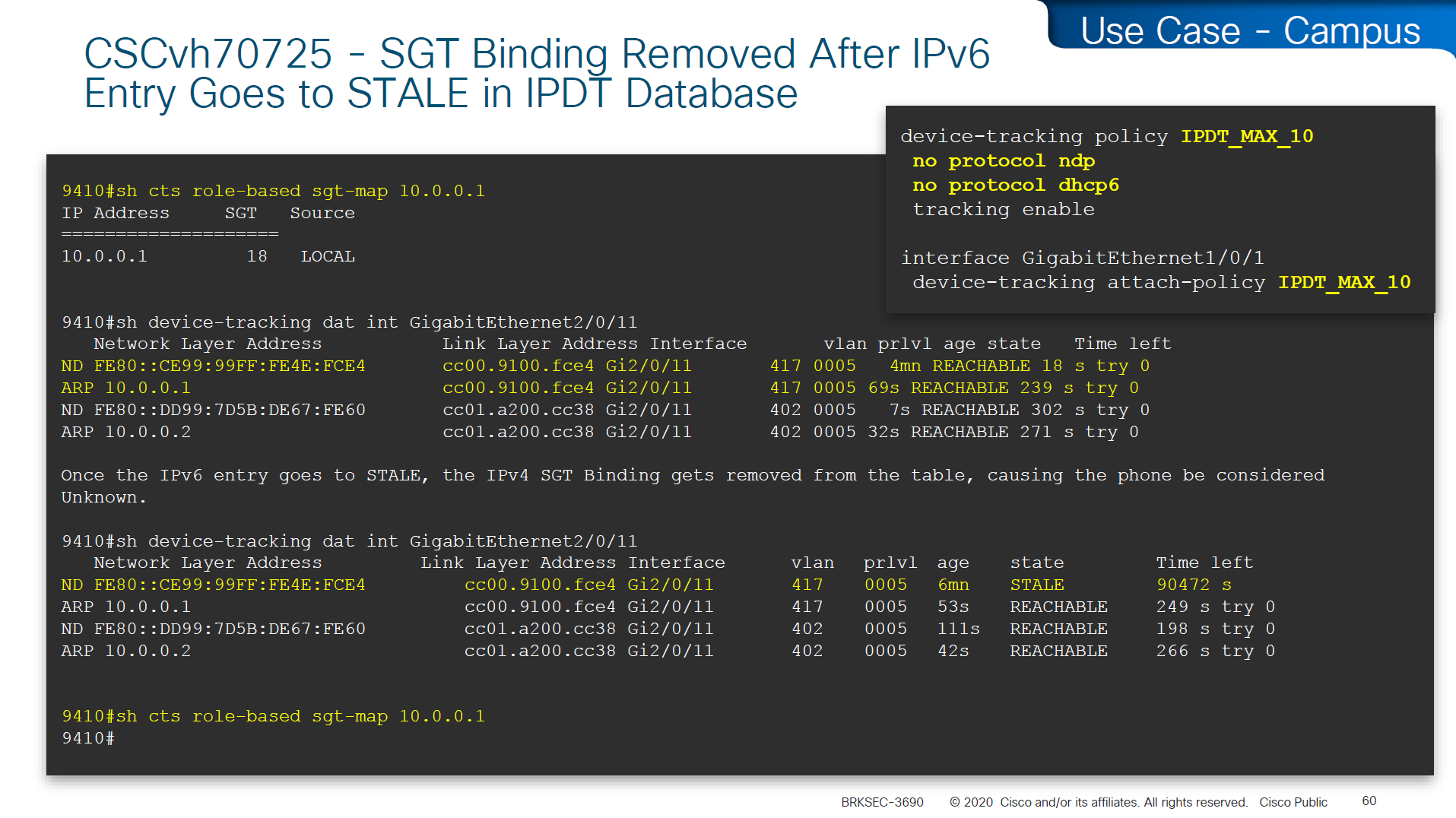
In case you have SGT disappearing from host, then check if this bug is in effect and usually happens on older unpatched code, the workaround was to turn off ndp (which is IPv6 ARP mechanism) tracking from IP device tracking and also turn off dhcpv6 tracking

in case SGACL download is not happening we need to check following:
Make sure pac is present
show cts pac allMake sure AAA servers are marked alive
show aaa servers Make sure device can reach ISE
show cts environment-dataCheck ISE to make sure SGACL is formatted properly
Make sure there are no errors in device-tracking as whole solutions rides on device-tracking to work
Sometimes bad implementation of SDWAN can cause fragmentation of large packets and sometimes that can cause ISE to device download of SGACL of DTLS (PAC based) to break for large packets causing “partial download”, that is why it is so important to first test for fragmentation over greenfield or brownfield deployment and also test large elephant connections with large packets – on the side note large elephant connections over IPSec based tunnels are heavy on platform’s ability to encrypt large traffic
So if you see partial download of SGACL, then always check for fragmentation issue, because by default for this pac based DTLS connections DF bit is set and routers from all vendors do not like DF bit
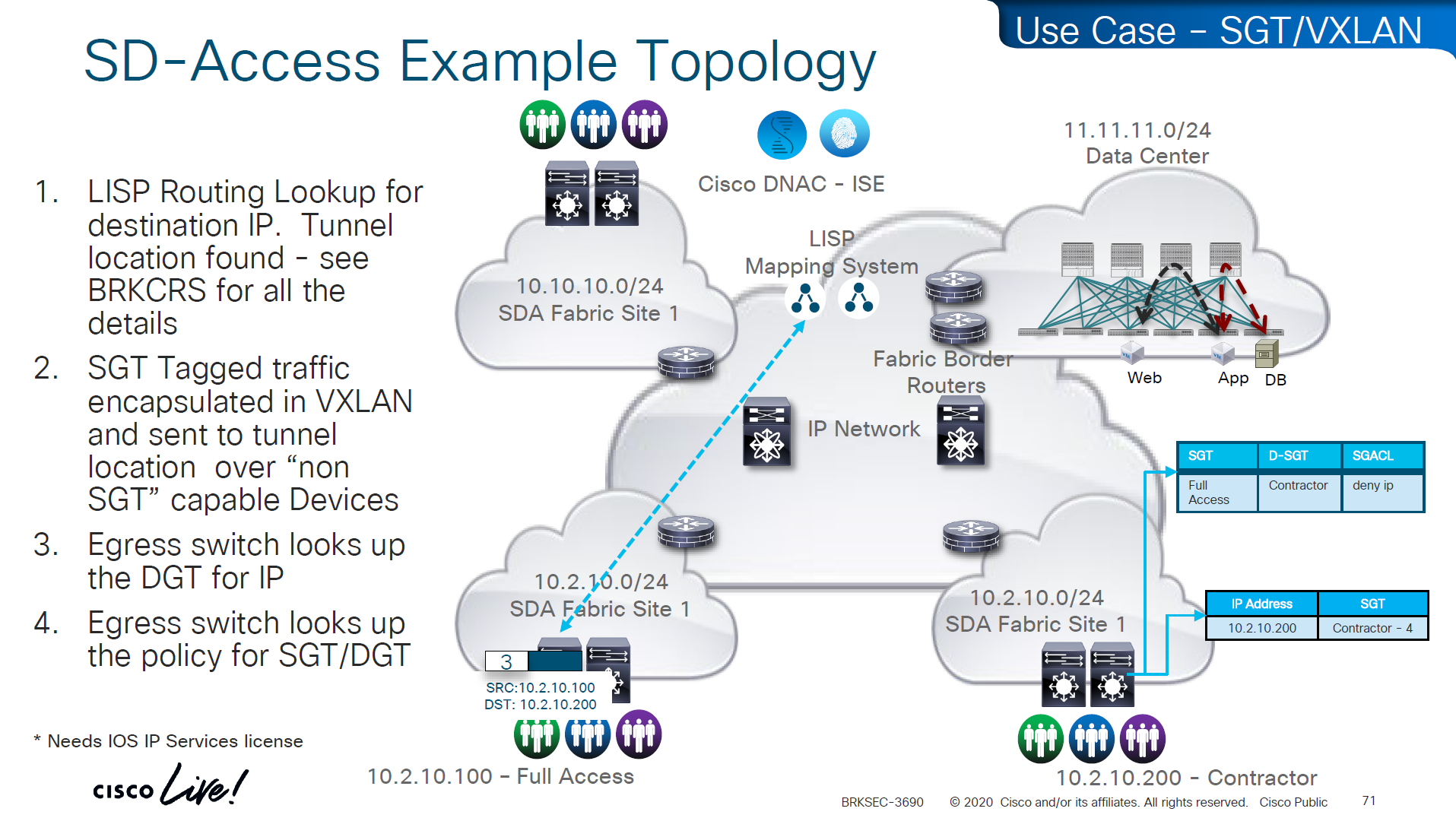
Software Defined Access (SD – Access) – SGT/VXLAN

