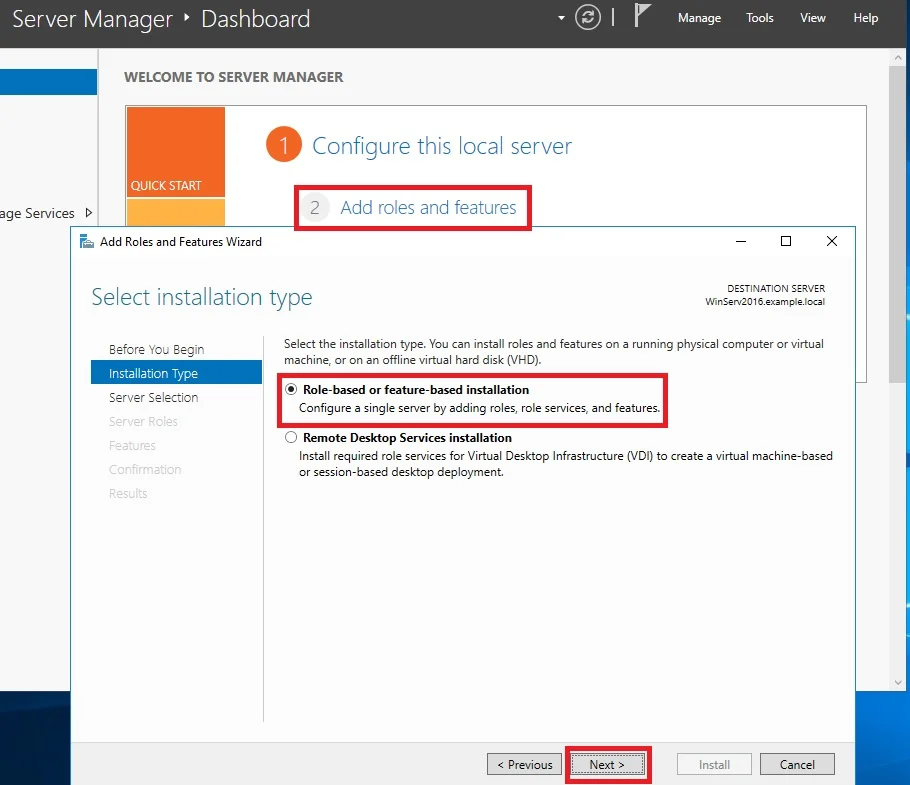
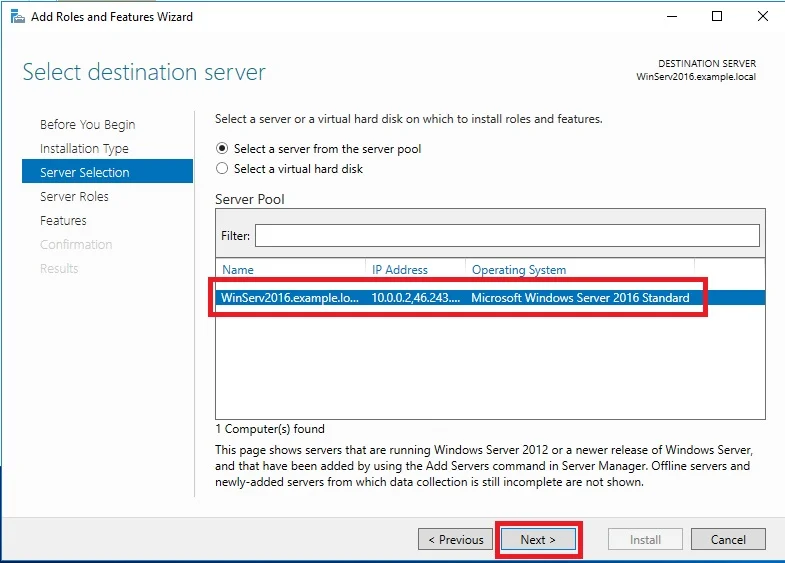
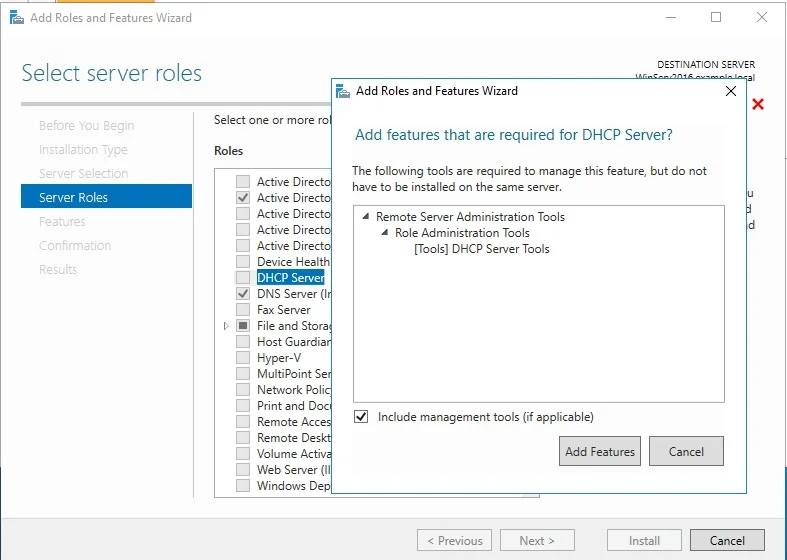
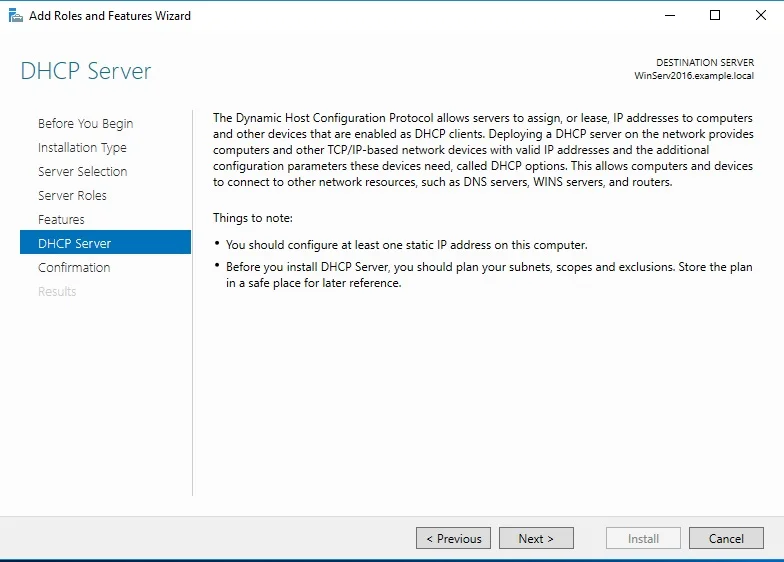
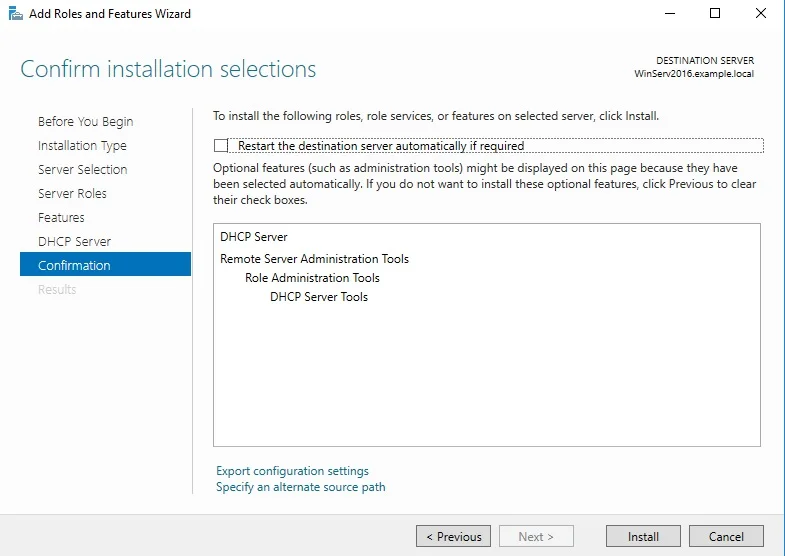
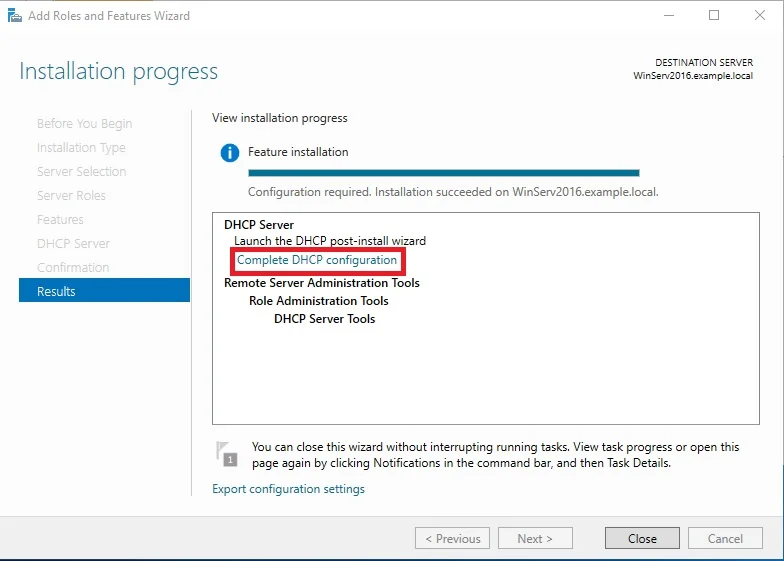
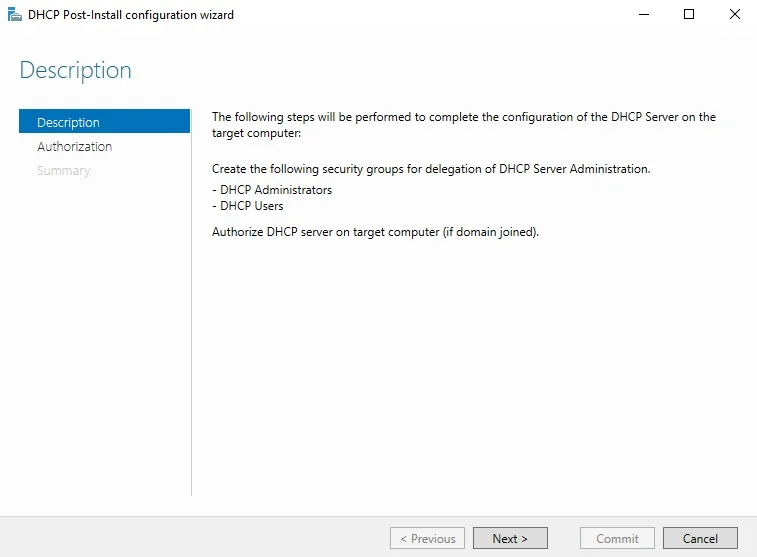
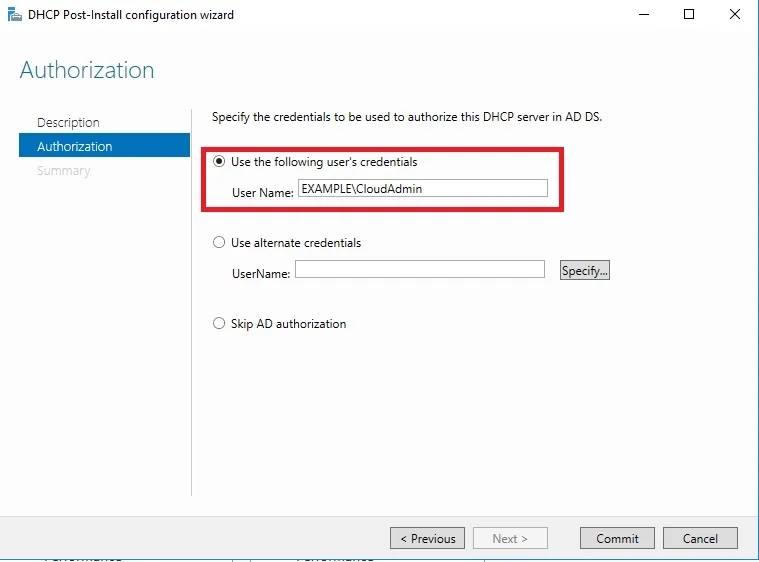
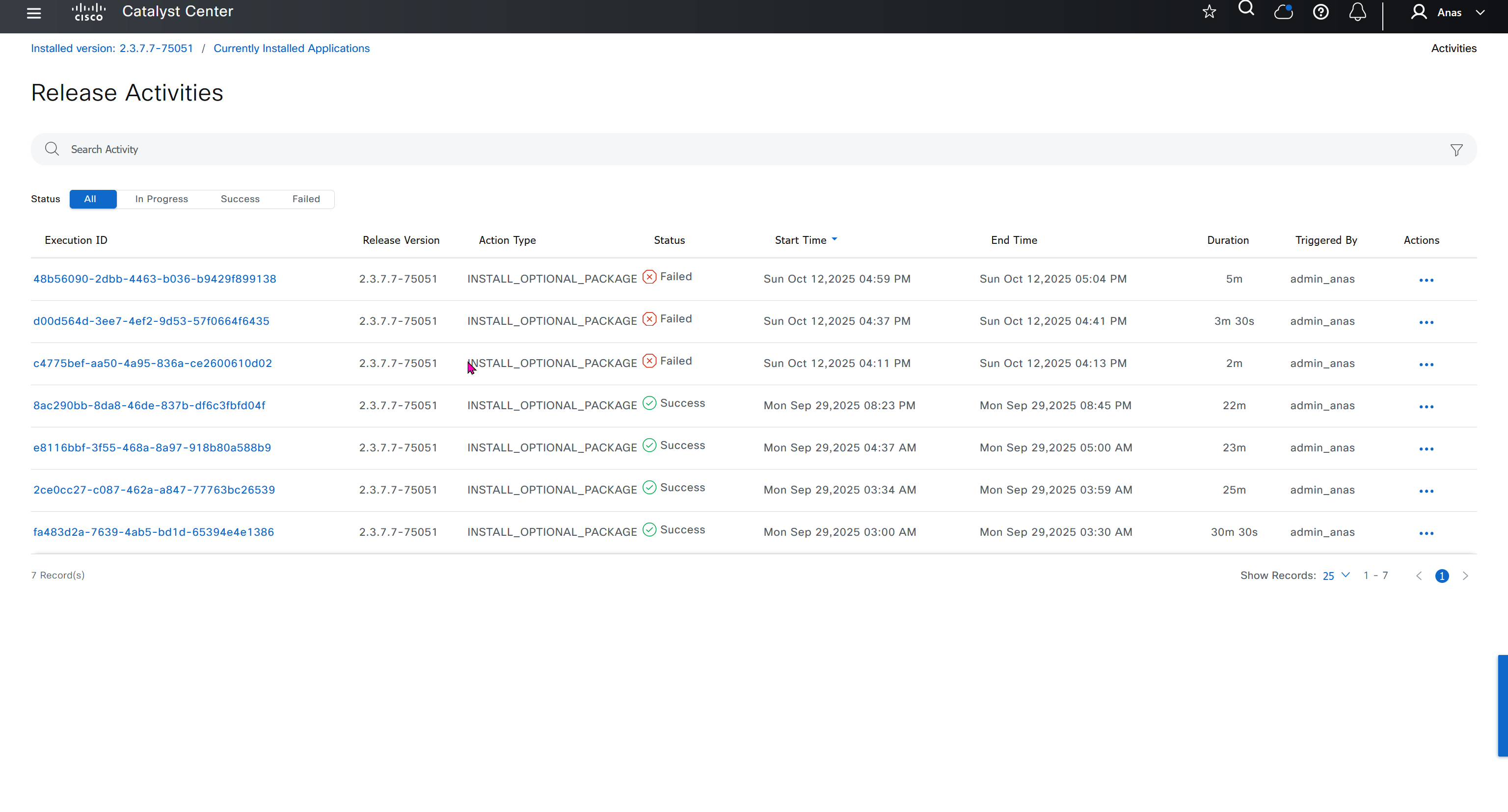
⊹ 93. CCIE SDA ⊹
SDA LM3 – Topology & Software Image Management
Videos
Topology & Software Image Management






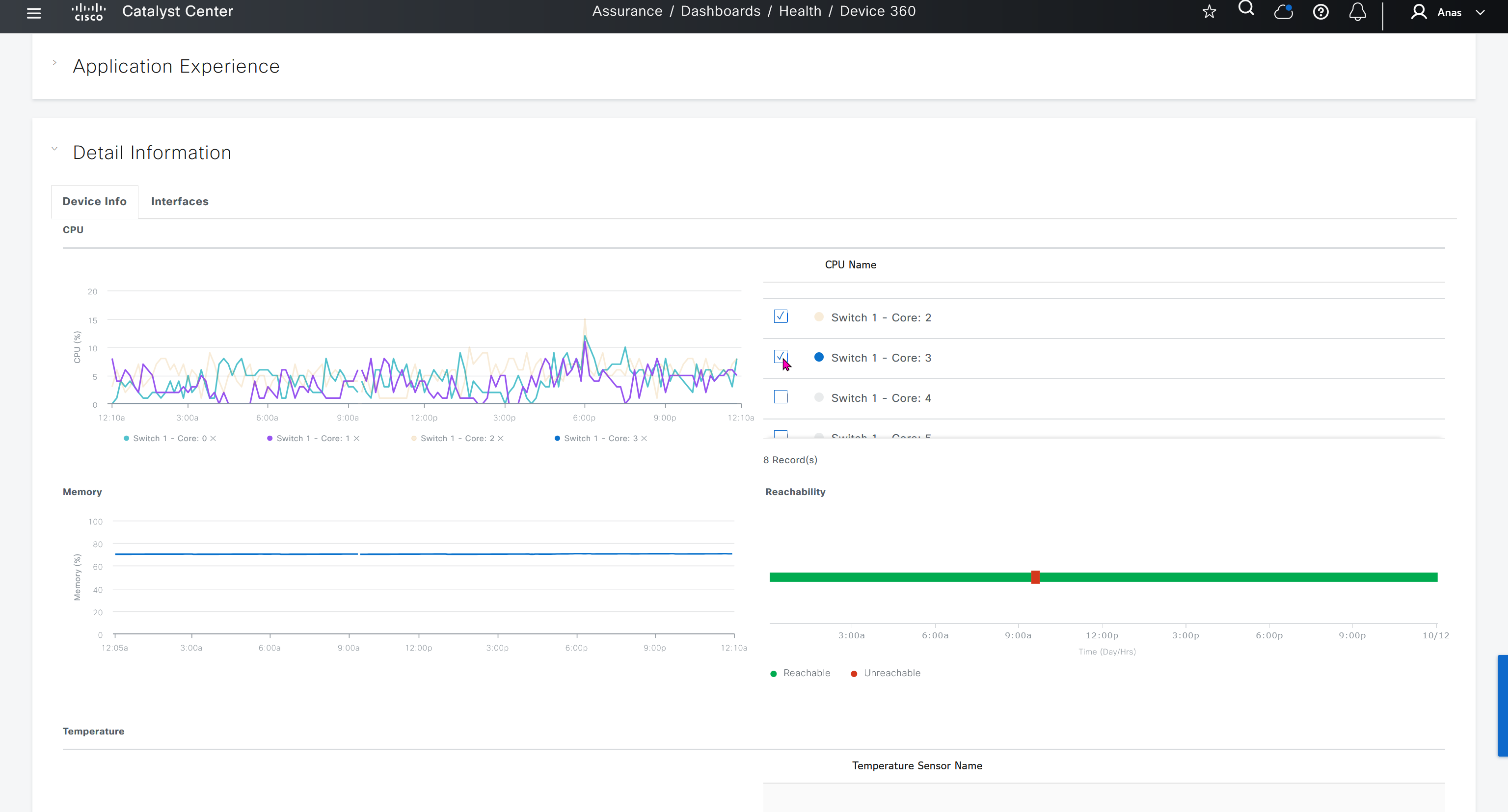



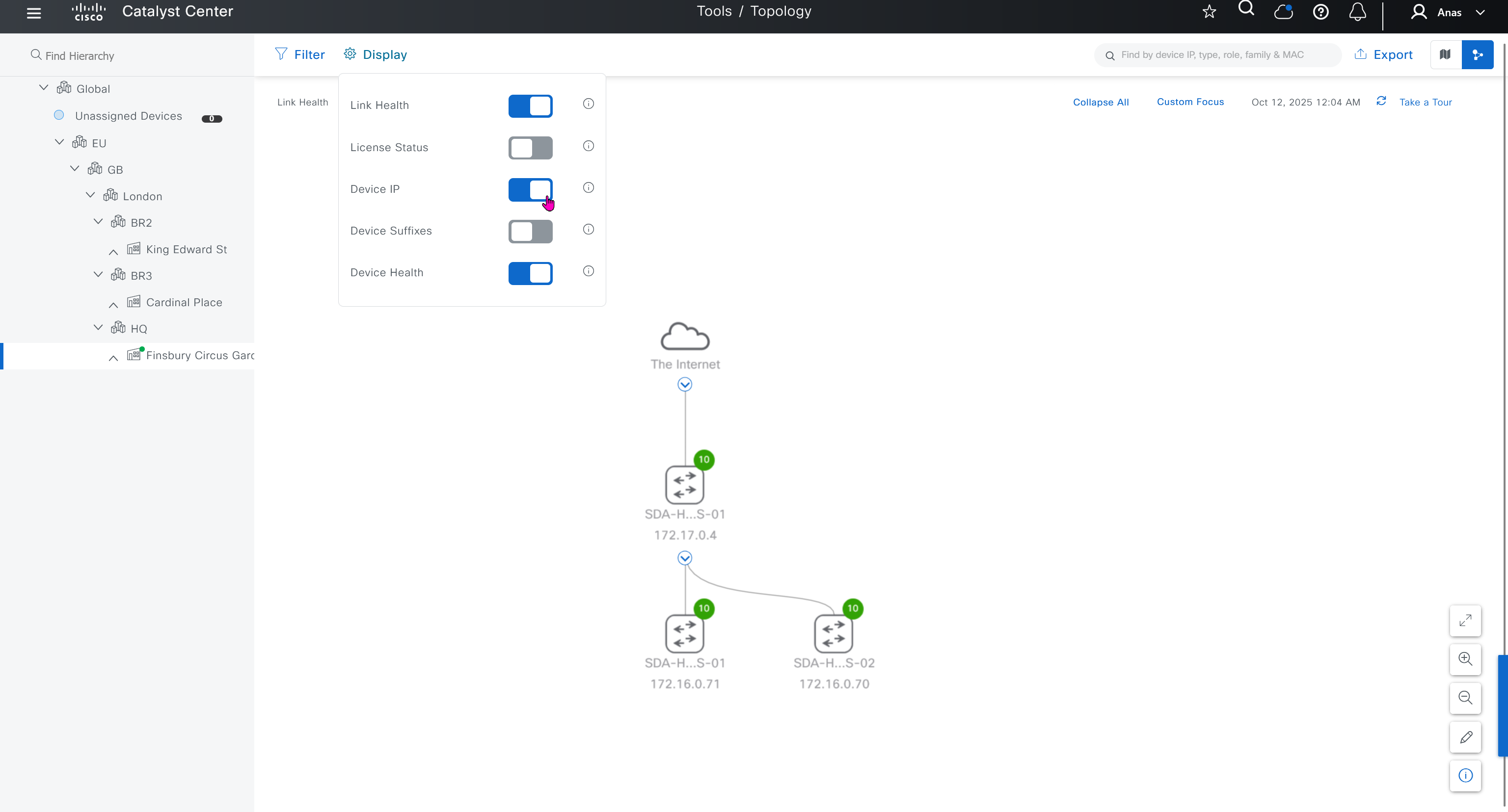

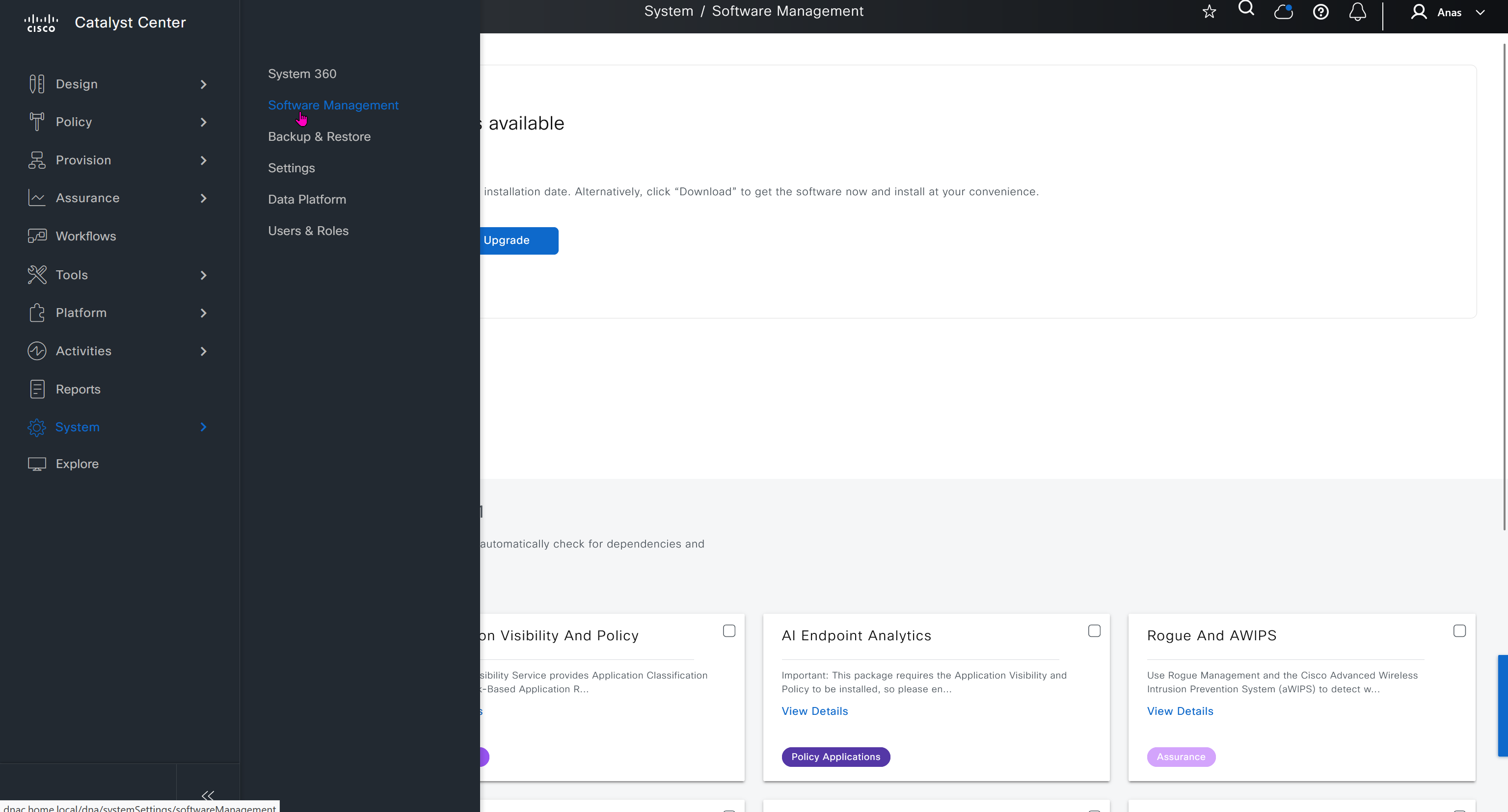
SWIM – Software Image Management
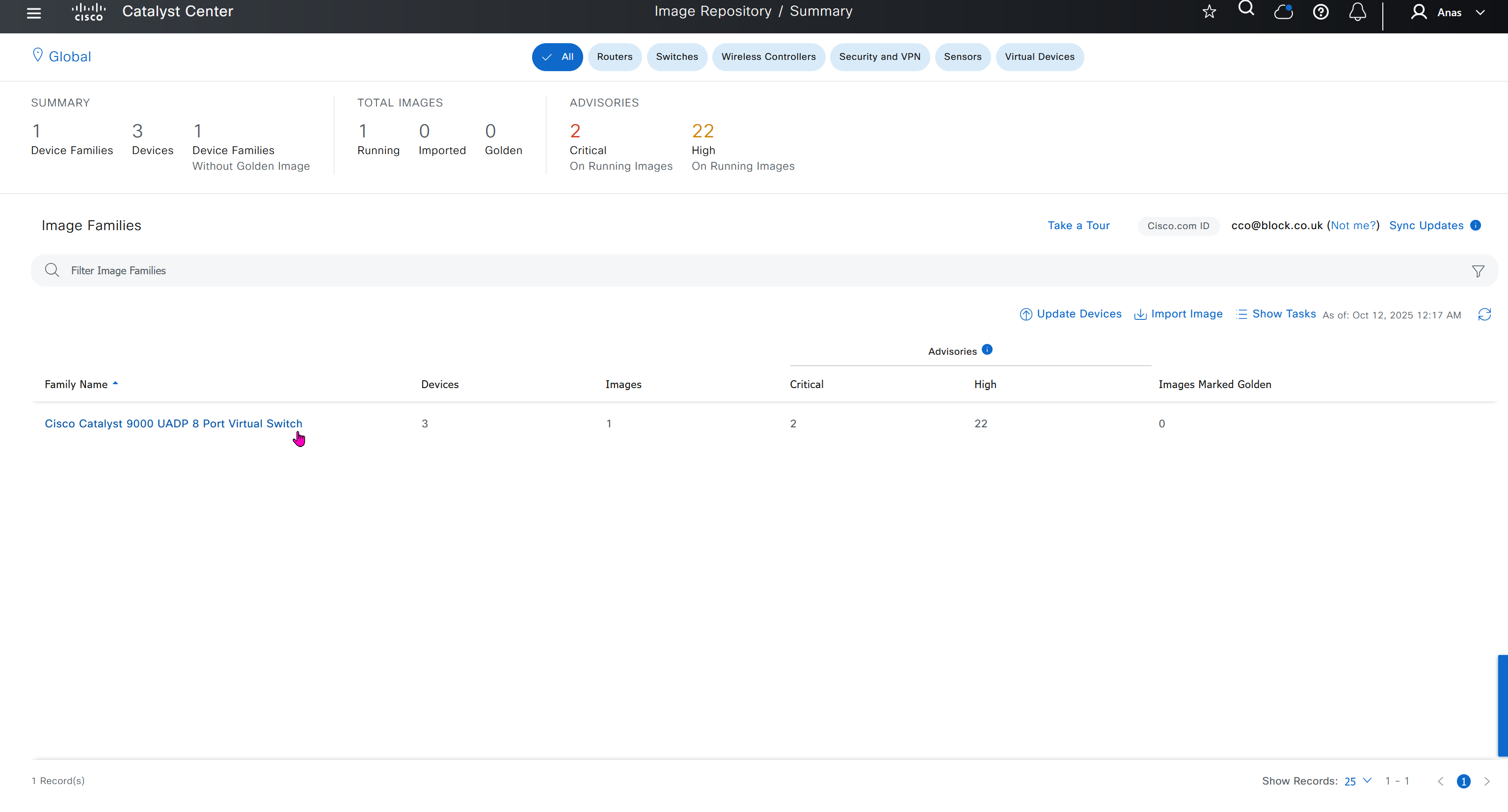