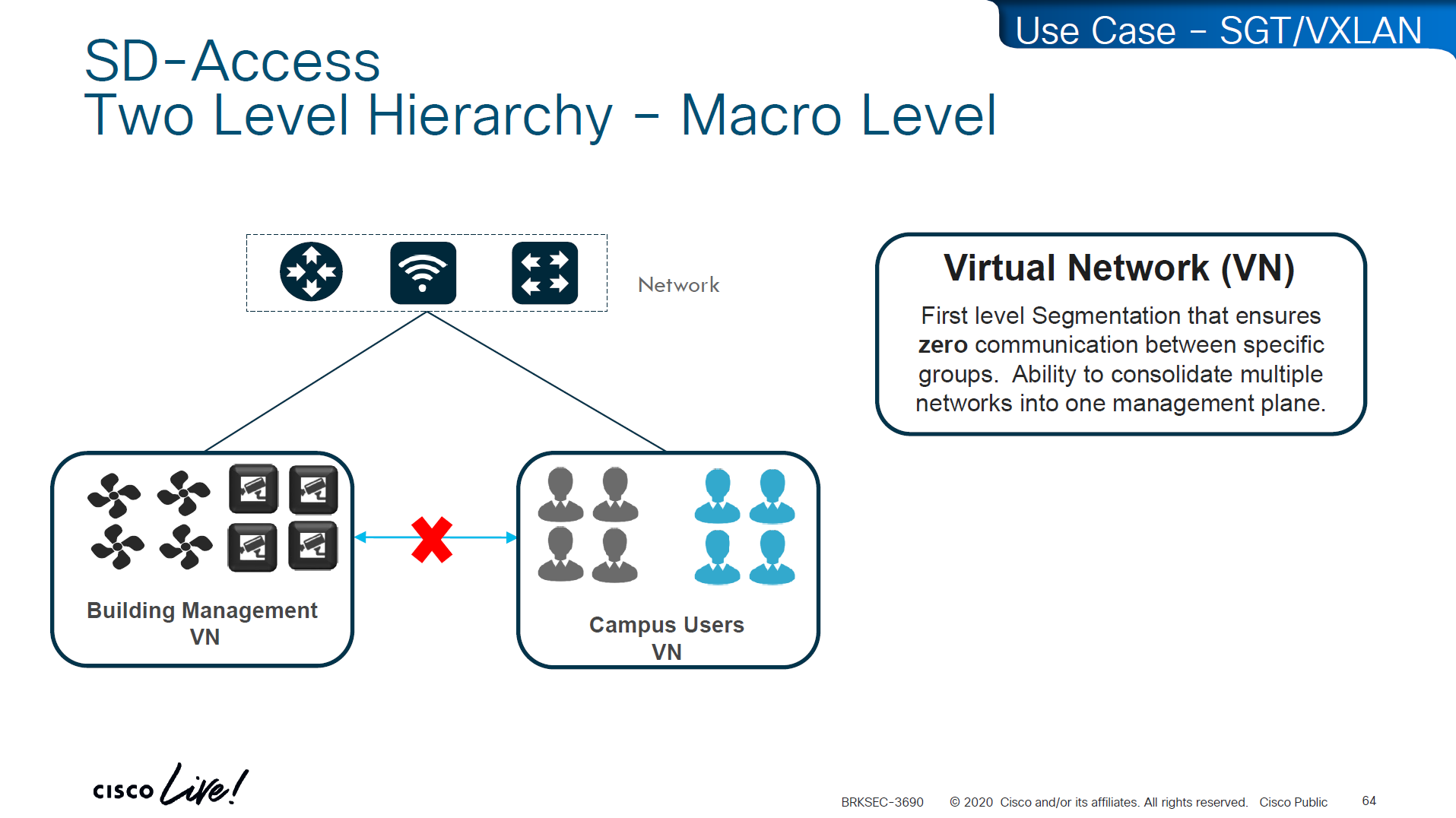
These SDA VNs are VRFs but these are campus wide VRFs,
Macro Level segmentation is devices of different management domains go in their own VN
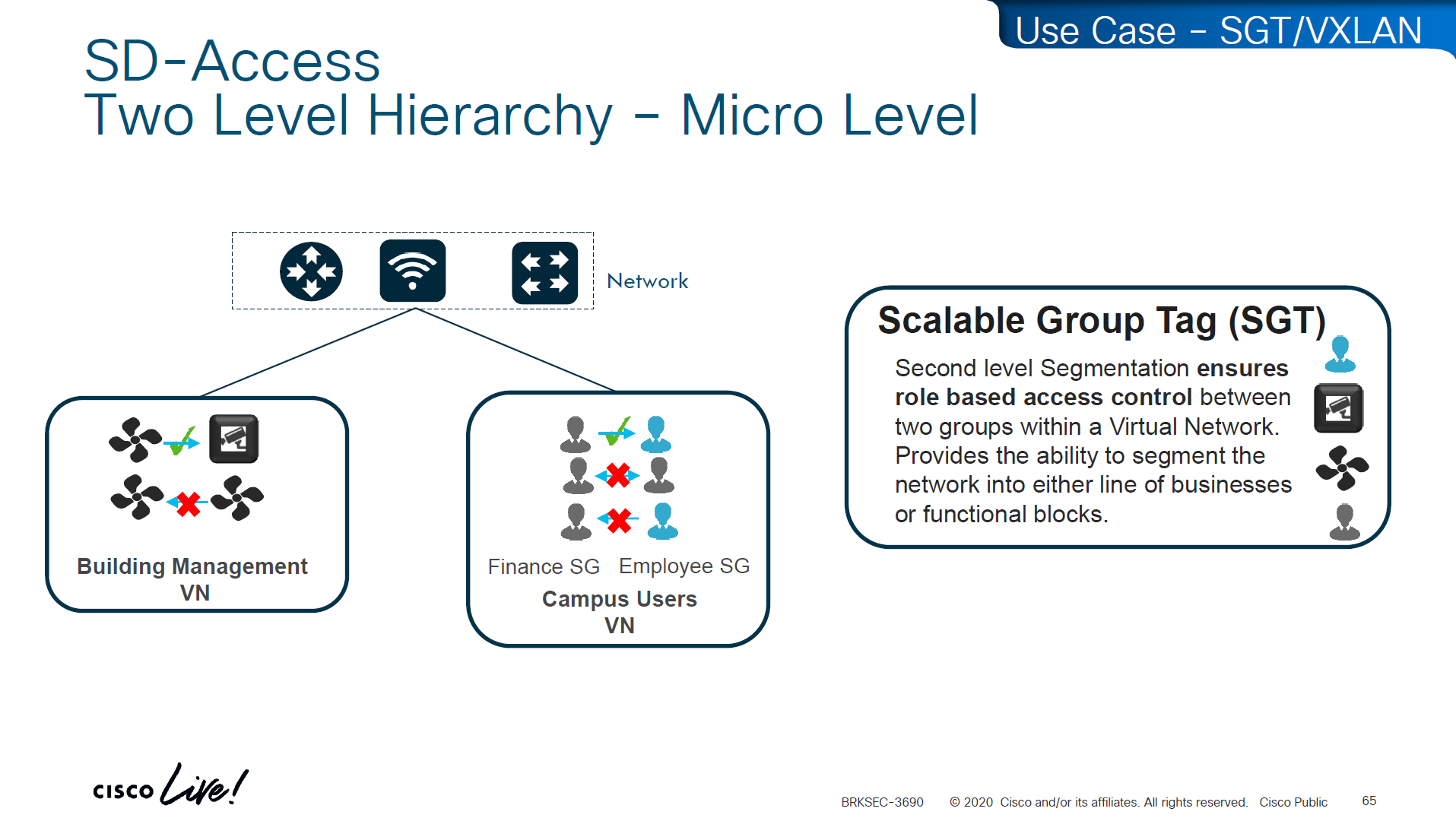
Micro Segmentation is used for access control within the VN
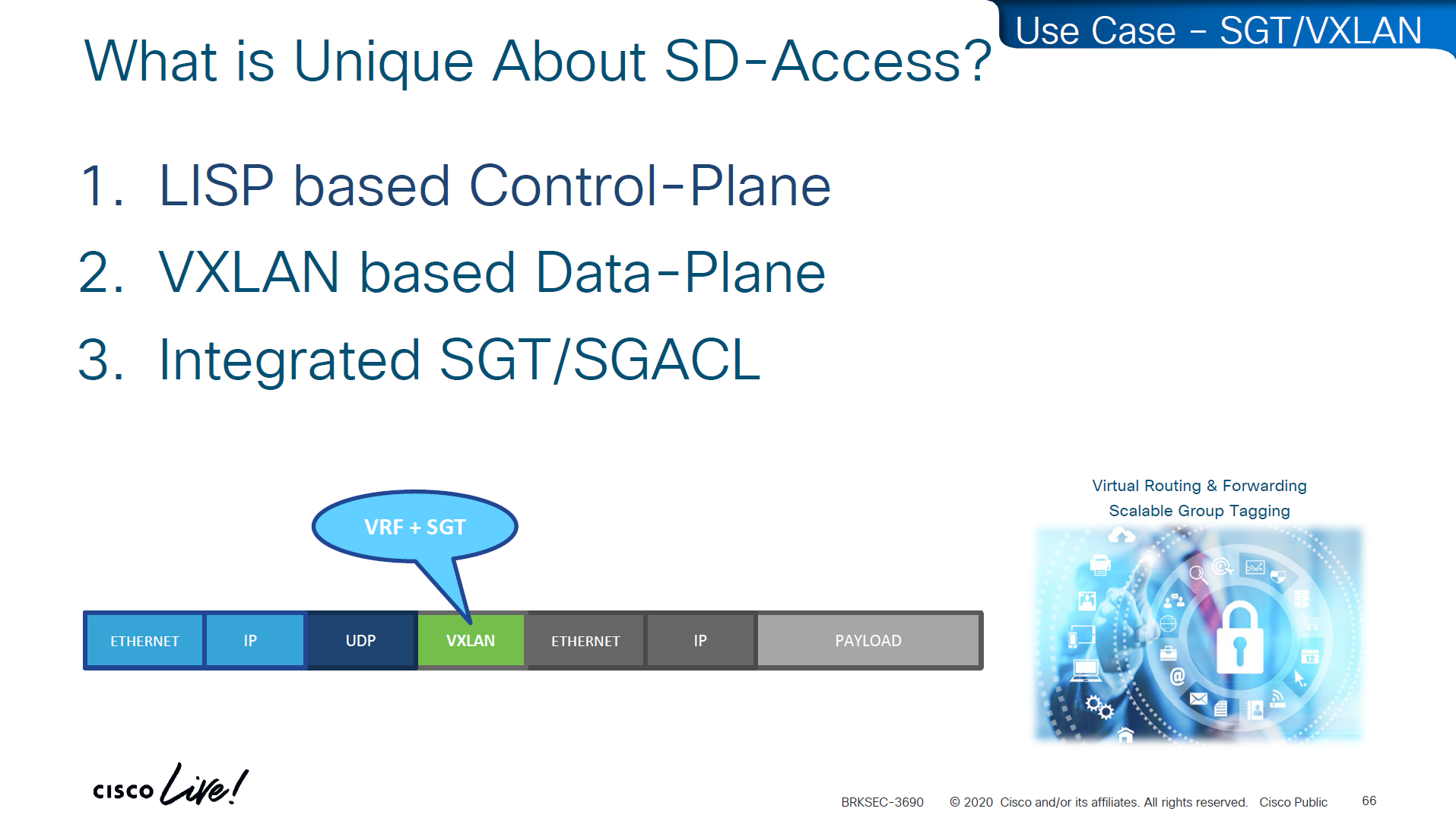
LISP is another great optimization at the access layer and it reduces or optimizes the routes by only installing /32 host routes on access layer switch to which its connected hosts are initiating connections to and from, access layer no longer needs to maintain the large routing tables, LISP installs routes in VRFed routing table of access switches
VXLAN encapsulates the whole ethernet frame, eats up or carries the whole frame and then VXLAN is carried inside UDP and then IP header and then ethernet frame
VN and SGT are carried inside the VXLAN header
The SGT (Security Group Tag) is not added to the original inner IP packet.
It is carried only in the VXLAN header as metadata, and in order to use SGT capabilities outside of the network with Cisco gear we can use TrustSec which uses SXP and with other vendors we can use PXGrid

Policy matrix is created on DNAC and then pushed to ISE , ISE then pushes the SGT environment data (SGT Tags and Trusted Server list) over TCP, SGACL using NDAC over PAC based DTLS and then finally IP to SGT mapping on border nodes using SXP?


ACL or contracts are defined in badge color cells

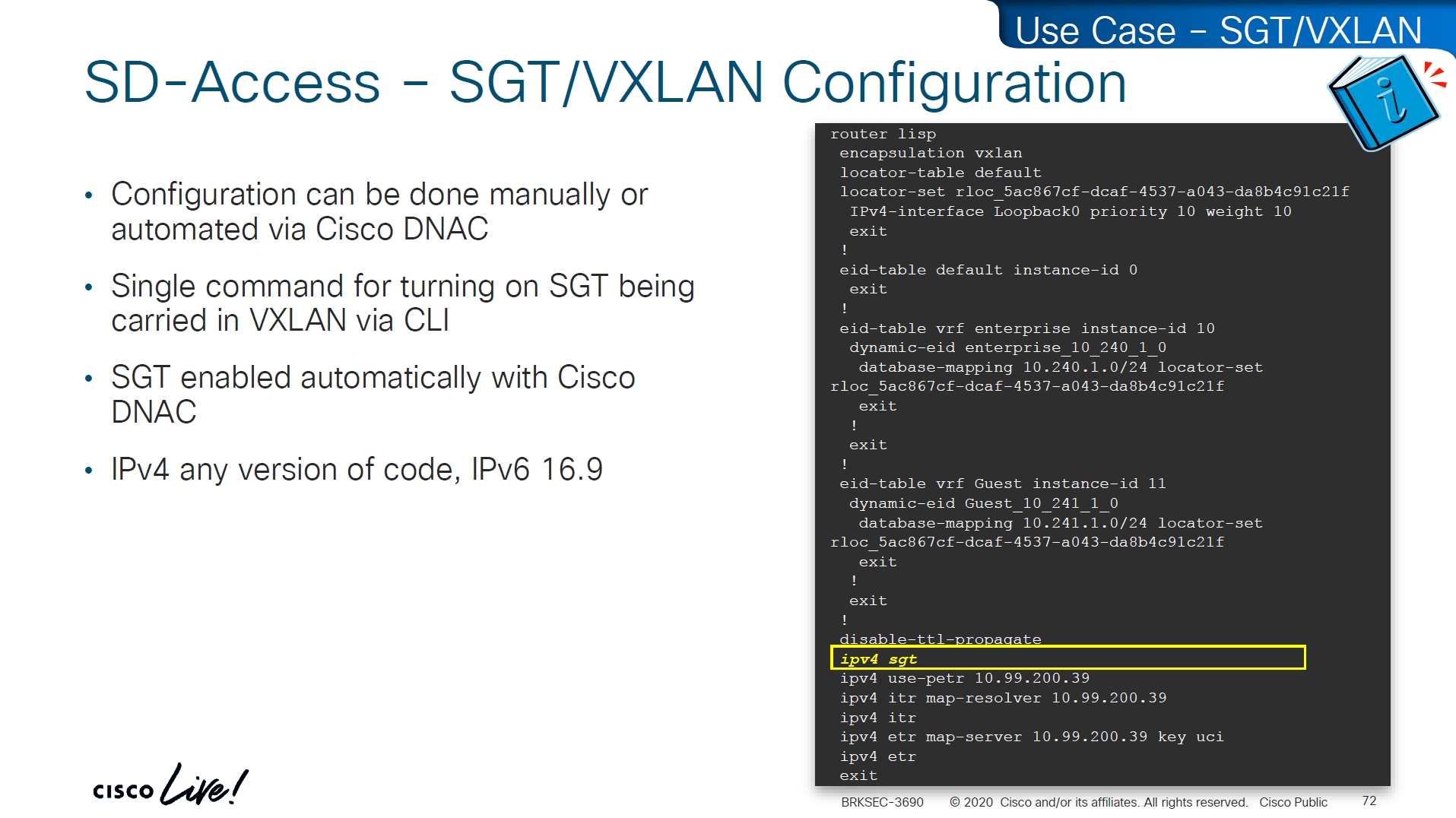
This is how it is enabled inside LISP
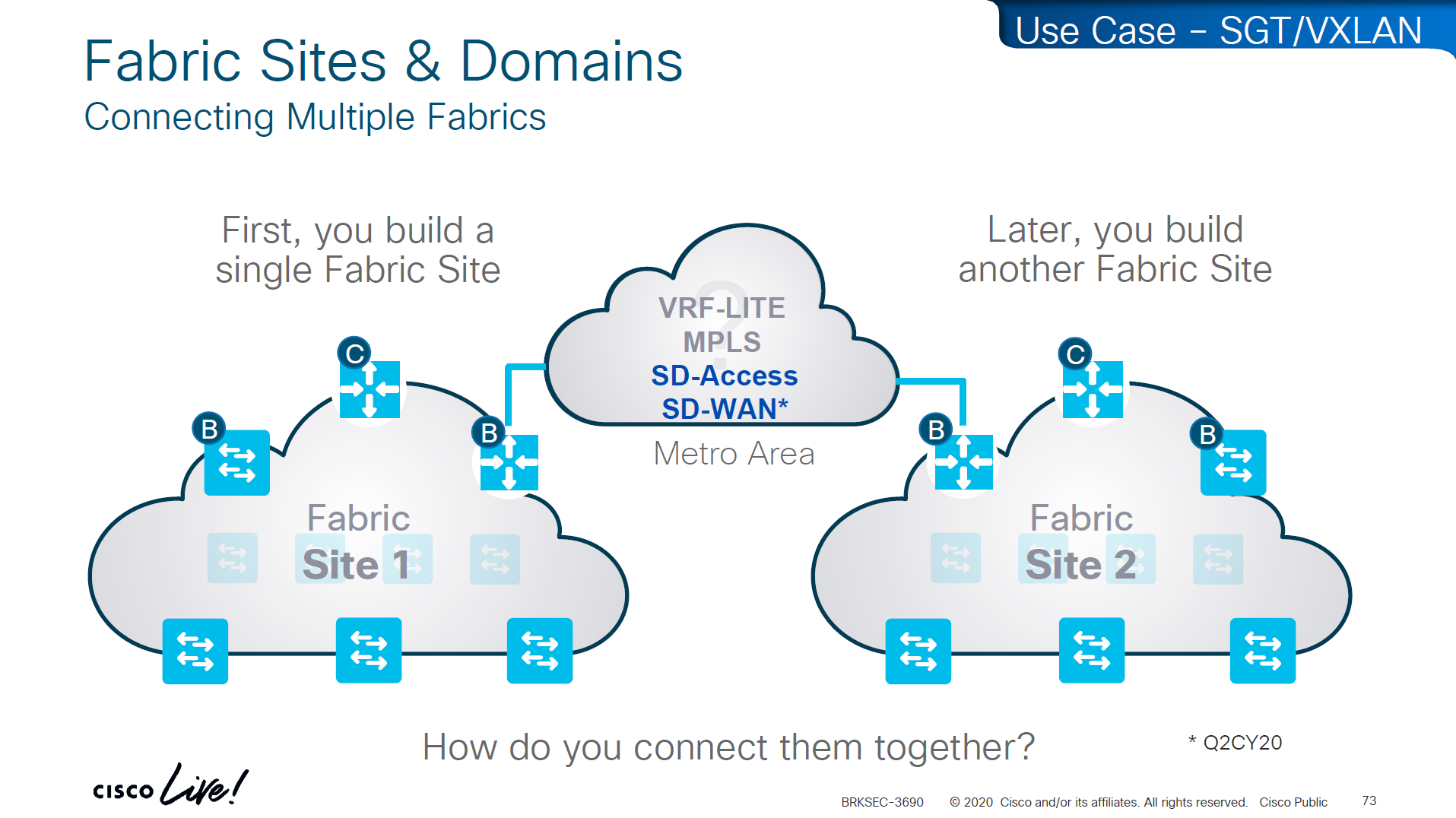
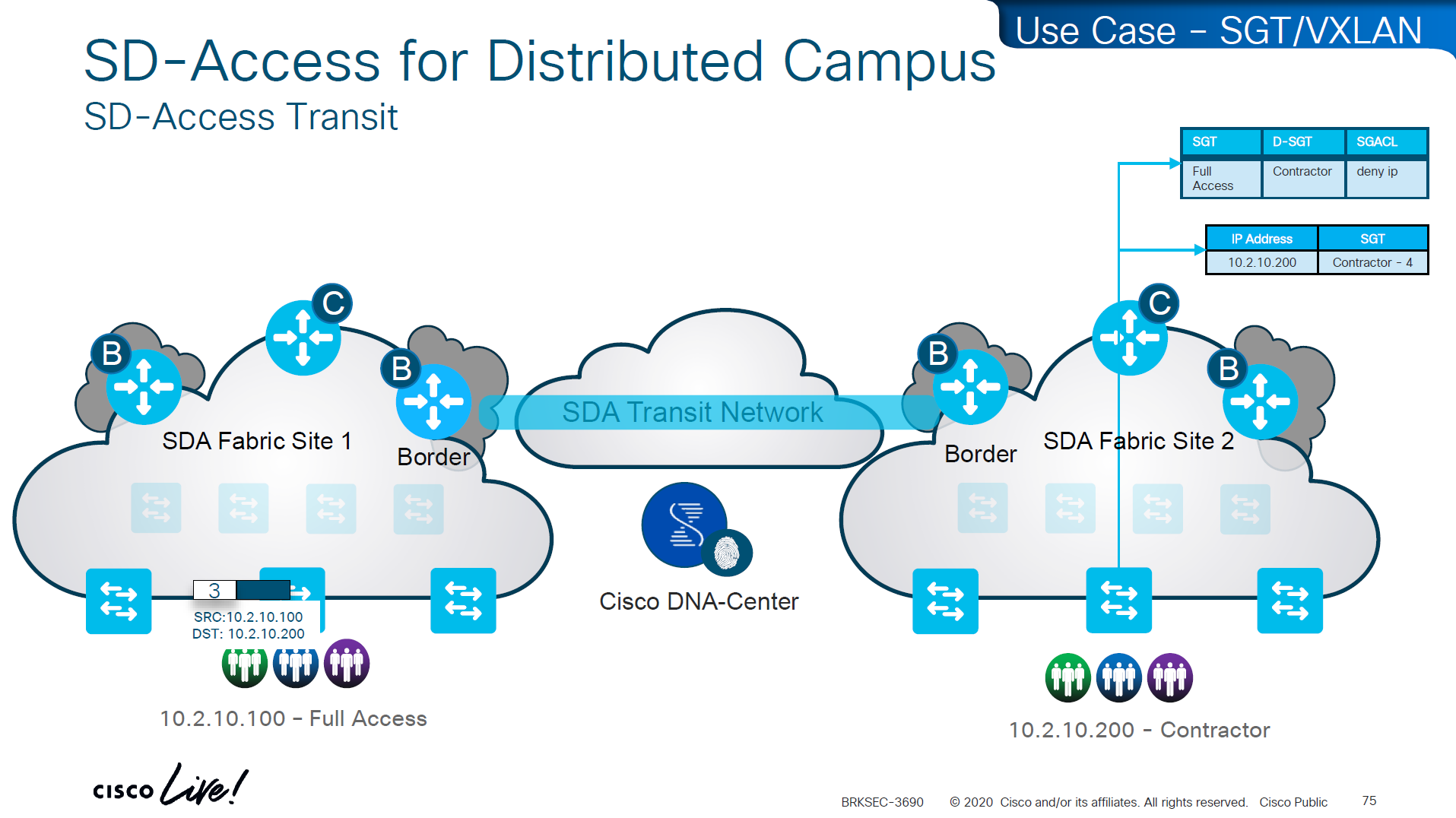
If we have SD Access transit or SDWAN, we can carry SGT to other fabric sites

SDA transit uses LISP as control plane between borders of both fabric sites
and then on data plane we have VXLAN header that crosses between fabric sites
but in order to accommodate the VXLAN header we will need 1588 or better 1600 MTU
Skipped Firewall Integration with SD-Access