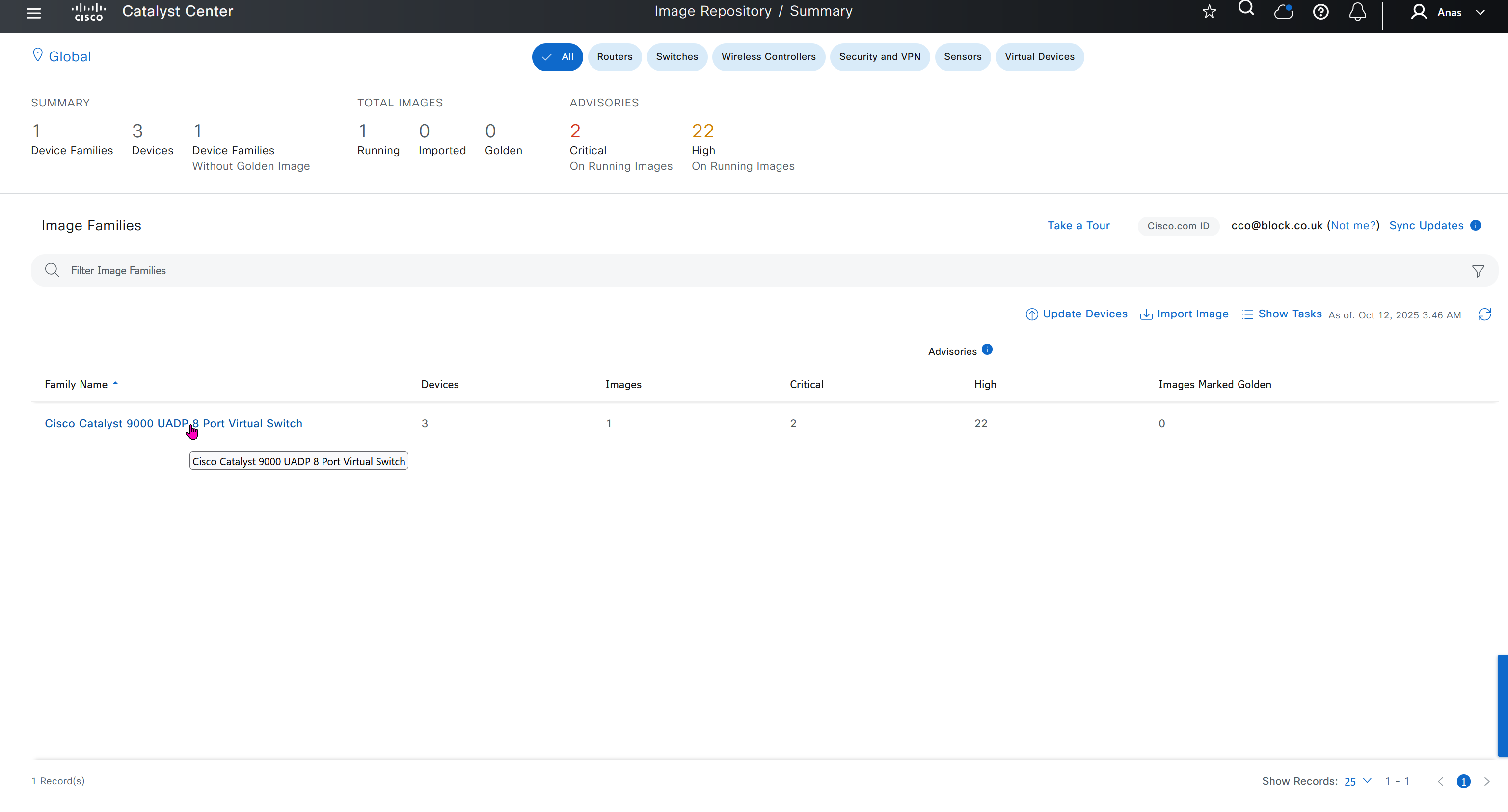


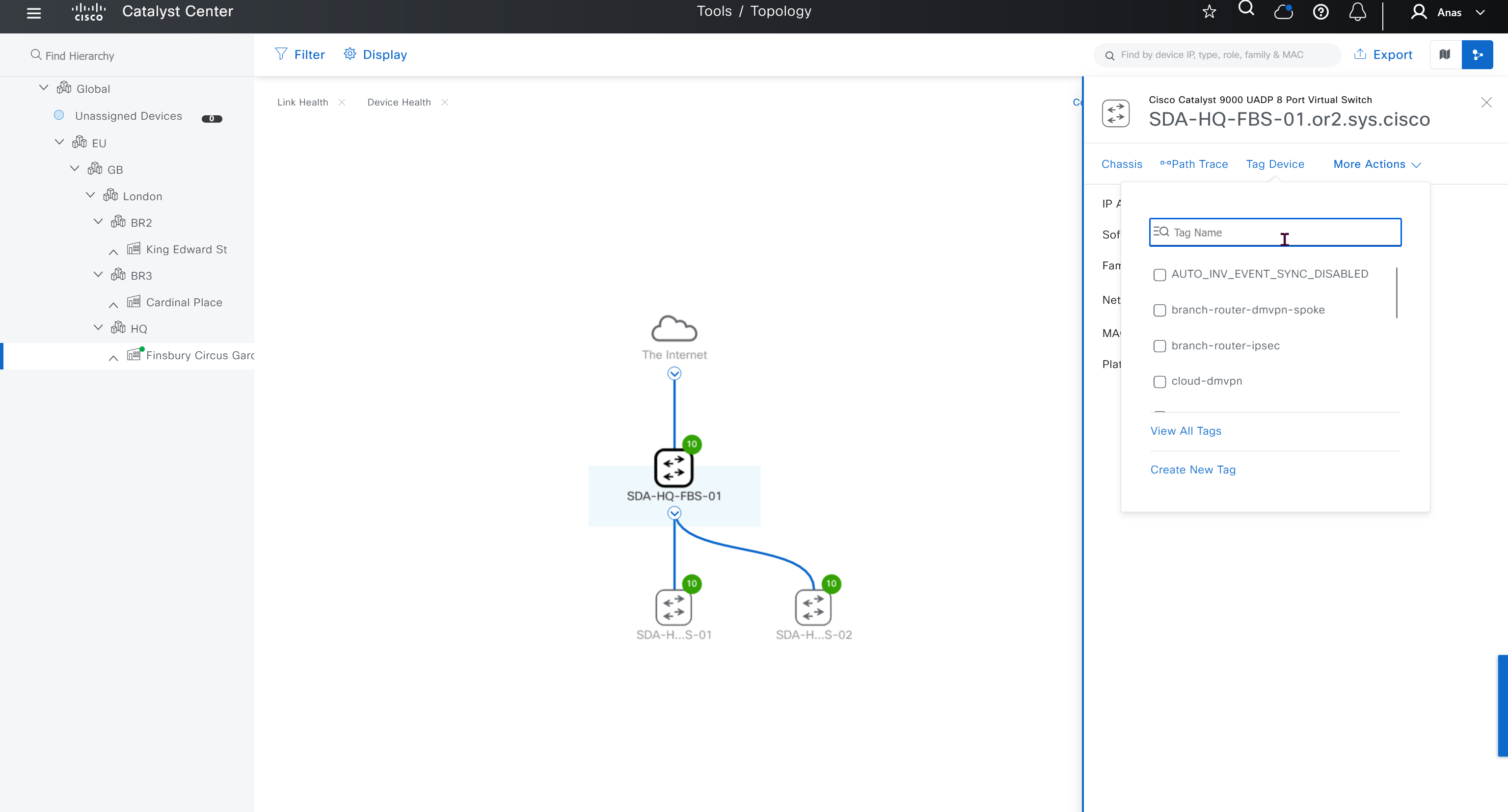
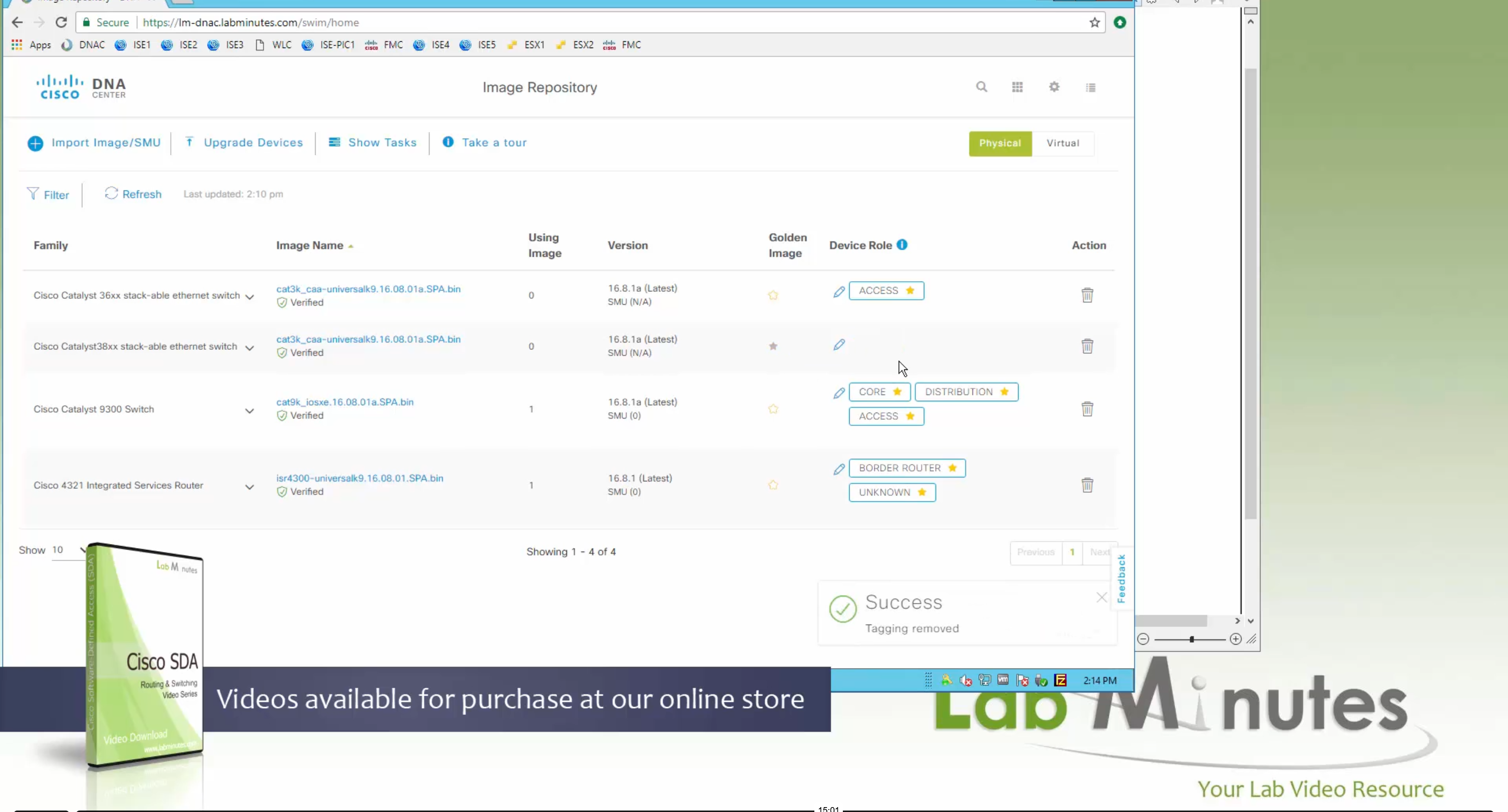
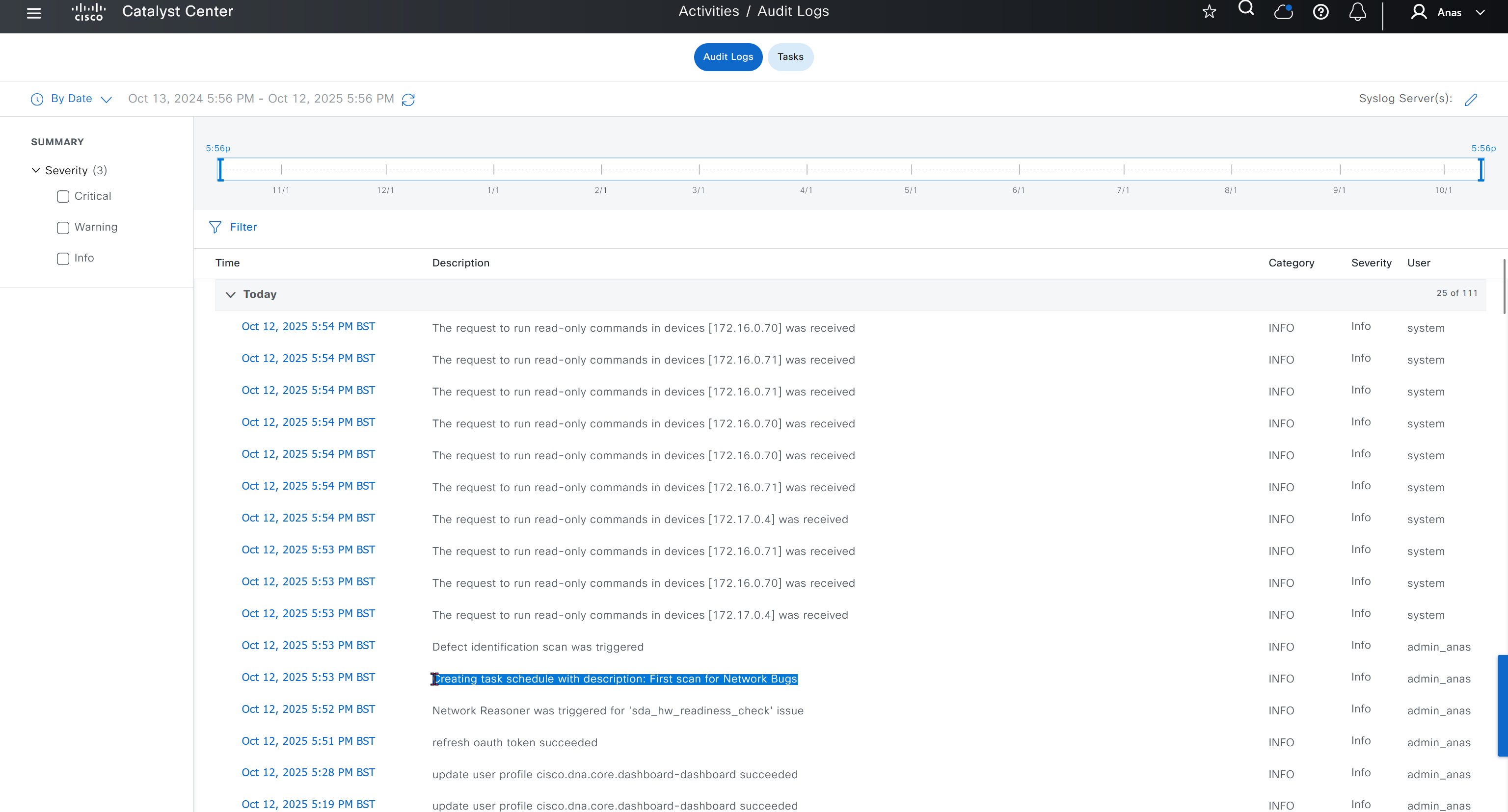
you can only start tagging devices one you have uploaded the image, because we have virtual C9Kv images there is no .bin or .smu images available for them, from ths point on we will have screenshots from lab minutes
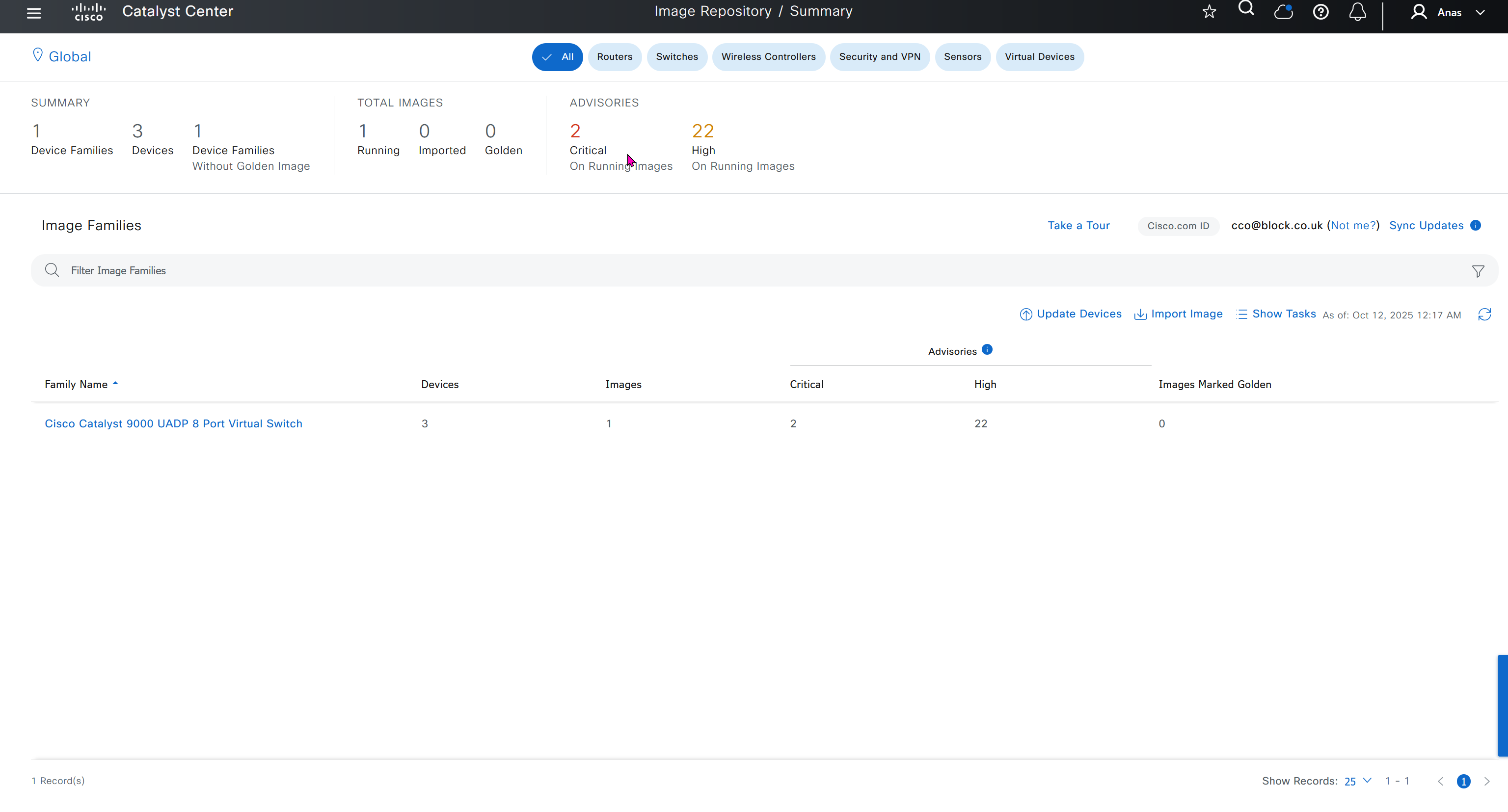
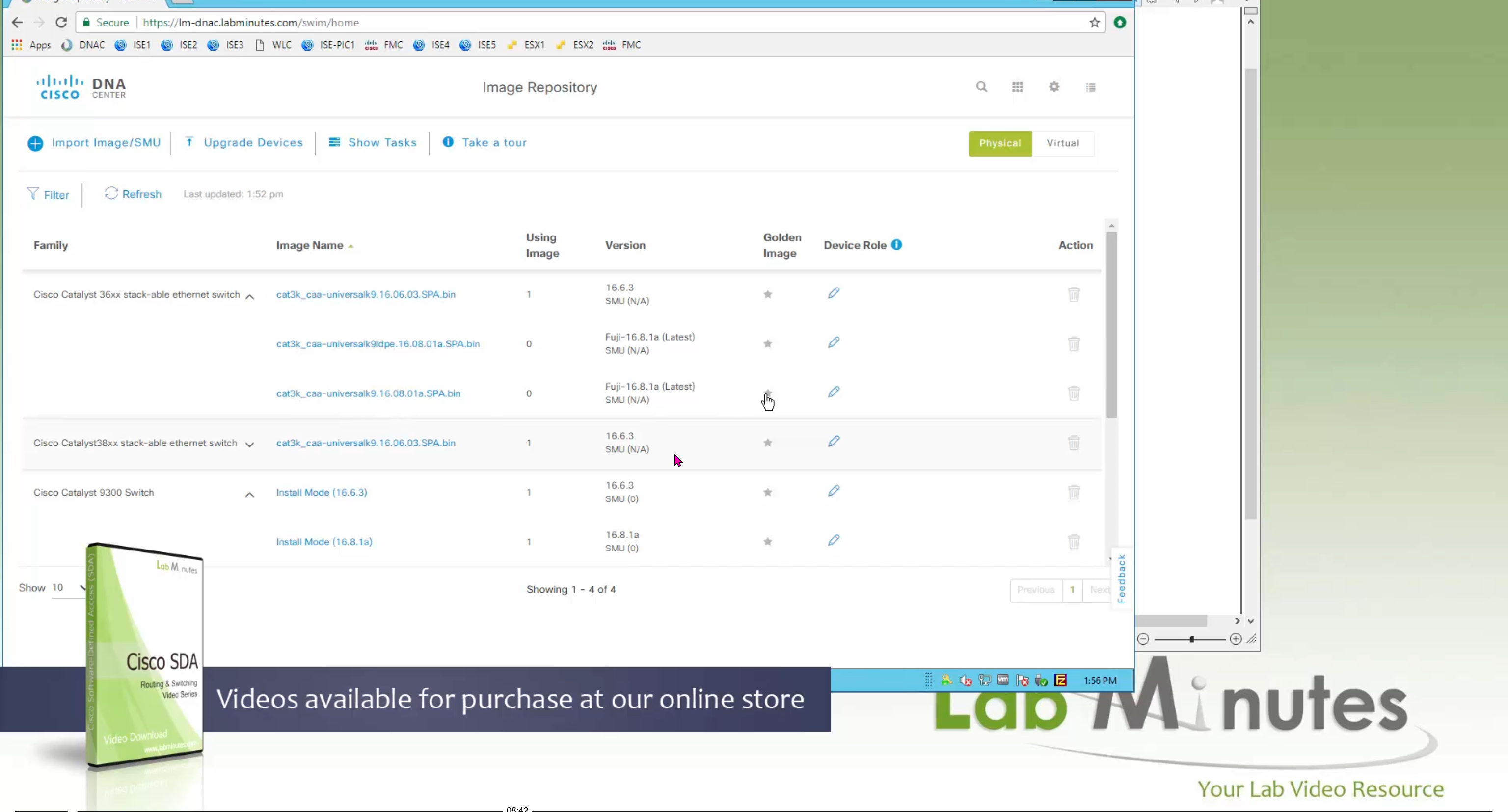
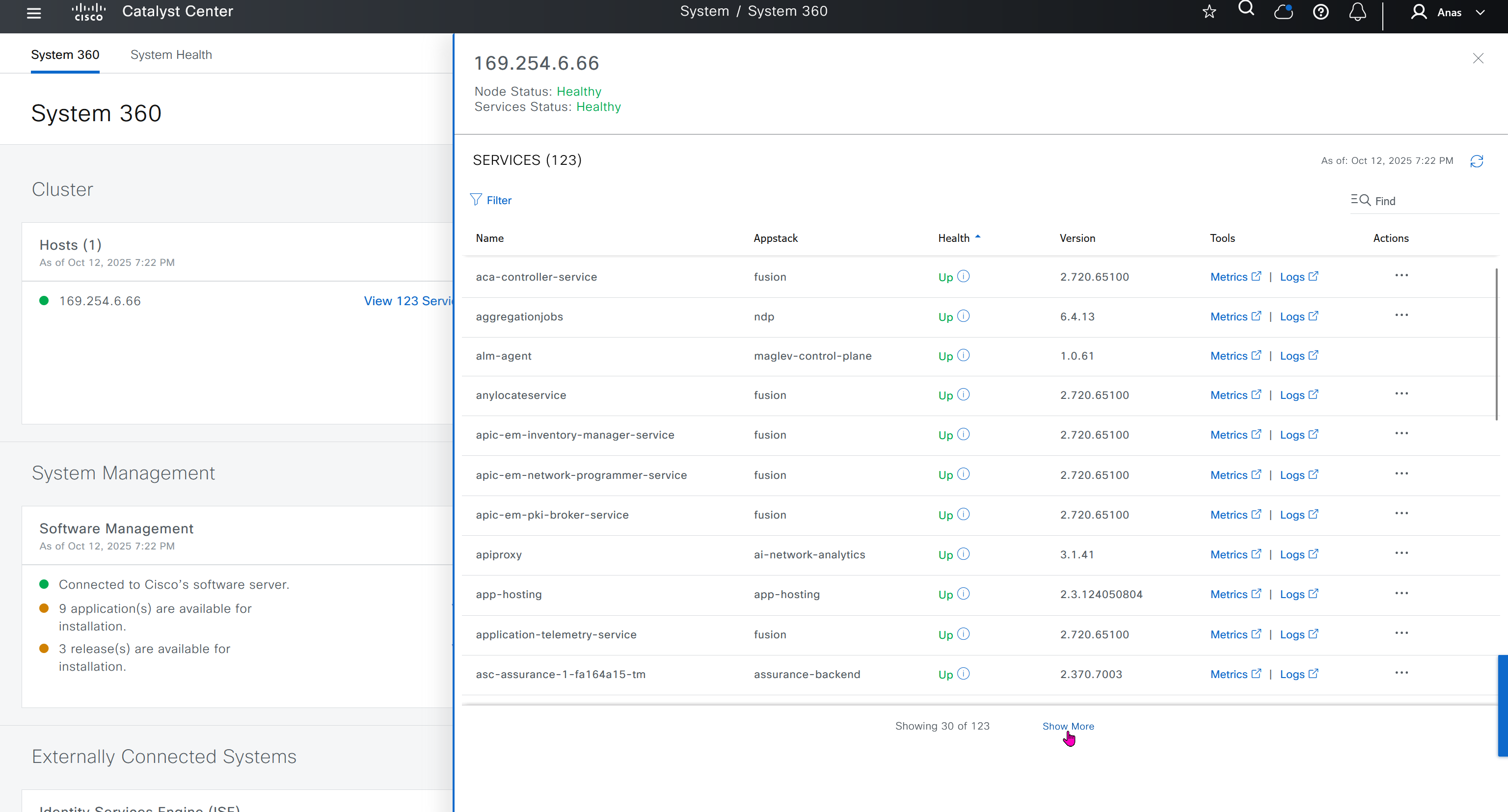
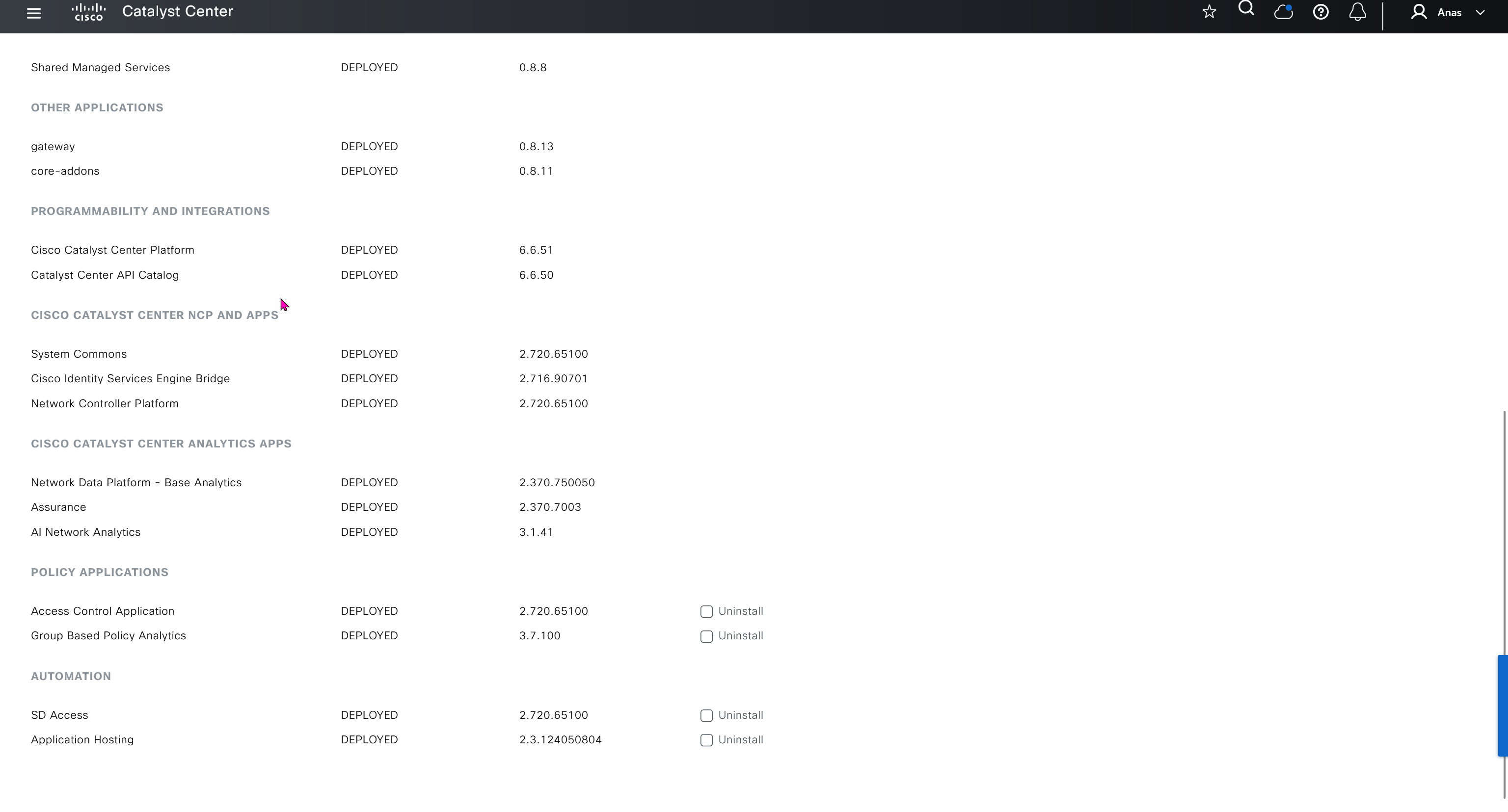
One image can be marked as golden image per device type either at the global level or at the site level, then any device that is not running that golden image will be marked as out of compliance
DNAC also supports auto clean up where it cleans up older image files
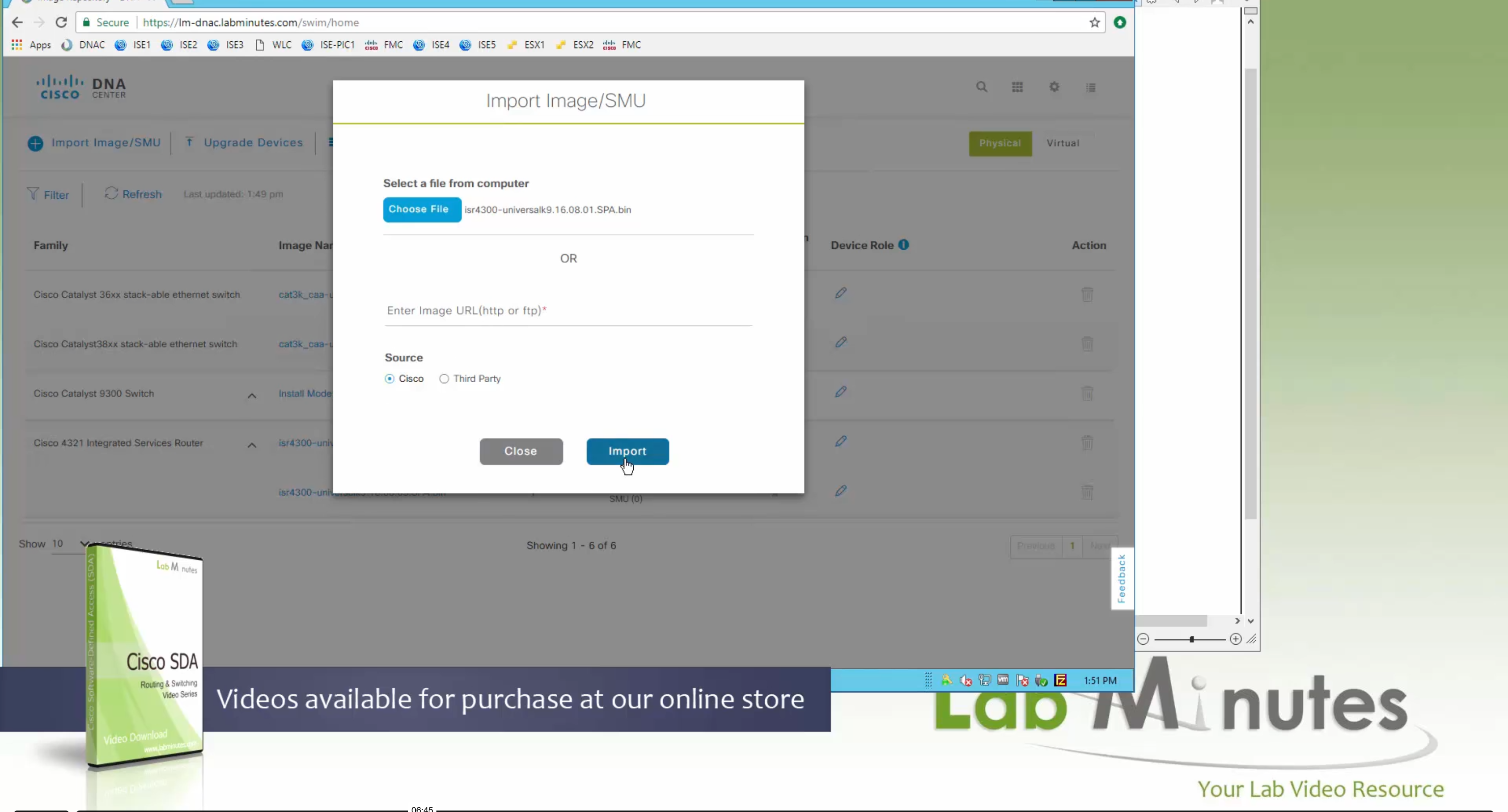
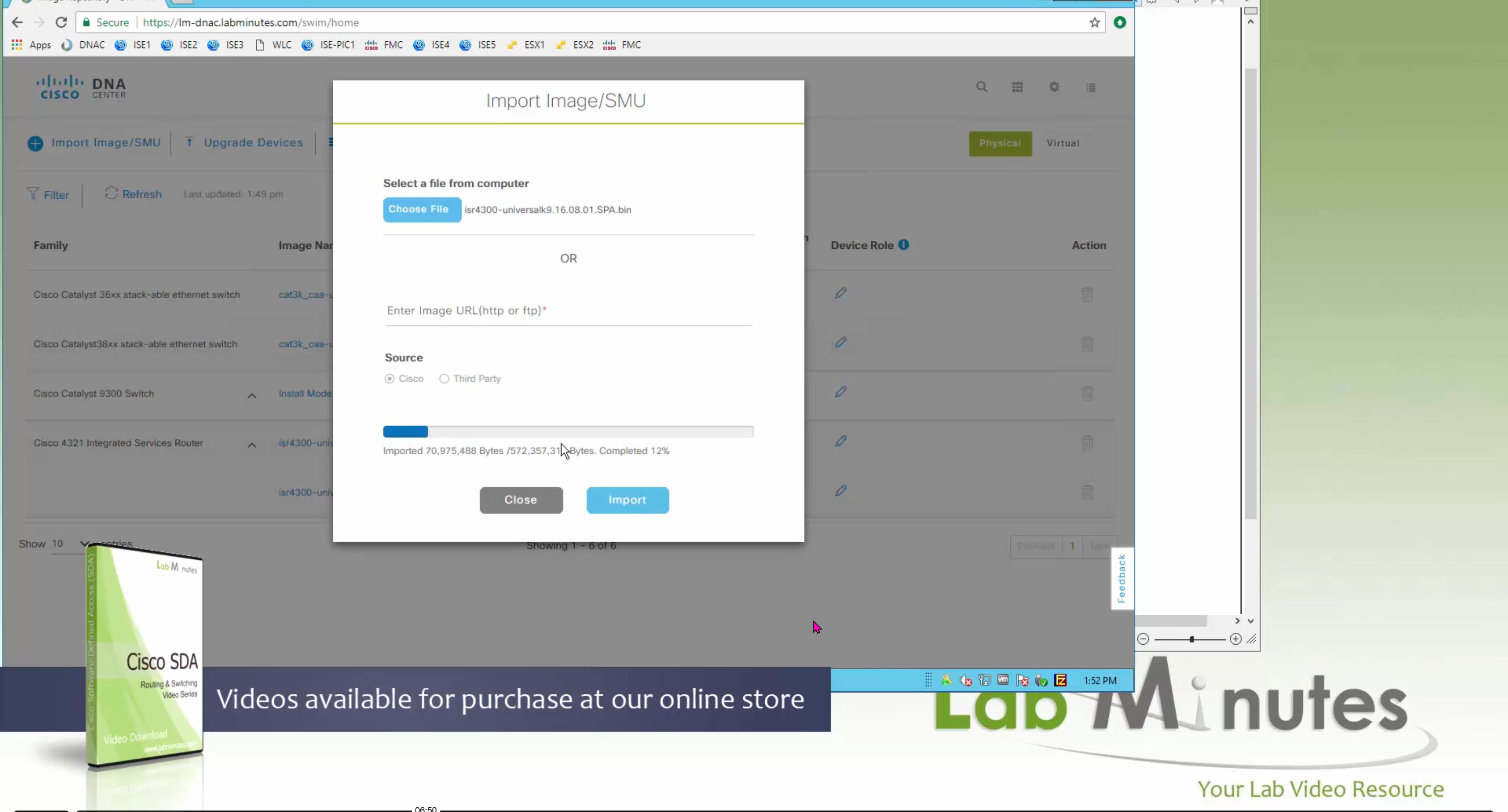
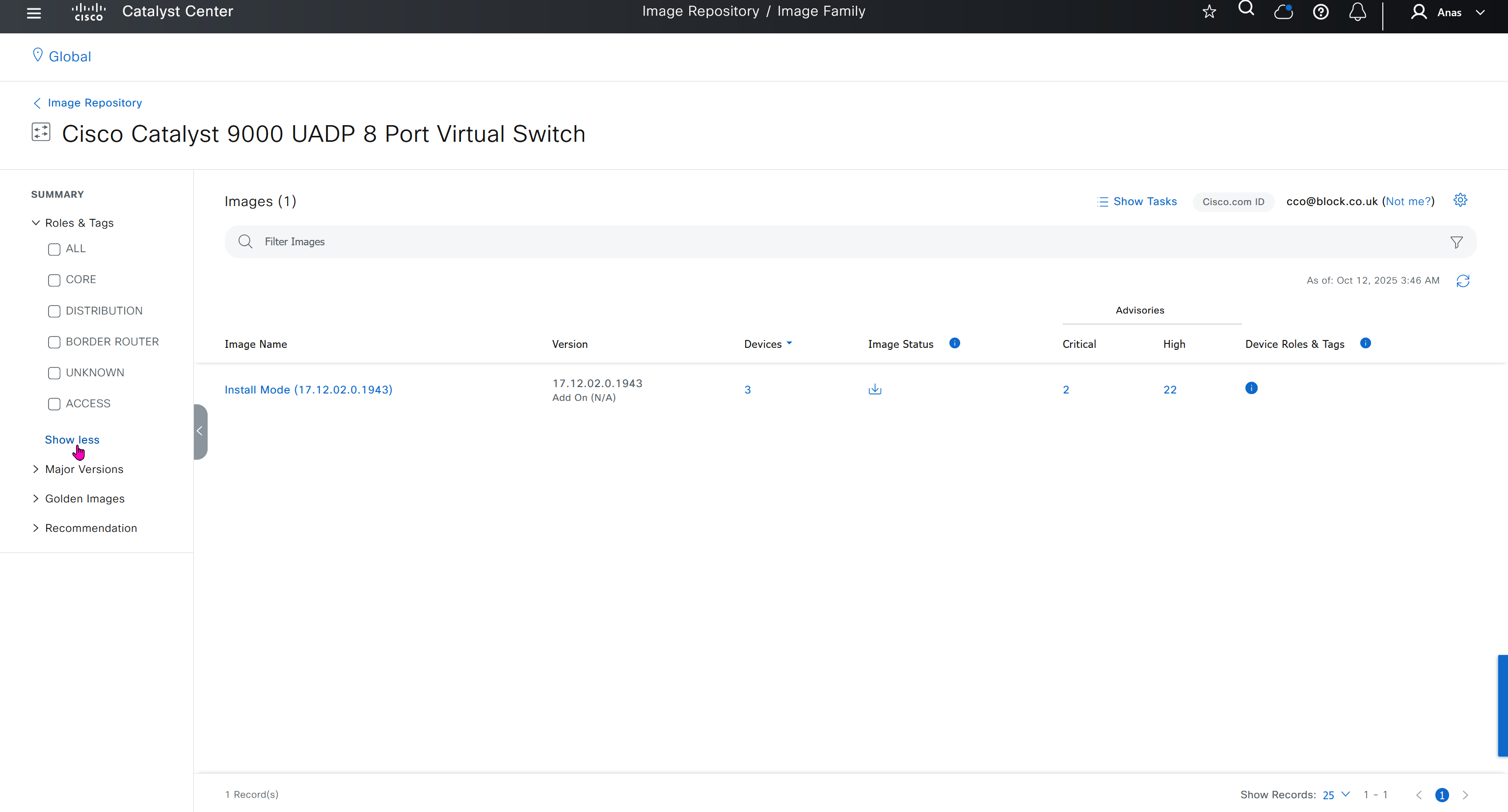
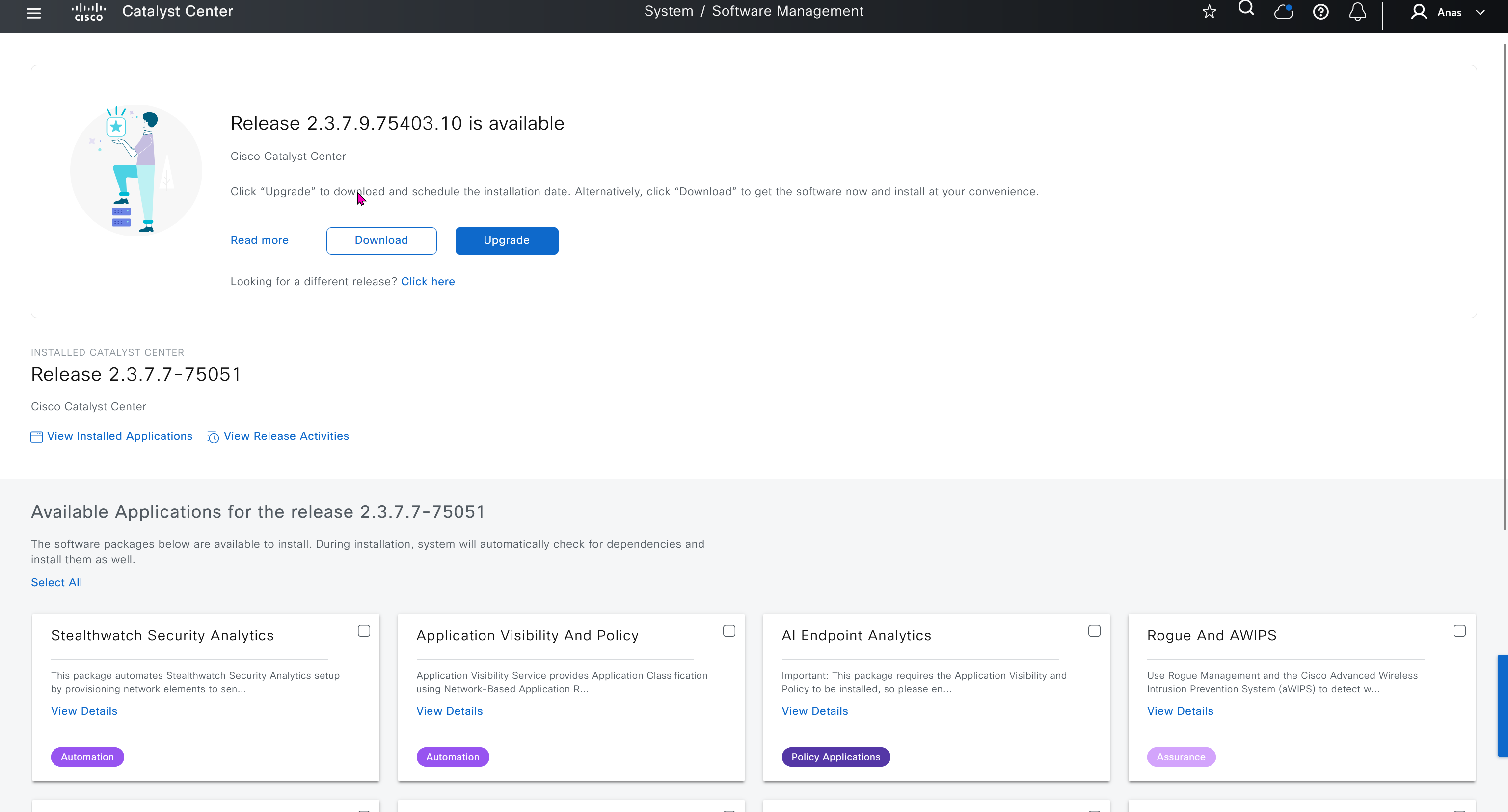
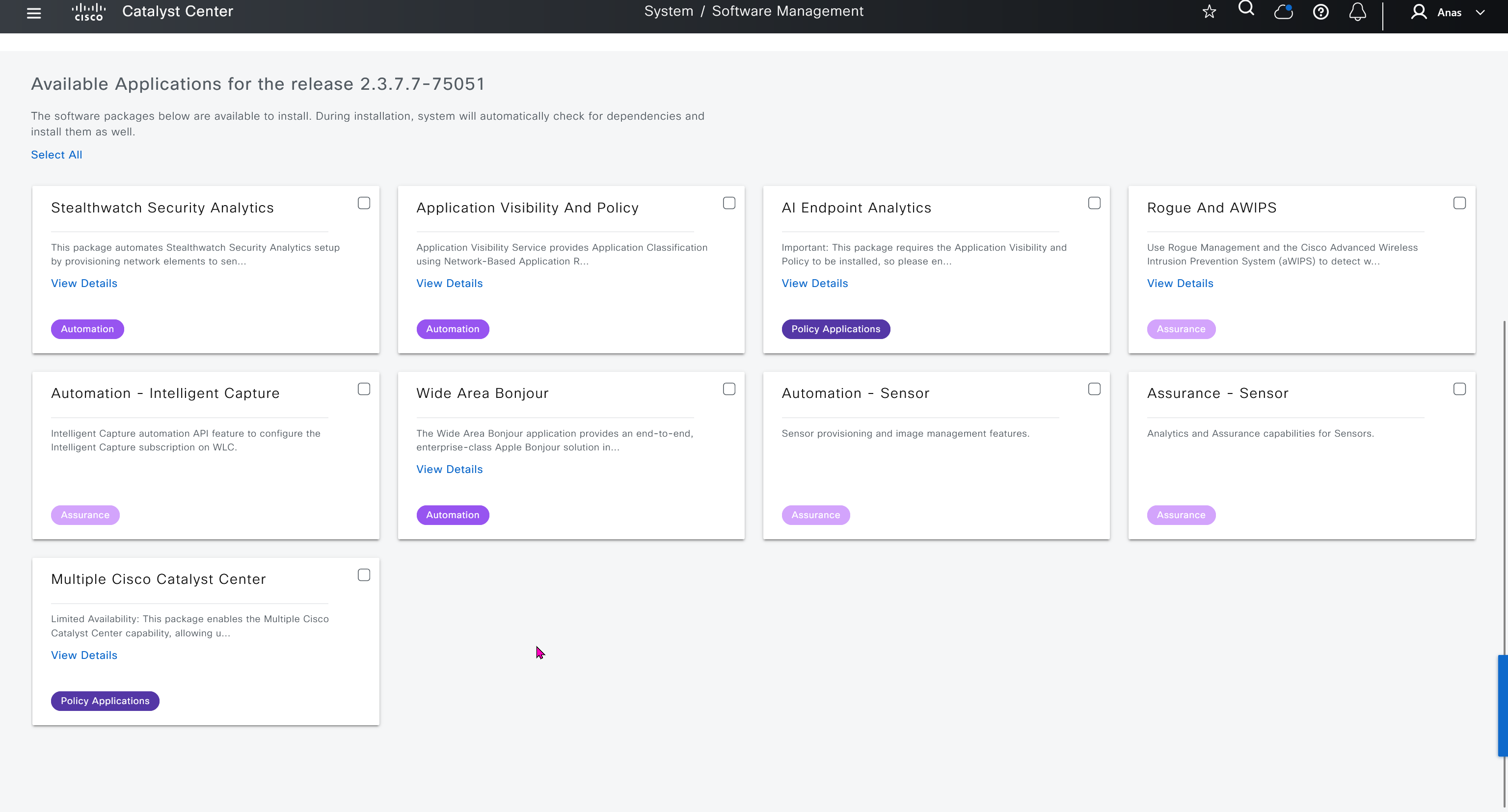
Using image column and version column with (Latest) means that these are the latest images, these images with (Latest) are being displayed from cisco.com and we can click on star icon to make them golden image
Making image golden enforces that image on that hardware model
Same thing can be repeated for different chassis or hardware types, their recommended Latest images can be marked as golden images
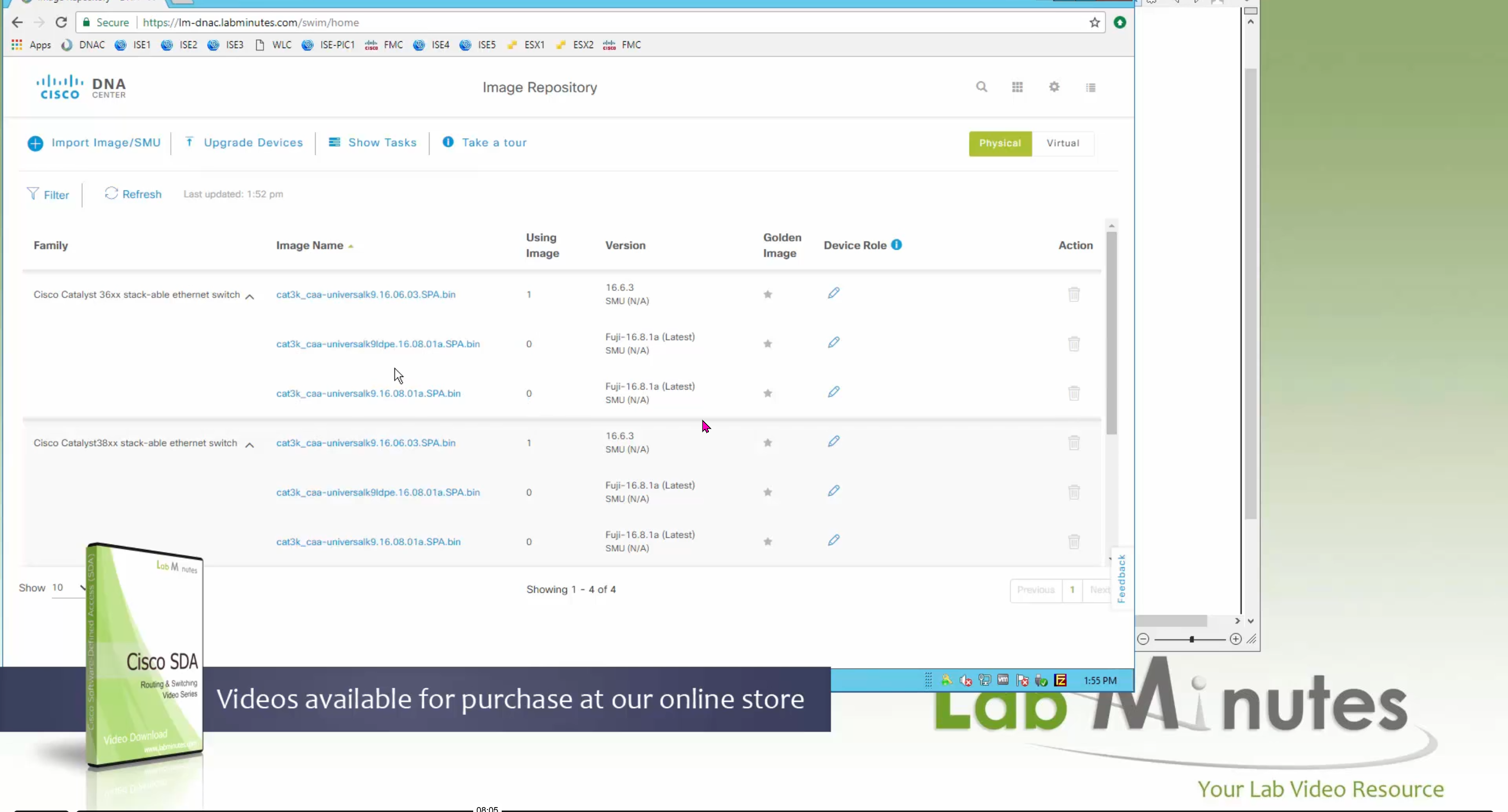
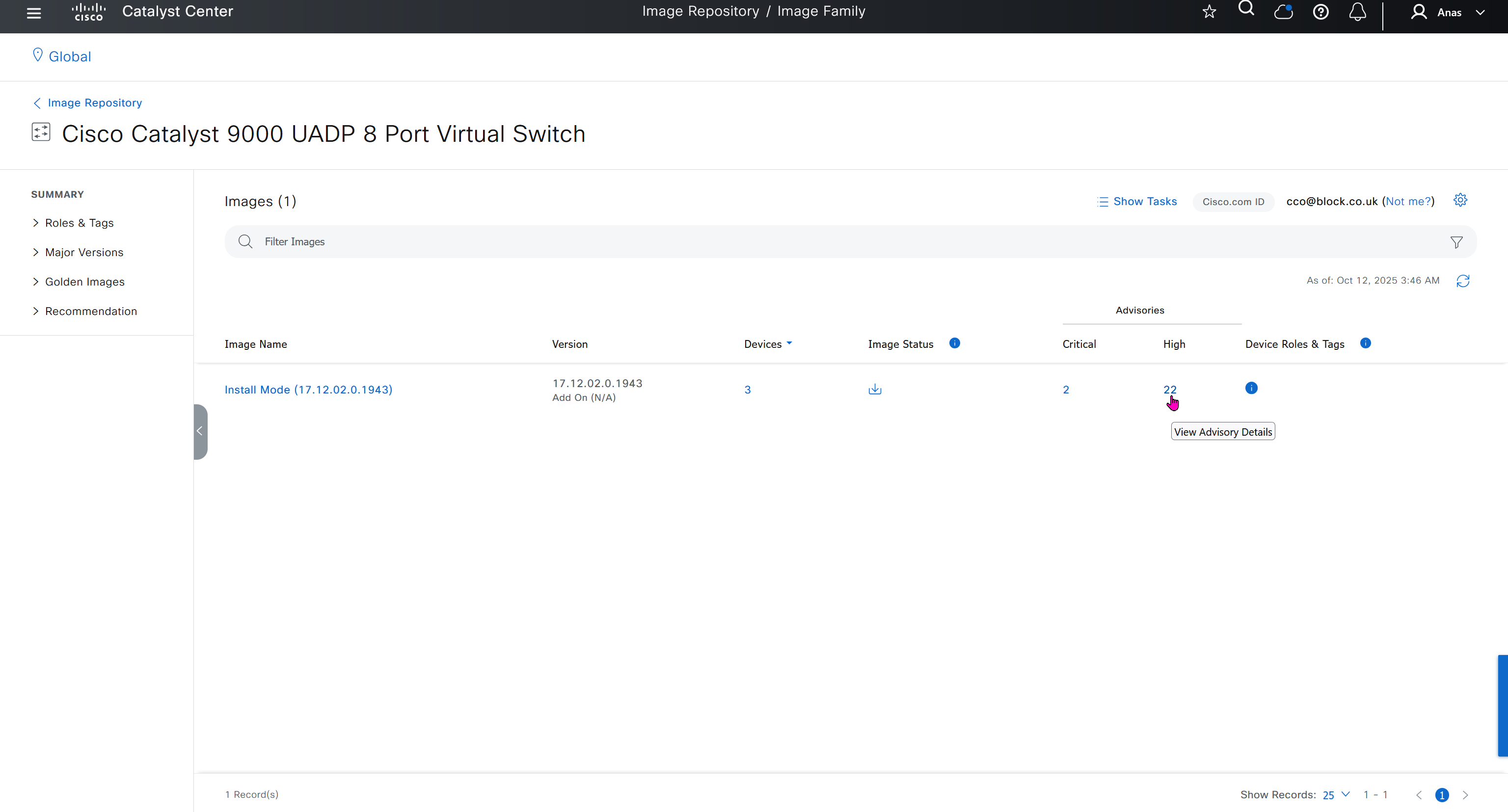
bundle mode images can be pulled from device and made golen image while for install mode we cannot pull from device and mark the image as golden image, instead we can either download from Cisco.com using gui or import image from file

Small “Verified” shows up next to image that shows that DNAC has downloaded the image, clicking that image makes it golden pretty fast because image is already on the DNAC server
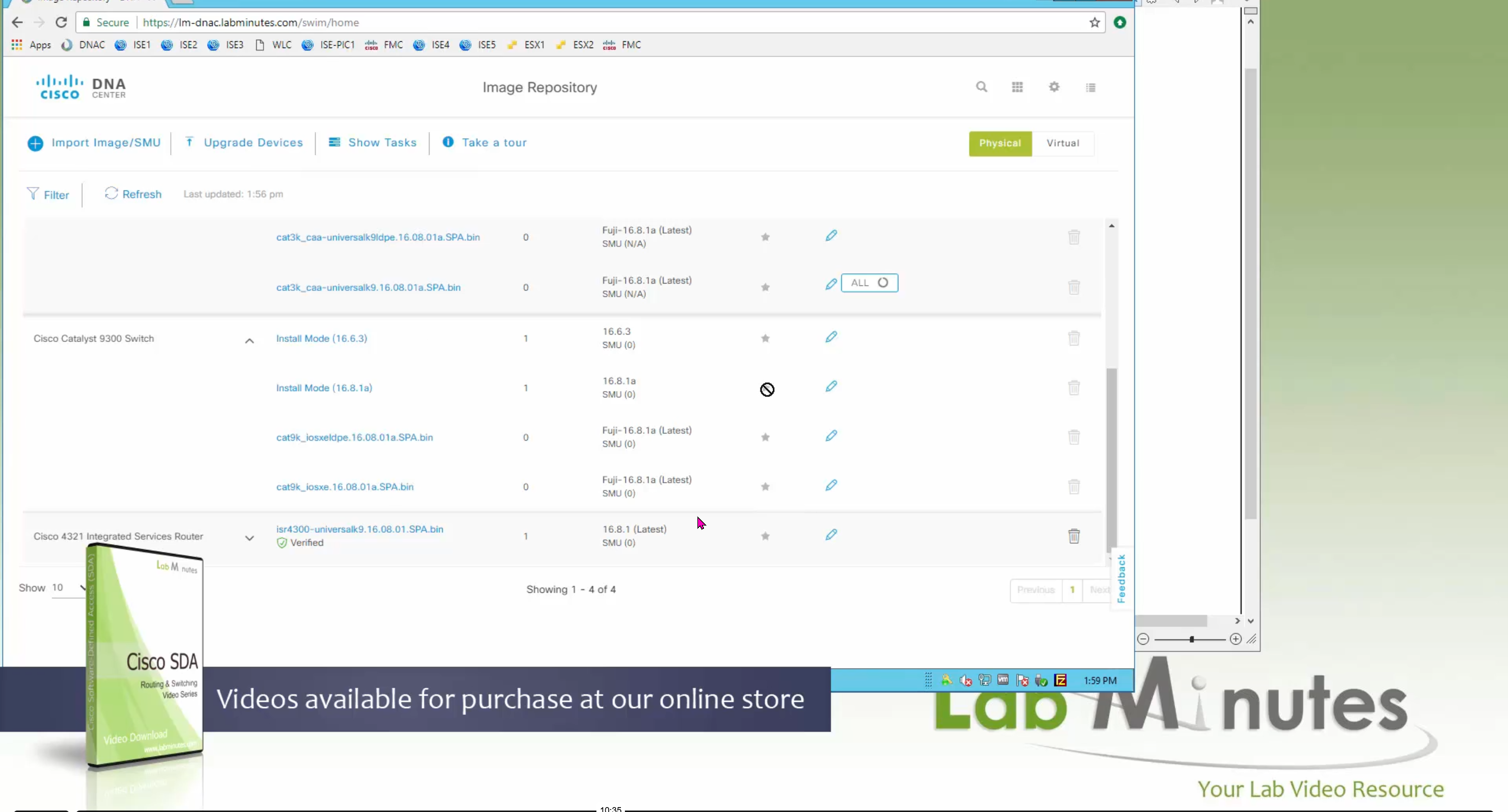
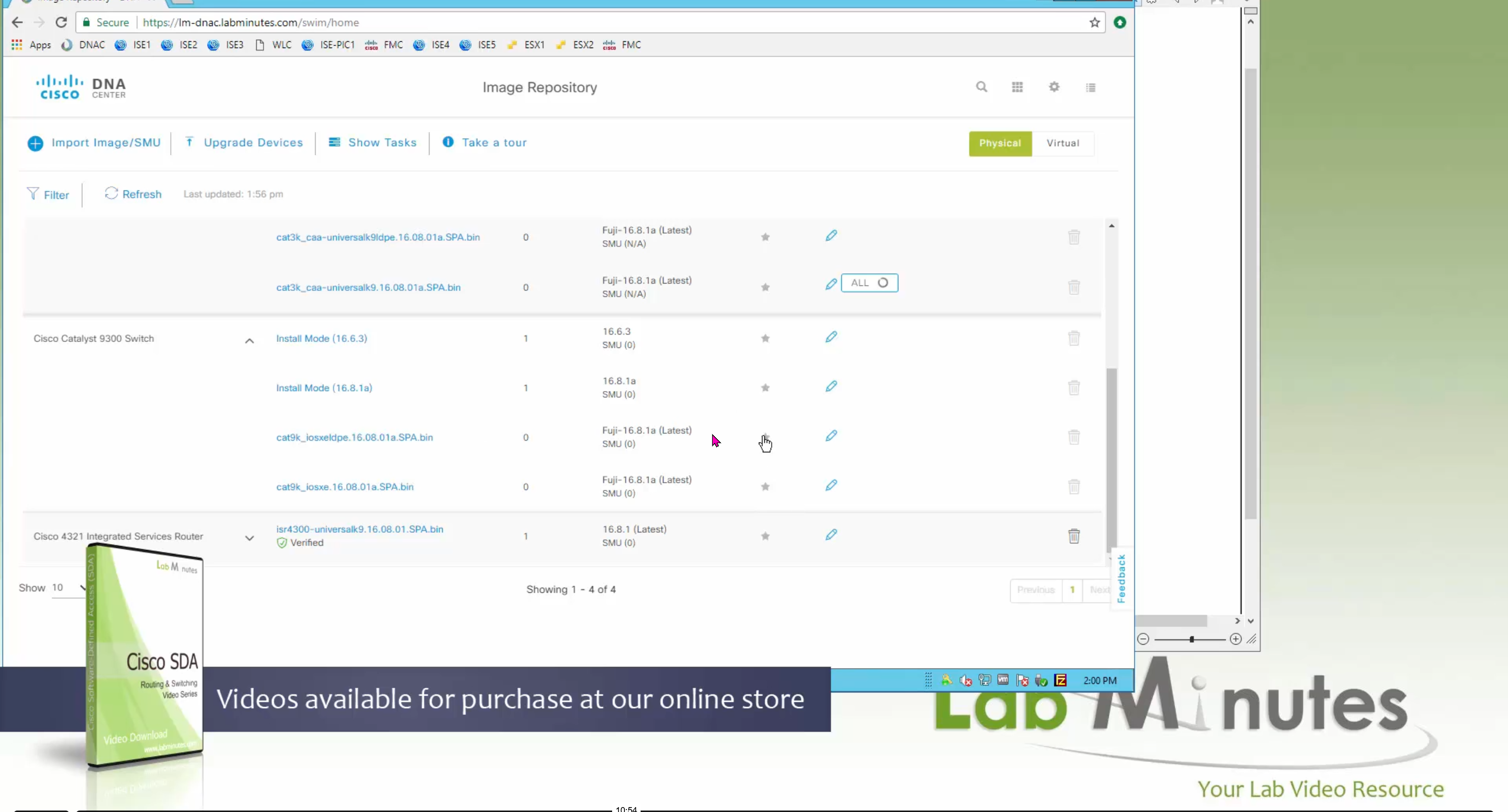
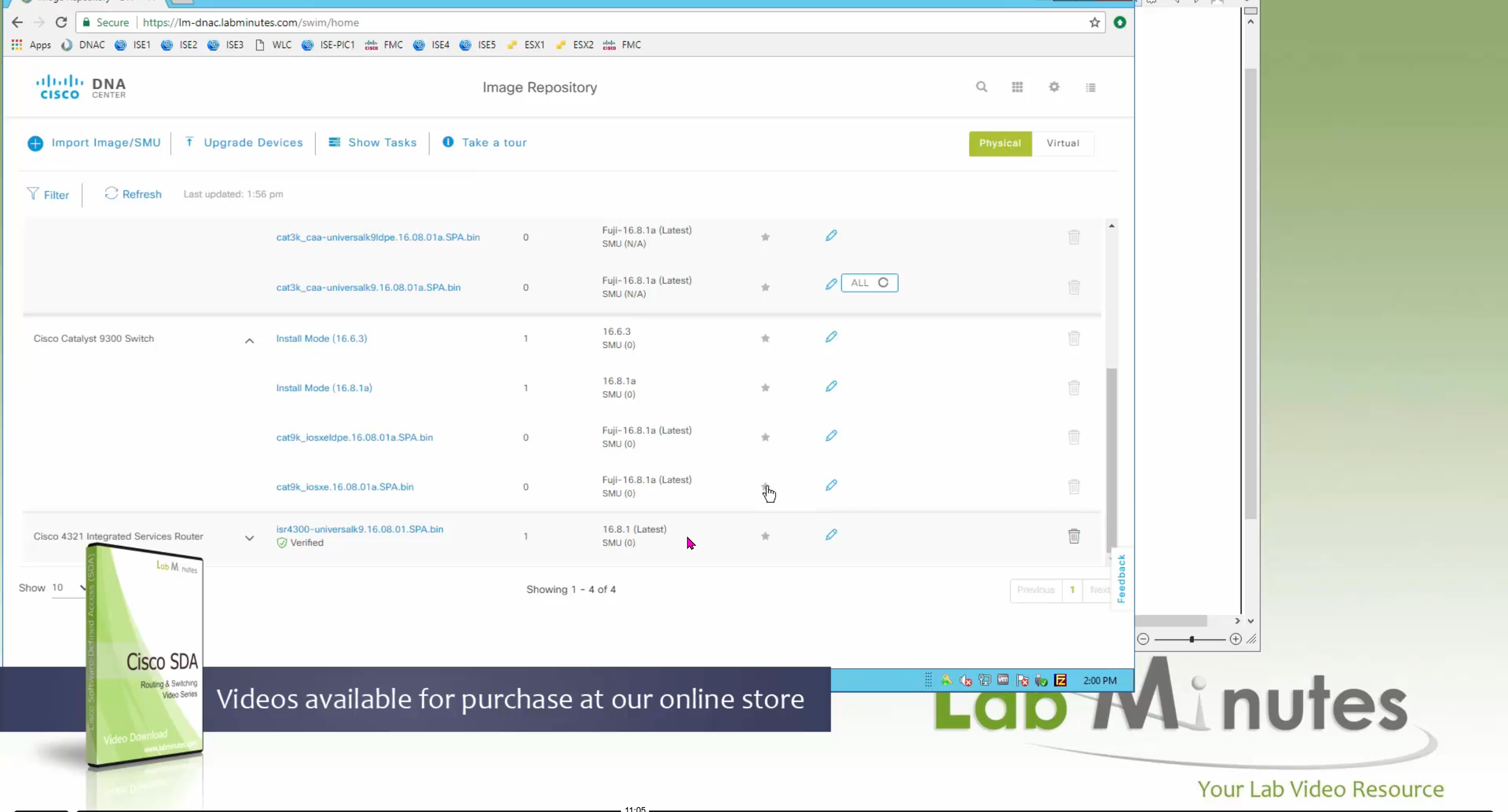
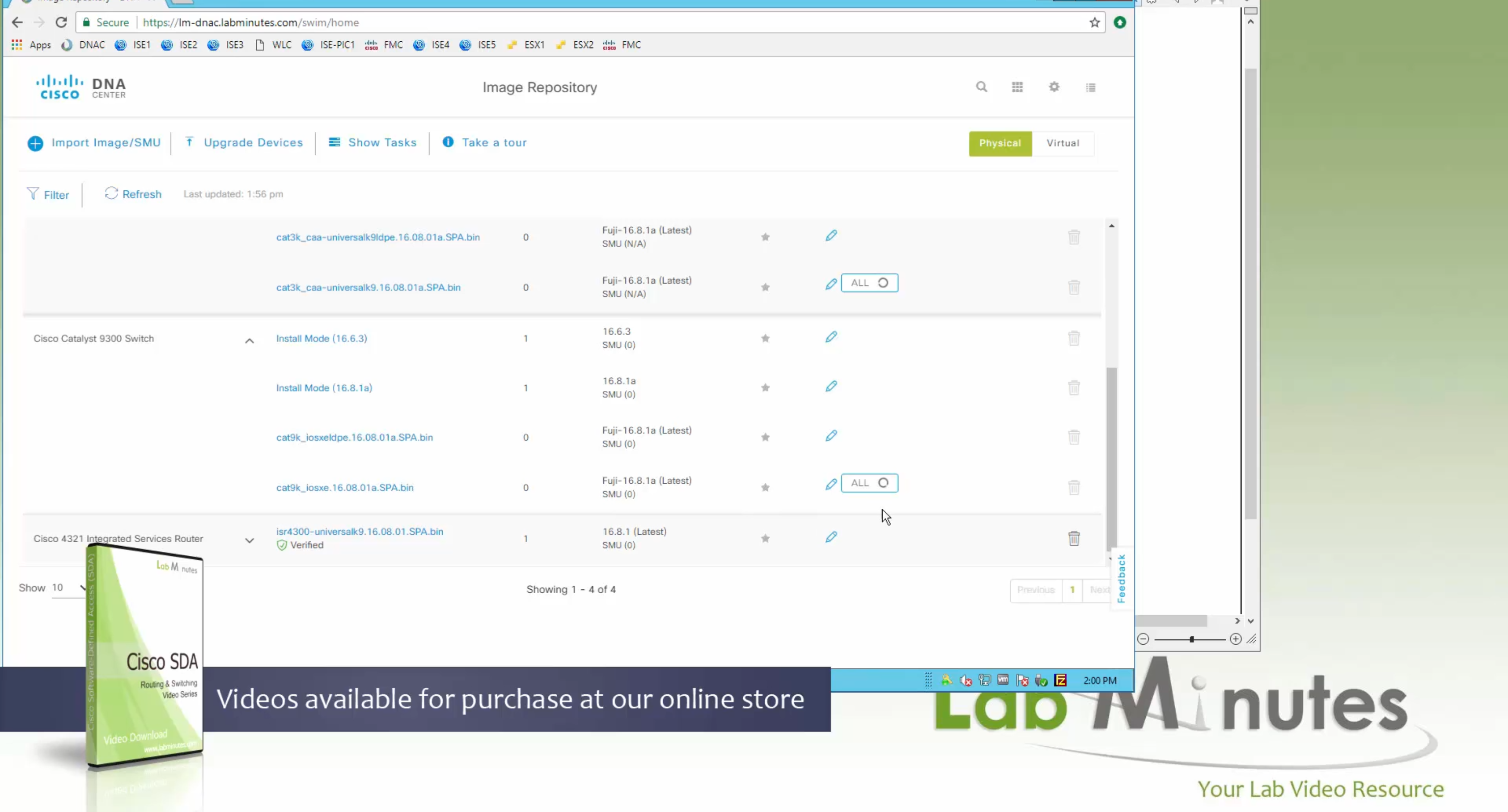




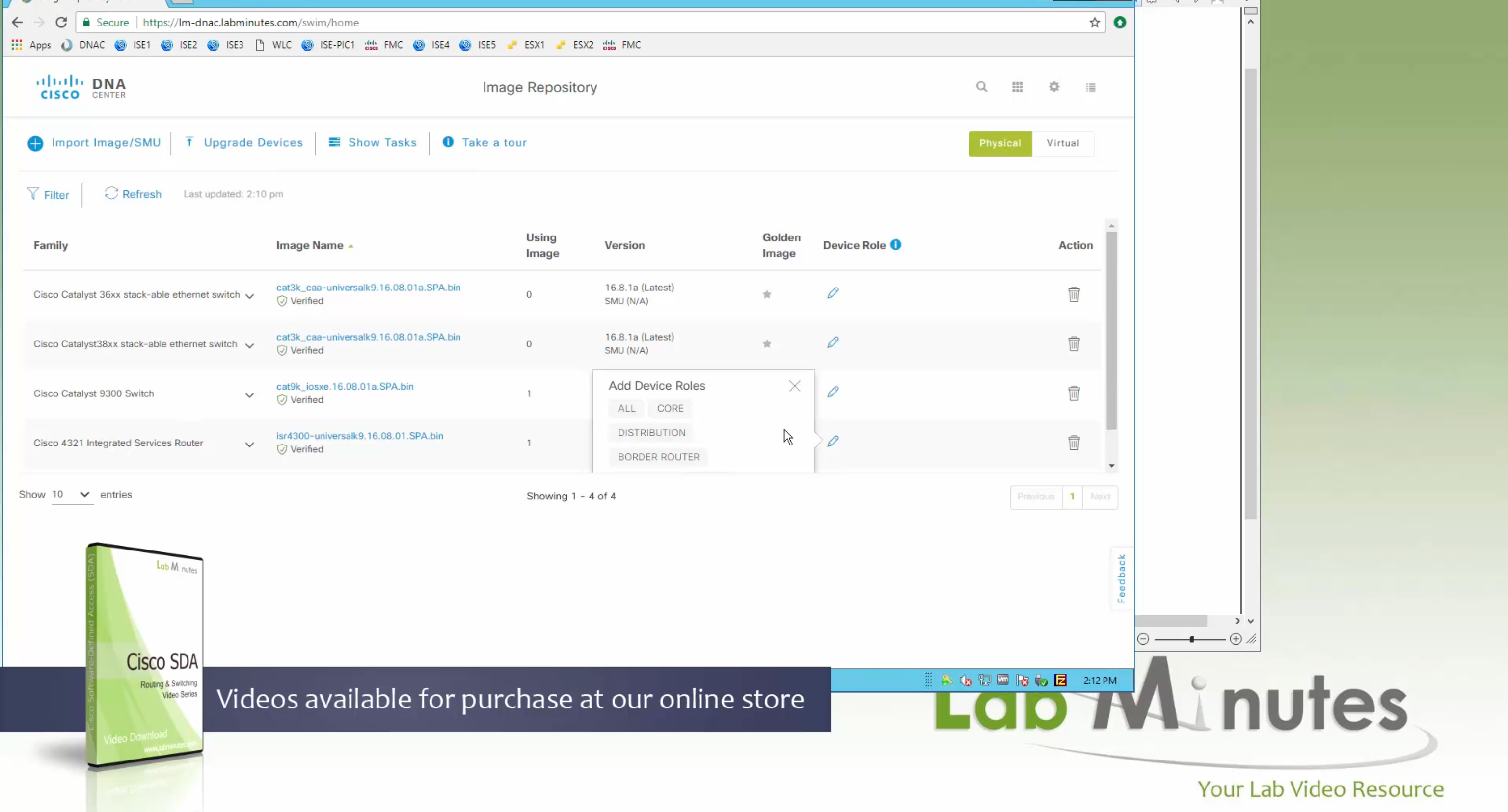
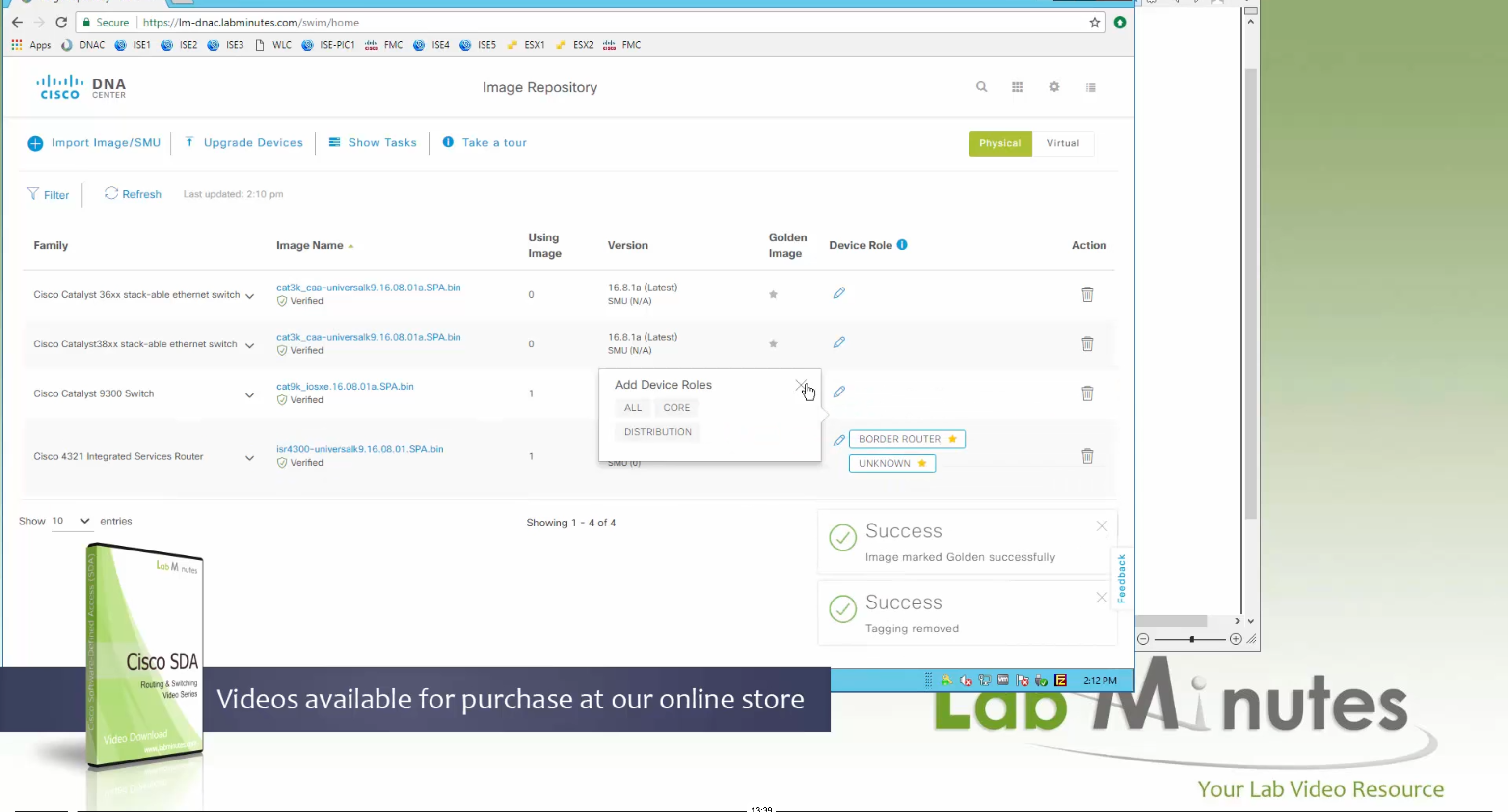
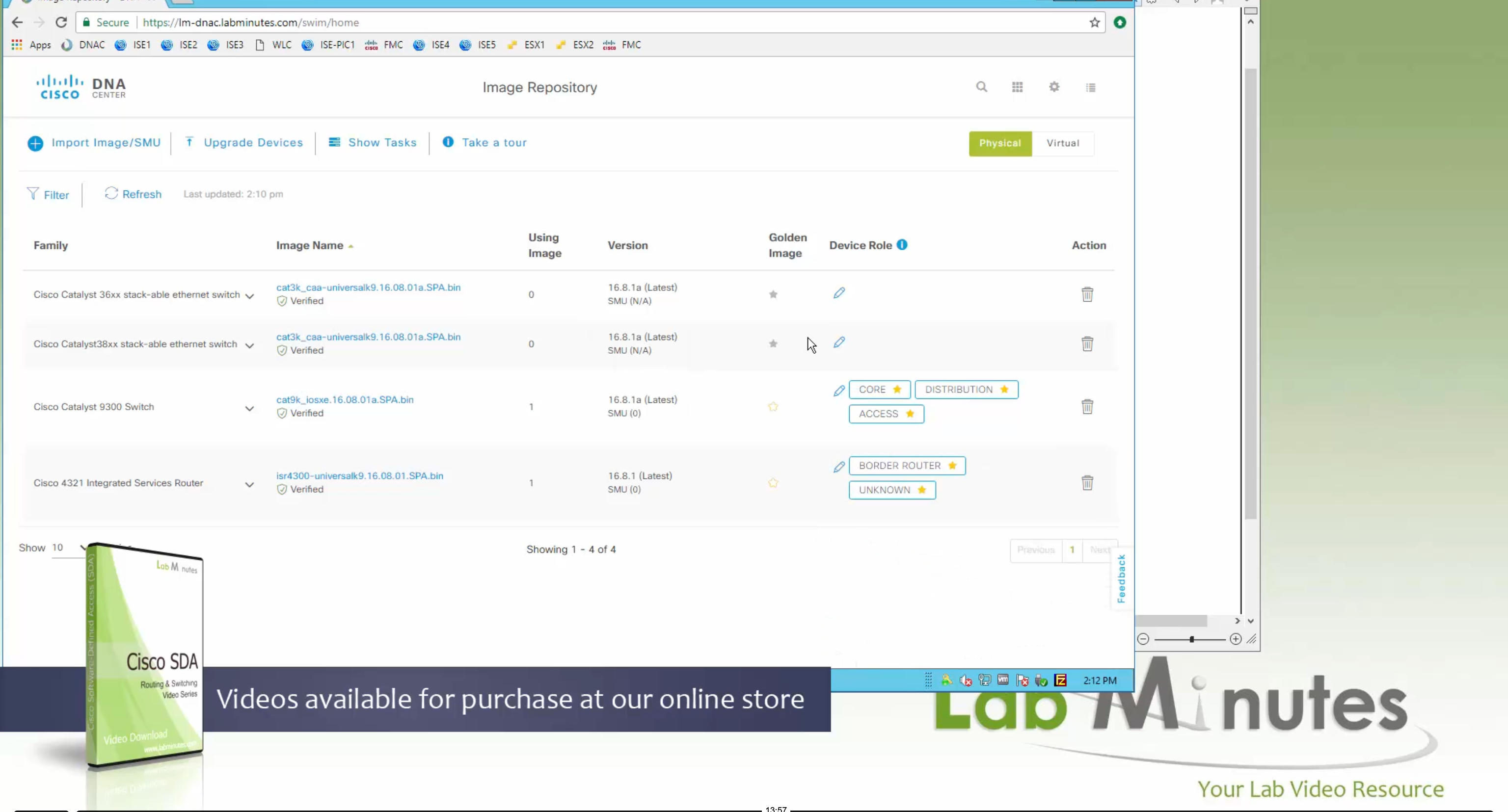

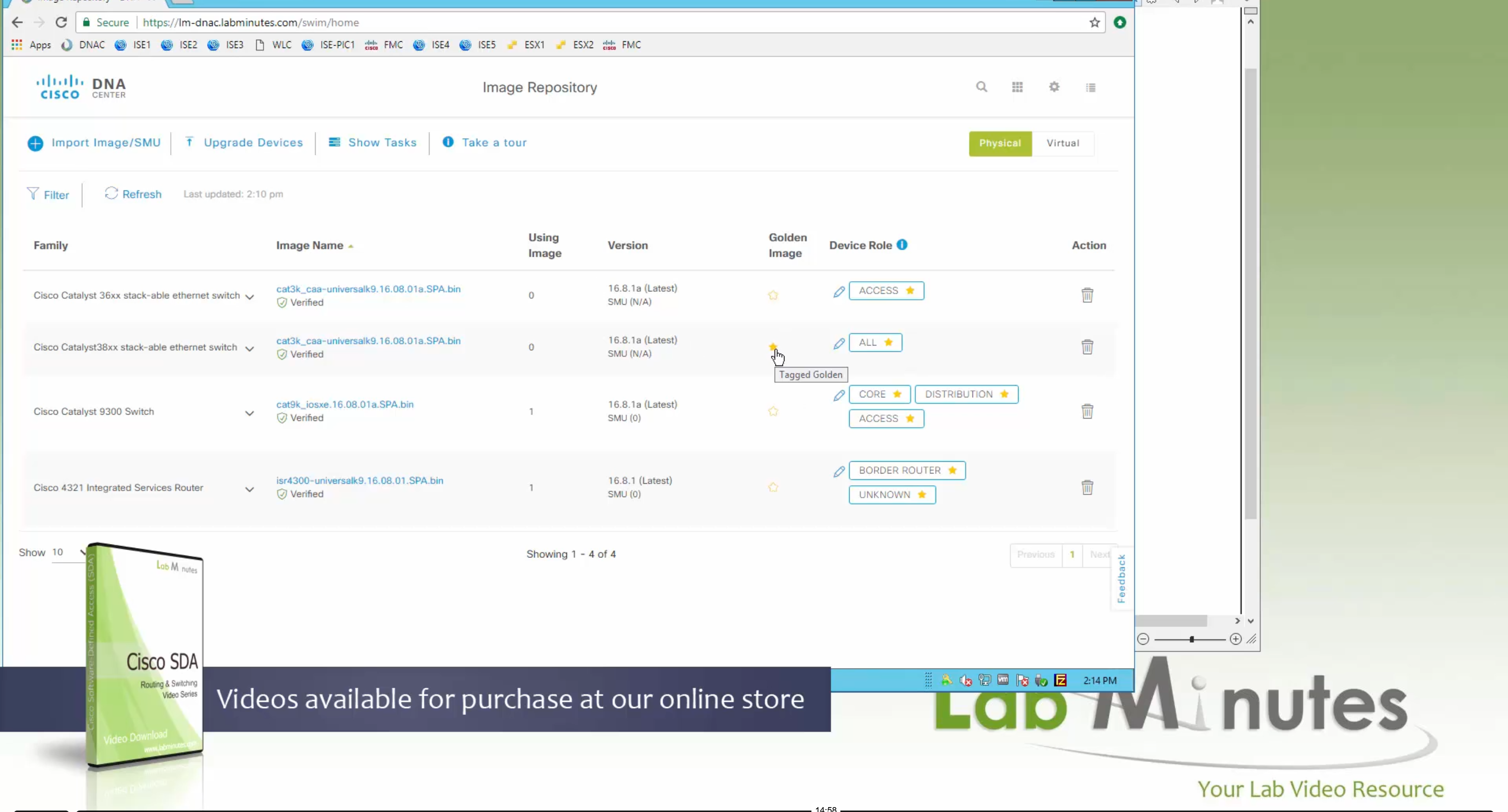
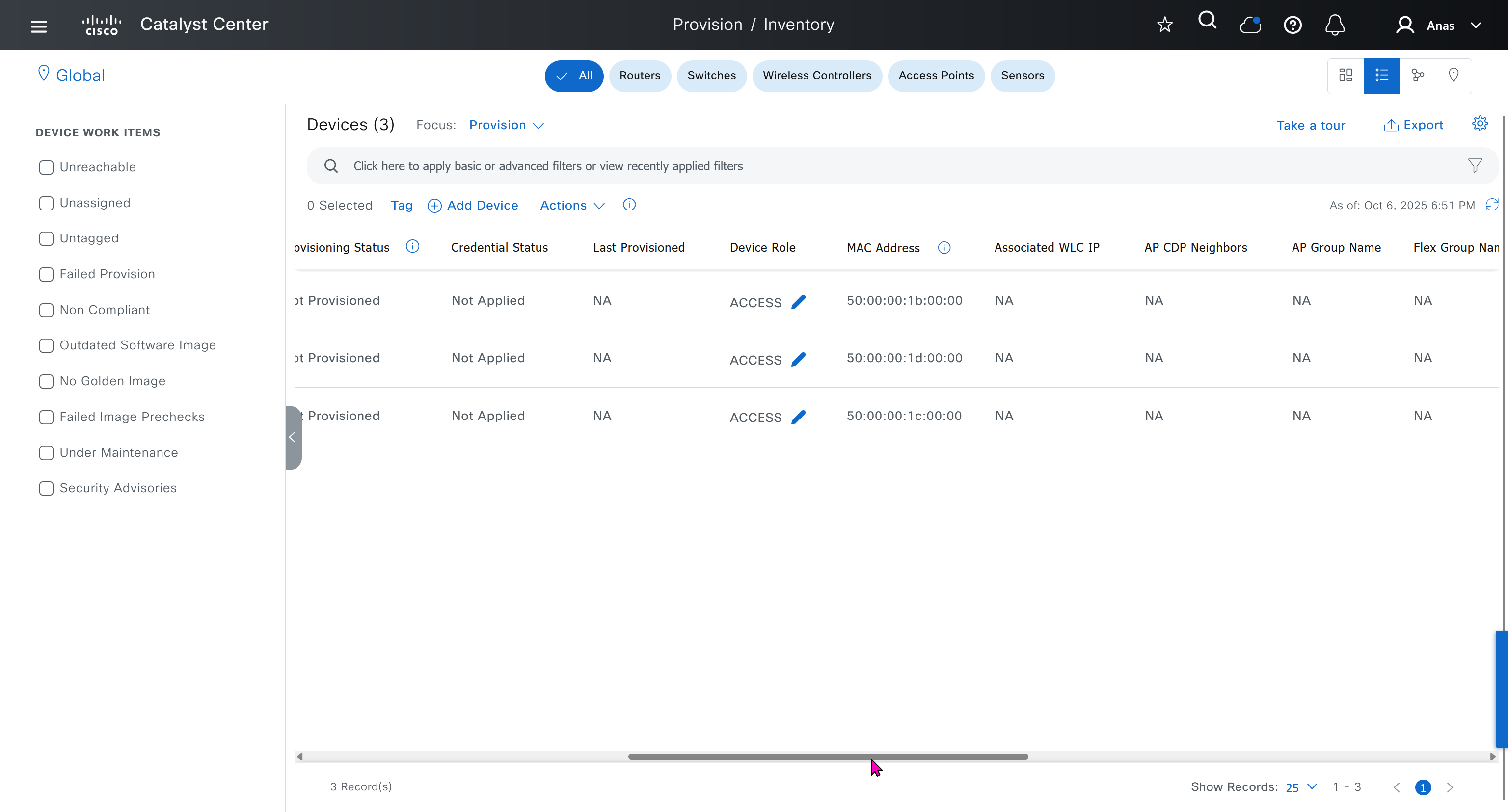
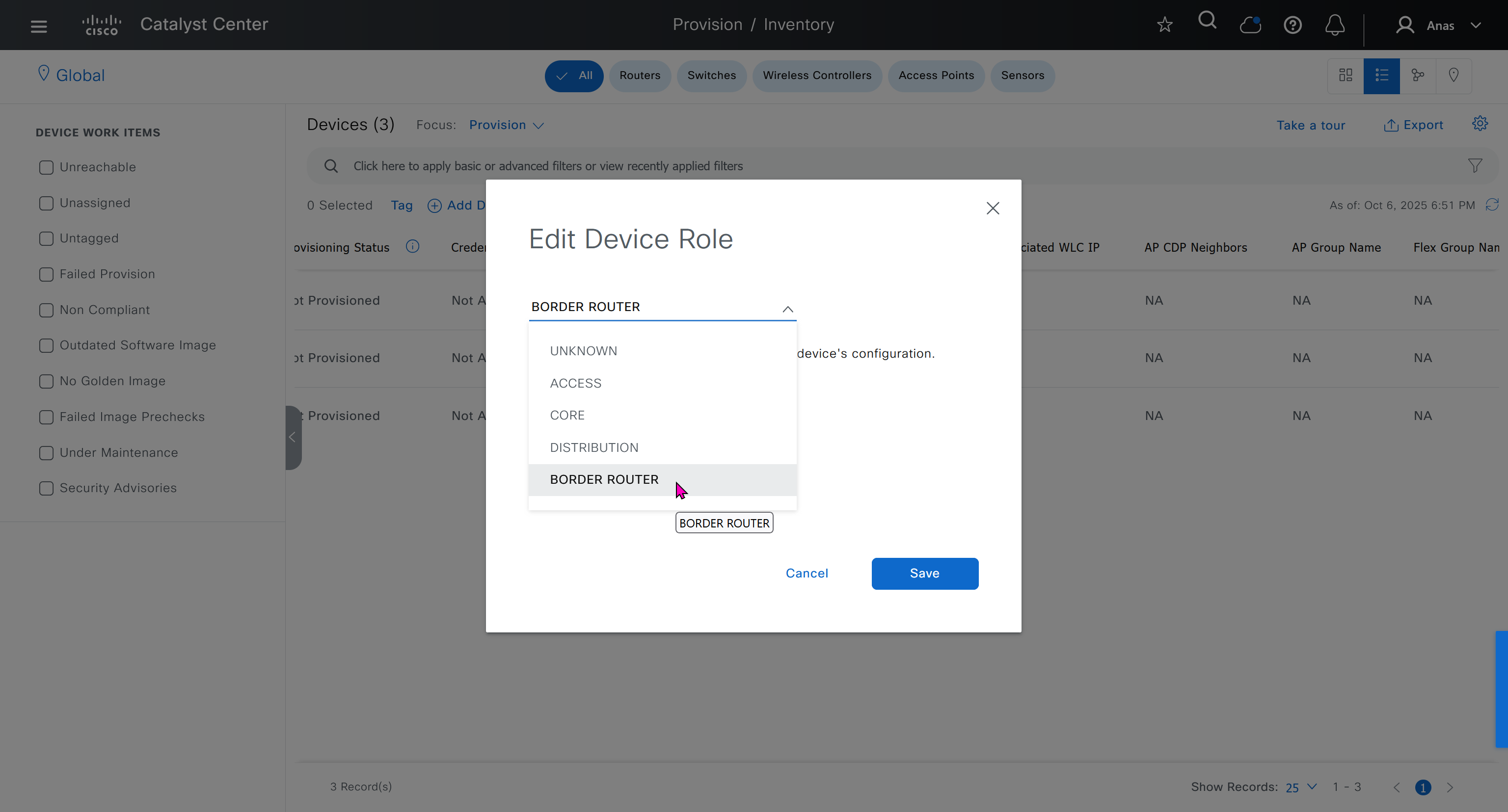
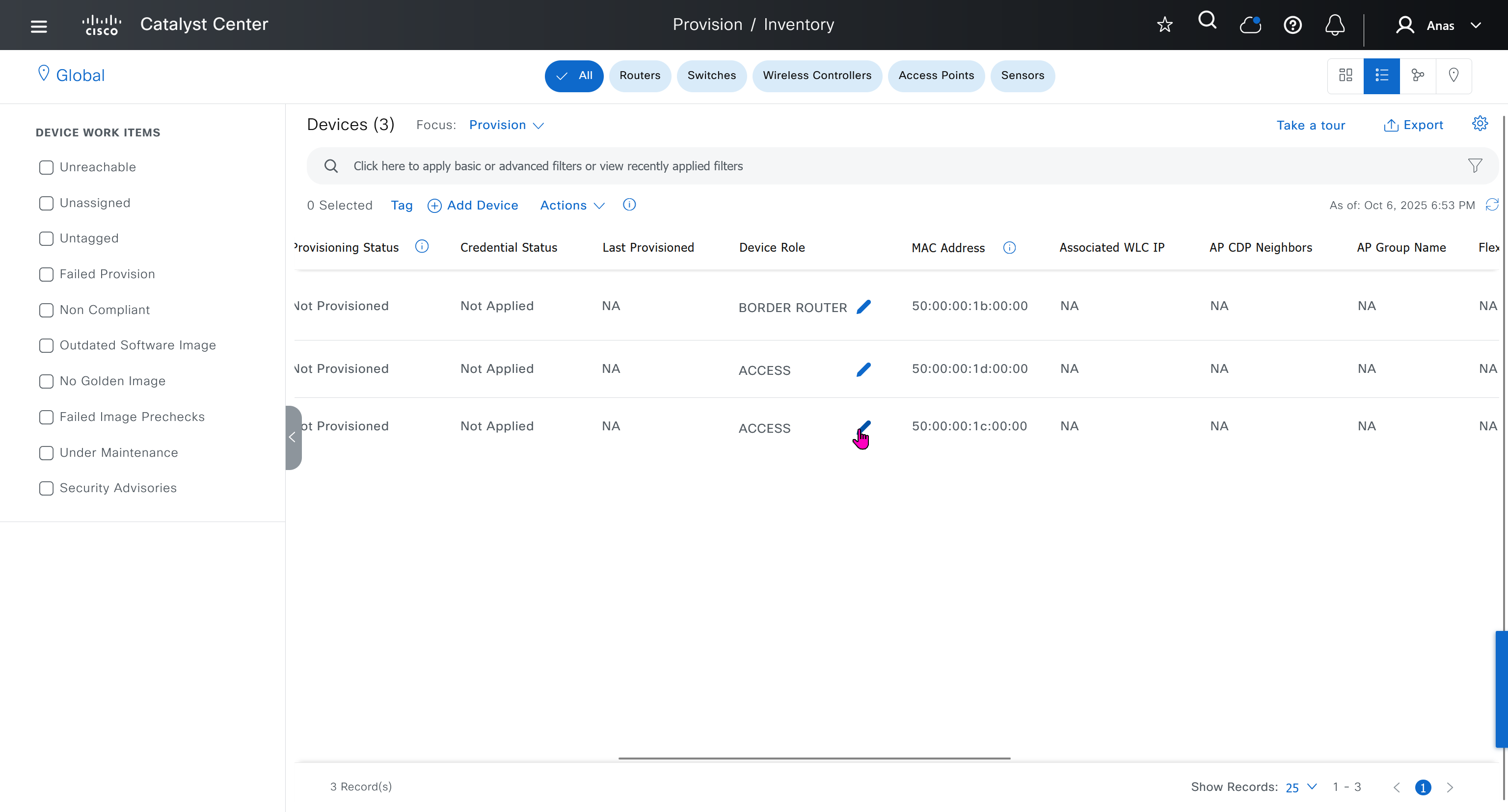
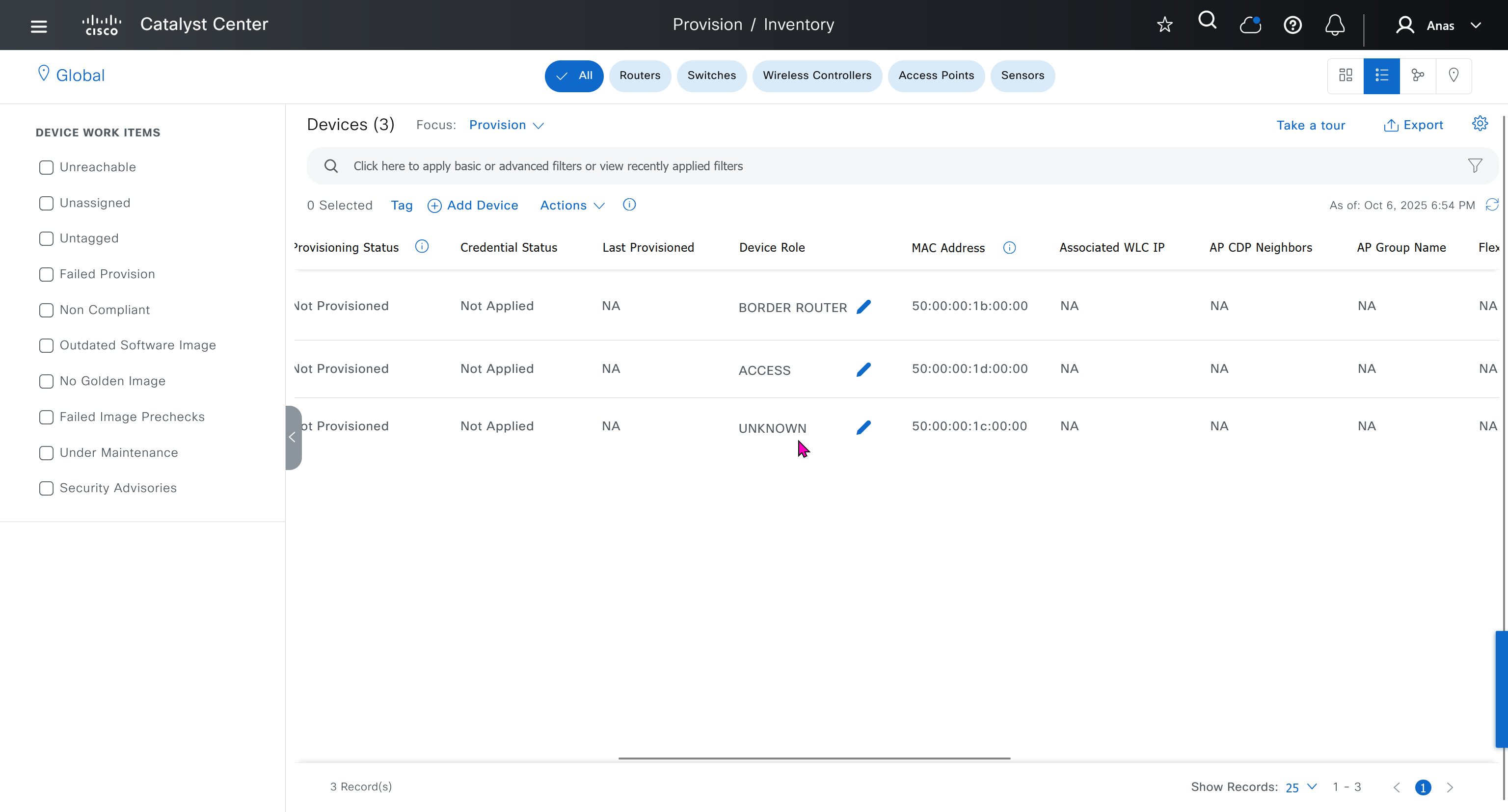
Now making an image golden makes it same for all devices of same hardware model same across different “Roles” and all locations (Globally) and sometimes you may not want that, you can click on edit icon in device role column and set golden image per hardware model per device role, such as all “C9300” / “Access” to have a specific image or you can even have golden image per hardware model per role per location – but first you must remove the golden image from global level and then set it on site level, there is no concept of override here, either set at global level or set at all sites independently