Skipped Meraki and 3rdParty Interop

Use Case Review -WAN


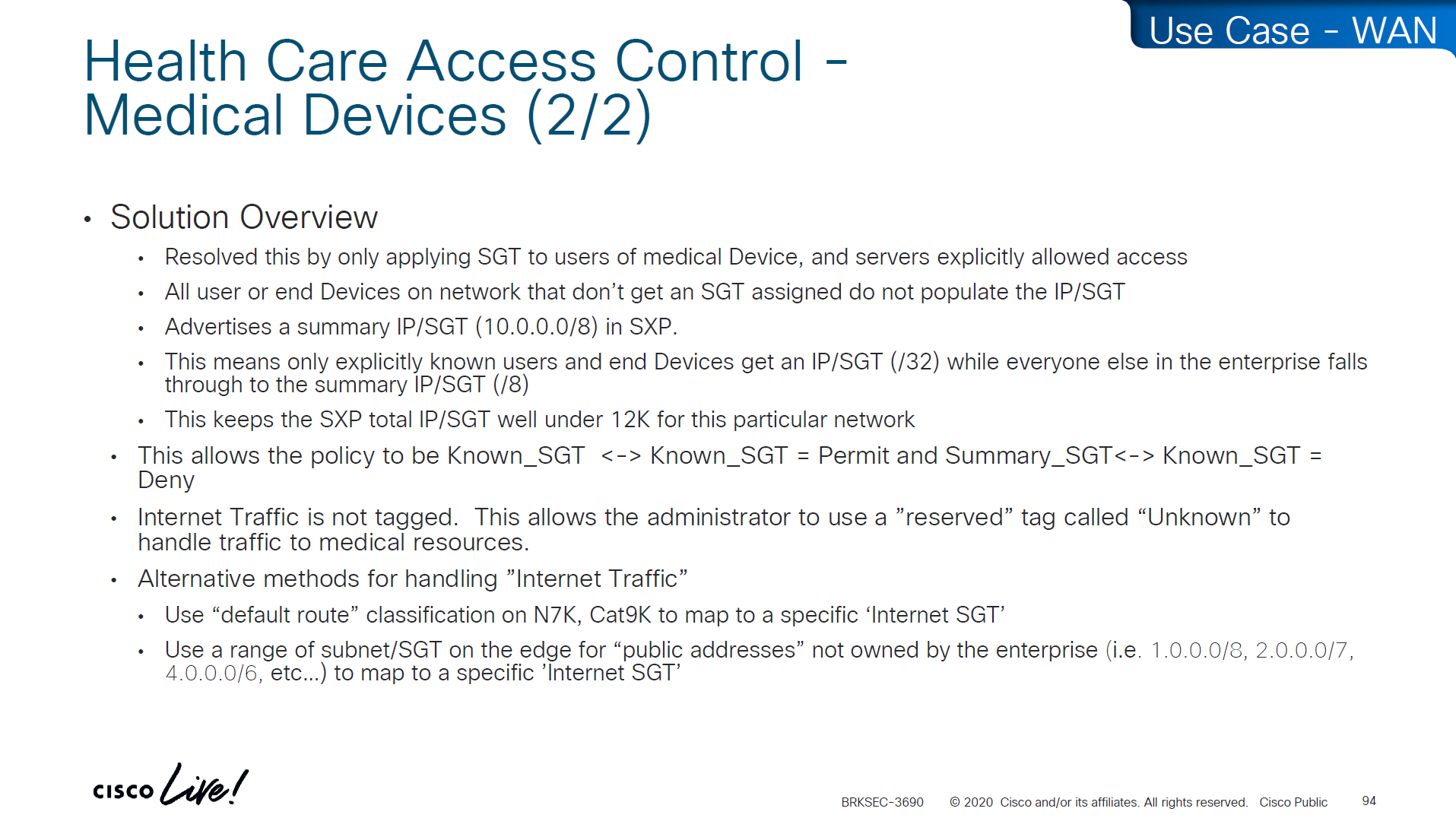
-medical devices and servers are assigned SGT and allowed to speak to one another
-Summary SGT of 10.0.0.0/8 in SXP for all users and devices in 10.0.0.0/8 space and this keeps the SGT under 12K
-Create a Policy Matrix that has Known_SGT <-> Known_SGT permit
-Create a Policy Matrix that has Known_SGT <-> Summary_SGT deny
-For Internet traffic default route is tagged as Internet_SGT
-above Internet_SGT leaves reserved tag called Unknown to handle traffic for medical devices that are not tagged
SXP Reflector Like Design

in above SXP connections, if one device speaks (has a speaker role) IP to SGT mapping then on the other end if there is a listener it will listen and learn the IP to SGT mapping and if a device listens (has a listener role) then on SXP connection it can learn IP to SGT mapping from a speaker
once a new mapping of IP to SGT is learned by aggregation Listener, it “speaks” those mapping to all the listeners

Above shows Medical_device <-> Medical_server allow
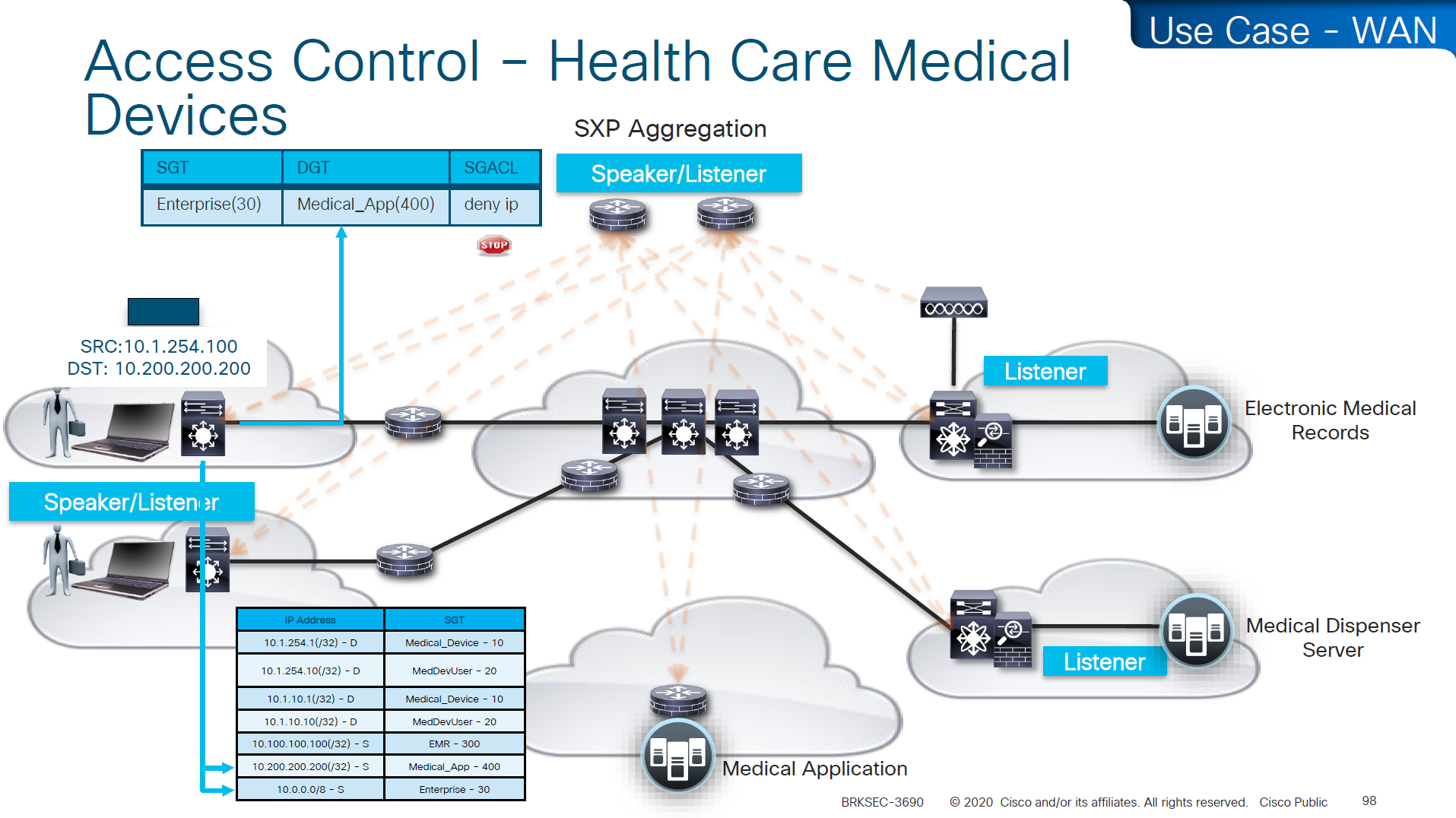
Above example is the source on 10.0.0.0 network that has fallen on 10.0.0.0/8 SGT of Enterprise and is trying to speak to Medical_device and by policy that is denied