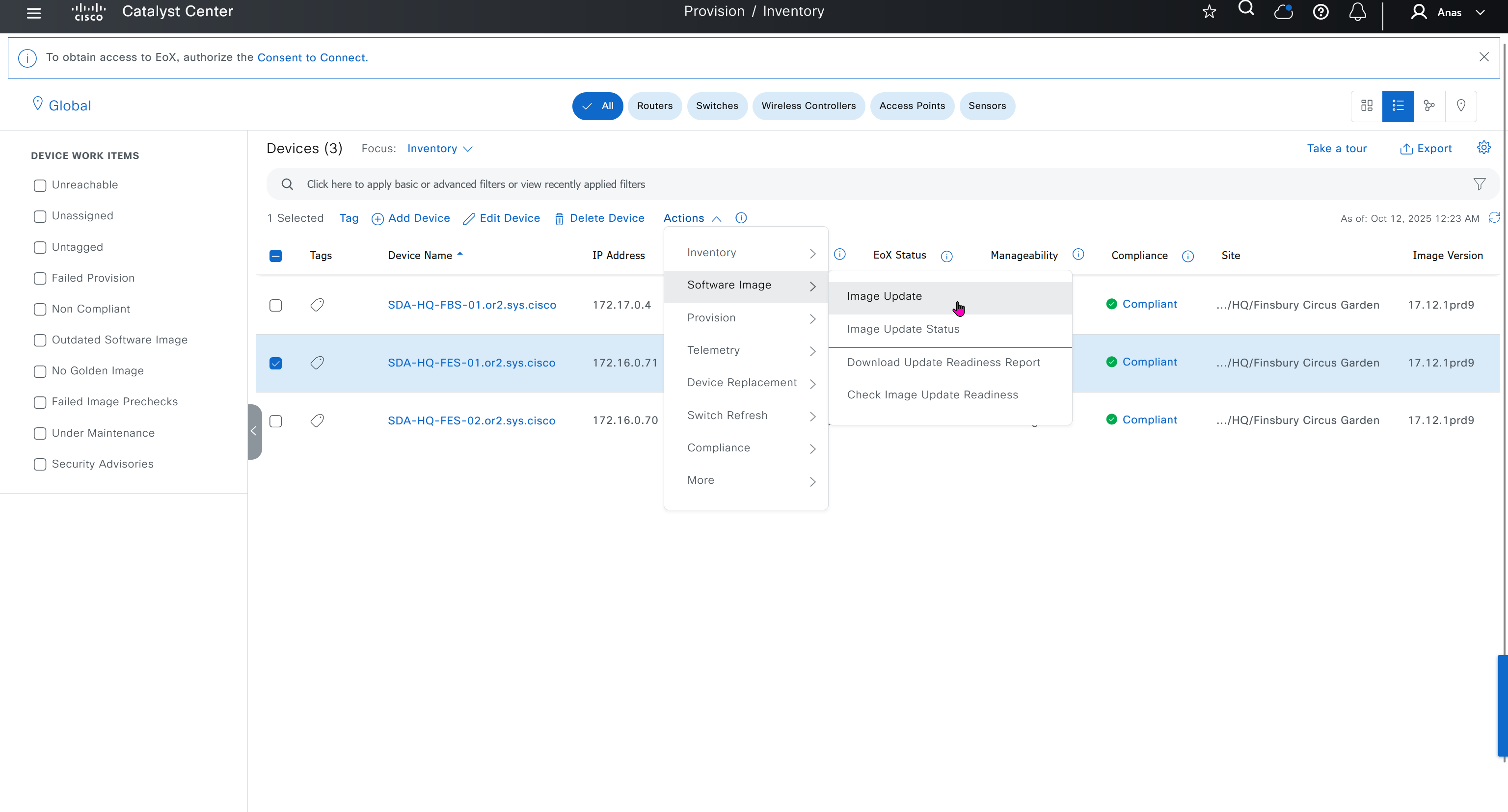
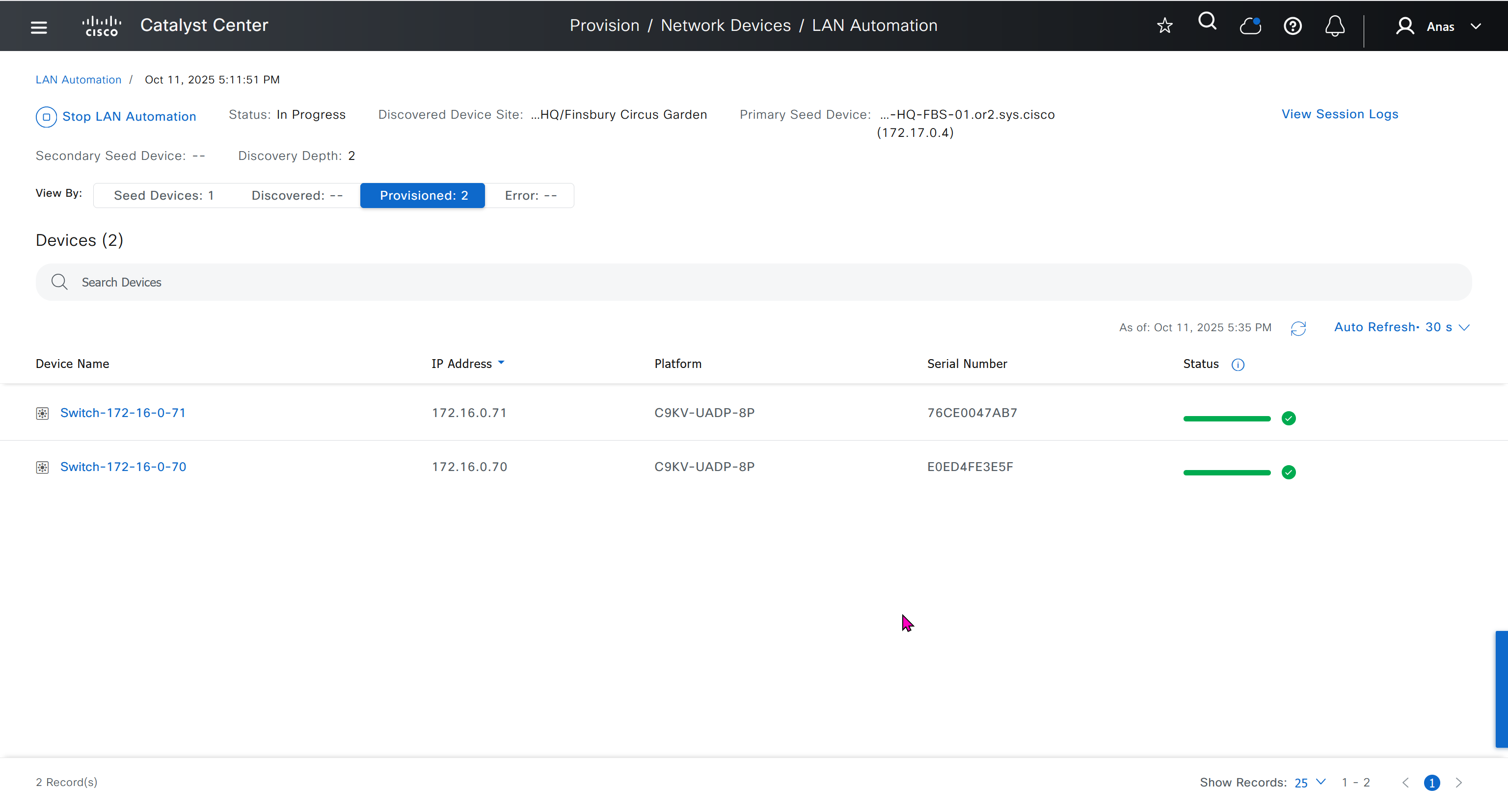
Next step is to see which devices are not in compliance and upgrade them in provision > OS image column


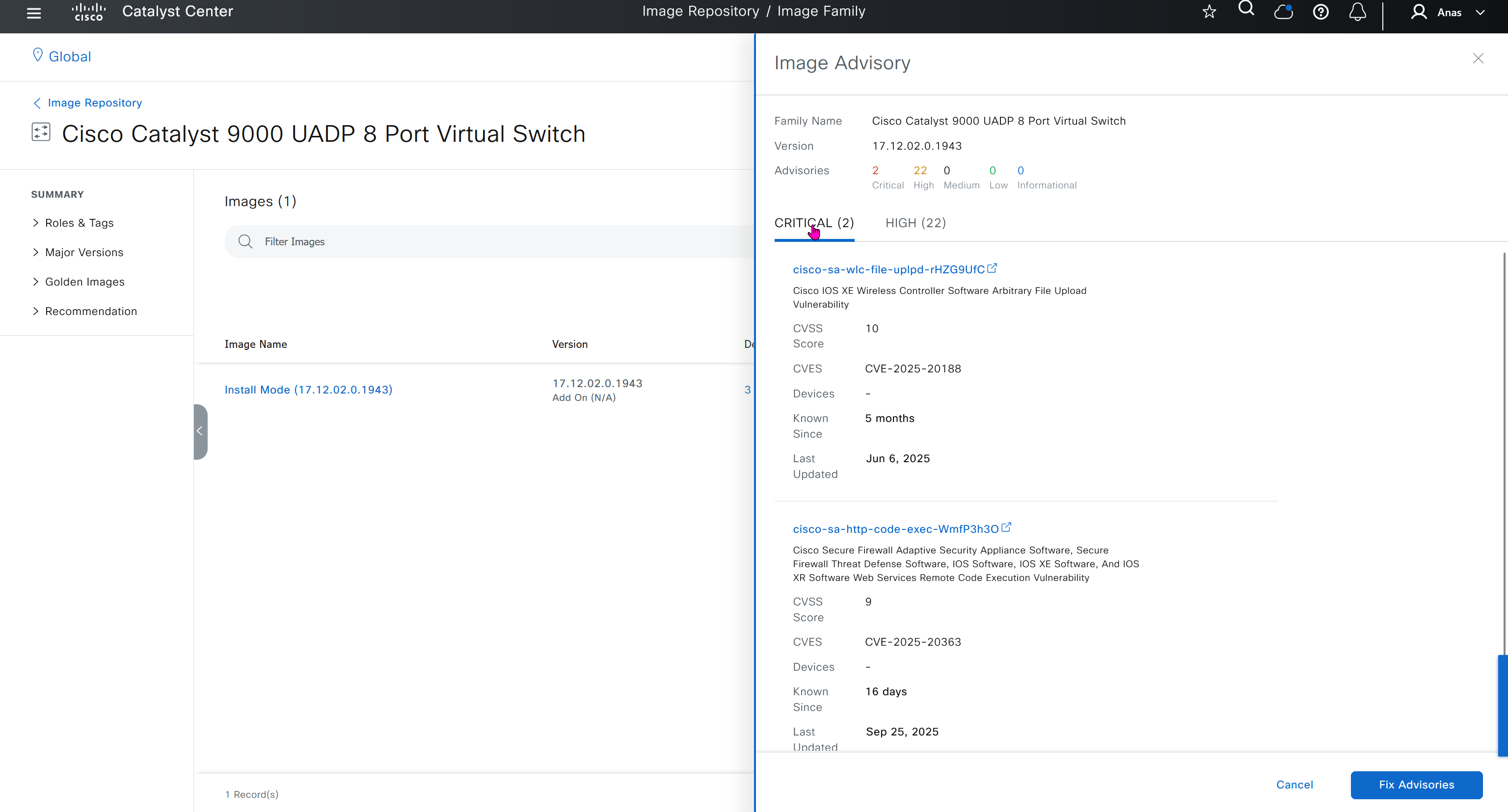
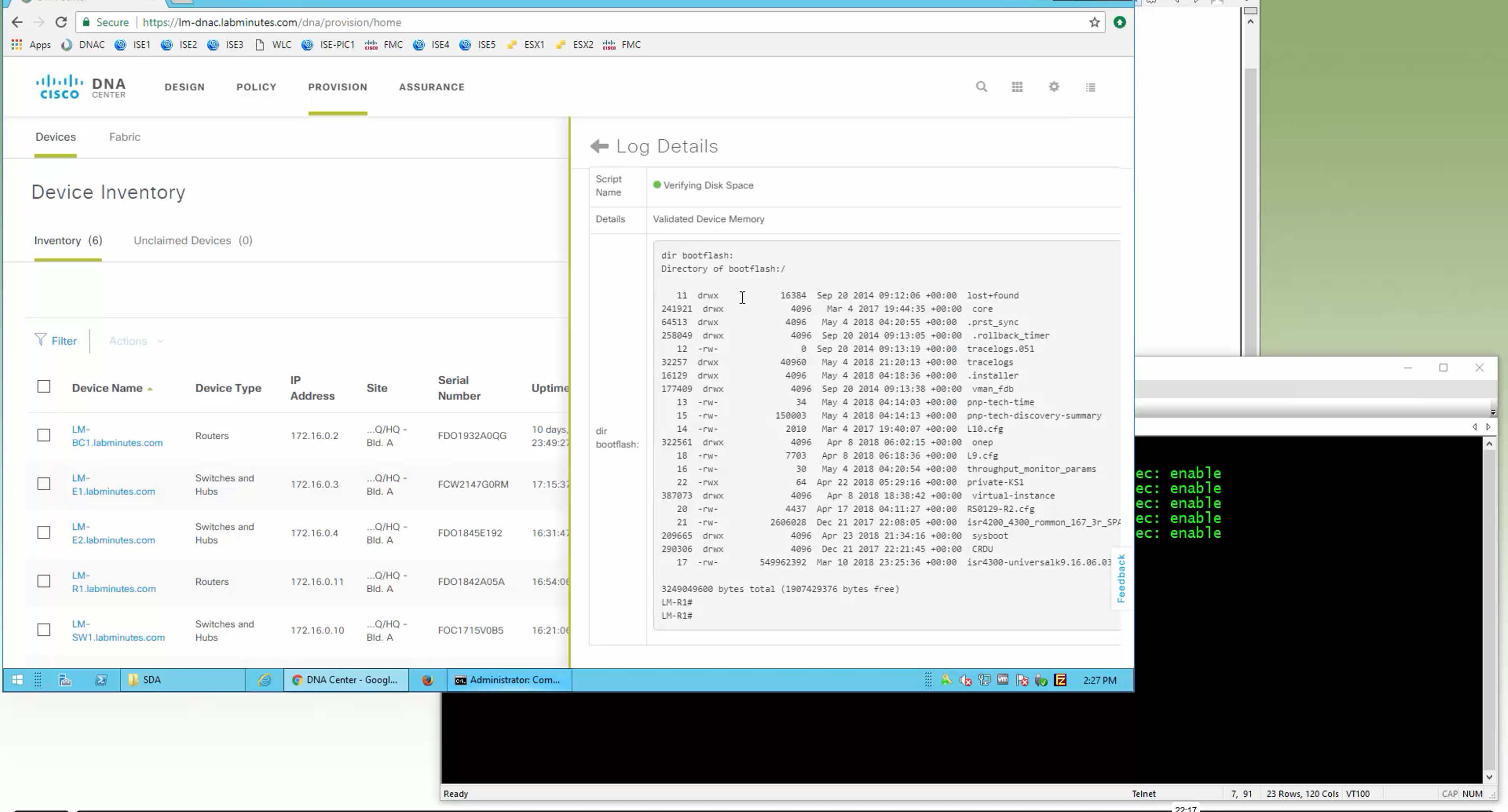
DNAC validates Flash, RAM and Reboot required


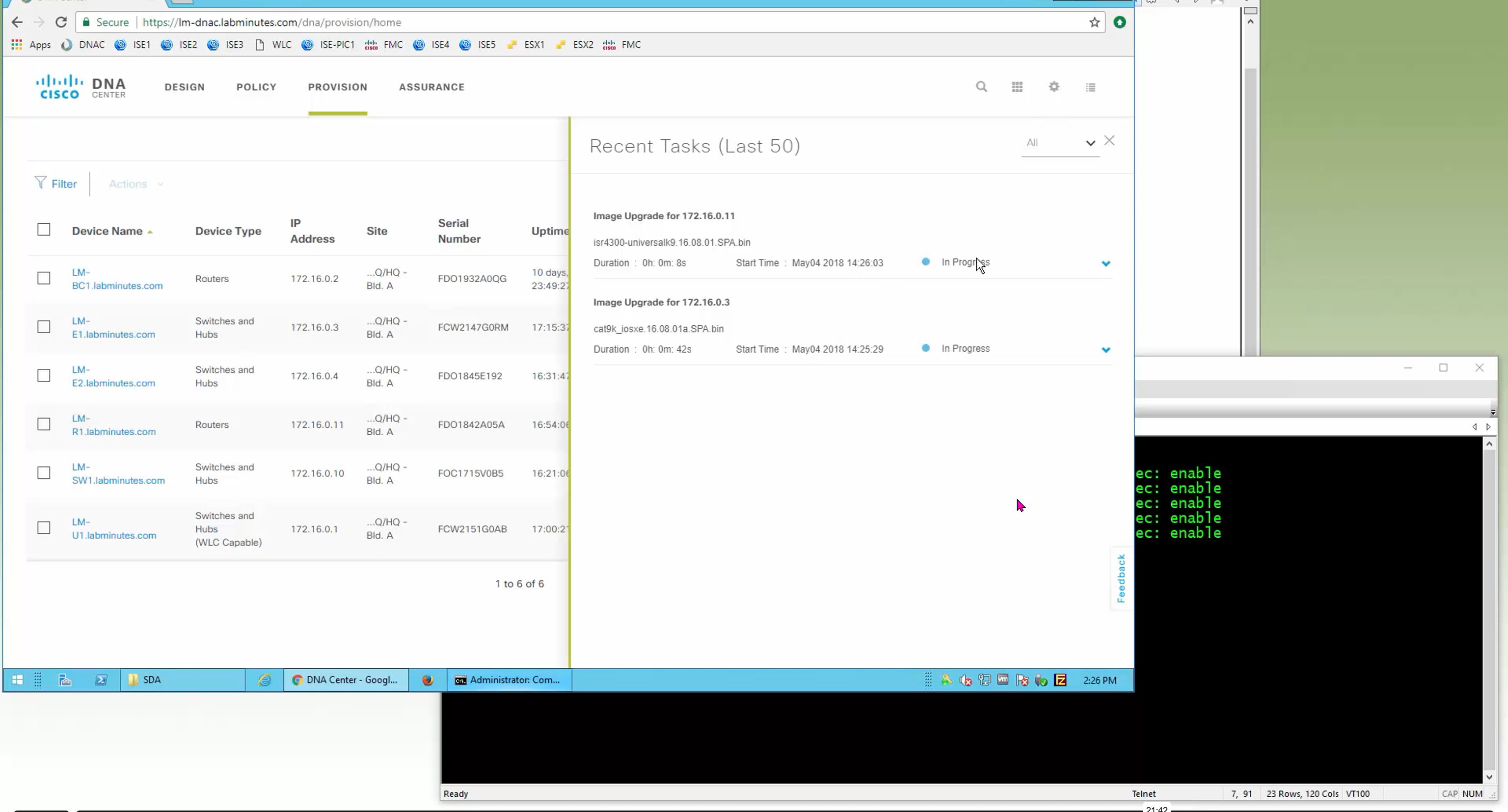

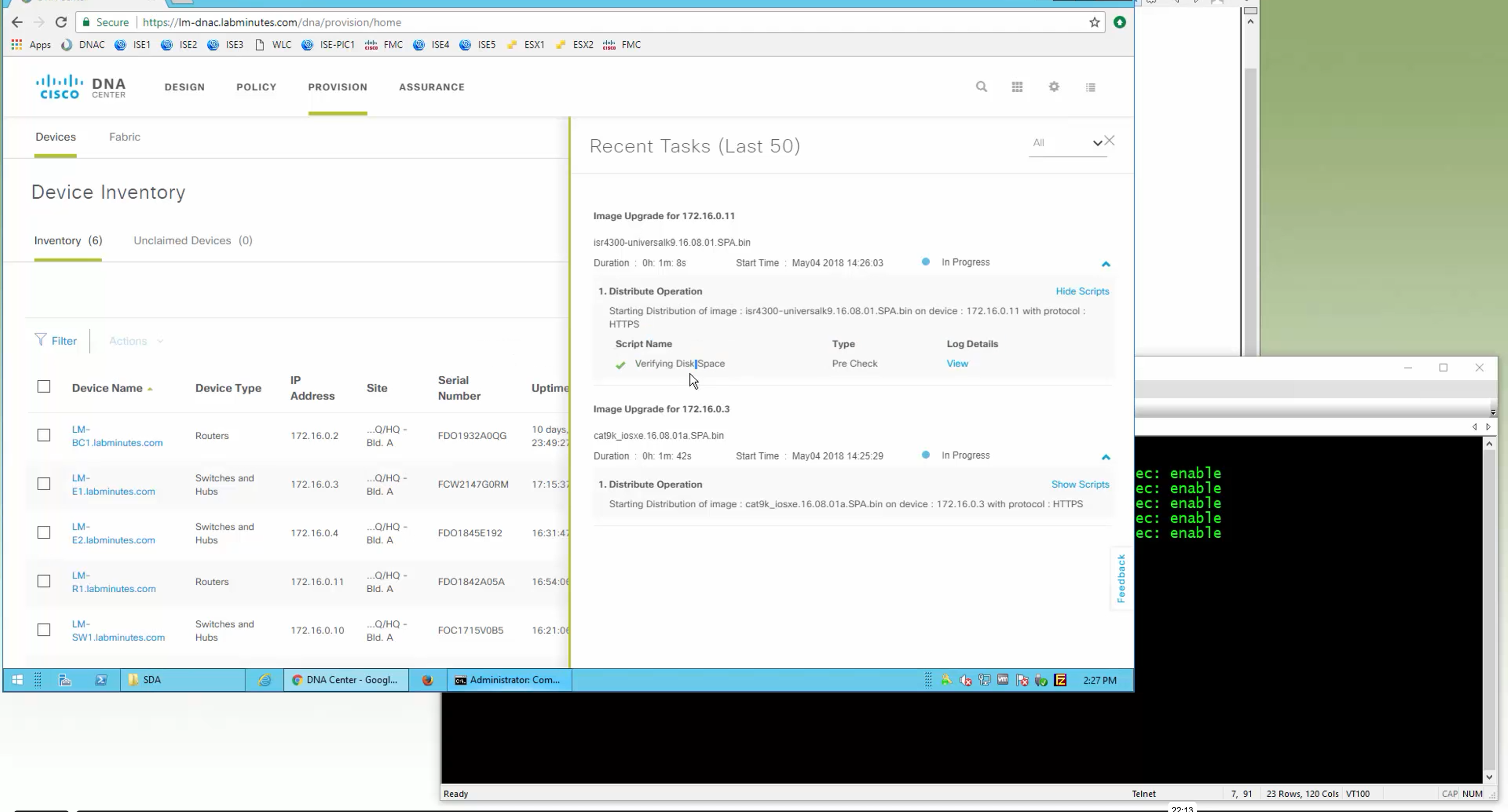

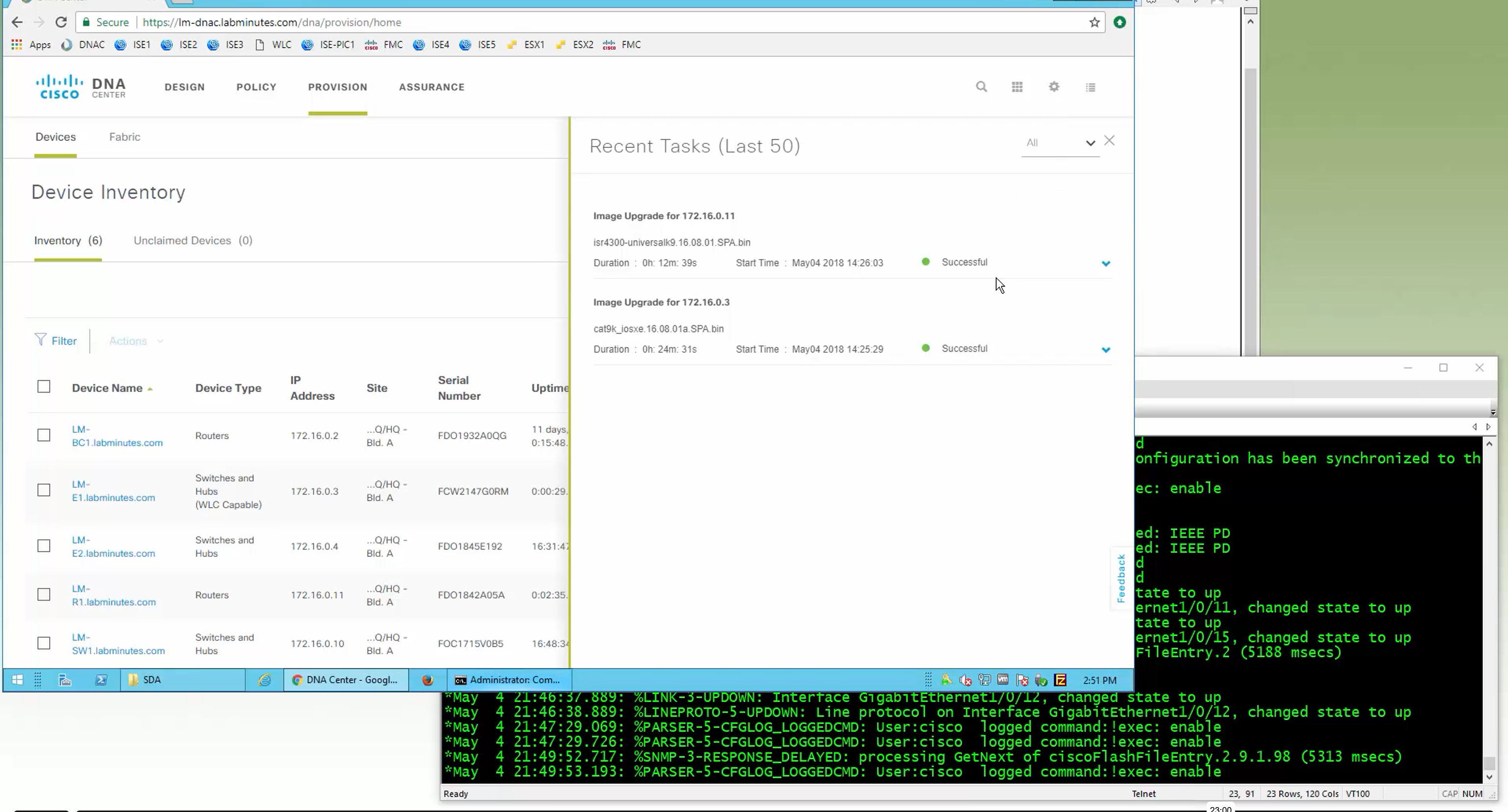
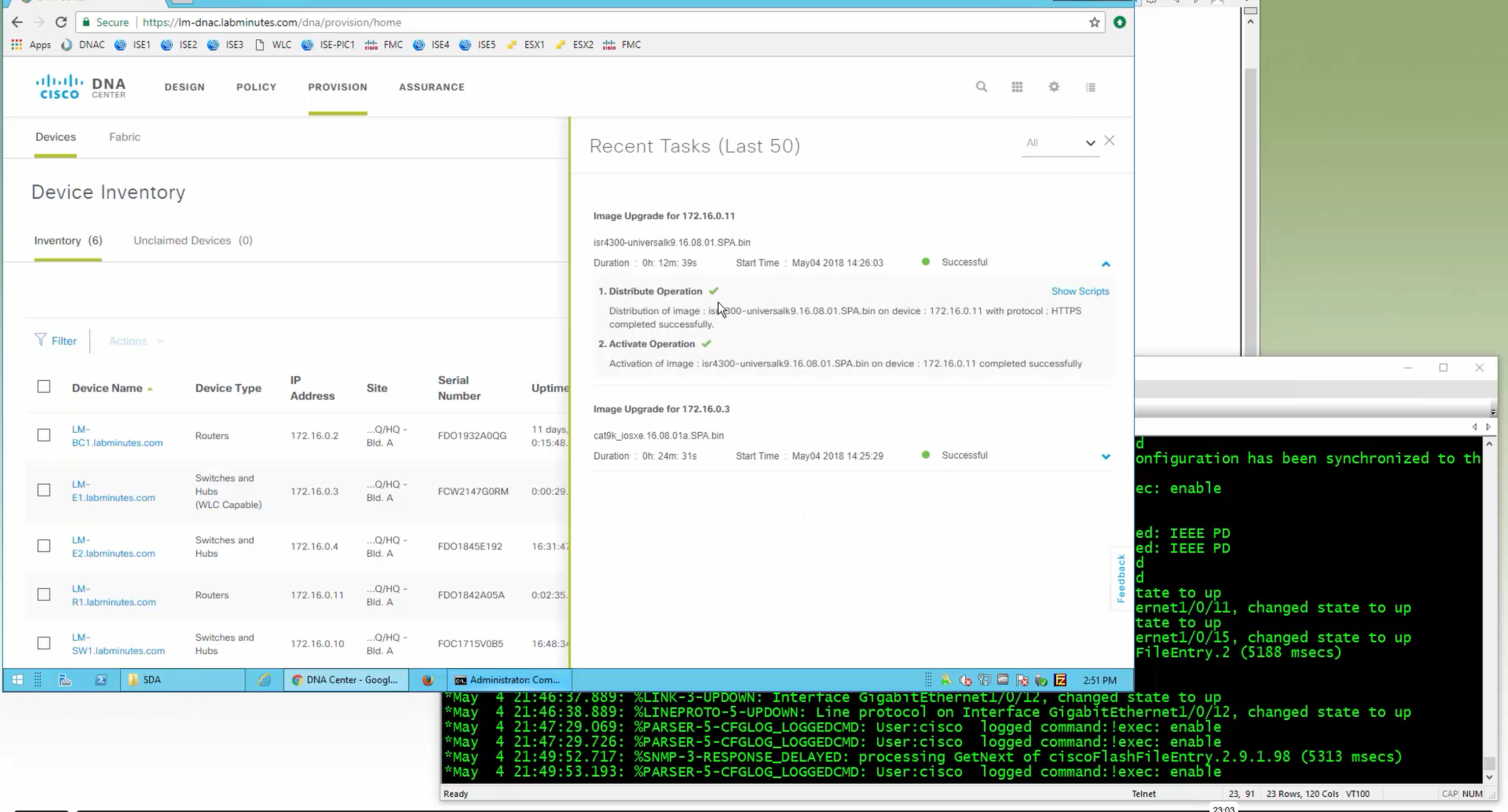

SMU(0) means that there is no SMU for this image version

one big improvement in version 2.1 is that you can download image from local server instead of DNAC over the WAN
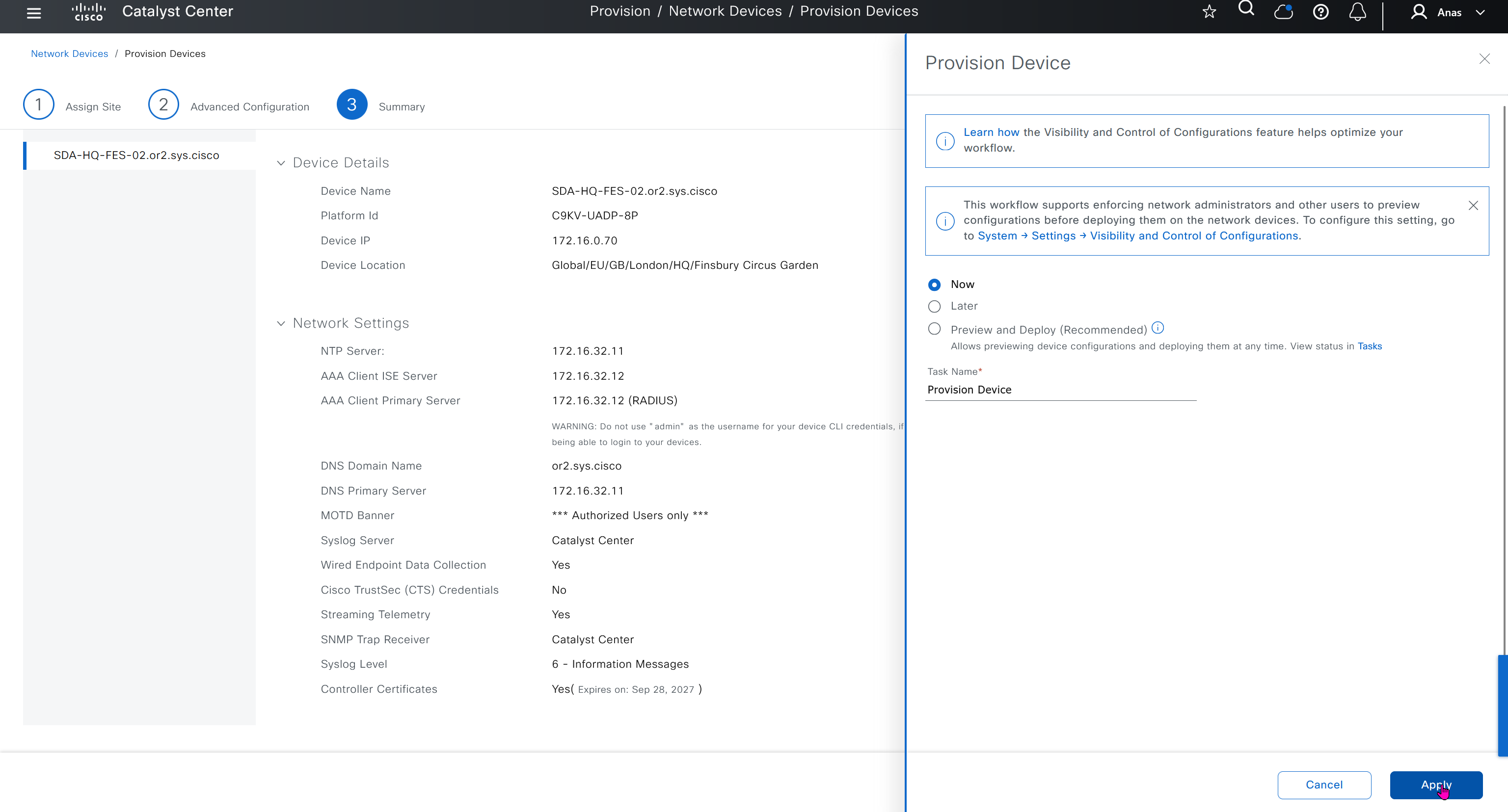
“Provision > provision device” pushes the remaining config as config assigned during assignment of device to site is not full config, full config is deployed when device is provisioned
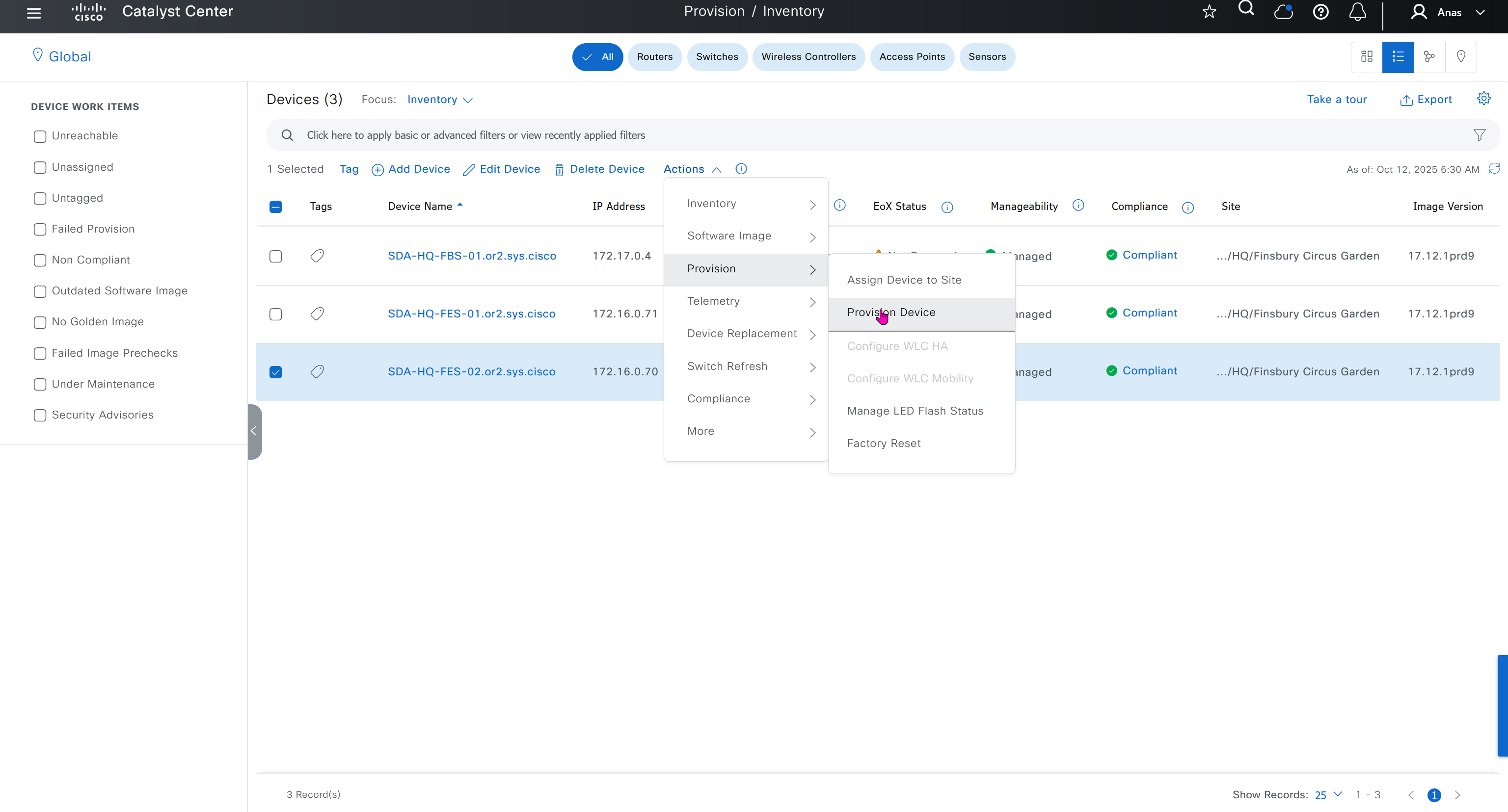