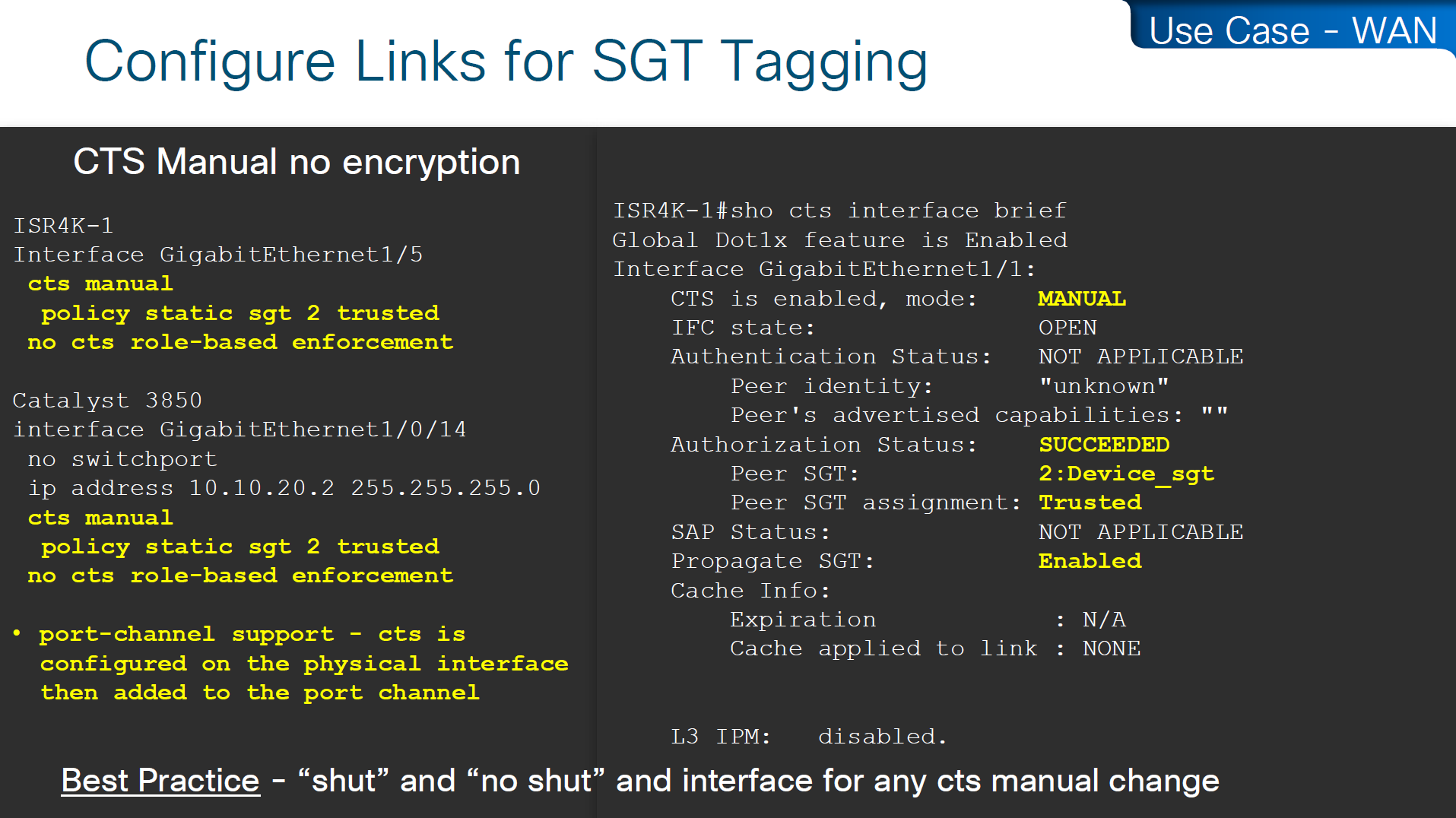
cts manual – tells the router interface to assign sgt manually to traffic over this interface
policy static sgt 2 trusted – All traffic that enters or exits this interface is tagged with SGT = 2
“Trusted” means this interface accepts incoming SGT tags from the peer without overwriting them. If the link partner already sends SGT-tagged frames, the ASR1K trusts them instead of stripping or replacing them.
no cts role-based enforcement – on the router interface or layer 3 interfaces which are in the middle of the path, we have to turn off any kind of enforcement in order to avoid dropping any traffic , Because the ASR1K in this use case is only tagging packets, not enforcing access control. This keeps the device acting as a TrustSec transit / tagging device rather than a policy enforcement point.
cts manual
policy static sgt 2 trusted
no cts role-based enforcementso above config achieves – tag outgoing traffic, trust the tag from connected device for incoming traffic and disable enforcement because this is a transit node and not access layer policy point

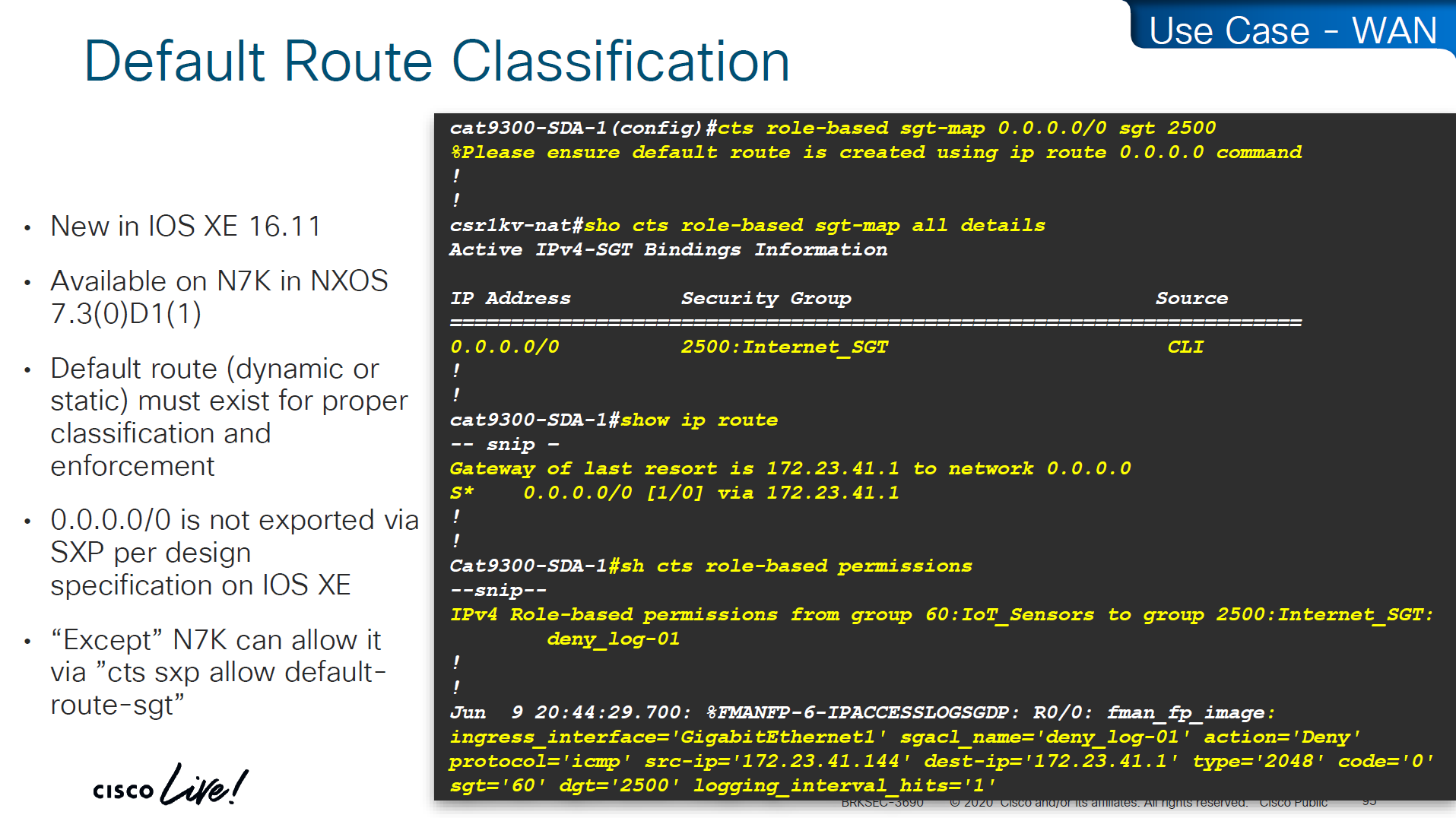
show platform hardware fed switch active fwd-asic resource tcam utilization
! Max Values column
! Used Values
! first value is IP "/" second value is SGT
! "Directly or indirectly connected routes"
! for 9300 10K limit officially for both IP and SGT combined
! "Security Access Control Entries" are number of ACEs
! "SGT_DGT" is number of cells from Policy Matrix
This healthcare provider hit the scale limit of SGT on access layer so they moved the enforcement point on routers as router hardware has much more scale