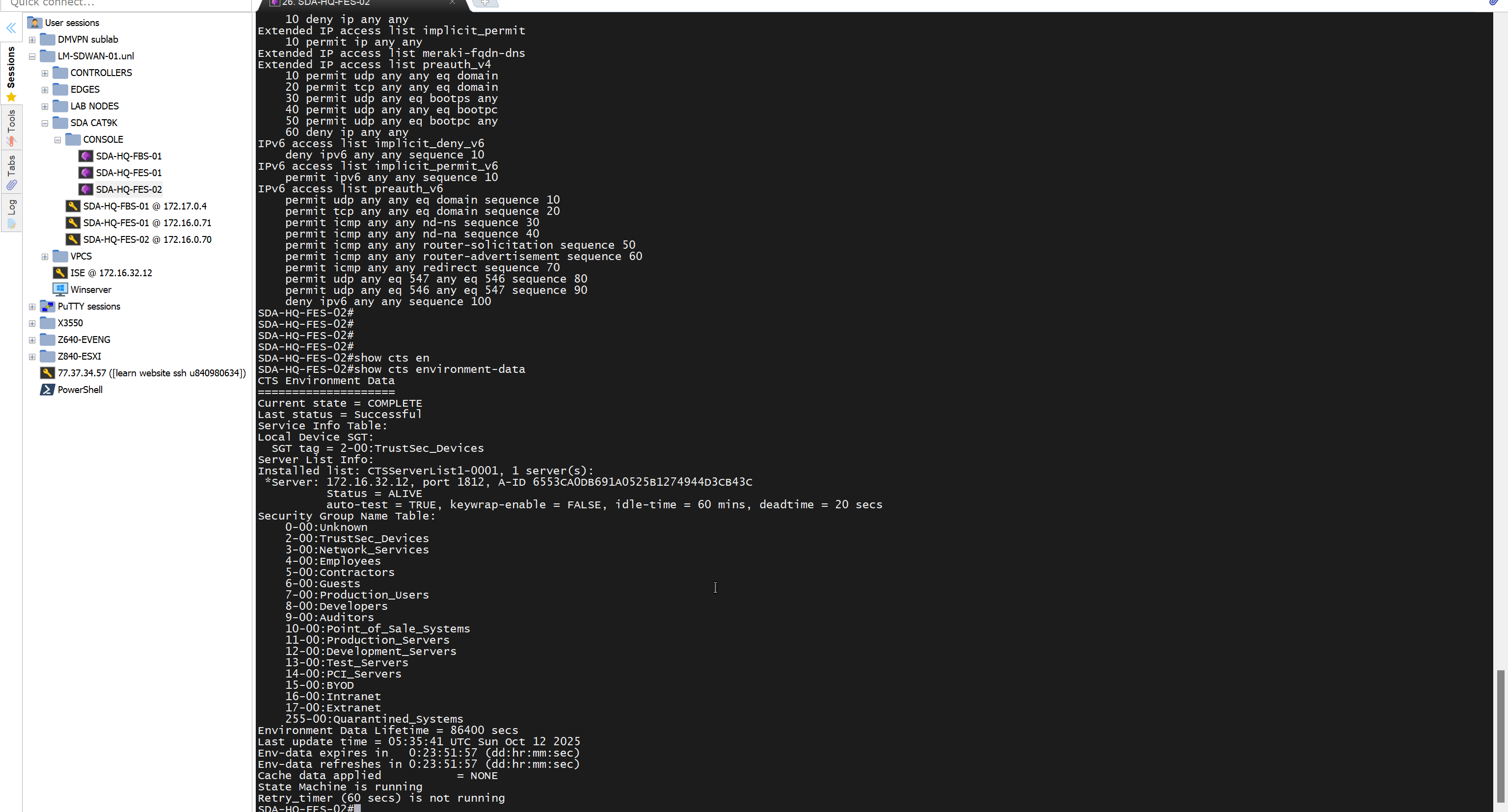
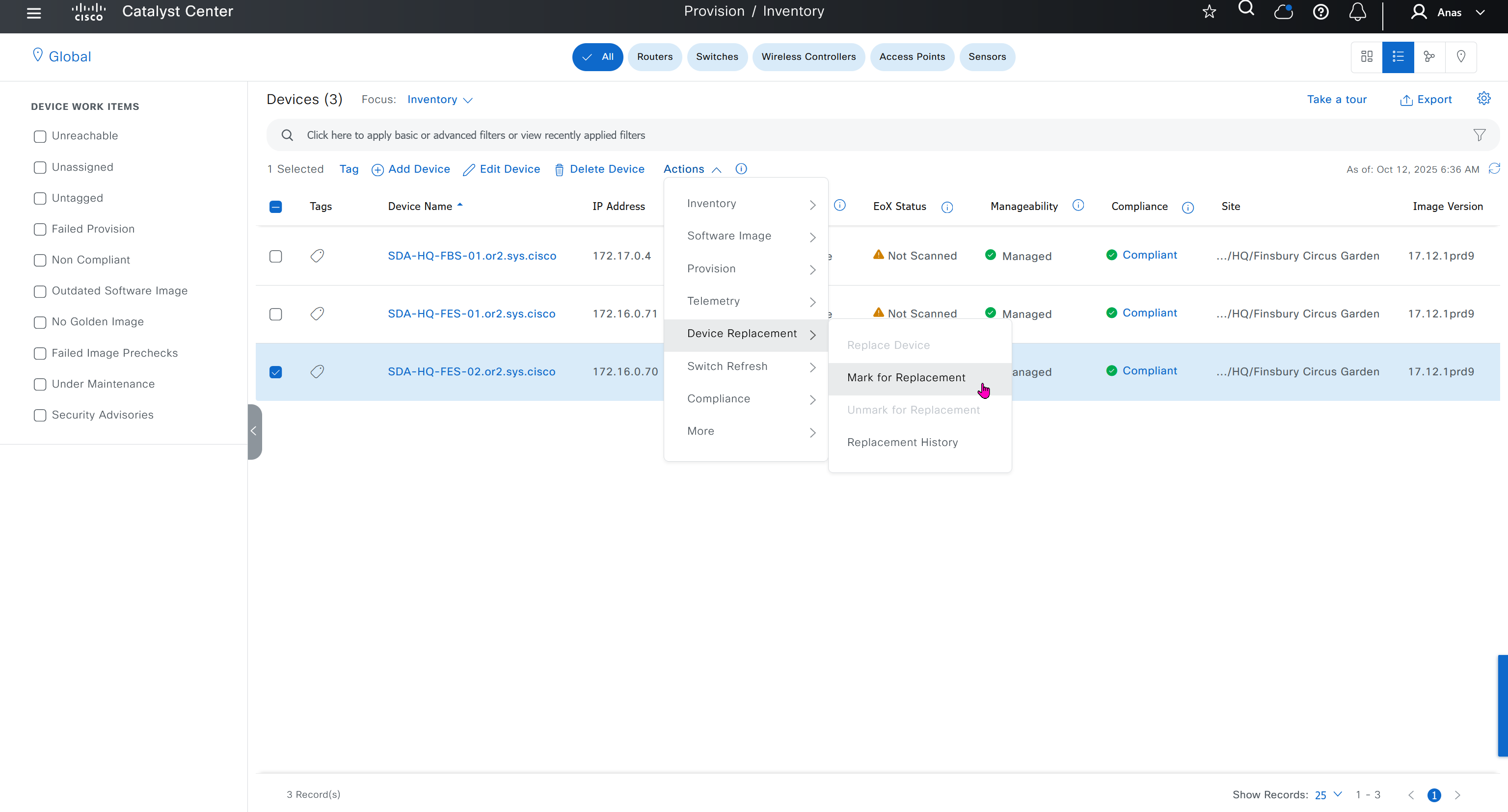
Mark for replacement is when we have to RMA the device
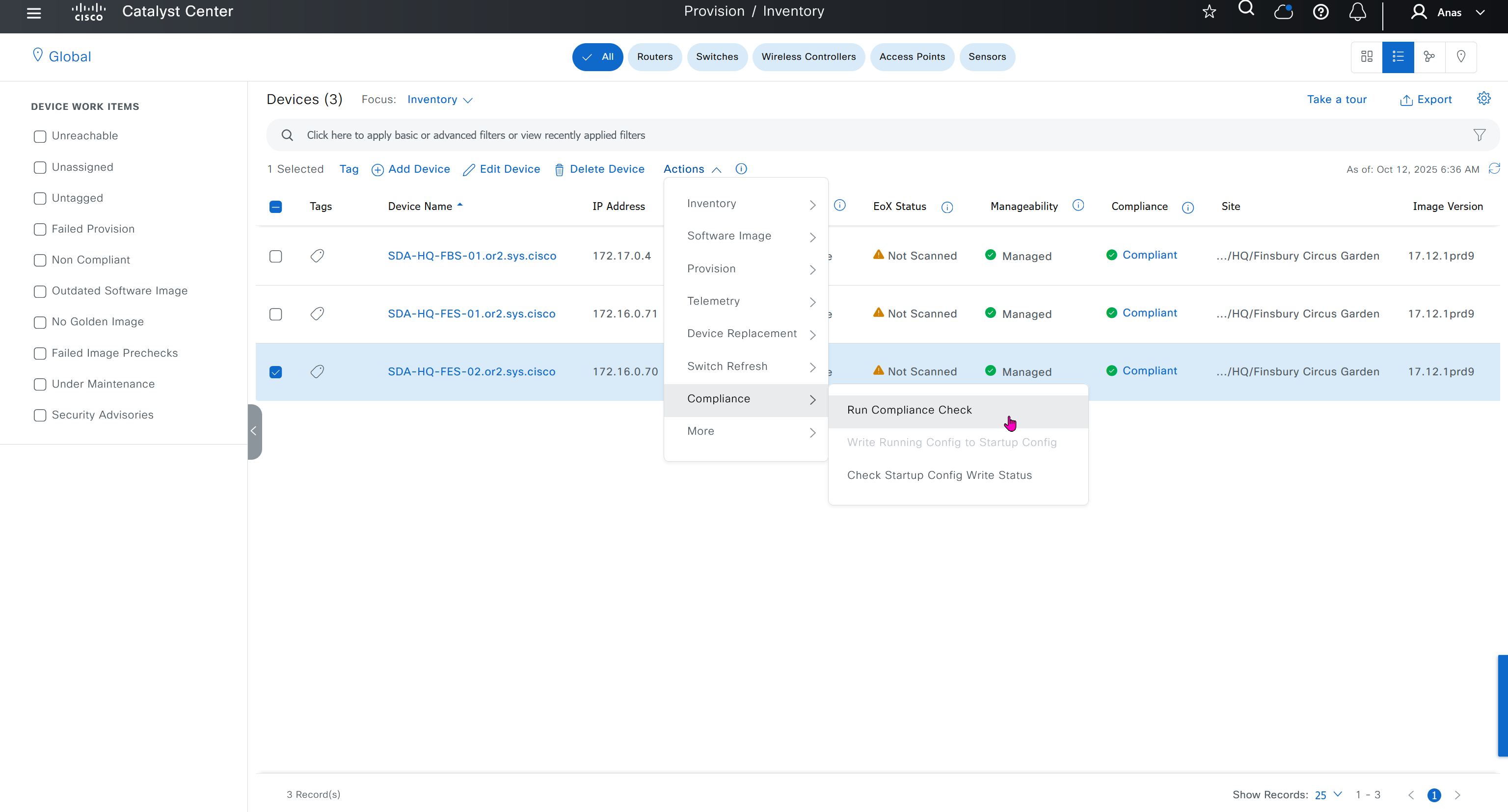
Compliance > Run Compliance, this is manual trigger of the compliance and checks if device has golden image and if startup-config is same running-config etc
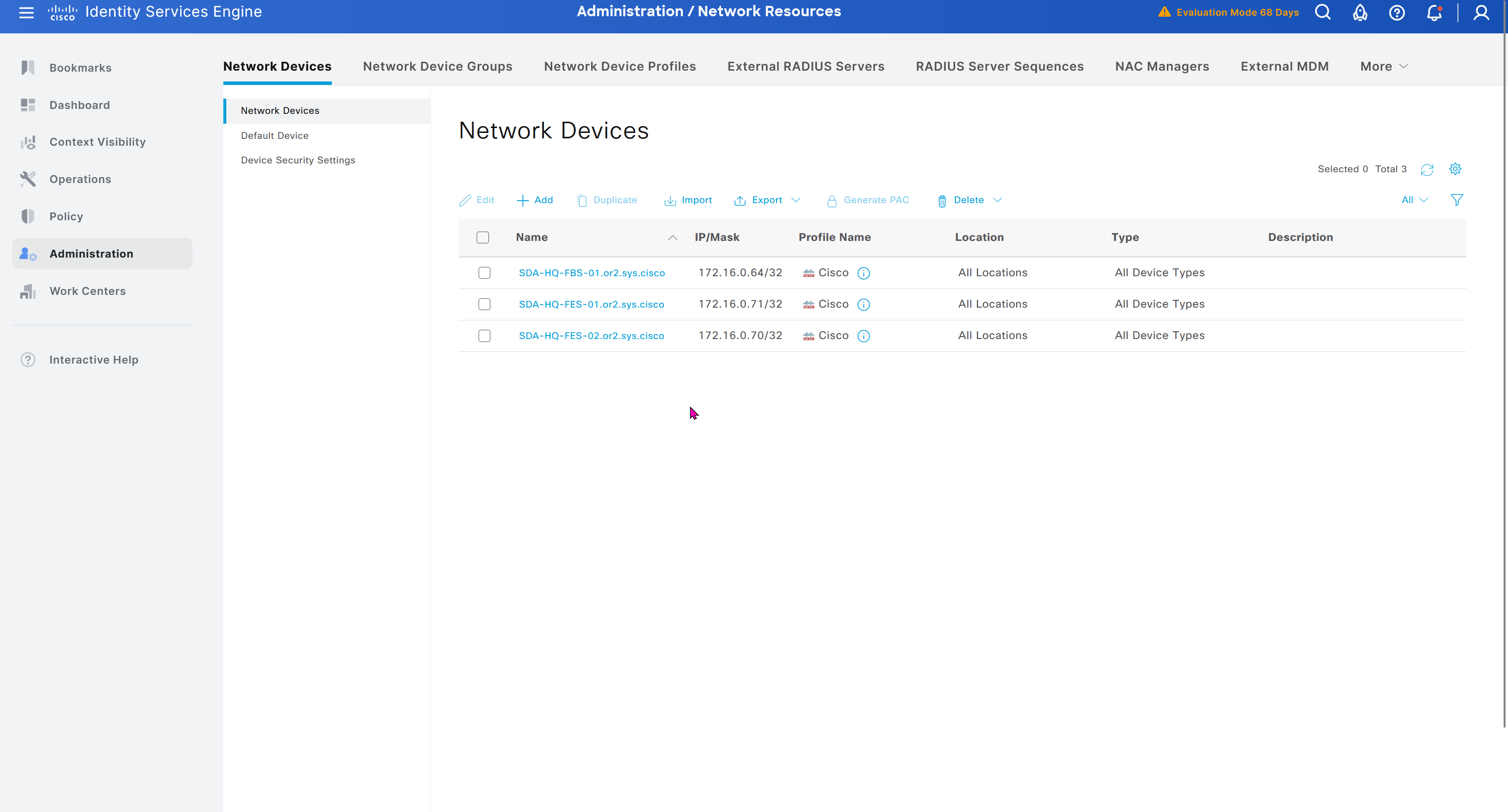
As devices are discovered in DNAC, it is also added in ISE
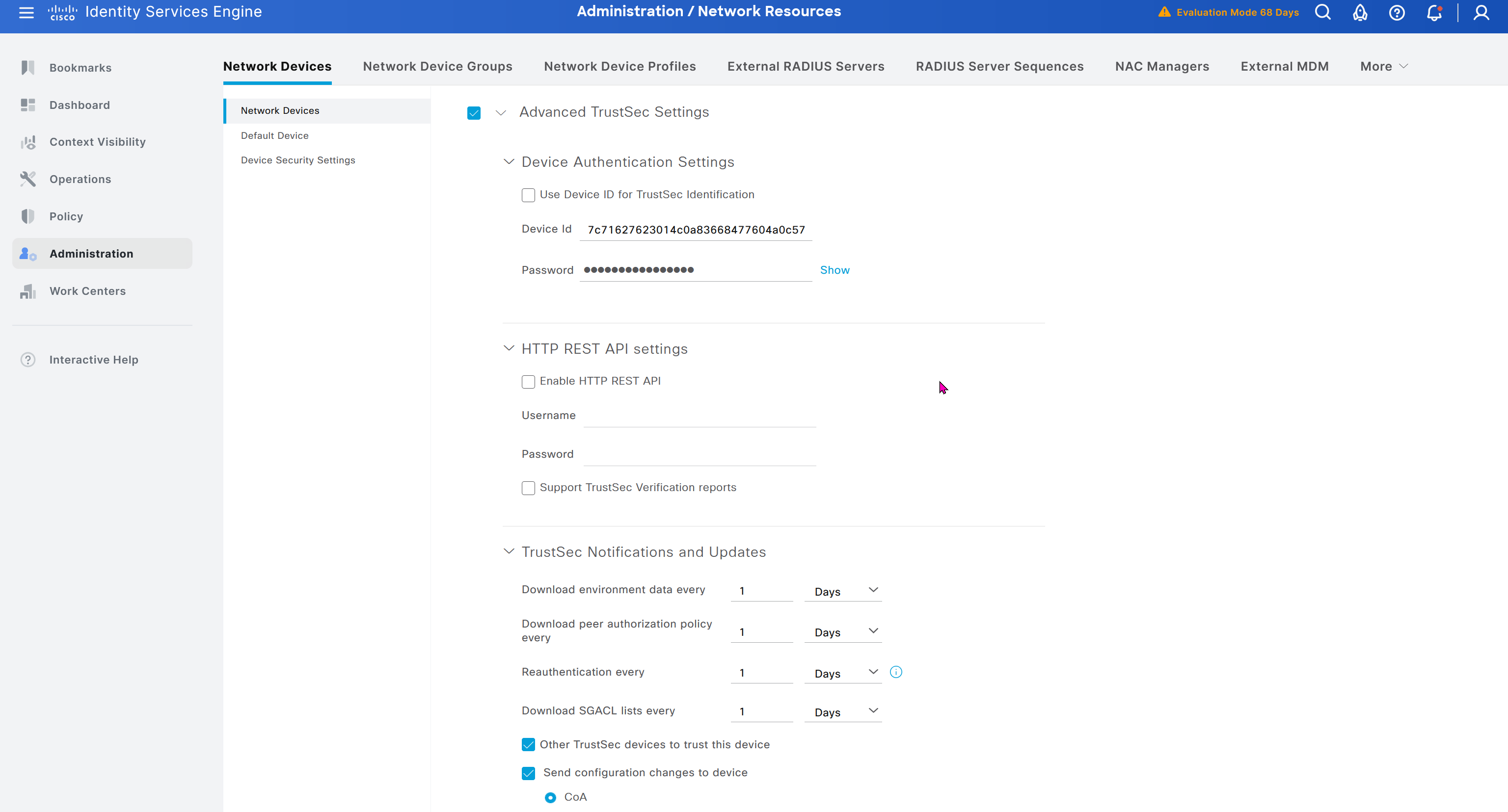

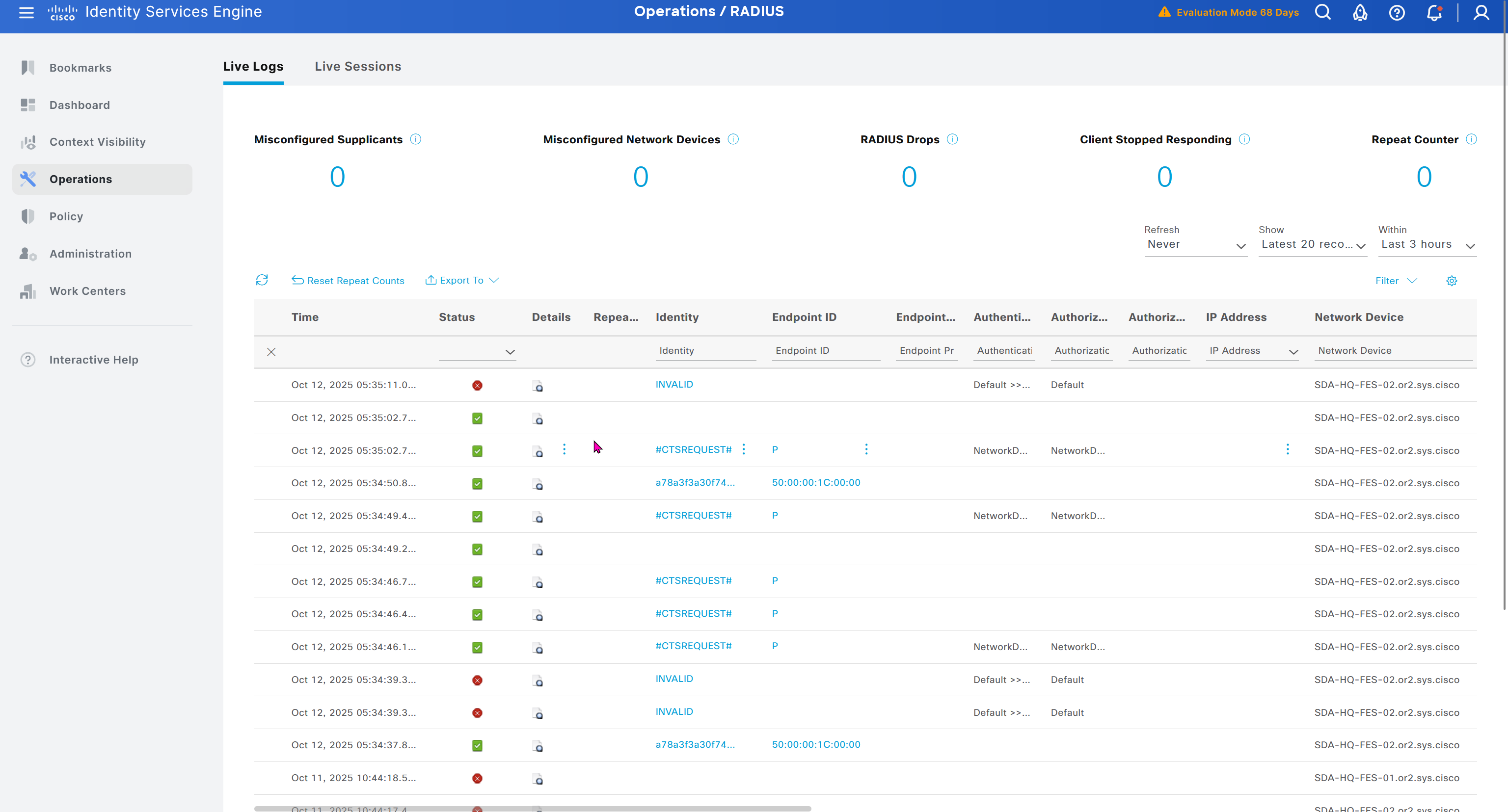
In ISE live logs we can see entries for devices authenticating to ISE for Trust Sec Device authentication
next post
SDA LM5 – SDA Fabric Virtual Networks
Videos
SDA Fabric Virtual Networks
Fabric Site
Fabric Site contains its own components such as border node, control node, access switches and Wireless controllers – imagine a typical site or building or campus that has network components
A fabric site can span multiple building but only over a high speed, low latency network and not WAN connection
Transit Network
Transit Network either connects multiple Fabric Sites together or connects a Fabric site to an external network
and there are different types of transit networks which will be discussed
Fabric Domain
Fabric Domain is made up of one or more Fabric Sites
Geographic distance between buildings and location decides the fabric site’s boundary
Type of WAN decides the Transit Network type
Depending on the version of SDA and cisco documentation, fabric site can only be so big and scale, if fabric site is bigger than what is supported by SDA, then you will have to break up the single fabric site into 2 Fabric sites
So make sure to check scalability number in Cisco documentation
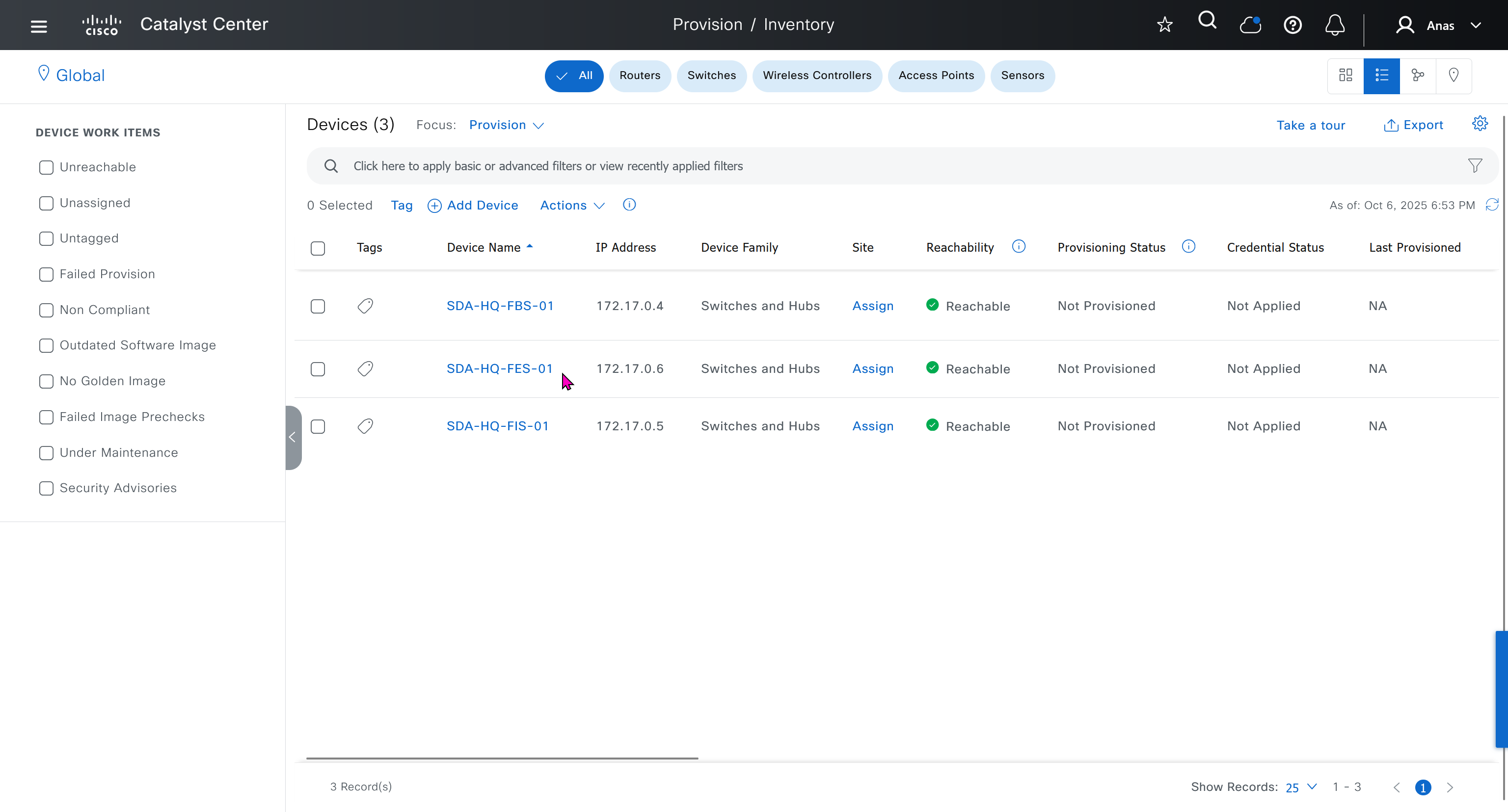
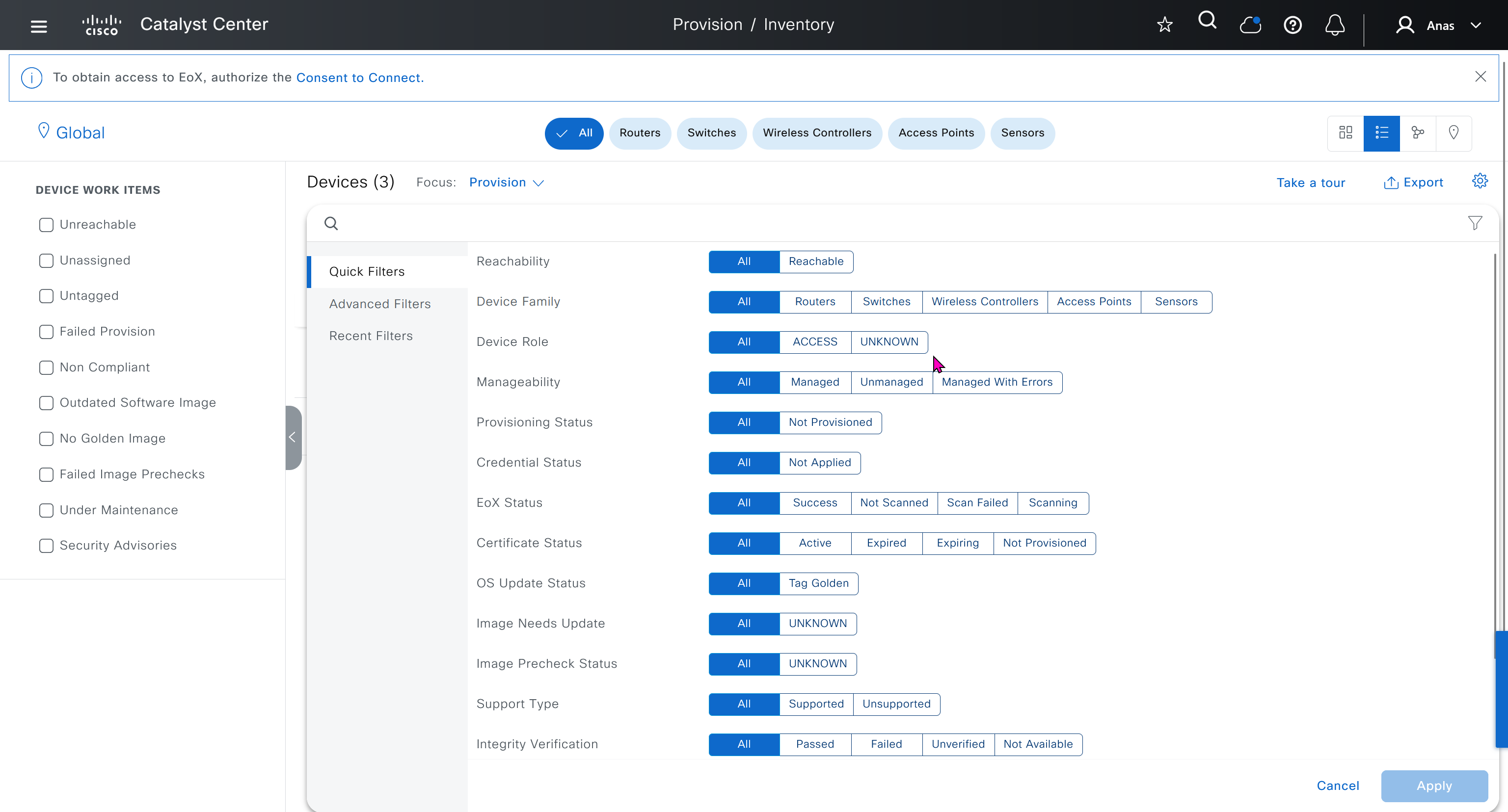
Make sure you have all devices that will be part of the fabric already discovered, reachable, managed and synced and LAN Automated, preferable compliant also

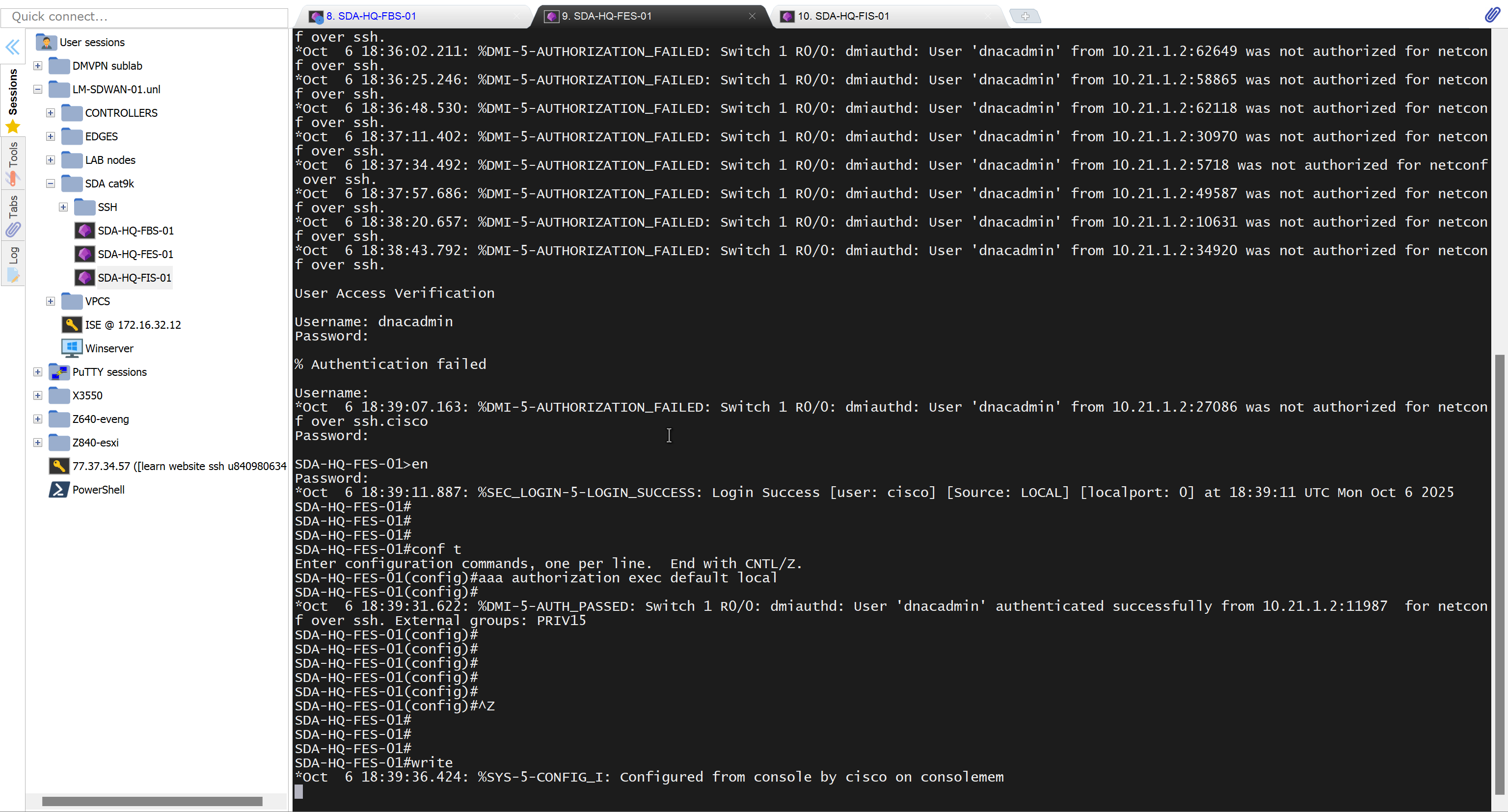
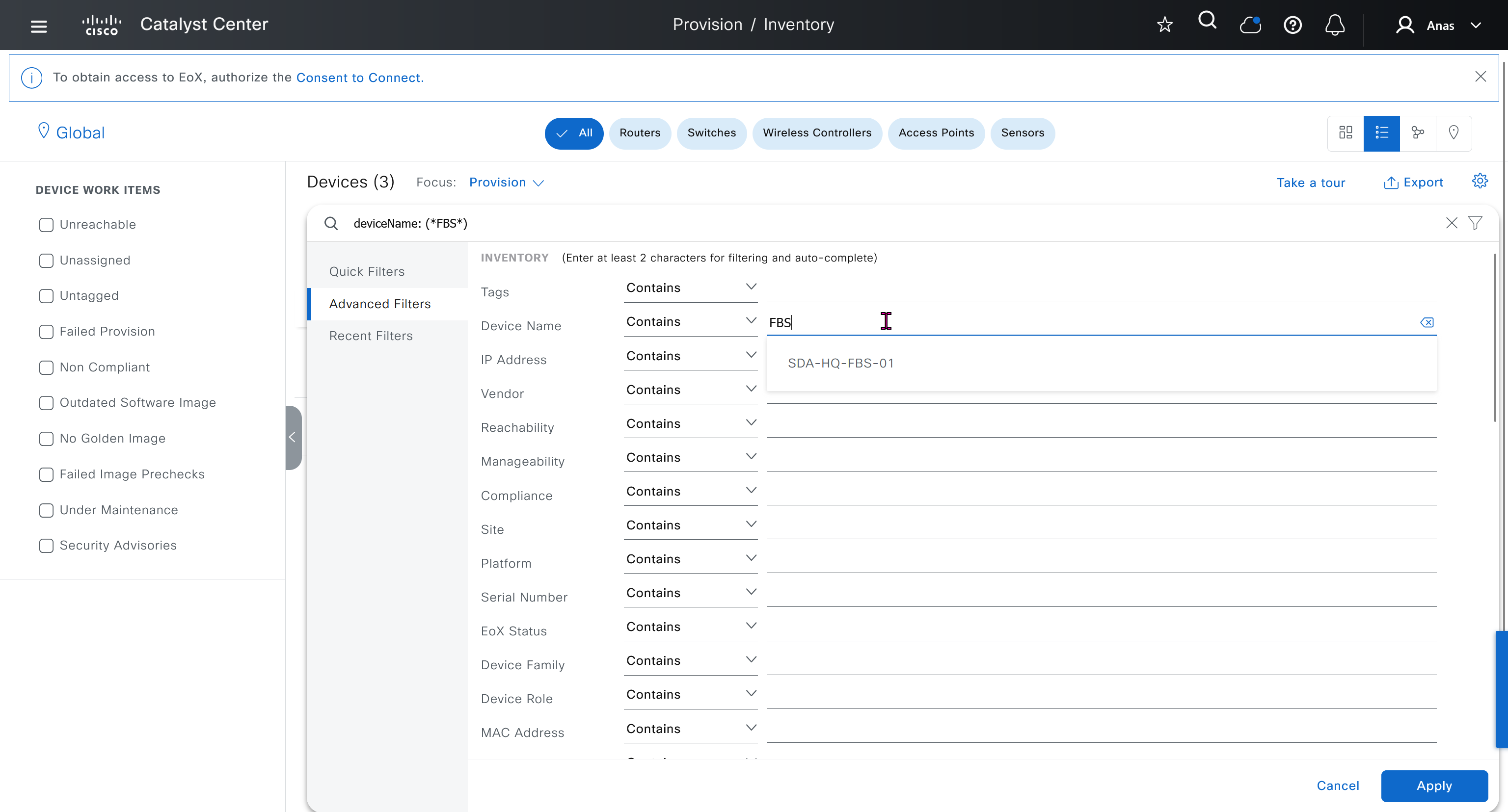
- Second most important thing is that, make sure that your edge devices do not have a route to DNAC via their default route and must have a specific route, I learned this the hard way
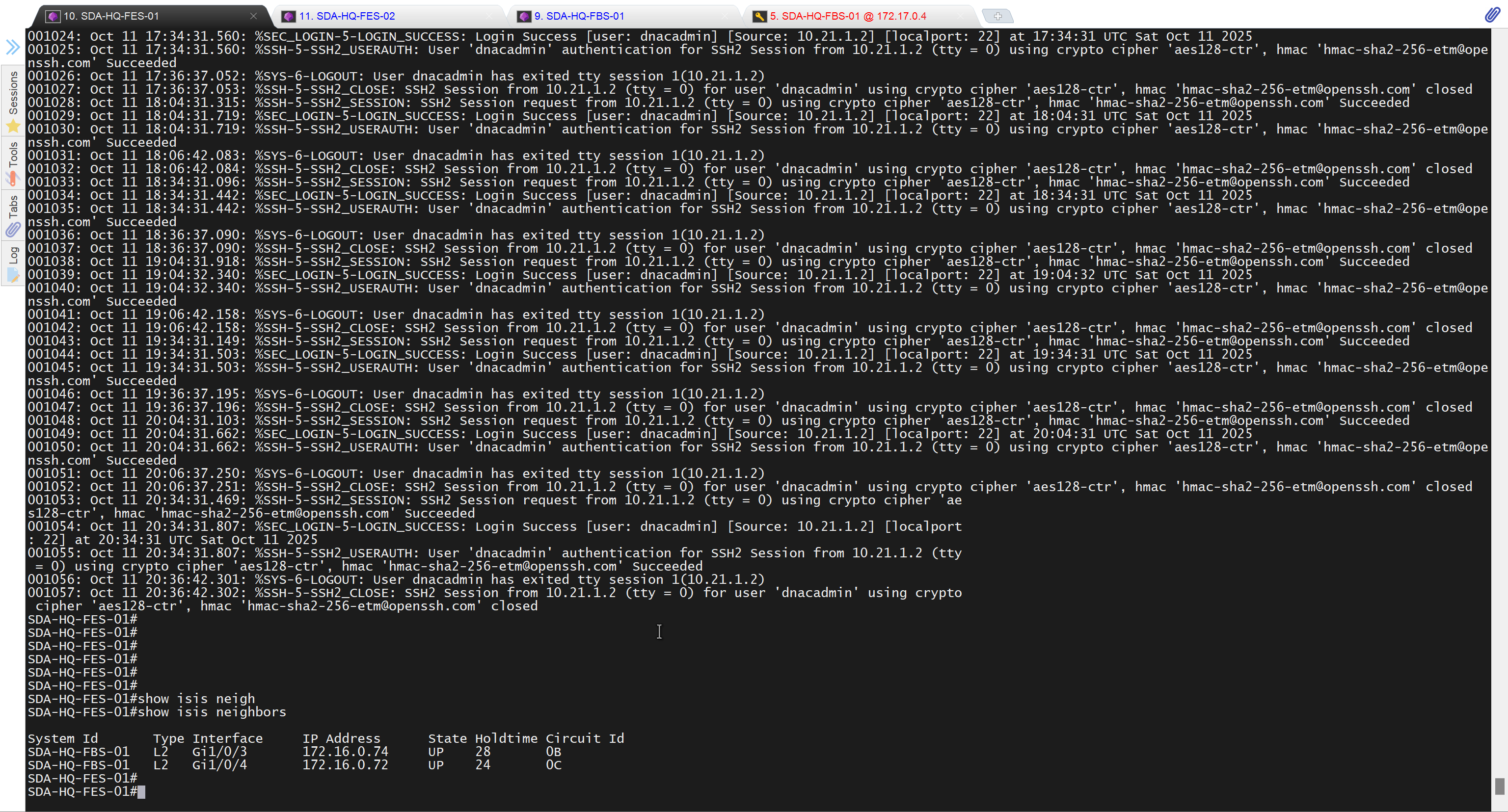
SDA-HQ-FES-01#show ip route 10.21.1.2
% Network not in tableSDA-HQ-FBS-01
conf t
ip route 10.21.1.0 255.255.255.0 172.17.0.3
!
router isis
redistribute static ipSDA-HQ-FES-01#show ip route 10.21.1.2
Routing entry for 10.21.1.0/24
Known via "isis", distance 115, metric 10, type level-2
Redistributing via isis
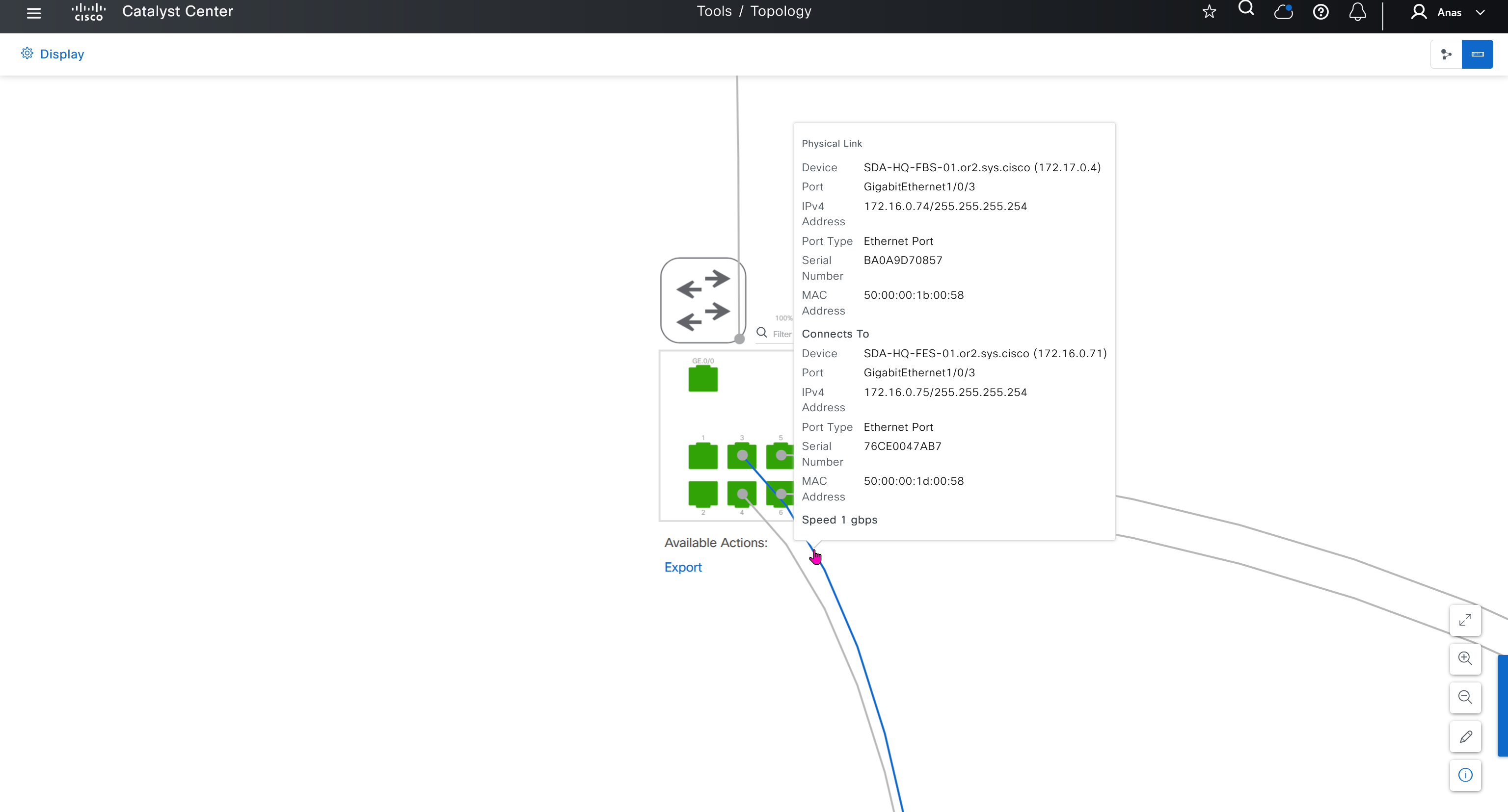
Last update from 172.16.0.72 on GigabitEthernet1/0/4, 00:00:05 ago
Routing Descriptor Blocks:
* 172.16.0.74, from 172.16.0.64, 00:00:05 ago, via GigabitEthernet1/0/3
Route metric is 10, traffic share count is 1
172.16.0.72, from 172.16.0.64, 00:00:05 ago, via GigabitEthernet1/0/4
Route metric is 10, traffic share count is 1SDA-HQ-FES-01#ping 10.21.1.2
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.21.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 114/131/164 msSDA-HQ-FES-01#ping 10.21.1.2 source loopback 0
Type escape sequence to abort.
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 10.21.1.2, timeout is 2 seconds:
Packet sent with a source address of 172.16.0.71
!!!!!
Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 111/122/134 ms
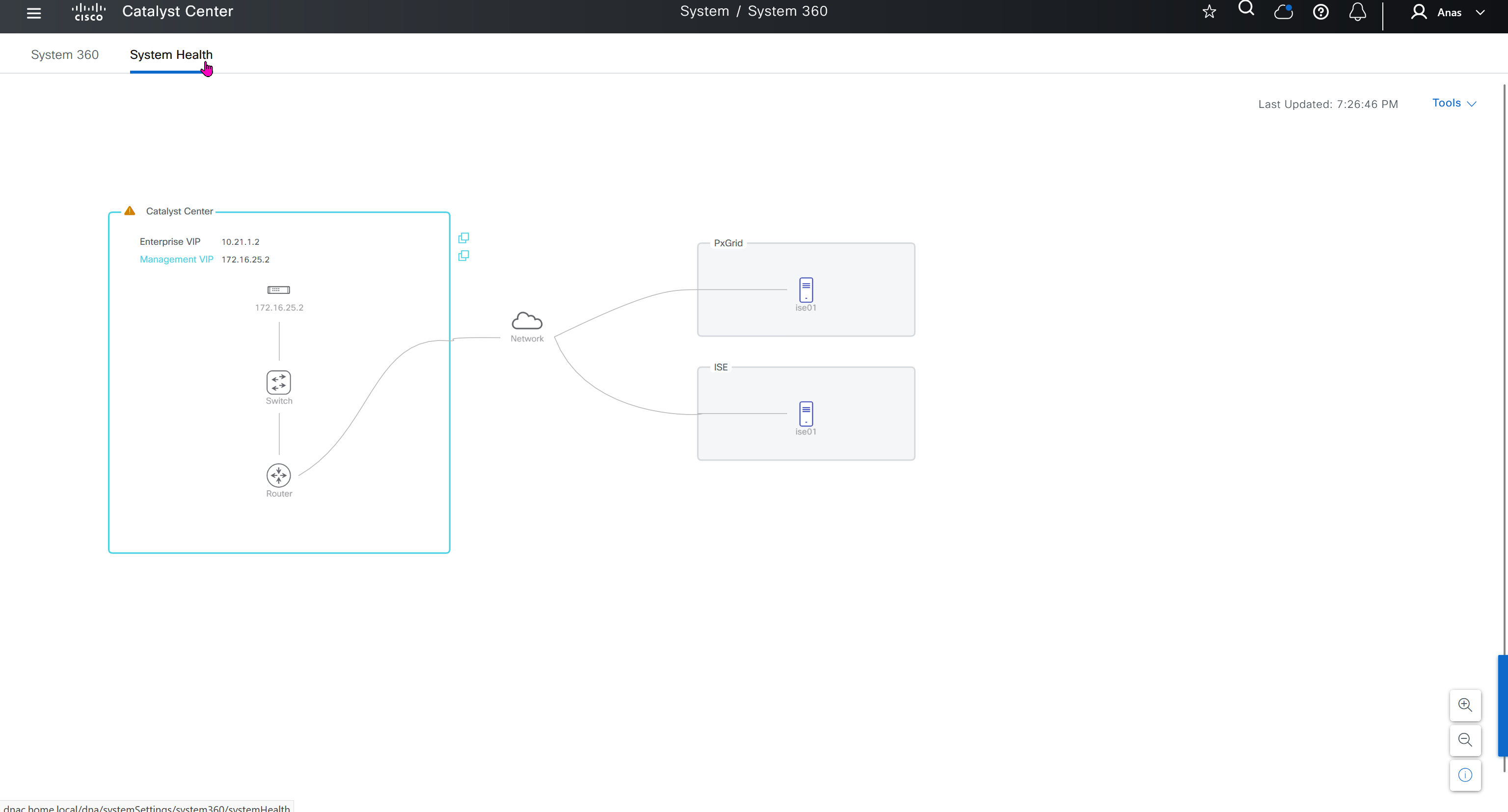
DNAC comes with default LAN fabric
We can either choose to use this or create a new fabric
We should always create a new fabric and not use the default
next post
SDA LM4 – DNAC Web Interface
Videos
Introduction to UI
You can modify these authentication templates but cannot define more
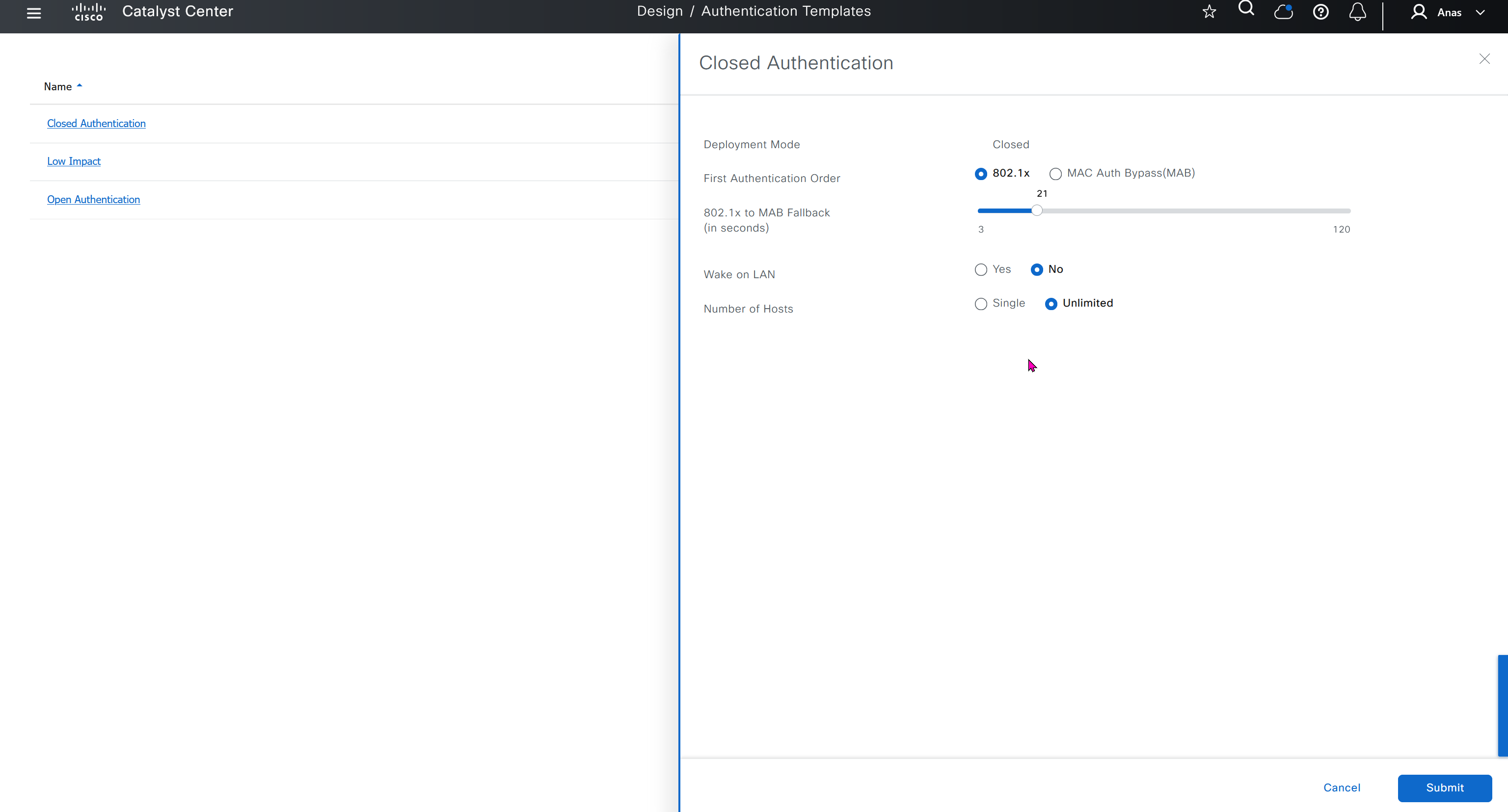
If you want to define different SSID in europe or you want different ISE server for europe then use hierarchy and go to site specific level and override


IP based access control is used when you create non fabric based wireless and this is a very specific use, if we dont use non-fabric wireless then we will not have to touch this page
AI Endpoint Analytics
With new DNAC, AI Endpoint Analytics was introduced and this leverages AI capabilities in cloud and uses deep packet inspection in Catalyst 9K infrastructure to “identify types of endpoints” – this information can then be fed to ISE and can then be used as part of endpoint authentication, this provides additional network packet level context along side the profiling probes that ISE performs on its own and that information is communicated to ISE using PXGrid
Application policies is the feature that was known as Easy QoS and it allows you to deploy QoS end to end in your network, for more details checkout RS0122 – SDA Application Policy (EasyQoS)
Traffic Copy is the way to span traffic from Fabric to a remote destination and this is part of SGT, as you can capture traffic between specific contracts or tags
Finally Virtual networks which are essentially VRFs and separate different (virtual) fabric on same network
Service catalog, these are different services that are offered
User defined network is a cool concept as it allows users to create personal network on top of shared infrastructure, users can then register their personal devices using an app and also invite other users into that network using same app and these networks are like bubbles
These 4 services are also listed under the services section of provision tab
Assurance does not just measures health and experience of network devices but also includes clients and helps us measure client’s experience on the network also and it does not stay at client but its scope one level more deep into application as well

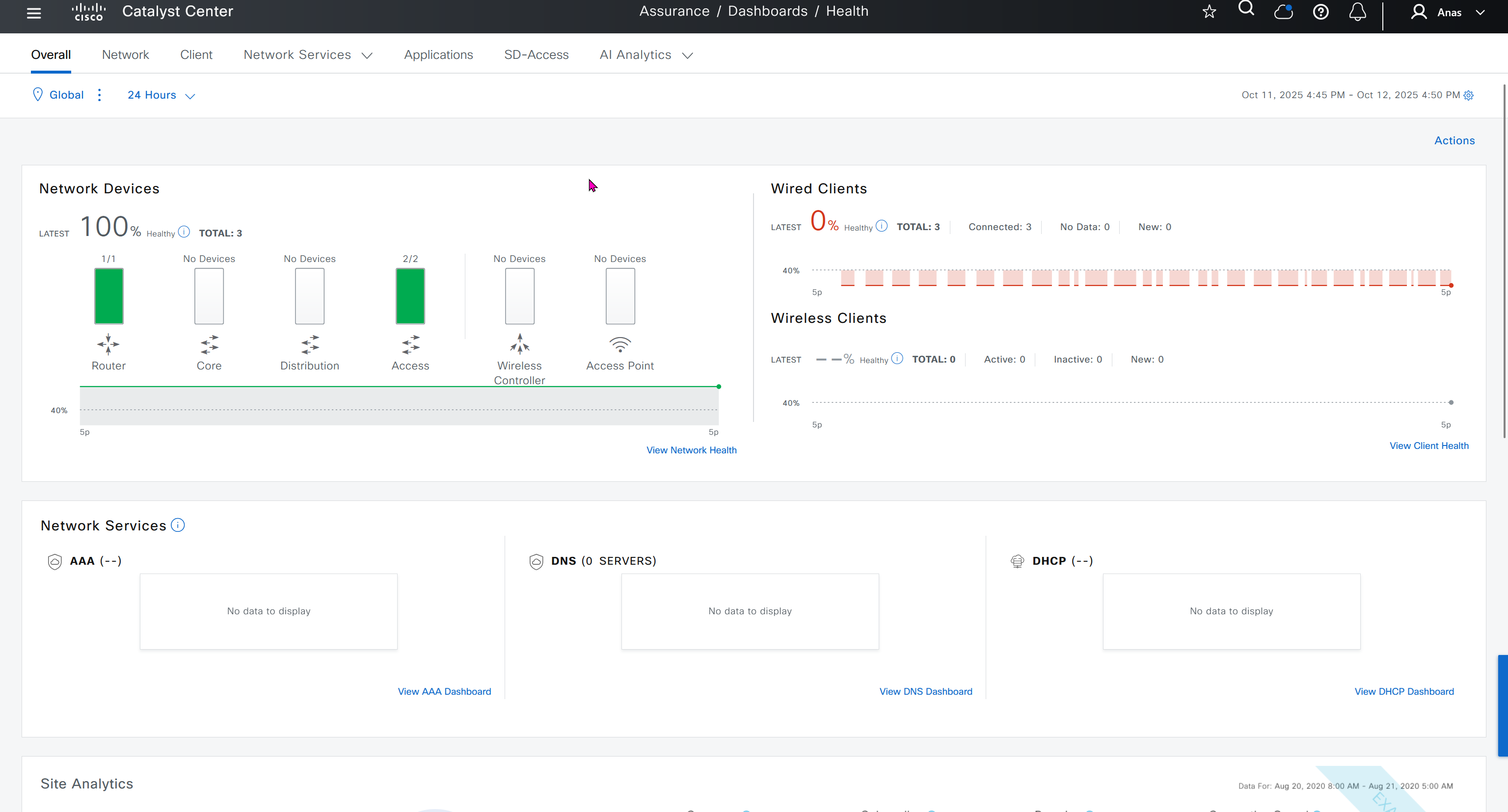


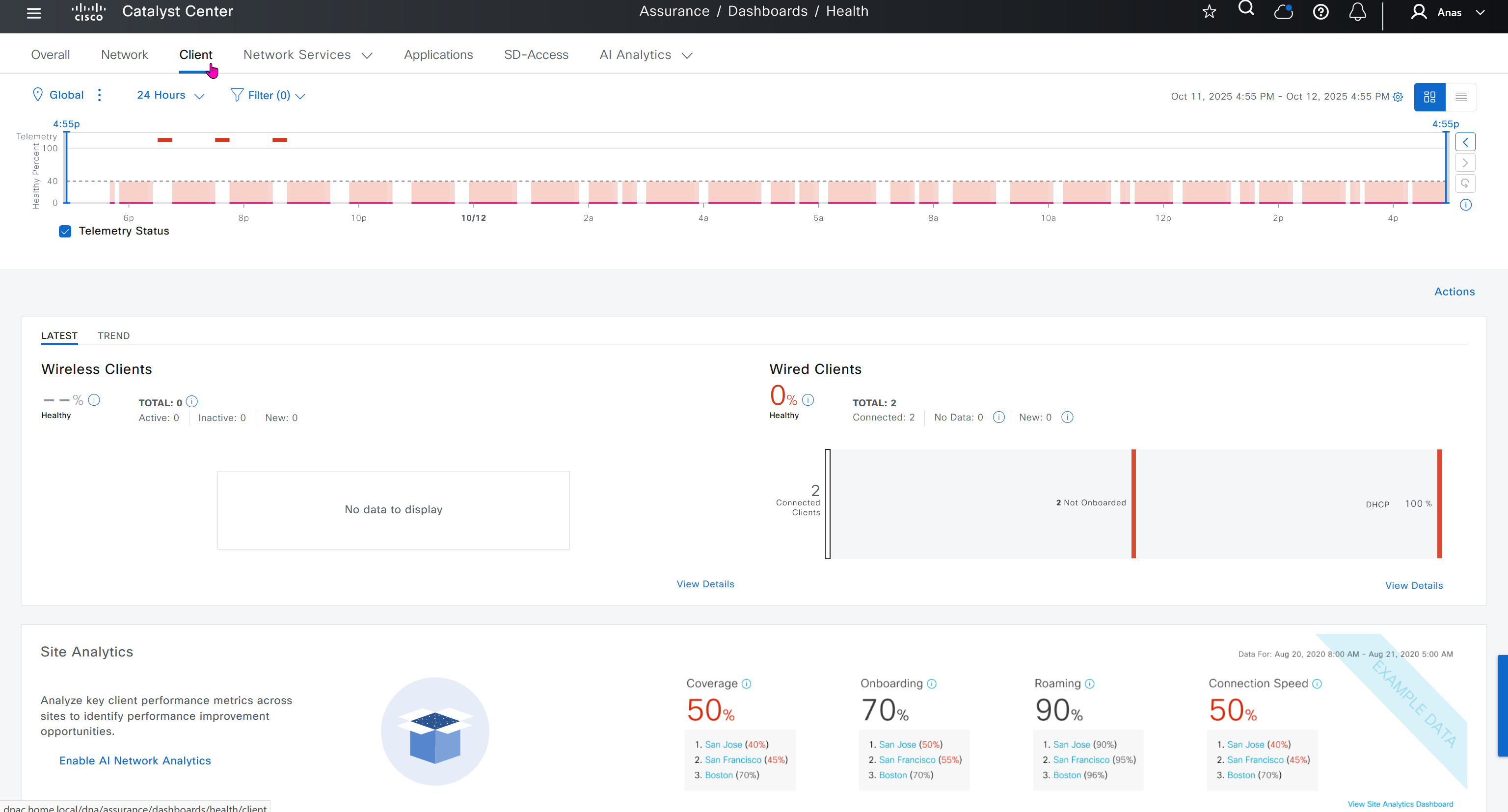



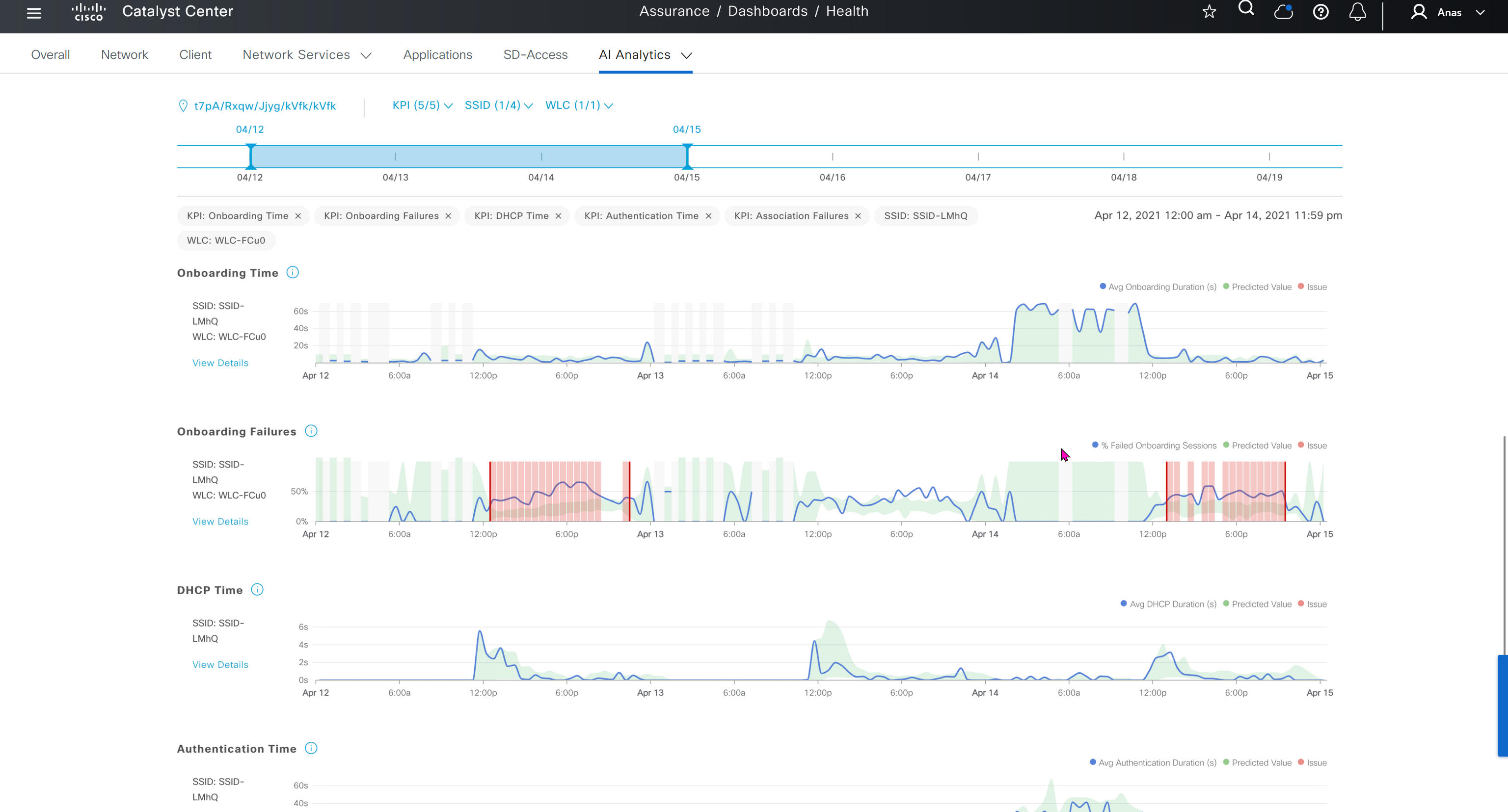
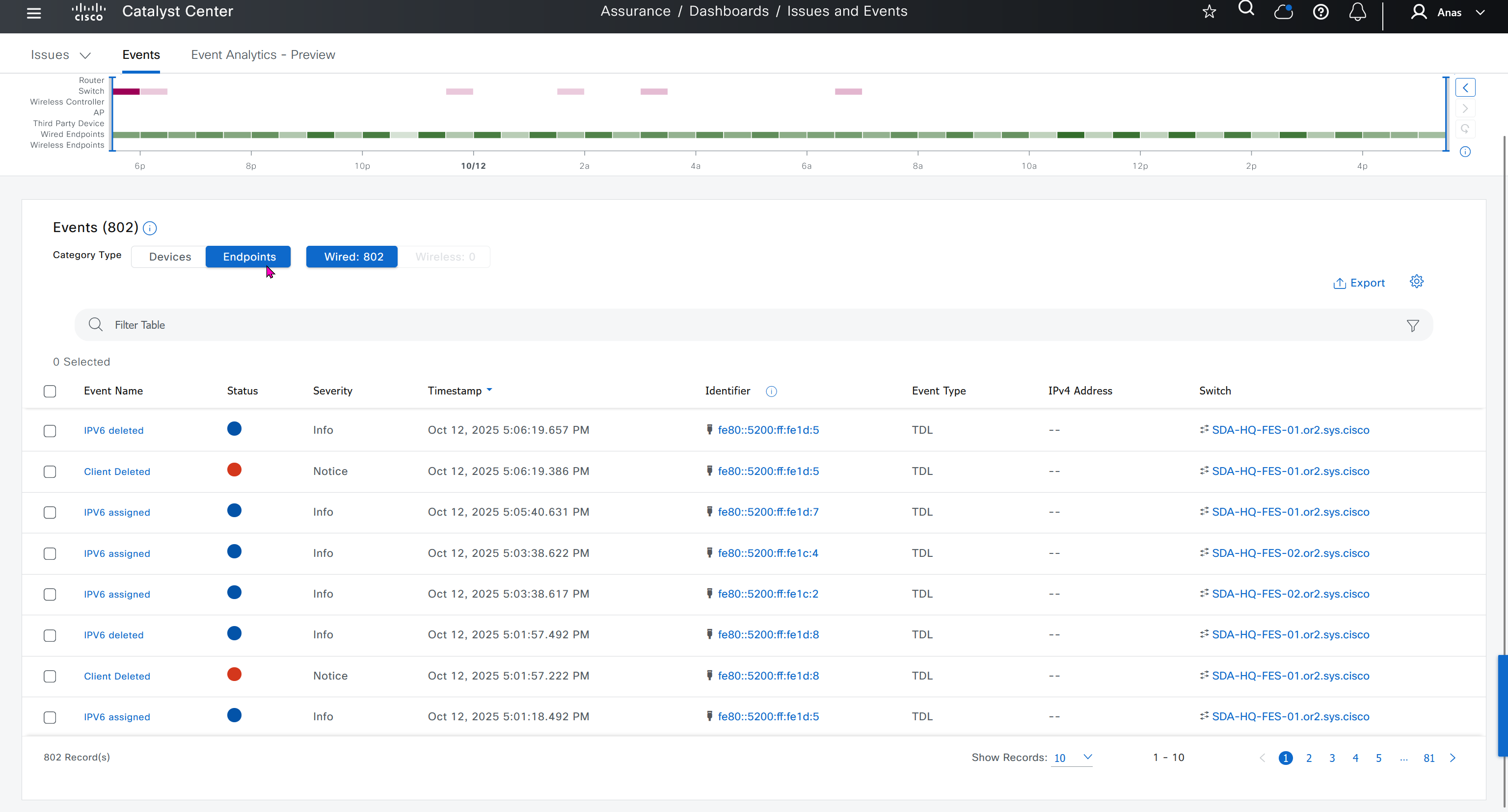
Events are for both Network devices and also for the clients, these are any events that happen in the network for network devices and its connected clients

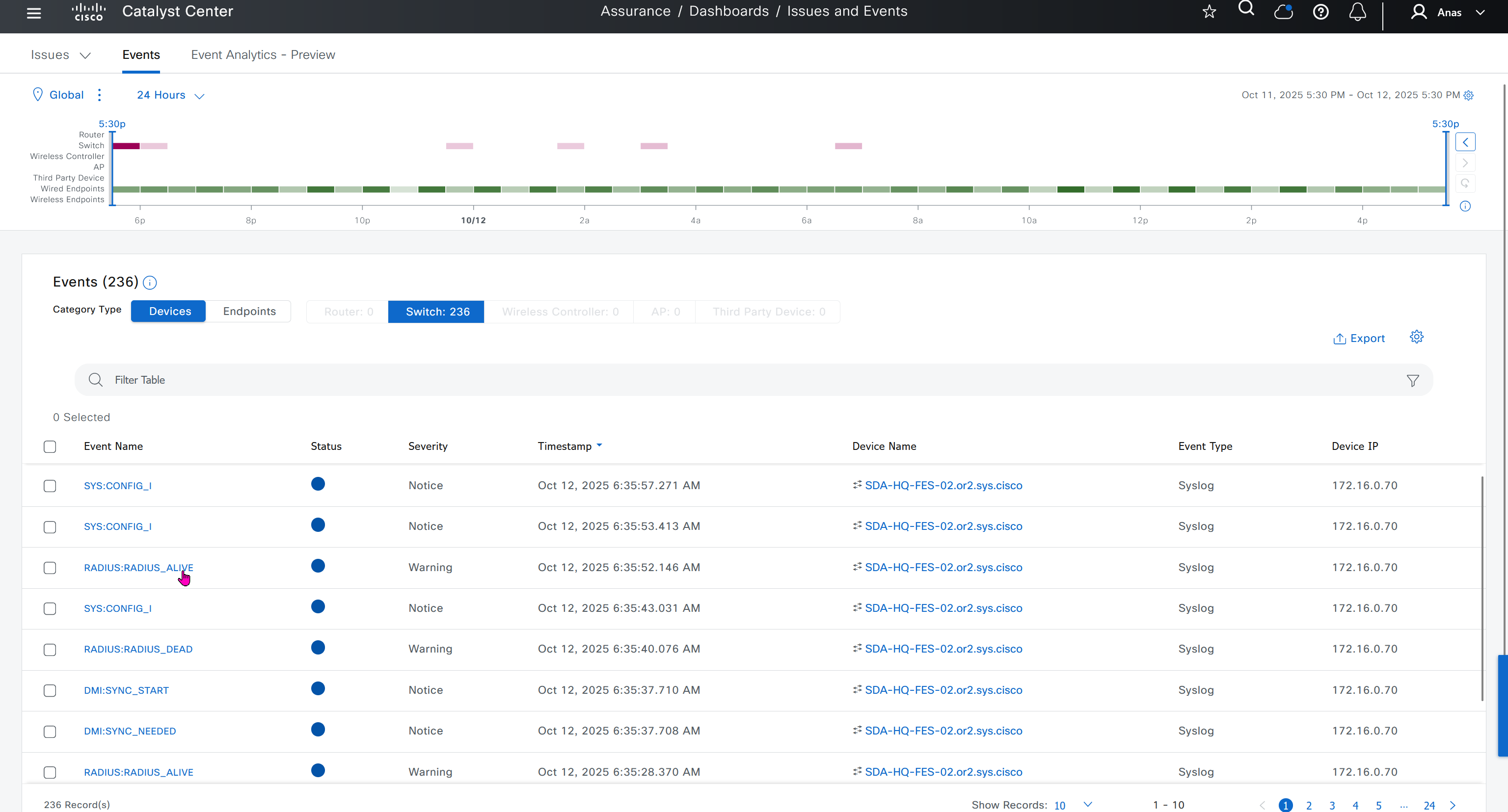
DNAC offers dedicated sensors that can perform series of tests to gauge performance from client perspective. These wireless sensors join network as wireless device and these can either be dedicated sensors or an AP can also be converted to a wireless sensor
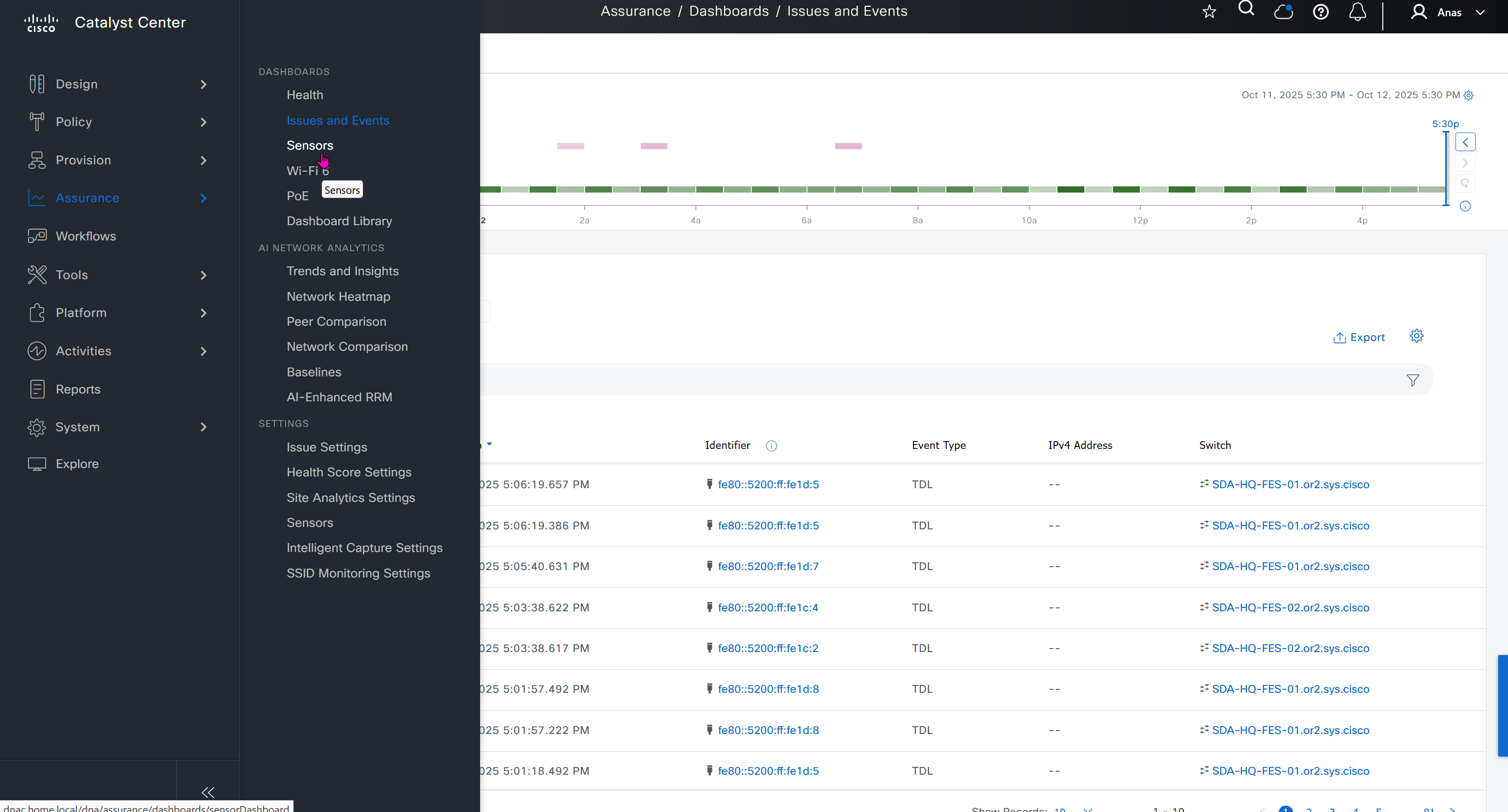


Wi-Fi6 section is for Wi-Fi6 readiness assessment which shows us the percentage of AP and clients that are capable of Wi-Fi6, if large number of clients support Wi-Fi6 then we can think about more APs to be deployed that support Wi-Fi6


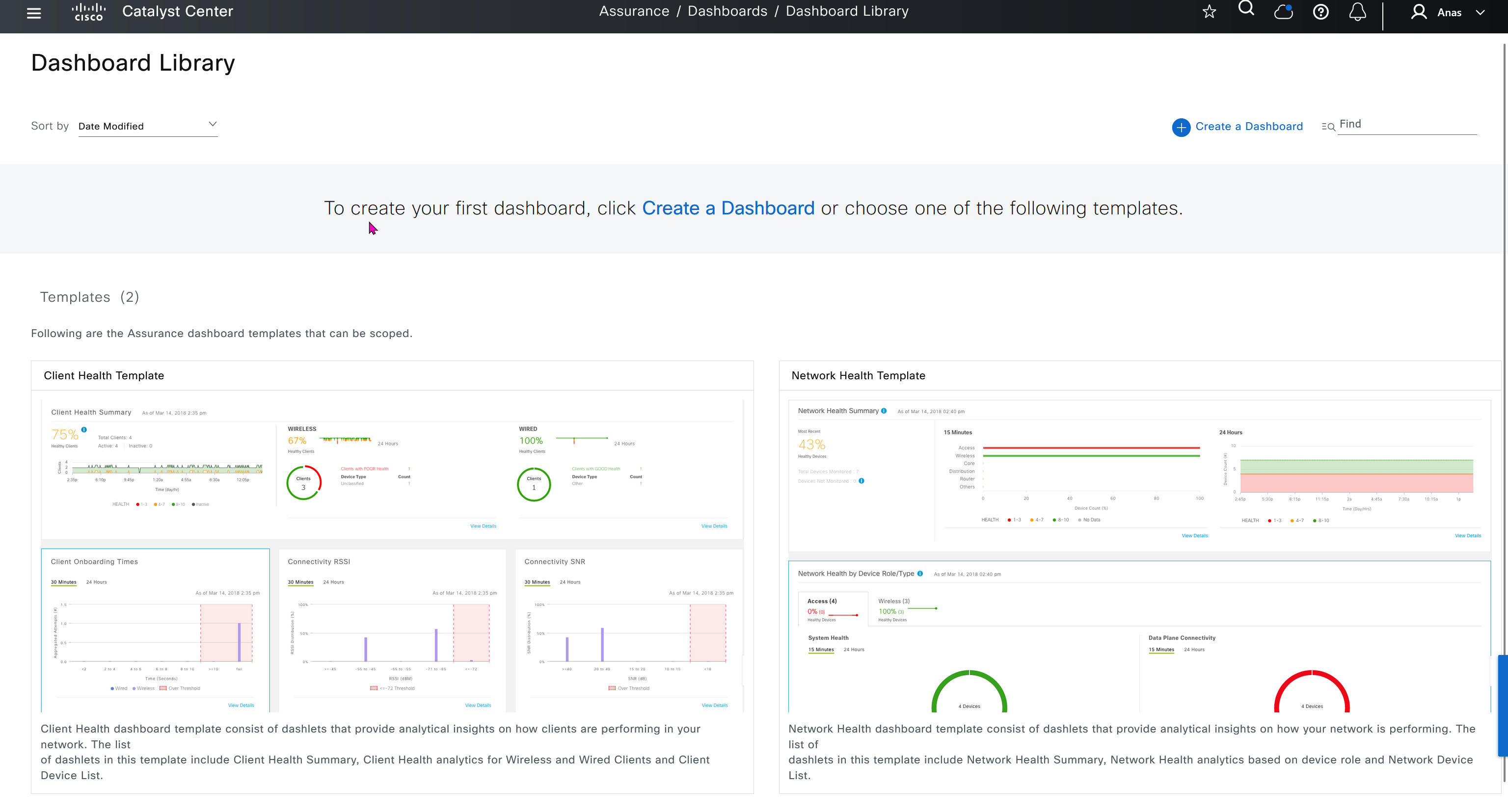
Dashboard Library is where we can create our own dashboards
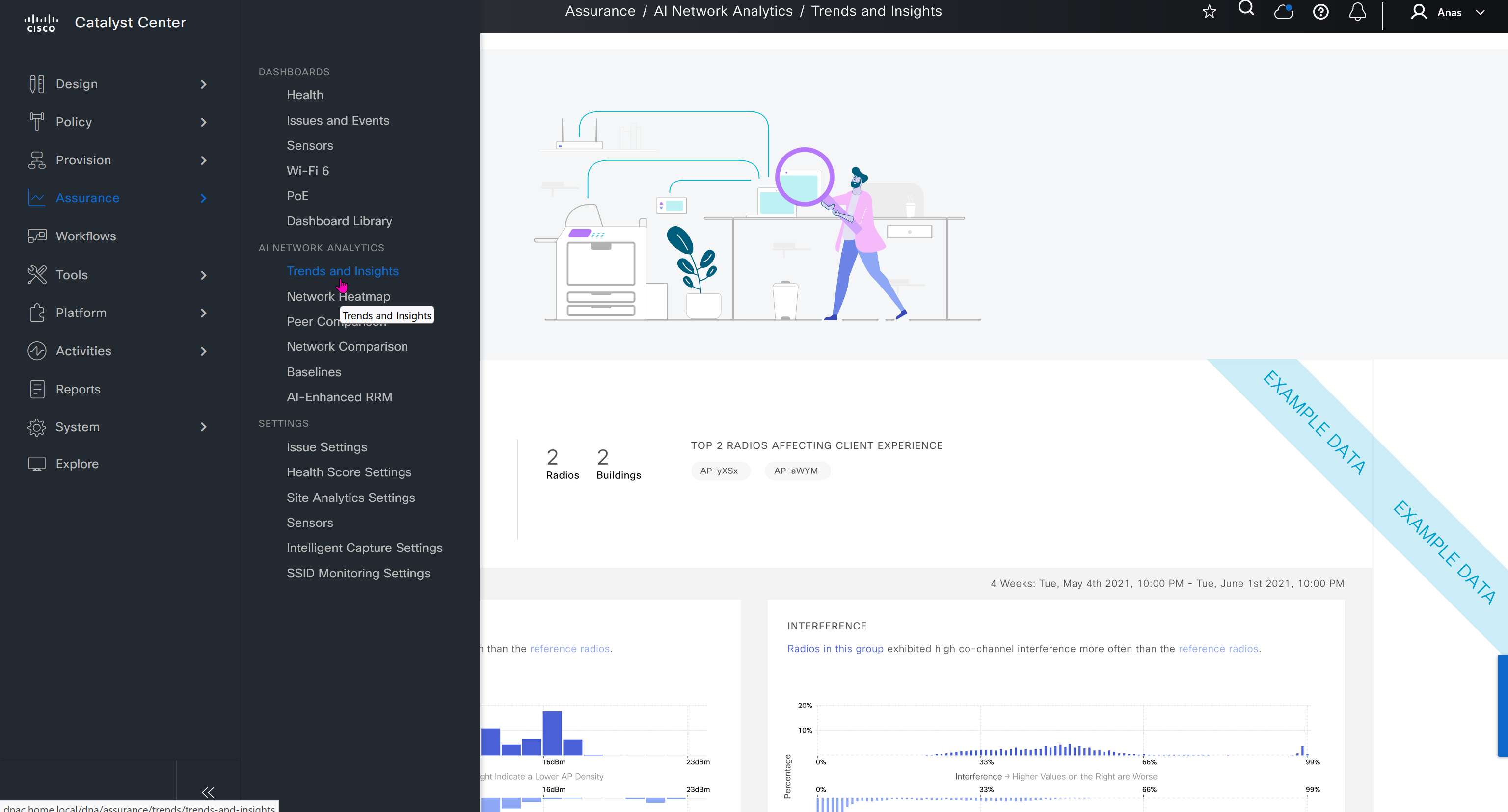
This Trends and Insights leverage AI in Cloud and Machine learning to spot issues in network,
Trends and Insights deals with deviation in capacity and performance
Site comparison shows us how one site compares to another, as in some cases one site can perform worse than the others