If you want to know that you are tagging traffic, simply turn on netflow with cts with above commands and even if you dont export that flow anywhere, we can see local cache , great for tshoot
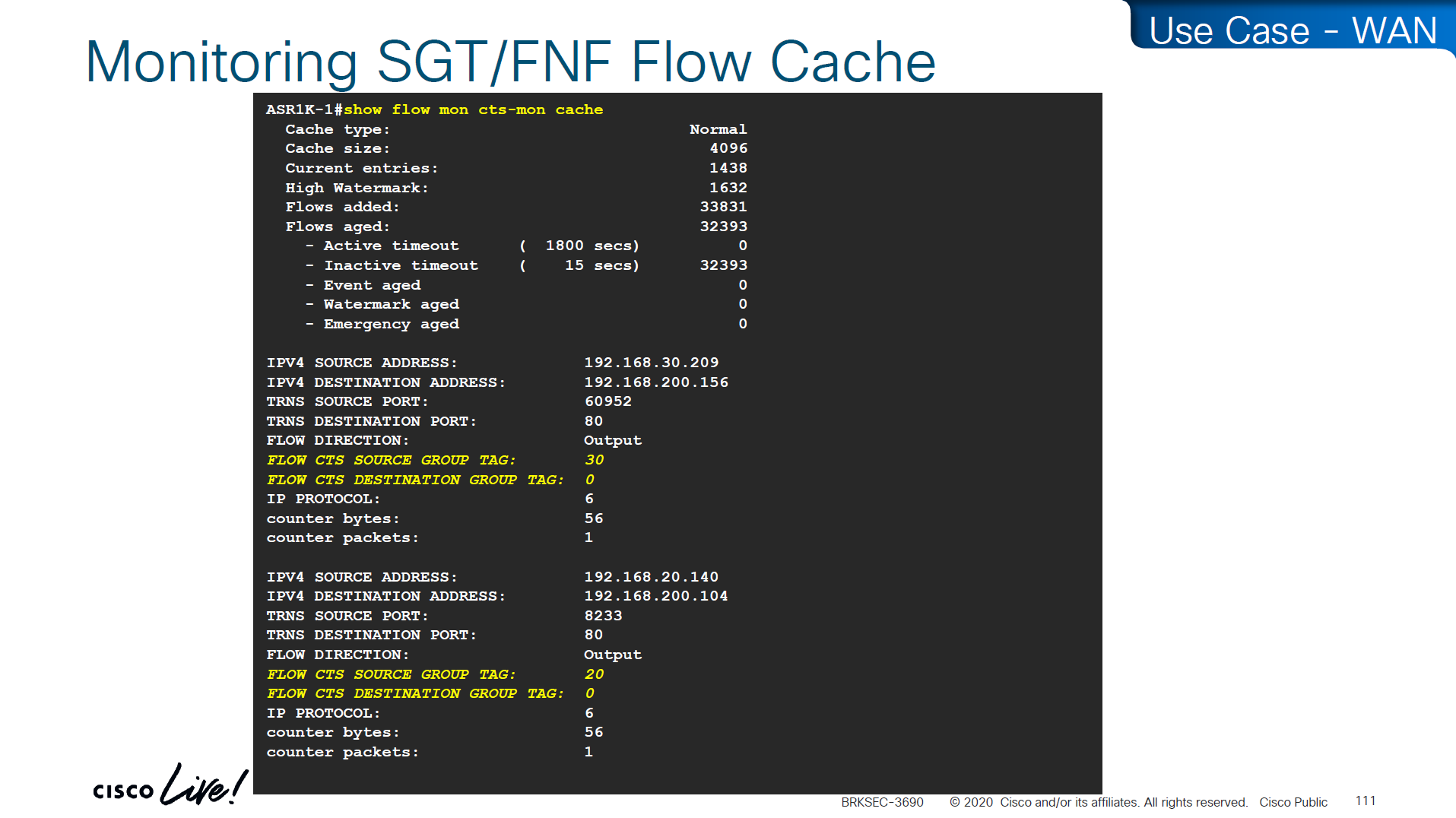
use this command to see the tagging info
show flow mon cts-mon cacheyou will see that in above output we see destination tag as 0, because we are running this command on ingress or access layer where there is no info about destination host or its assigned SGT