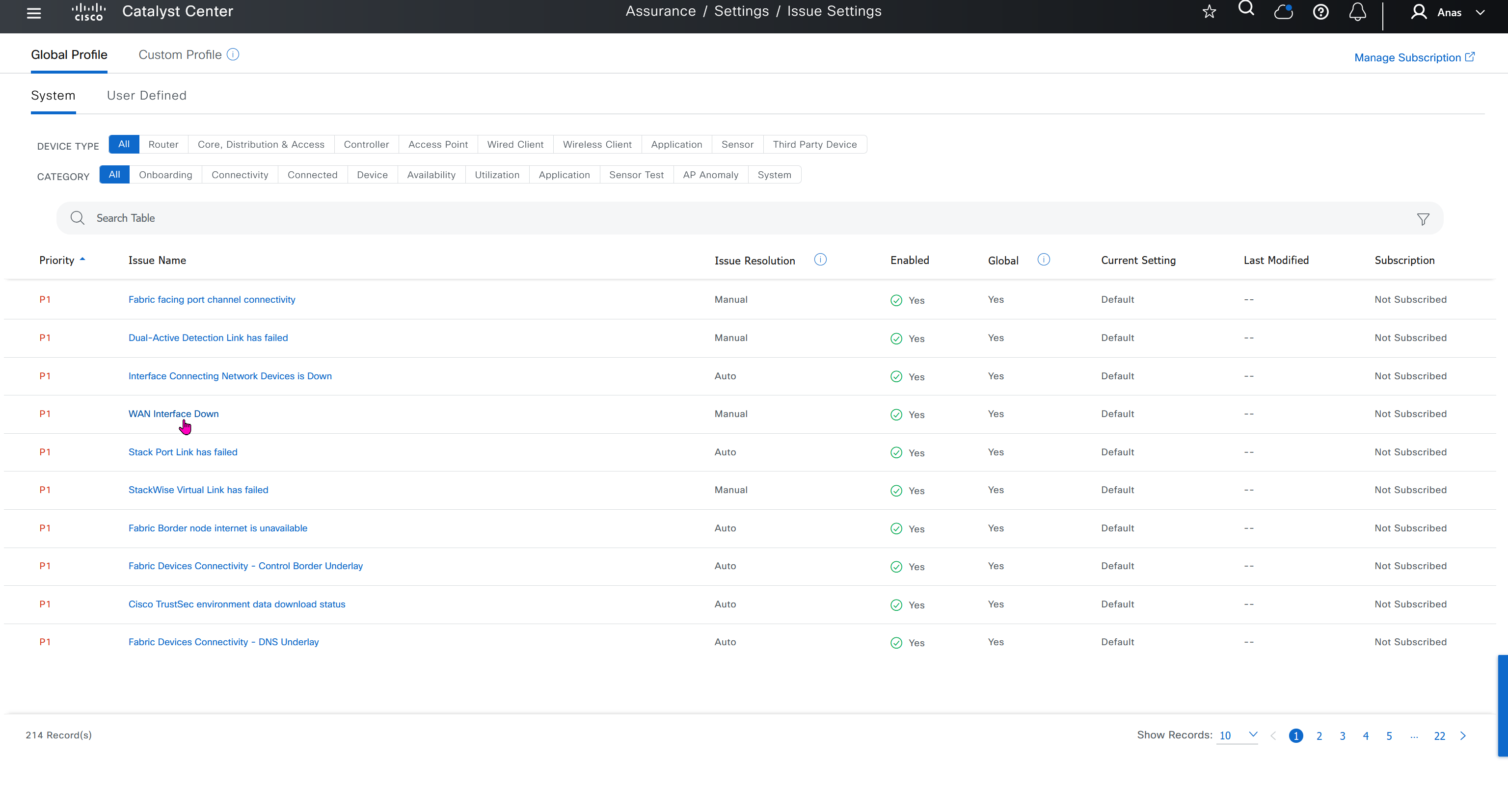
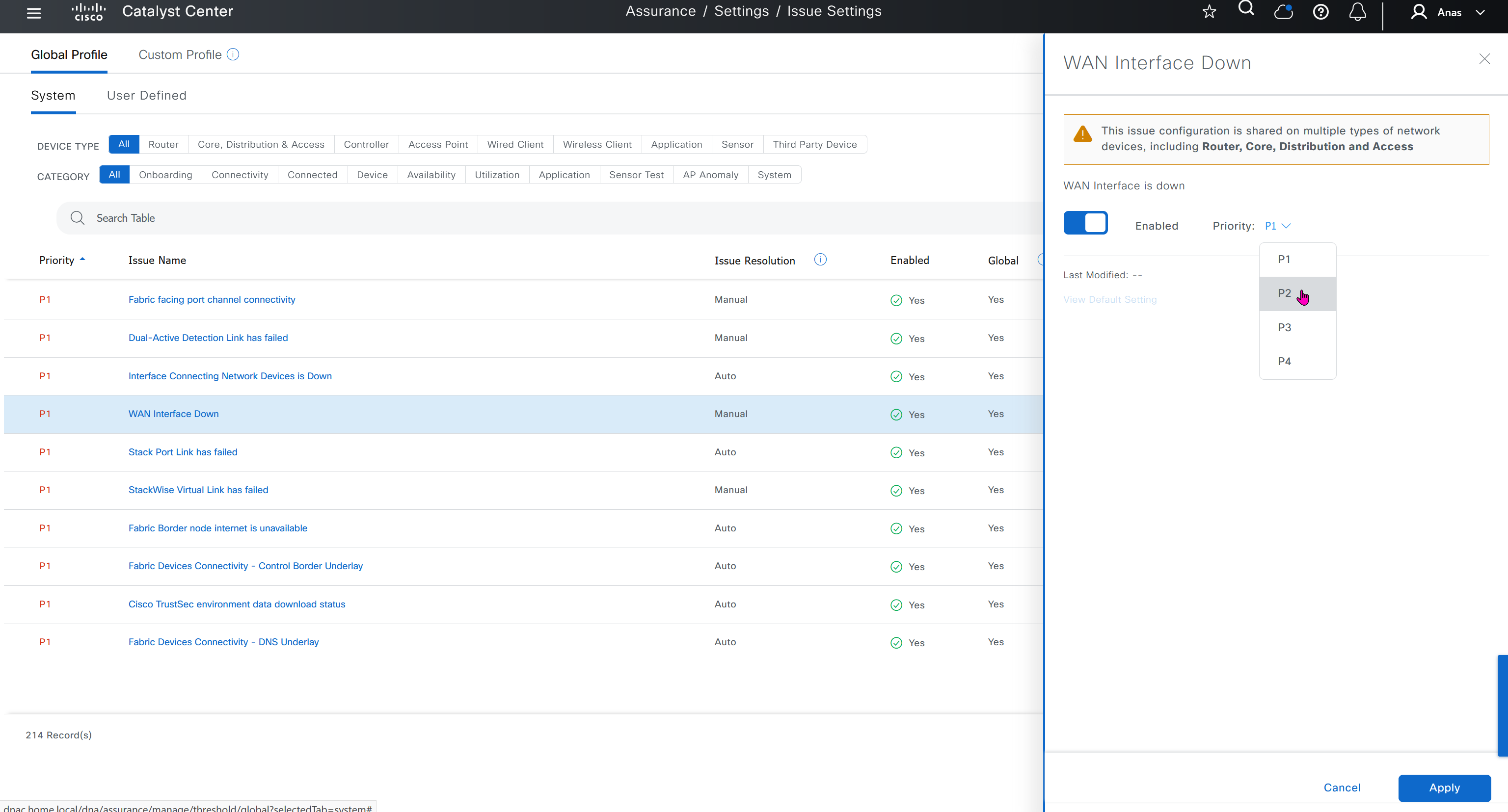
Issue settings is where we can control what issues such as P1 and P2 can be raised by DNAC such as Assurance > Issues & Events, we can enable or disable some of these issues if they are not important to us, we can also change priority on them

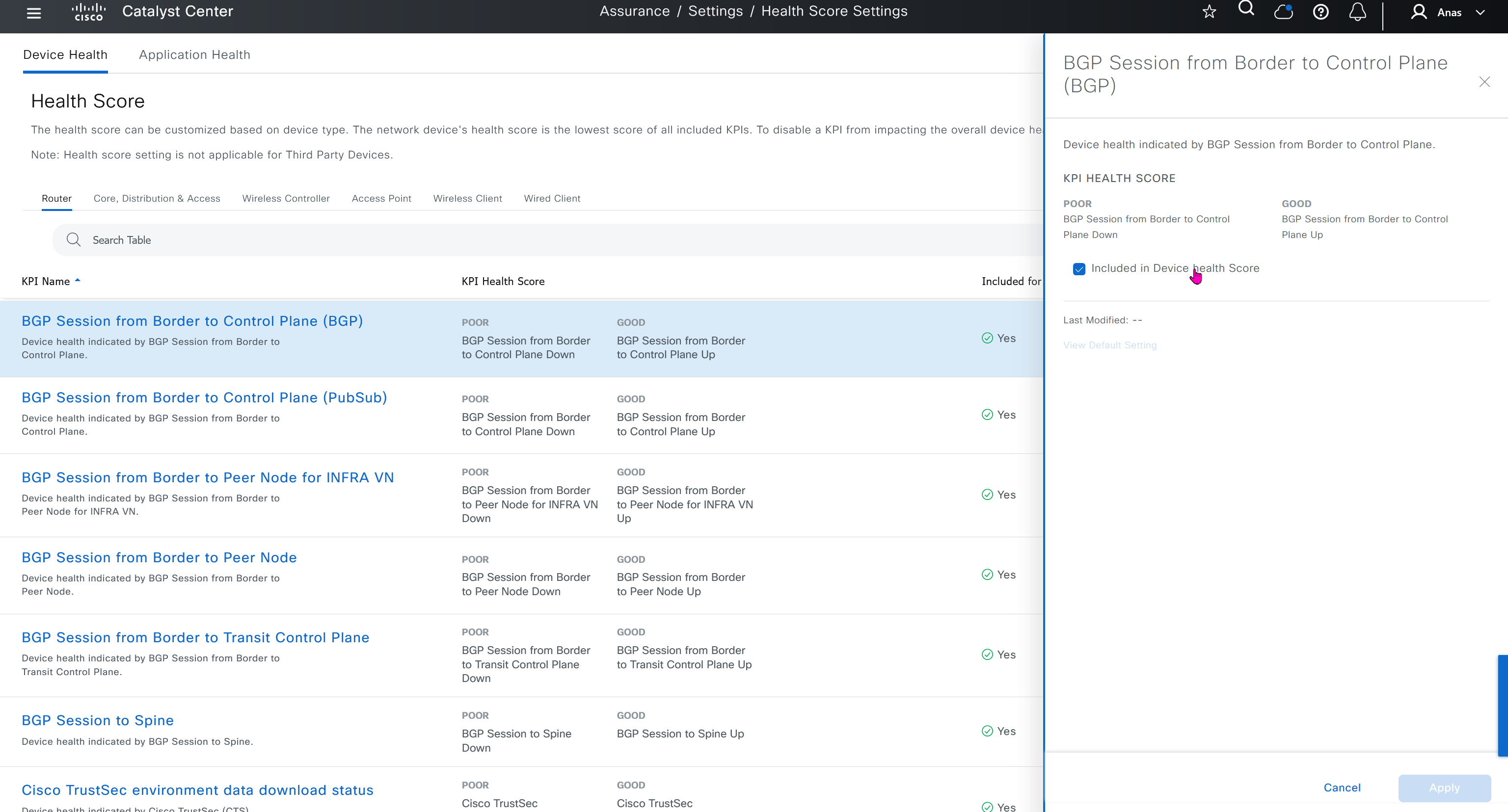
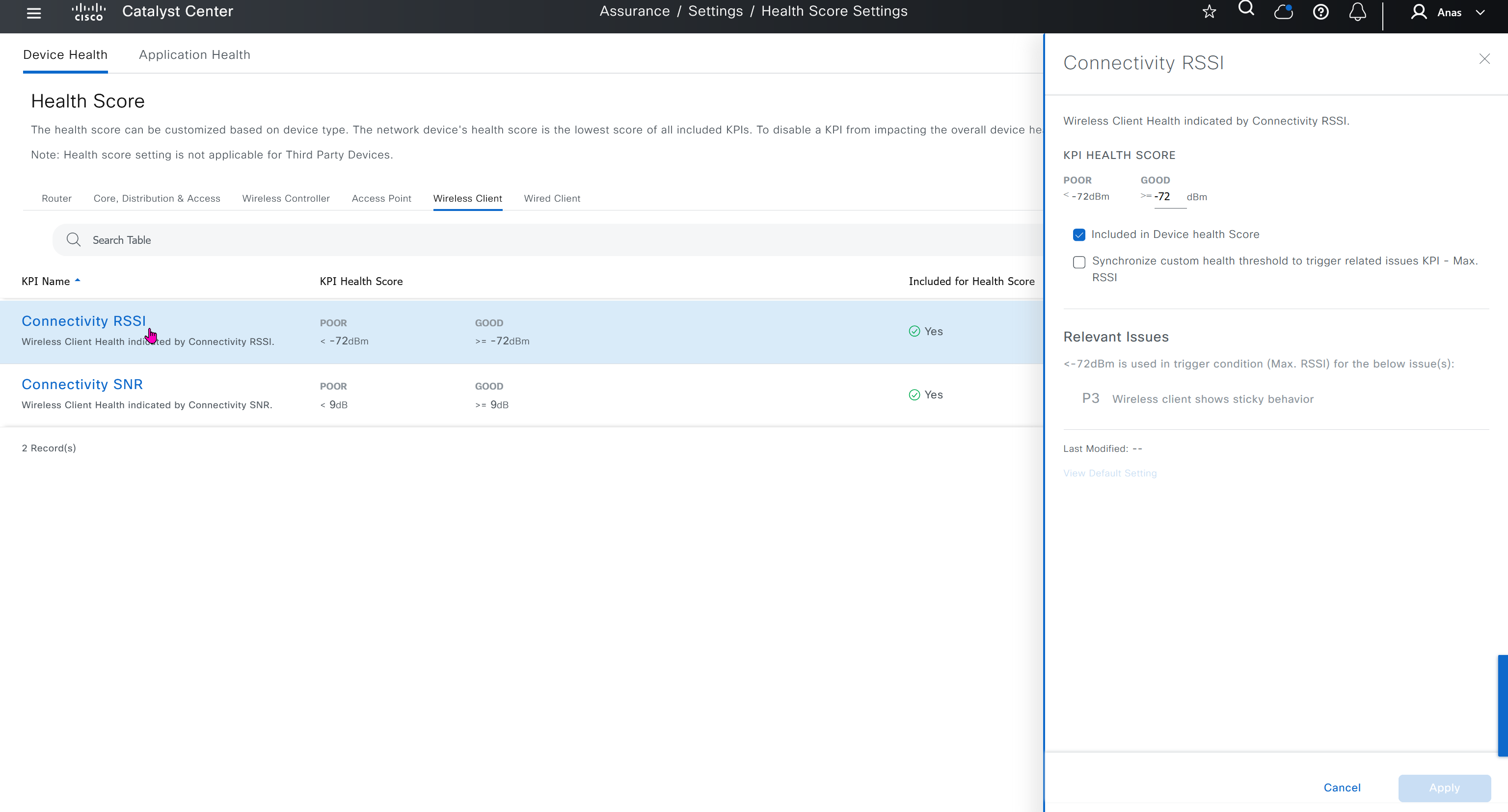
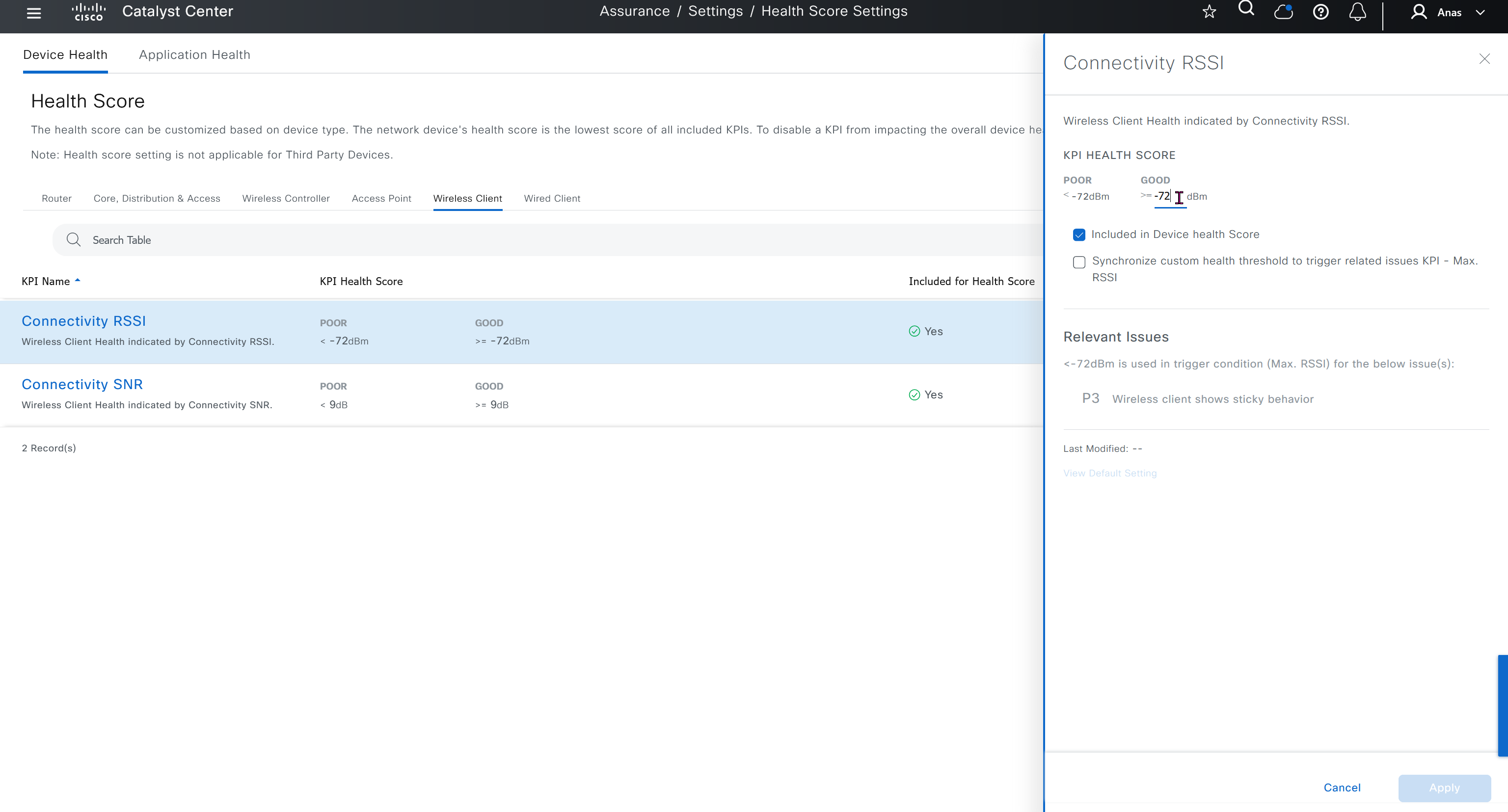
Health score is where you can turn on or off on what is included in determining device health score, these health score threshold values can be modified as well



Sensor section here we define test settings such as ping, HTTPs, association test etc
Intelligent capture is where you define how and when you want your AP to perform capture of client traffic
Workflows make things easy for us as they are guided configuration wizards that help us configure things easily and quickly without making mistakes




CLI templates is where we create templates, when it is time to apply template then we apply them using Network profiles

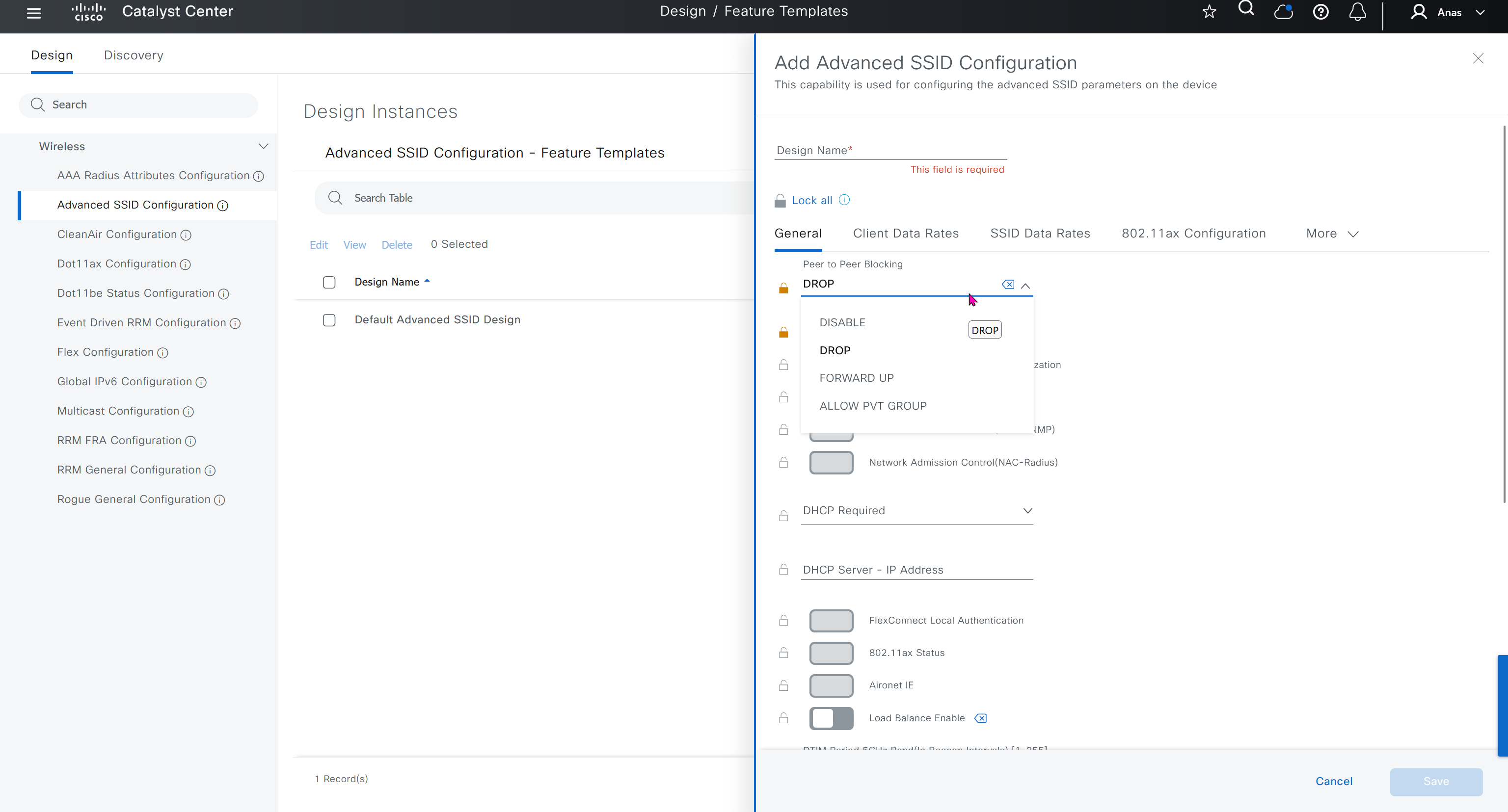
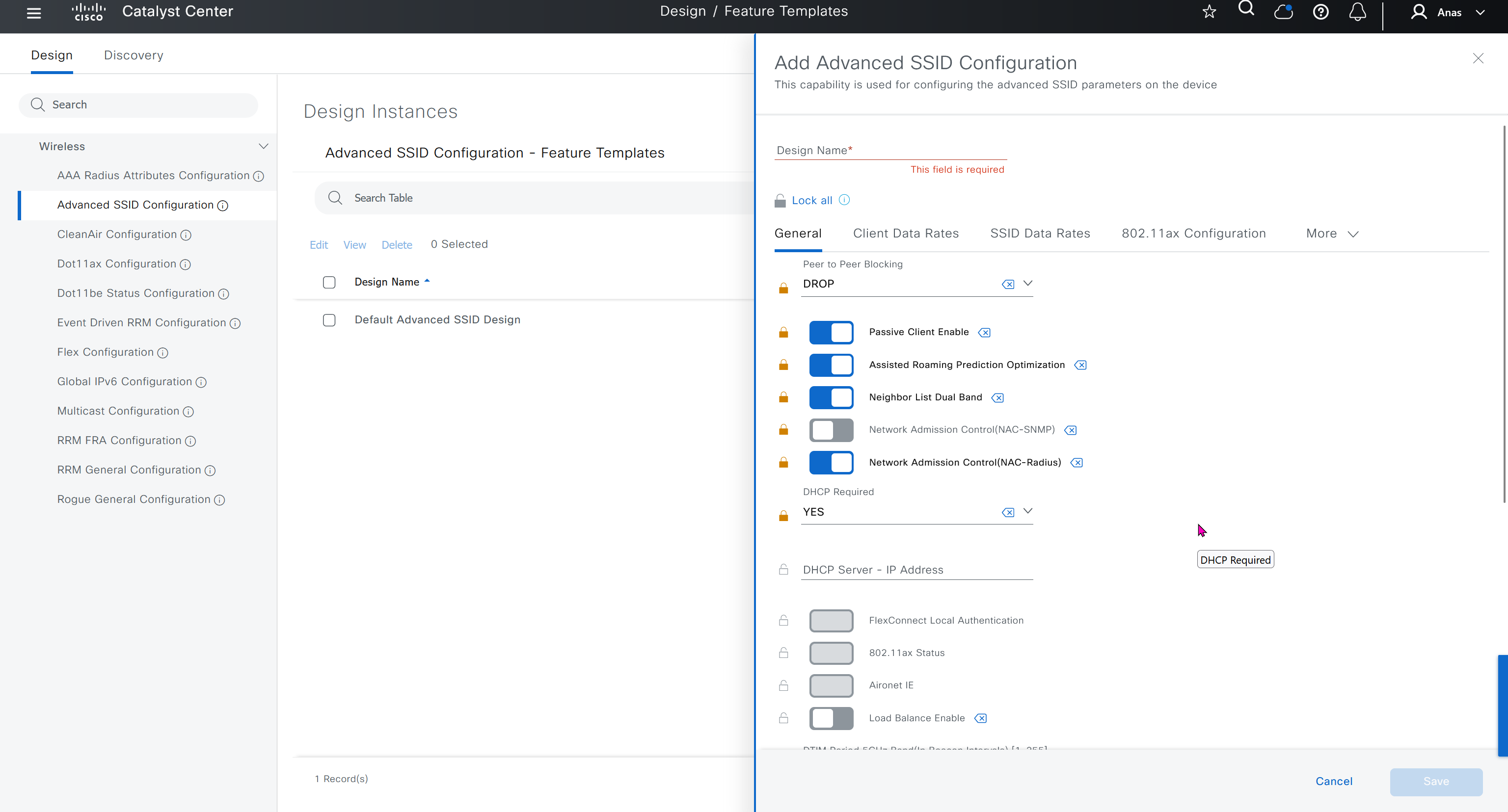
Feature templates are graphical UI based configuration unlike CLI template and they dictate best practice rather than manual CLI based templates, this makes configuration like Meraki but we only have this wireless at the moment

Network reasoner helps troubleshoot offered issues in Network reasoner dashboard

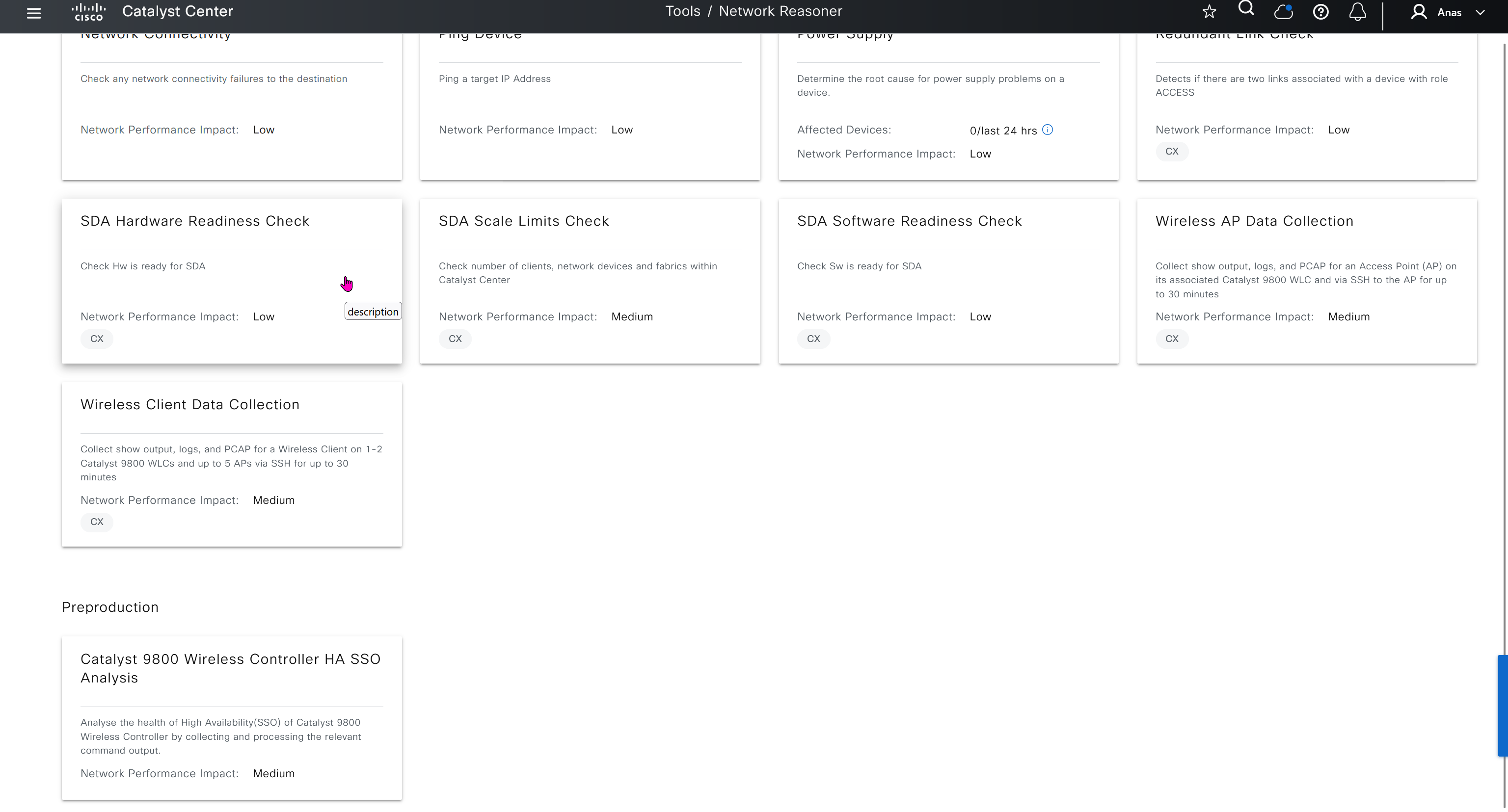
Platform section allows us to use DNAC API for automation and API interaction, it is also used to install device packs for non Cisco devices and also 3rd Party integration such as service now






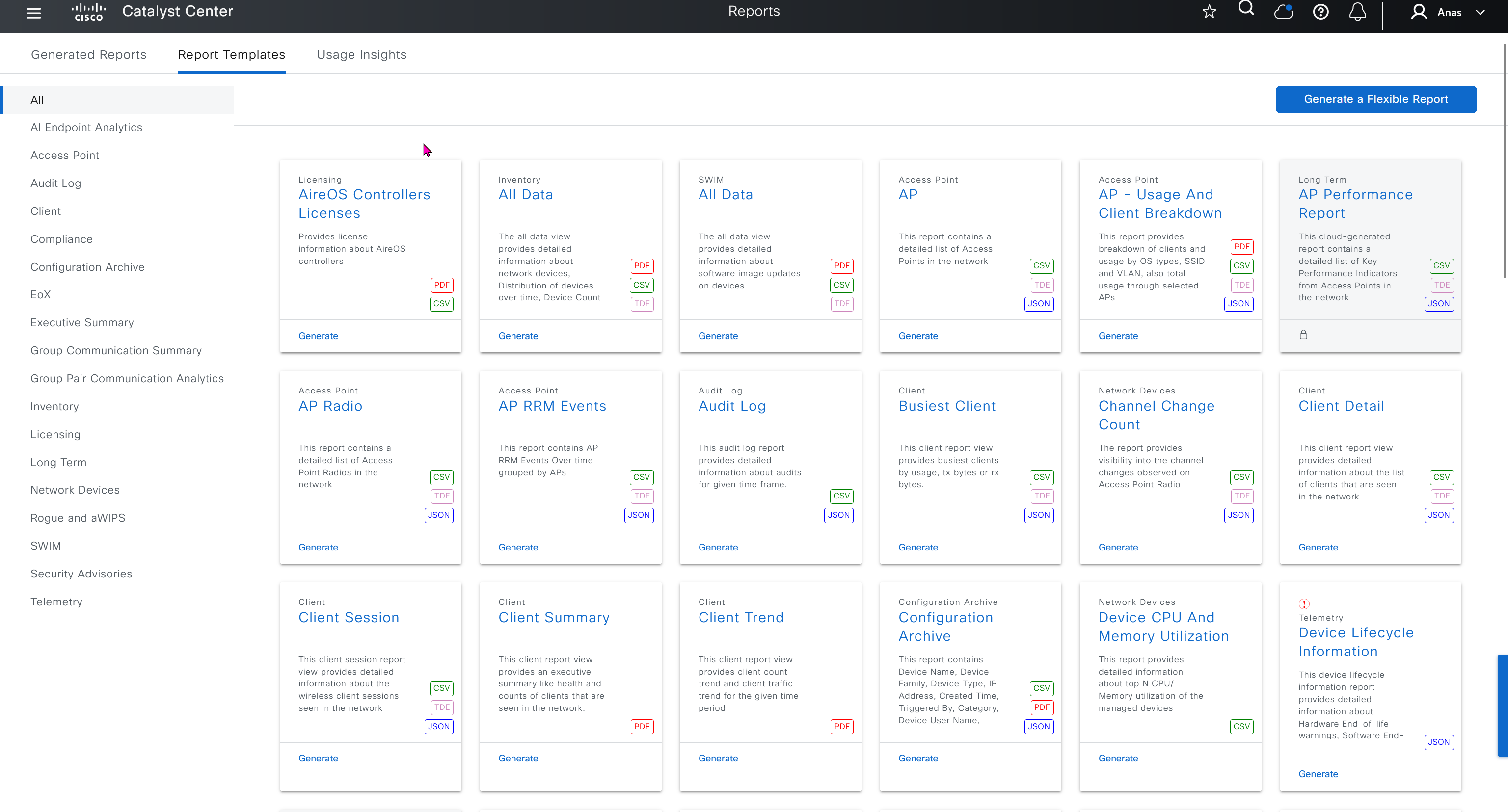
DNAC comes with report templates











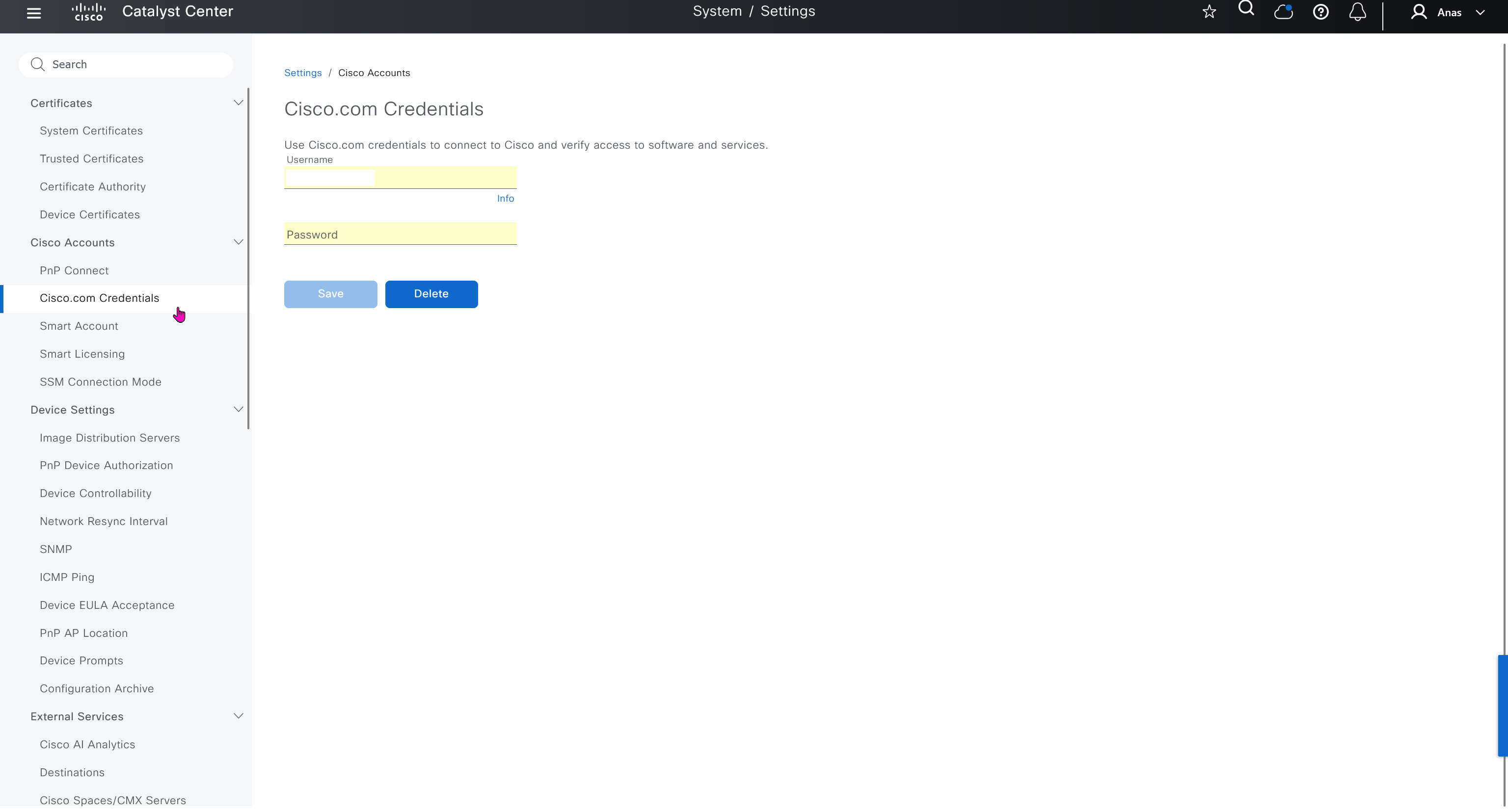
Cisco.com Credentials
Cisco credentials is the same credentials we entered after changing password for DNAC admin on first time login
PnP Connect
PnP connect lets you sync your devices from internet based Cisco’s PnP to DNAC directly, this is used for onboarding routers and switches using PnP in Cloud
Cisco Plug and Play (PnP) Connect is a cloud-based onboarding service that helps you automatically provision new Cisco network devices (switches, routers, access points, etc.) with Cisco DNA Center — no manual configuration or console access needed similar to SDWAN or Meraki onboarding
When a new Cisco device boots up:
- It connects to the PnP Cloud portal.
- The PnP Cloud checks the device’s serial number.
- The device is matched to your DNA Center project.
- The device is redirected to your DNA Center for zero-touch provisioning.
Smart account
“Auto register smart license enabled devices” allows devices to register to selectable “Virtual account inside the Smart account”

Smart Licensing
Smart account defined earlier is used in Smart licensing section, register a smart account and virtual account to have DNAC licensed and in compliance state
Device EULA Acceptance
For LAB I will not accept as not sure what might be the impact on CCO account against licenses
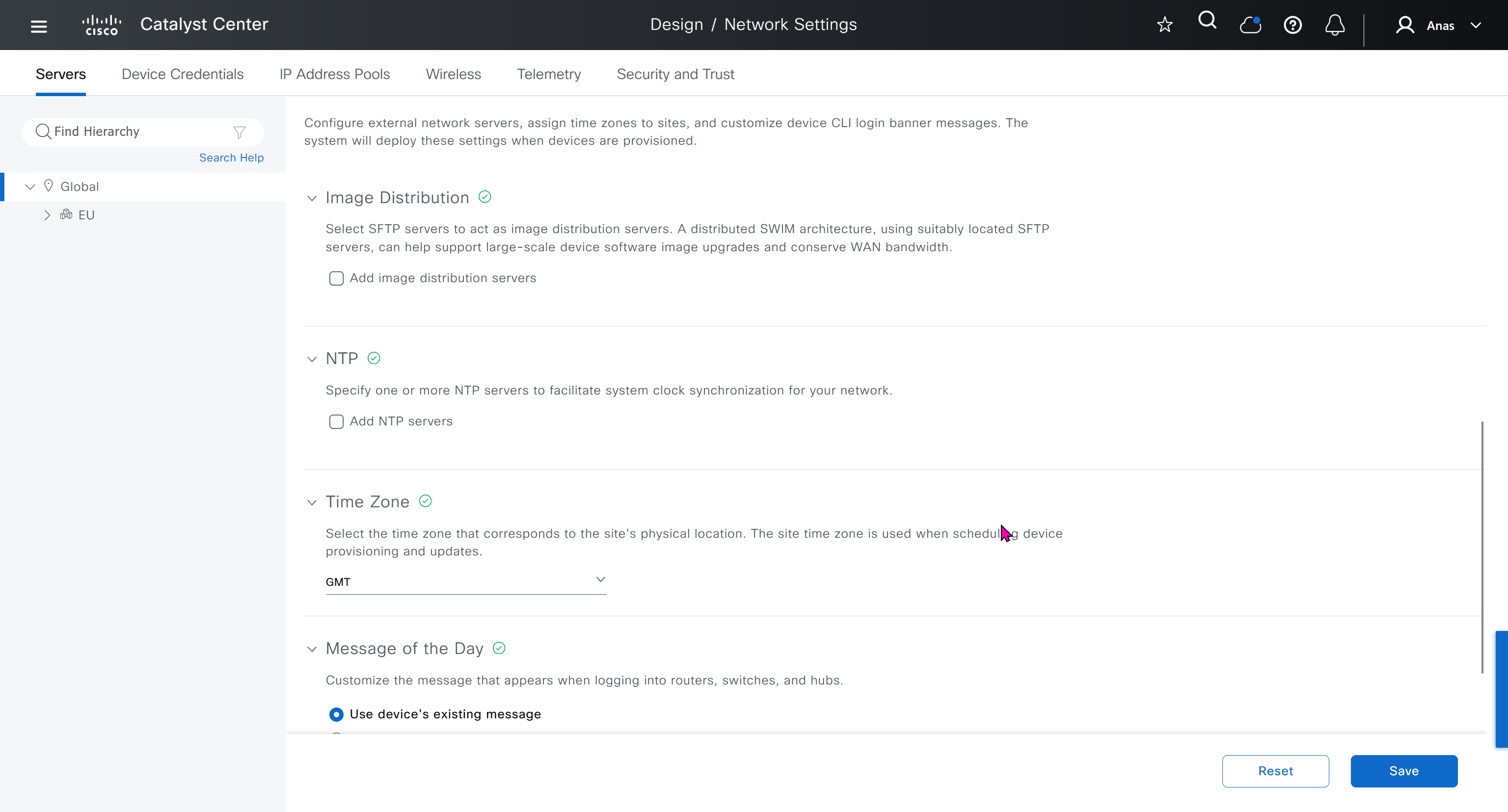
Image Distribution Servers
10.21.1.2 (LOCAL) is DNAC itself, but we can define other image distribution servers not to burden the WAN
Network Resync Interval
This is how often DNAC syncs with network devices, default is 24 hours