Stealthwatch has ability to specify source and destination tag

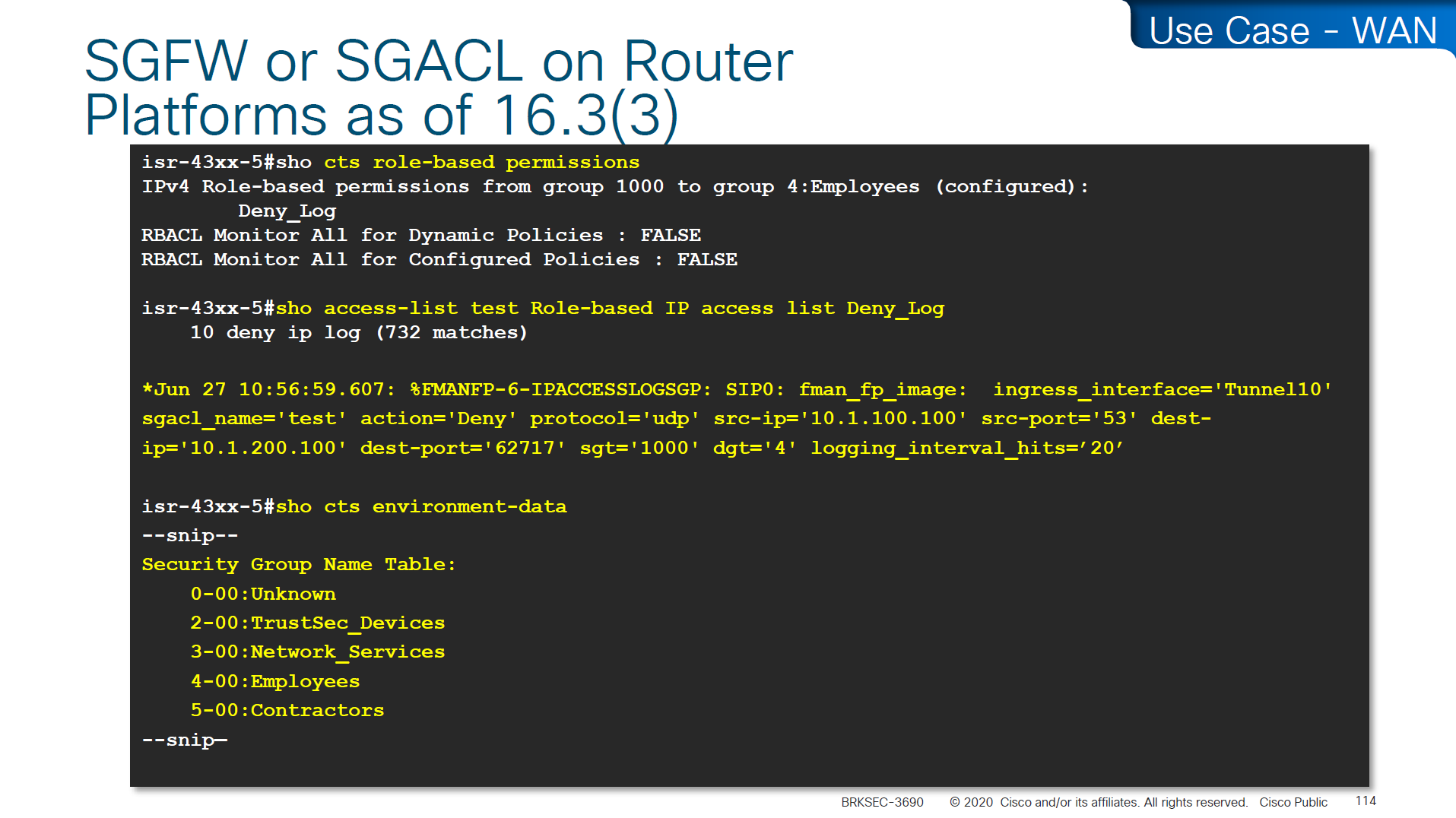


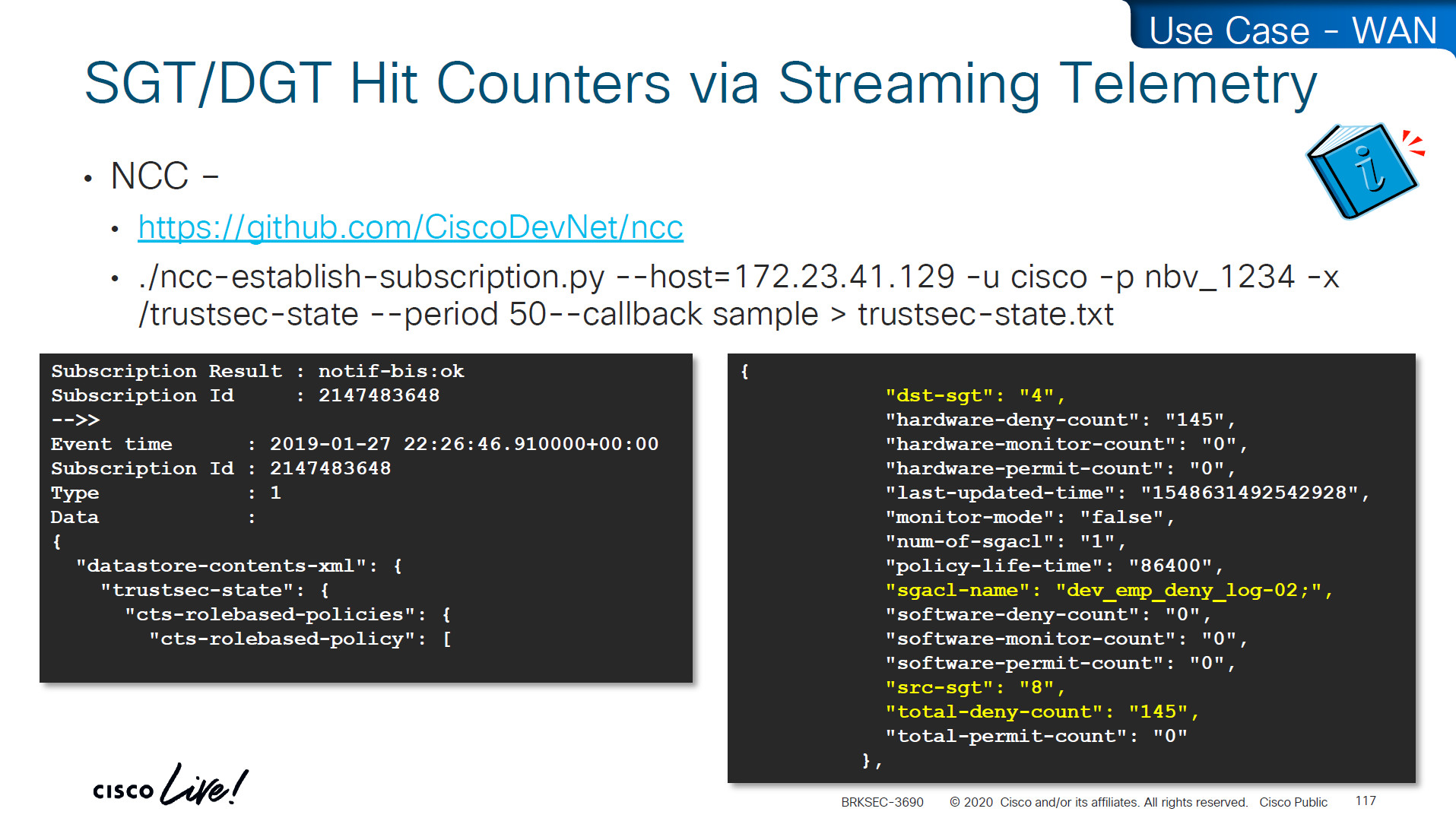

Skipped DMVPN SGT tagging
Skipped SGT/ACI
Skipped Cloud
SGT commands
! on ingress or access
cts sxp enable
cts sxp connection peer 10.1.44.1 source 10.1.11.44 password default mode local
! on core where we just learn from access as listener
cts sxp enable
cts sxp default password cisco123
! peering with Cat3K
cts sxp connection peer 10.1.11.44 source 10.1.44.1 password default mode local listener hold-time 0 0
! peering with WLC
cts sxp connection peer 10.1.33.24 source 10.1.44.1 password default mode local listener hold-time 0 0
! check IP to SGT table
show cts role-based sgt-map all details
! check SXP connection on on core
show cts sxp connections brief
----------------------------------------------
! Enable AAA
aaa new-model
! Define ISE as a RADIUS server (auth/acct) and include the PAC bootstrap secret
radius server ISE1
address ipv4 10.10.10.10 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813
key RADIUS_SHARED_SECRET
pac key RADIUS_PAC_SECRET
!
! send vsa or vendor attributes in RADIUS authentication request
radius-server vsa send authentication
key RADIUS_SHARED_SECRET
pac key RADIUS_PAC_SECRET
!
! send vsa or vendor attributes in RADIUS authentication request
radius-server vsa send authentication
! (Optional) put servers into a group and set a source interface
aaa group server radius ISE-GRP
server name ISE1
ip radius source-interface Vlan10
! CTS/NDAC: define the authorization list used for policy download only (not tags - tags are pulled before SGACL or policy is pulled) - as clients connect with new SGT , more policy columns are pulled
cts authorization list CTS-AUTHZ
! 802.1X + CTS use the RADIUS group
aaa authentication dot1x default group ISE-GRP
aaa authorization network CTS-AUTHZ group ISE-GRP
! aaa authorization network command is usually used to allow on network or authorize audience or entity authenticated through network ports and this config says that authorized list of server (which are allowed to make CLI or COA changes) will be downloaded from ISE-GRP
! which makes it look like this
aaa authorization network ( CTS-AUTHZ ) group ISE-GRP
aaa authorization network ( cts authorization list ) group ISE-GRP
! Define credentials for EAP-FAST I-ID, these are configured under enable mode and not in config mode
cts credential id DEVICE-ID password PASSWORD
! enable 802.1x on system level
dot1x system-auth-control
! enable CTS enforcement
cts role-based enforcement
----------------------------------------------
show cts environment-data
! shows local device SGT
! shows servers that are authorized list servers
! shows downloaded SGT tags on devices
----------------------------------------------
! define SGT for local servers connected to switch
cts role-based sgt-map 192.168.31.1 sgt 100
cts role-based sgt-map 192.168.32.0/24 sgt 20
cts role-based sgt-map 10.x.x.0 sgt 30
! tag default route to Internet_SGT
! This is incase you want to use Unknown tag for something else
! for default route tag, the device must have defafult route either as a static or dynamic for this tagging to work
! this allows us to do something like Medical_devices <-> Internet_SGT deny
cts role-based sgt-map 0.0.0.0/0 sgt 2500
! enableing SGT enformcement globaly
cts role-based enforcement
! or on specific vlans for slow rollout
cts role-based enforcement vlan-list 40
----------------------------------------------
! download or refresh SGT tags
cts refresh environment-data
! download or refresh SGACLs or policy
cts refresh policy
----------------------------------------------
show cts role-based permissions
! shows SGACLs
show cts policy sgt 4
! shows SGT and its related policies in detail
show ip access-list
show cts role-based counters
! shows * to * default rule
! also shows from and to columns
! SGACL is done in hardware, unless needs punting
! for example TCAM or hardware is full, log in the end of ACE or to the box traffic such as Trust_Devices SGT, makes SW counter increment otherwise concentrate on HW-Denied and HW-Permitted columns
----------------------------------------------
show device-tracking database
show cts role-based sgt-map 10.0.0.1
show device-tracking database interface gig2/0/11
----------------------------------------------
! If SGACL download errors happen
show aaa servers
! make sure AAA servers are marked alive
show cts pac all
! make sure pac is present
show cts environment-data
! check if device can communicate with ISE
----------------------------------------------
router(config)#interface Ten1/1/1
cts manual
policy static sgt 2 trusted
no cts role-based enforcement
! tag outgoing traffic,
! trust the tag from connected device for incoming traffic
! disable enforcement because this is a transit node and not access layer policy point
show cts interface brief
----------------------------------------------
show platform hardware fed switch active fwd-asic resource tcam utilization
! Max Values column
! Used Values
! first value is IP "/" second value is SGT
! "Directly or indirectly connected routes"
! for 9300 10K limit officially for both IP and SGT combined
! "Security Access Control Entries" are number of ACEs
! "SGT_DGT" is number of cells from Policy Matrix
----------------------------------------------
flow record cts-v4
match ipv4 protocol
match ipv4 source address
match ipv4 destination address
match transport source-port
match transport destination-port
match flow direction
match flow cts source group-tag <<<<
match flow cts destination group-tag <<<<
collect counter bytes
collect counter packets
flow exporter EXP1
destination 10.1.1.1
source Gig1
flow monitor cts-mon
record cts-v4
exporter EXP1
interface vlan 10
ip flow monitor cts-mon input
ip flow monitor cts-mon output
show flow mon cts-mon cache