SNMP
is timeouts and retires

Authentication and Policy Servers
defined ISE servers
Cisco AI Analytics
This is where you configure AI analytics
Destinations
This is to deliver event notifications when events happen on DNAC
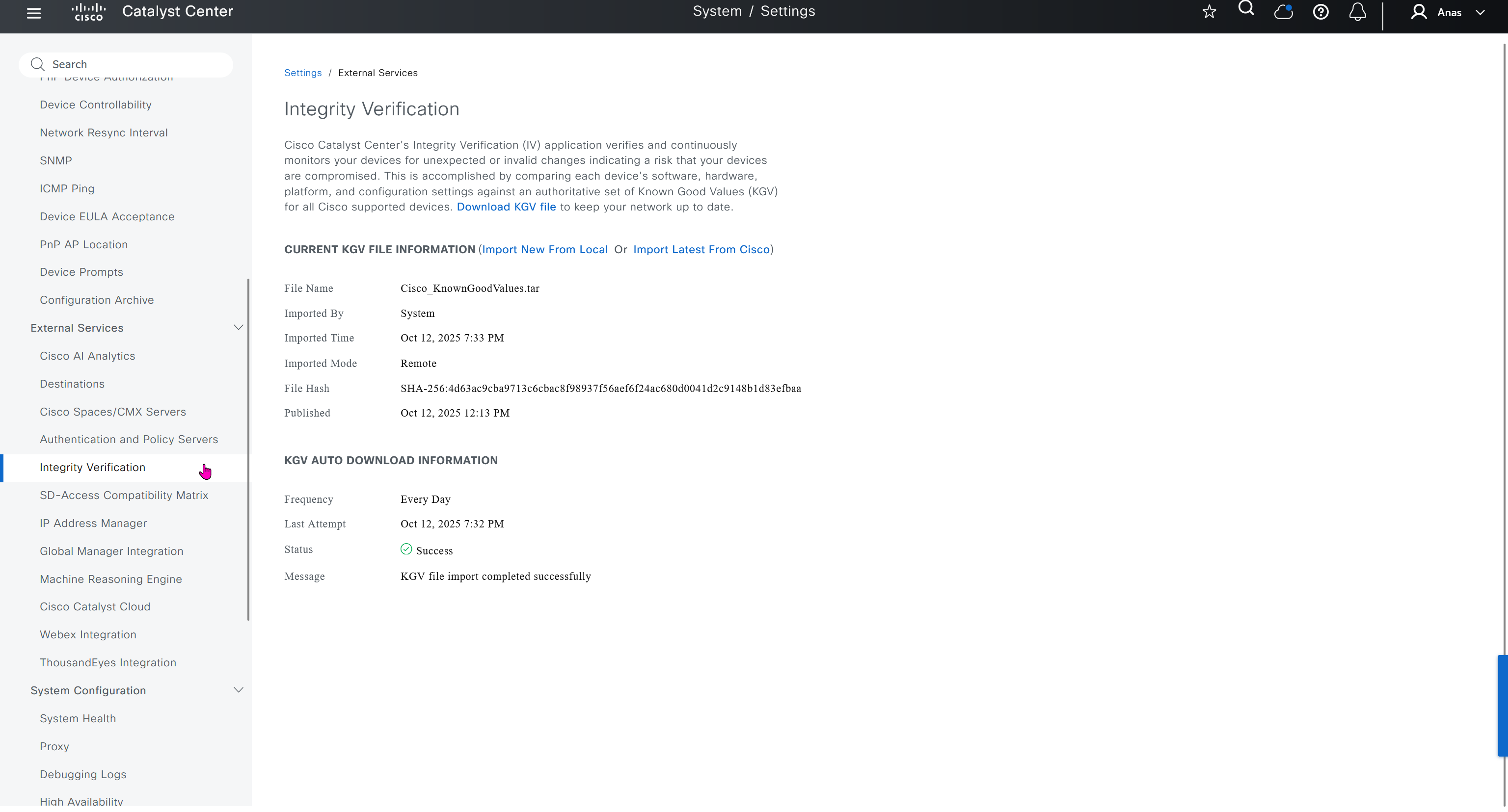
Integrity Verification
Checks if device is compromised on software, hardware level using Known Good Values KGV file from Cisco, which also requires updates from Cisco
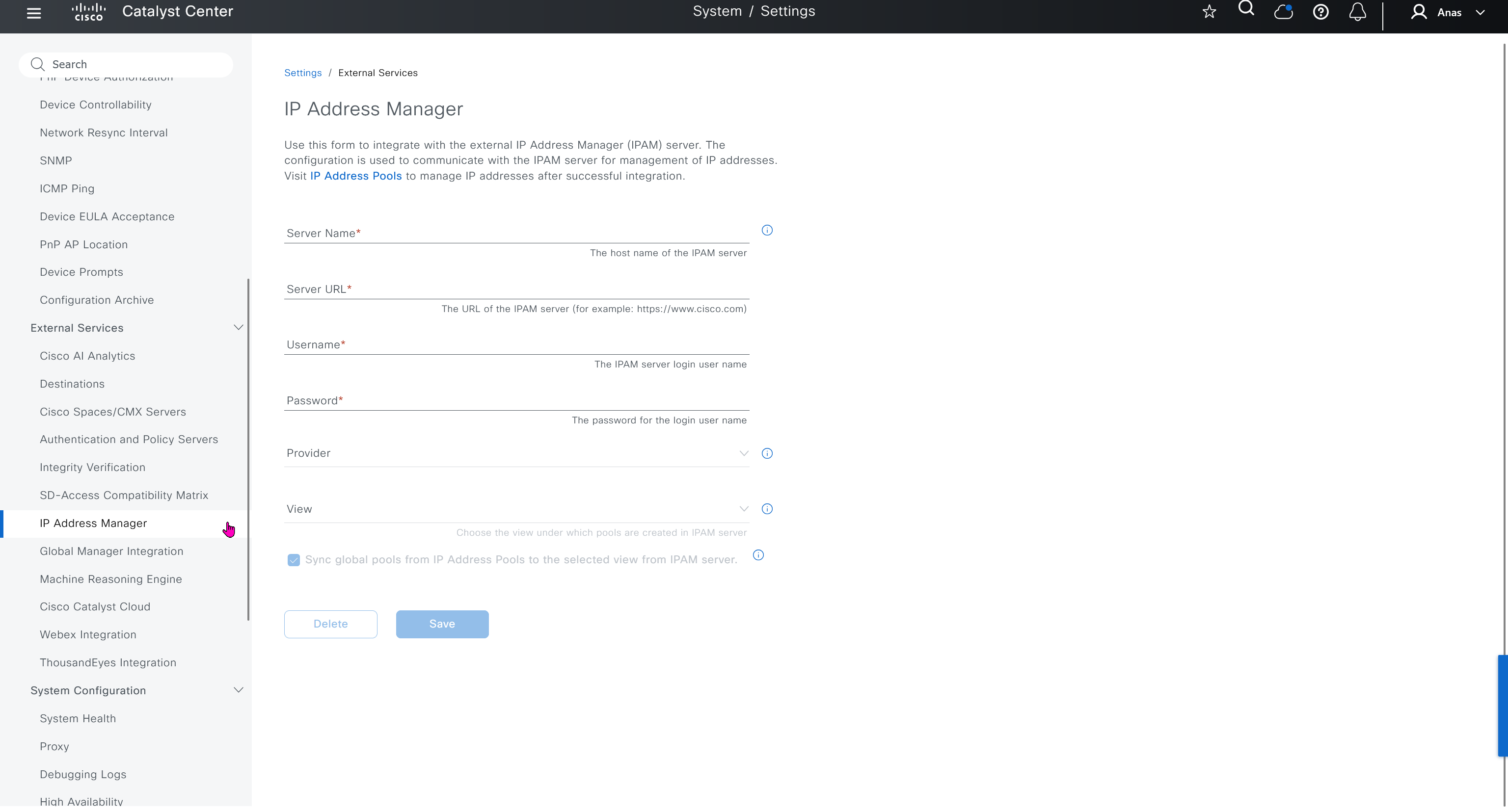
IP Address Manager
This is integration with IPAM
Machine Reasoning Engine
Download and keep upto date Cisco’s latest machine learned troubleshooting and reasoning database, make sure it is set to auto update


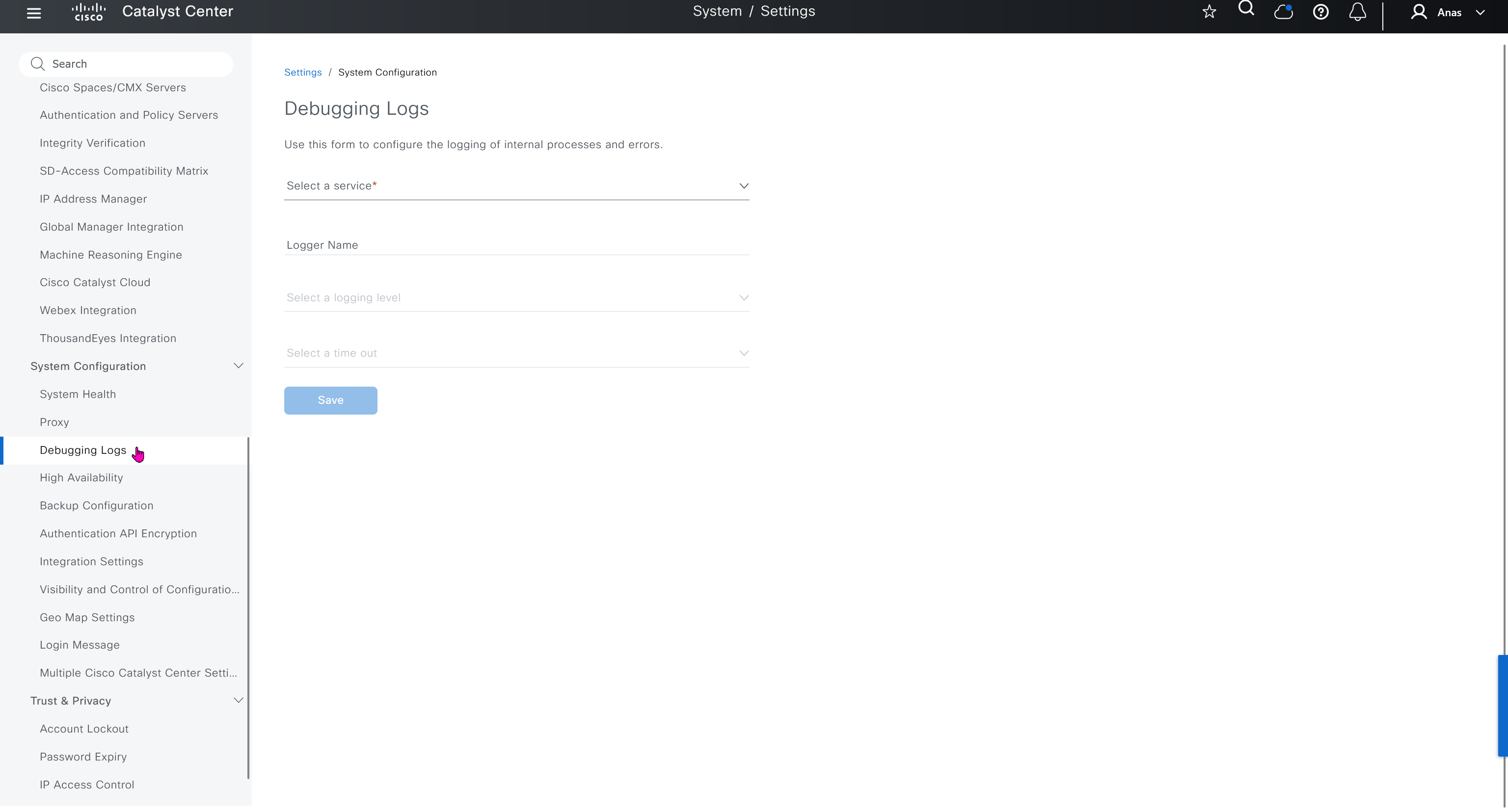
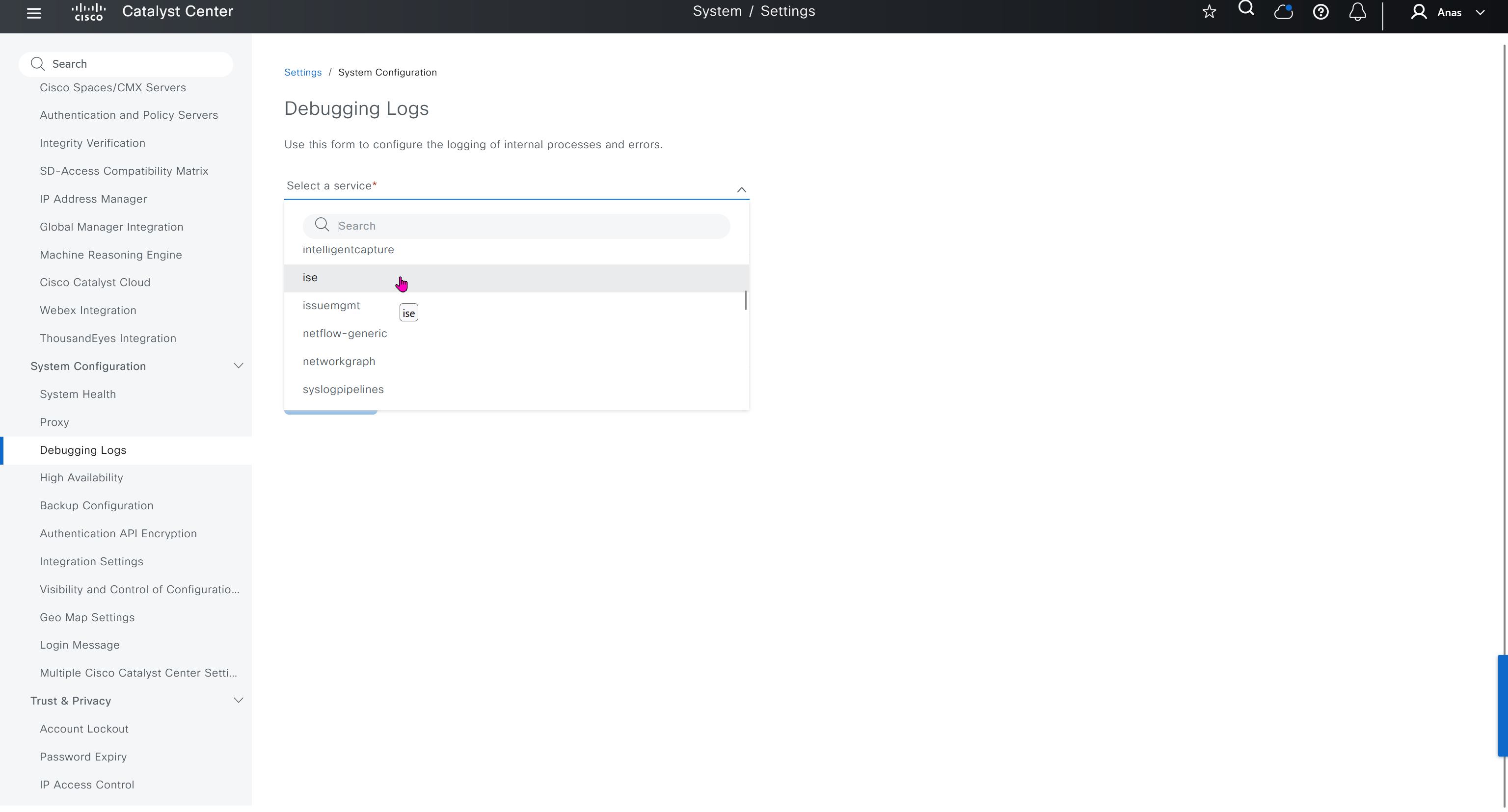
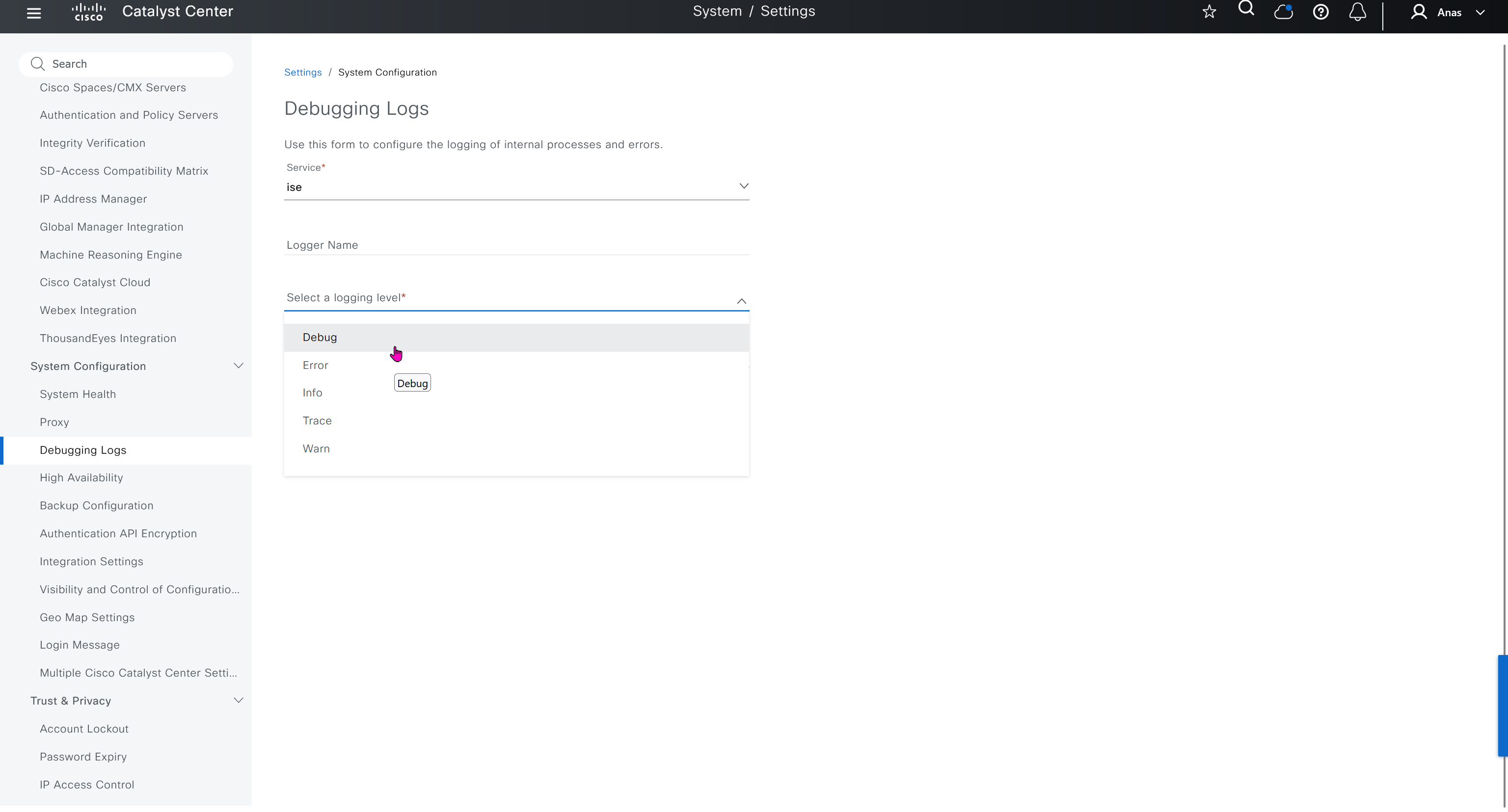
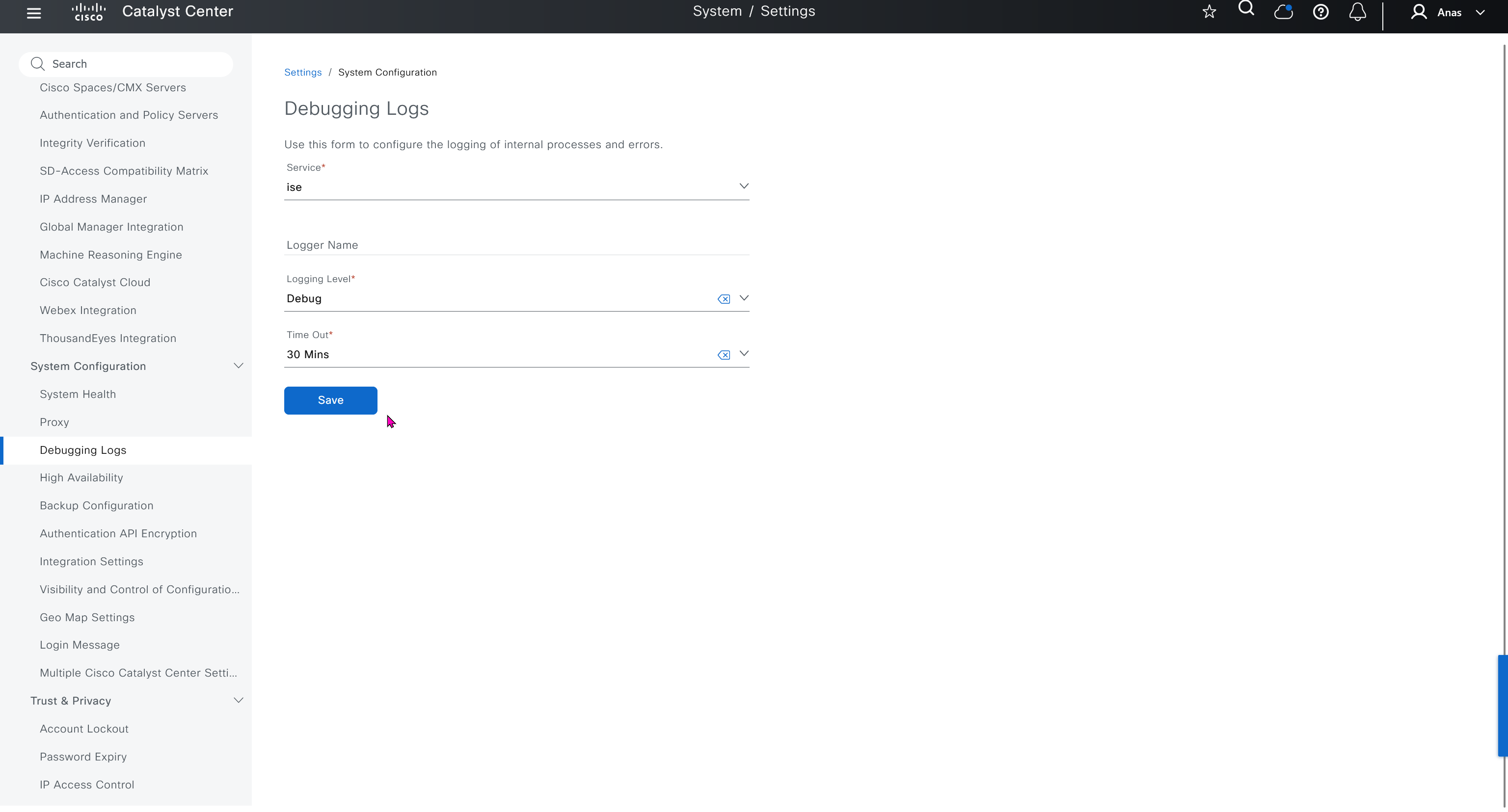
Debugging Logs
This is to debug logs for DNAC itself, specify a syslog server


Search
Search in DNAC is amazing and you can search clients by MAC address or IP address / track clients with Client 360 link in search result and even search IP pools
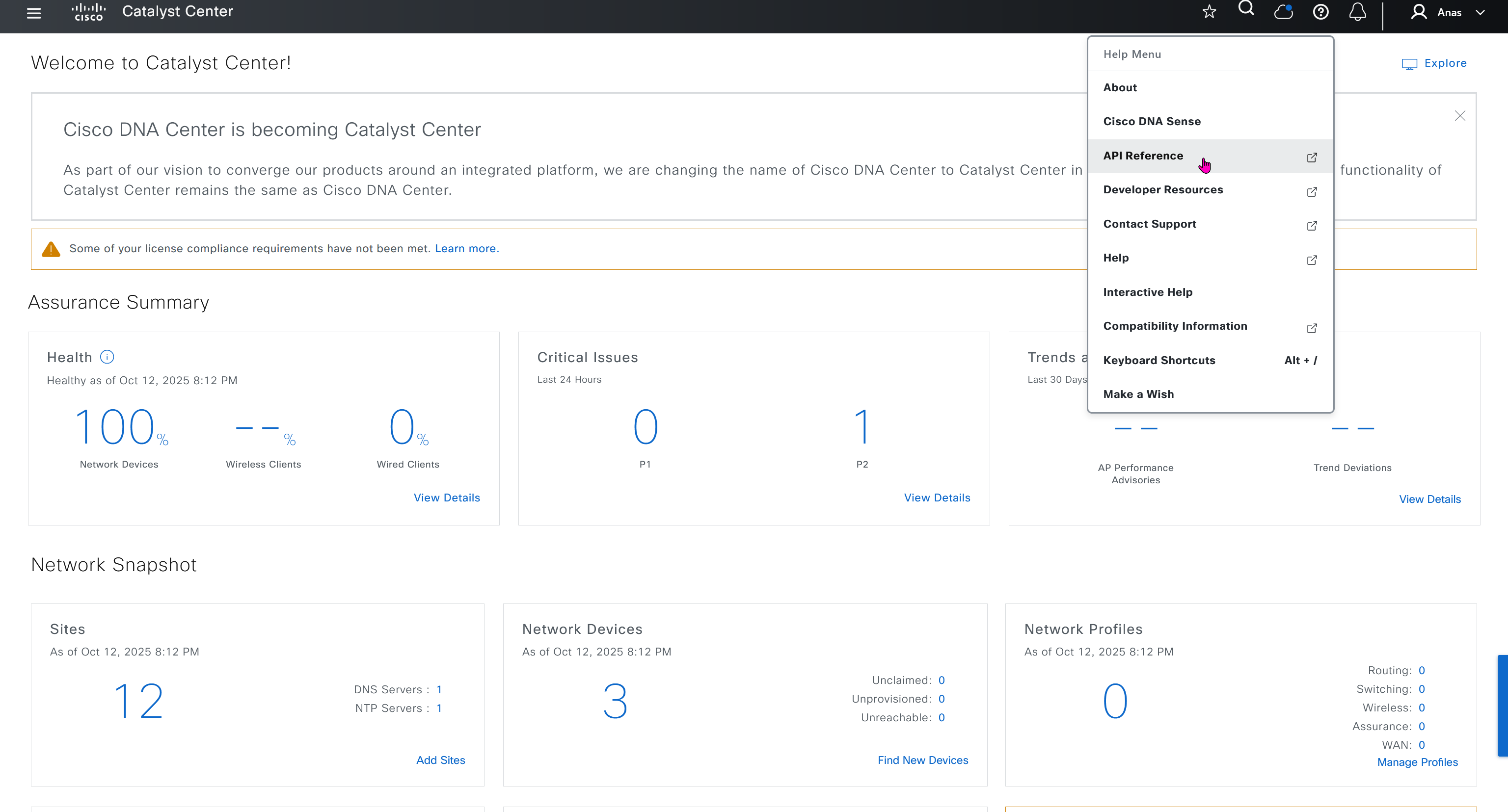
API Reference
This comes handy when you are working with API
next post
Enable logging of commands by DNAC
Configuration
conf t
!
! Enable the archive feature
archive
log config
logging enable
notify syslog contenttype plaintext
hidekeys
!
! Optional: Set up where the archived configs are stored
path flash:config-archive
write-memory
!
end
!
! Ensure syslog logging is enabled (optional but recommended)
conf t
logging buffered 64000
service timestamps log datetime msec
!
end
write mem next post
SD-Access LAN Automation Deployment
LAN Automation Deployment
LAN automation is a network management process that
simplifies underlay deployment
eliminates manual, repetitive network configuration tasks, and
establishes a standard, error-free underlay network.
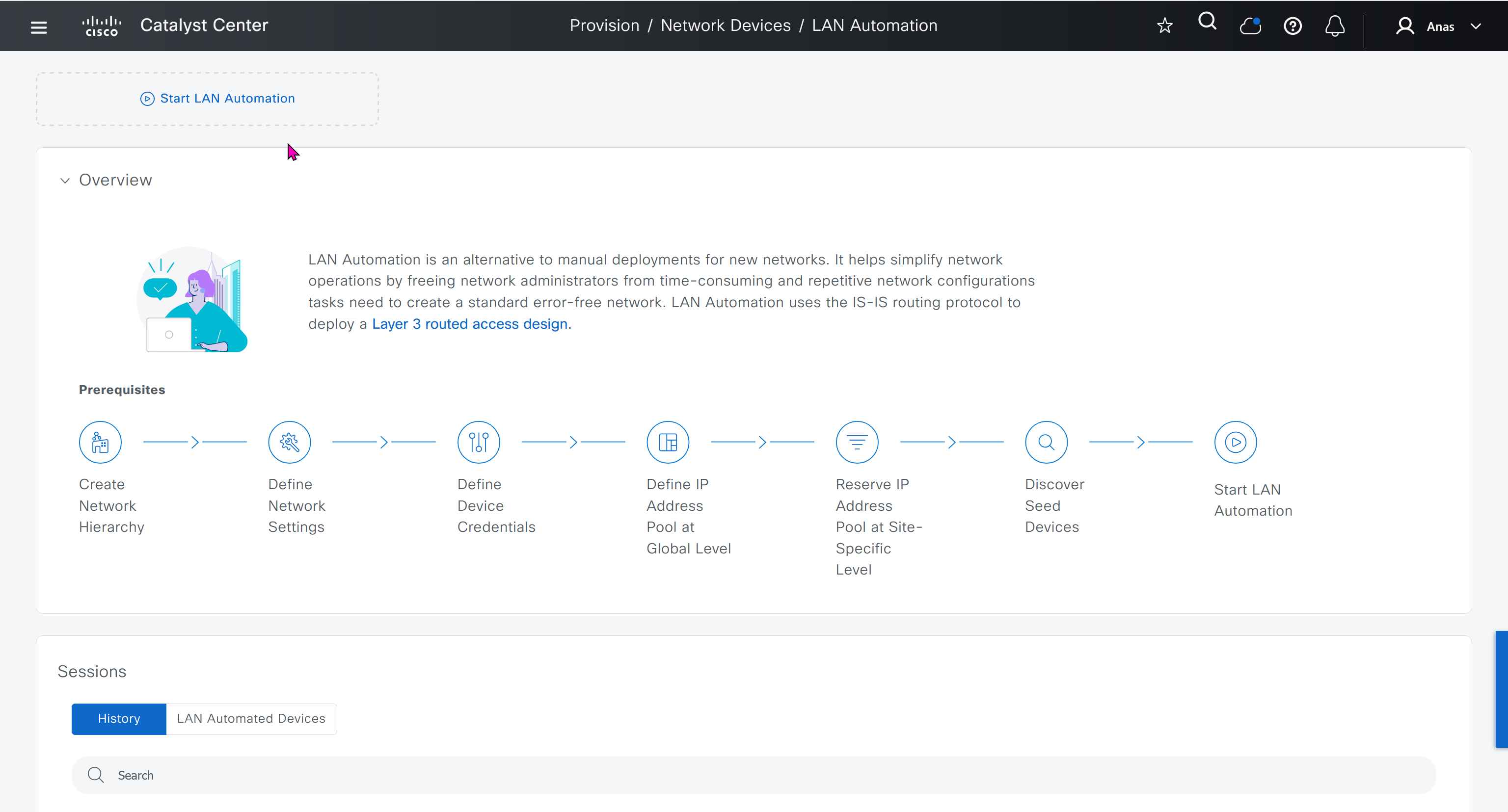
Cisco LAN automation provides:
Zero-touch provisioning: Network devices are dynamically discovered (CLI controlled), onboarded, and automated from their factory default state to fully integrated and configured state (templates can be configured since CLI controlled) in the network.
Dynamically build end-to-end routing topologies.
Cisco LAN automation enables redundancy and automates best practices to ensure resiliency during planned or unplanned network outages.
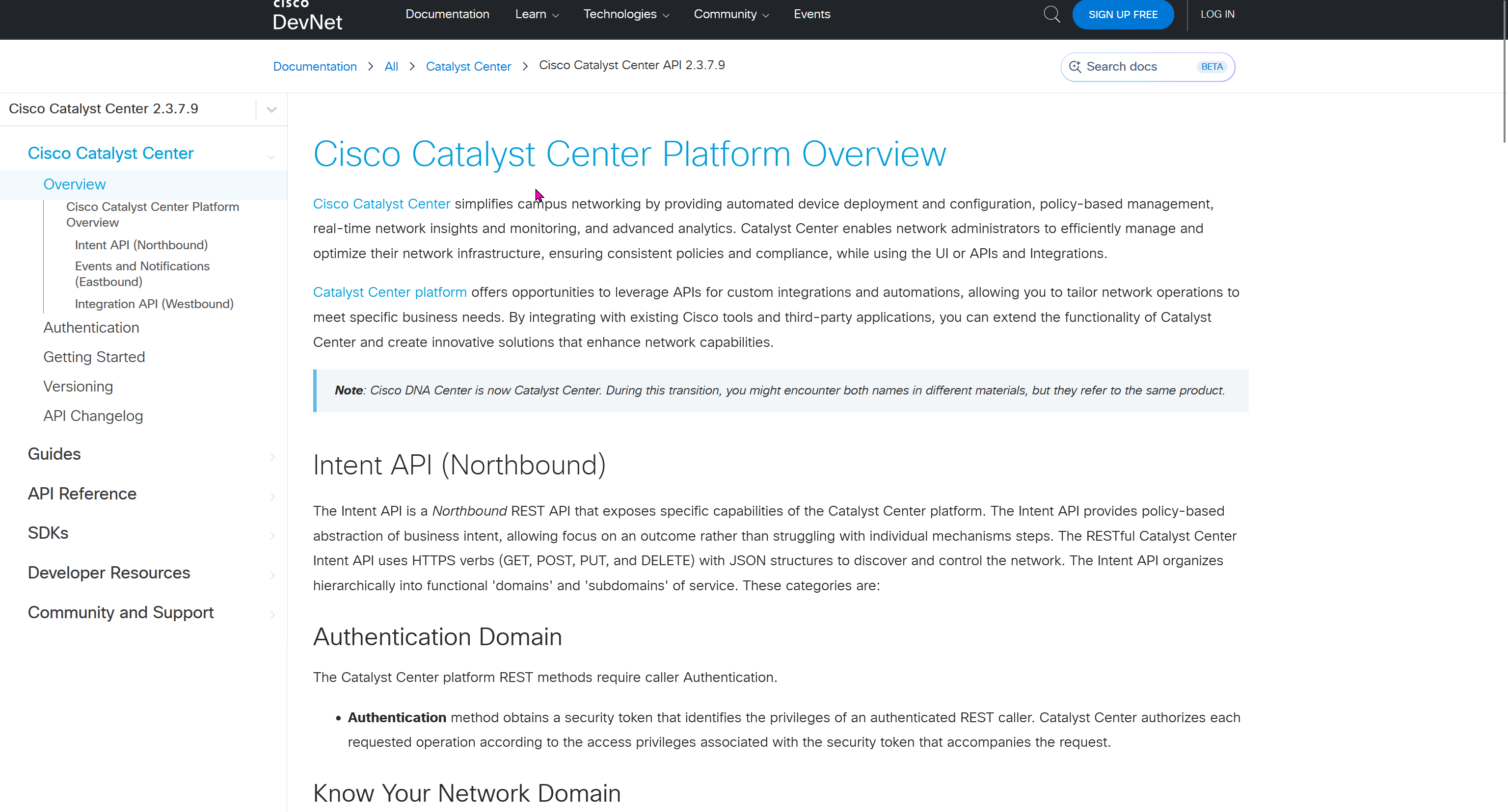
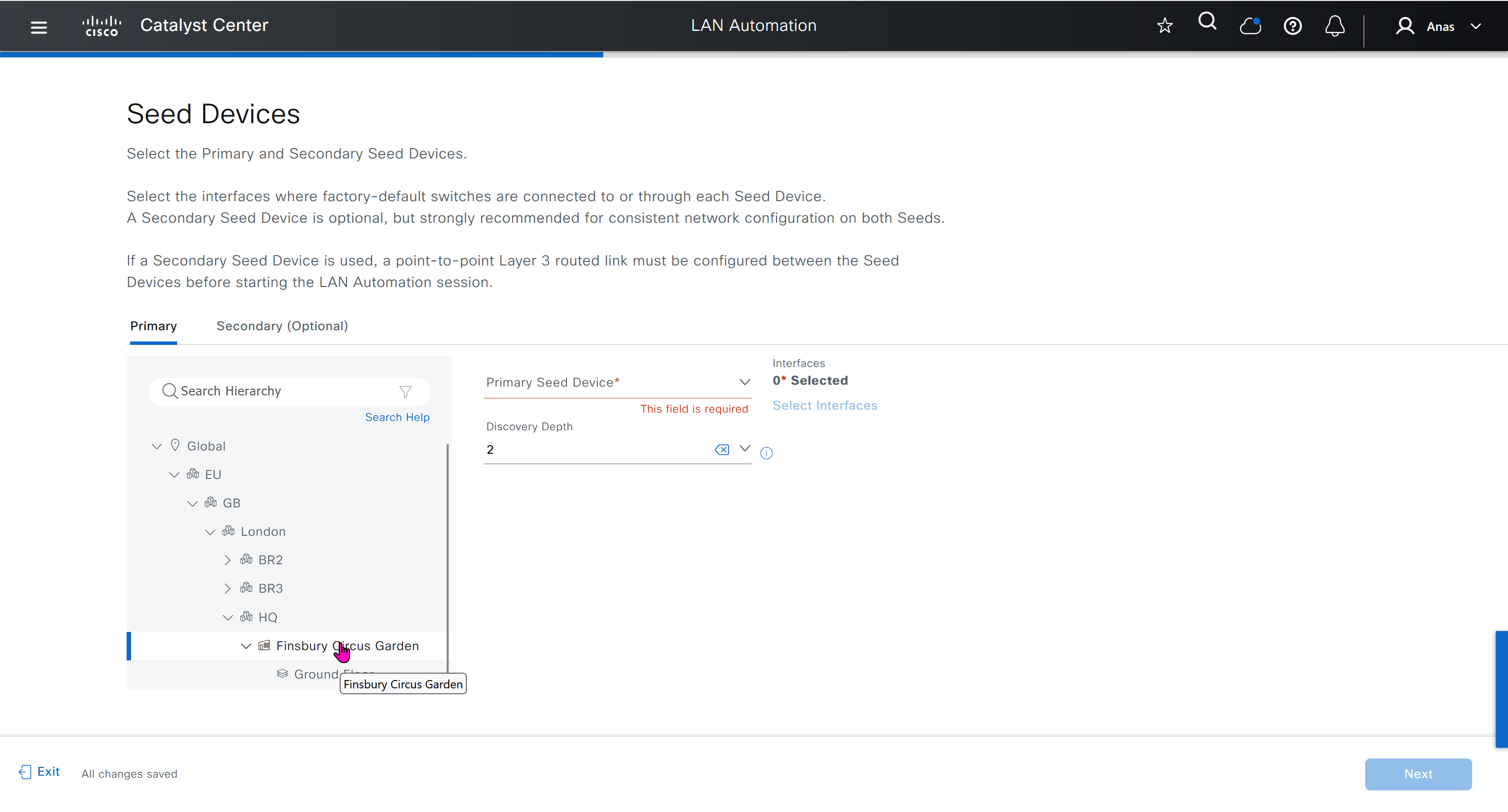
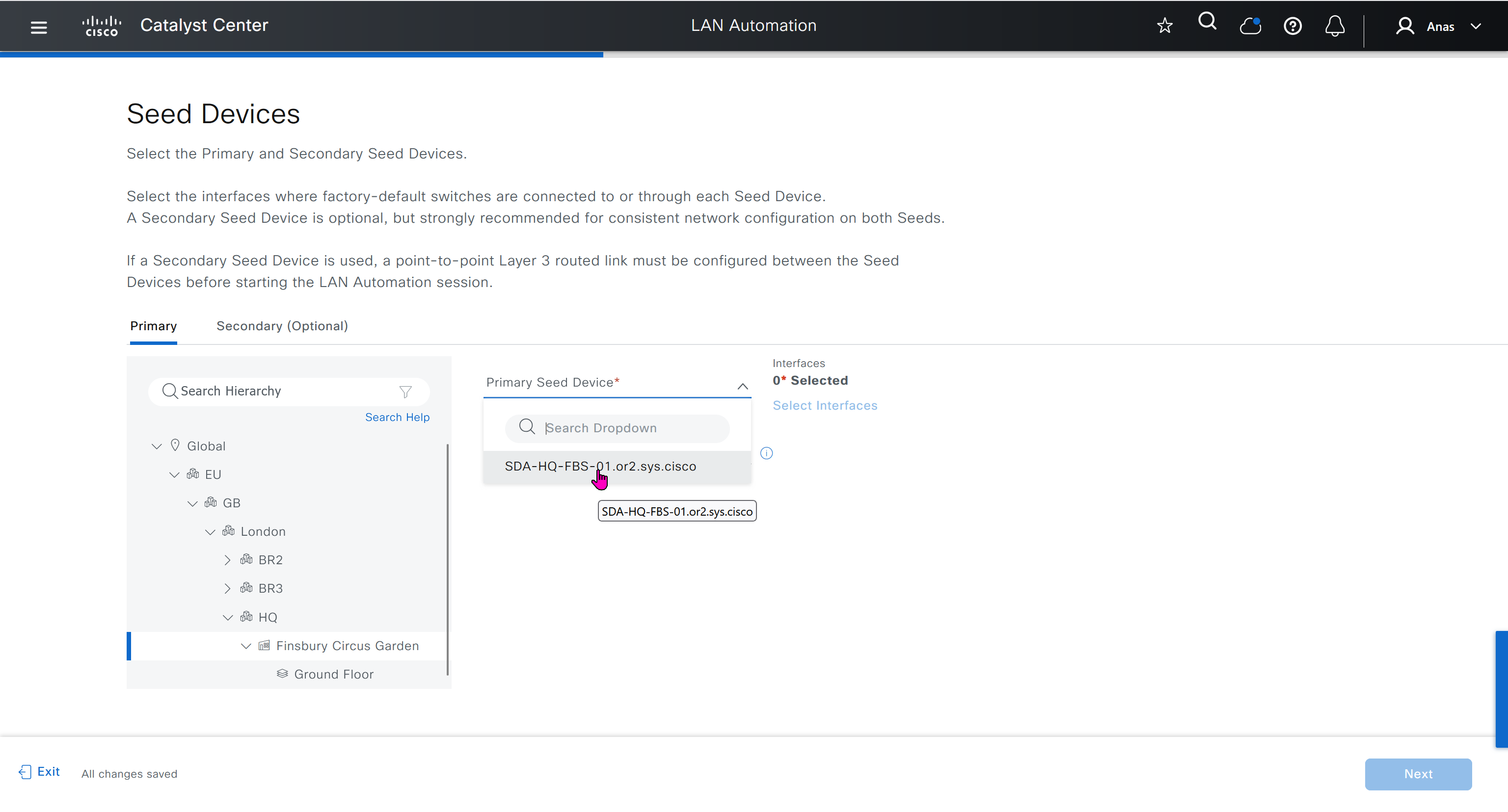
Seed device
Pre-deployed device and initial point through which LAN automation discovers and onboards new switches downstream
The seed device can run technologies such as Plug and Play (PnP) and zero-touch provisioning or configured manually.
Device discovery happens only on the primary seed device interfaces. One seed device can do the job but two can be deployed
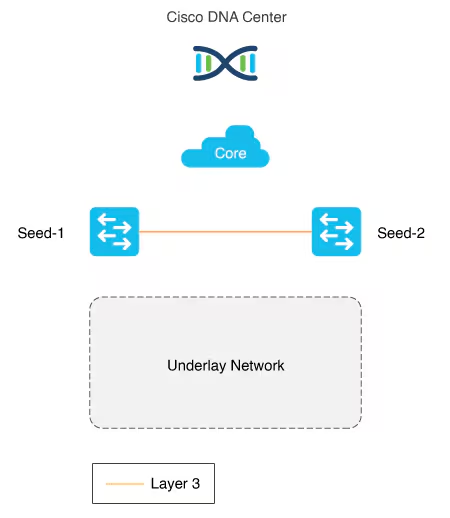
PnP agent
The PnP agent is a Cisco Catalyst switch with factory default settings
The switch uses 0 day communication to communicate with Catalyst Center (PnP server)
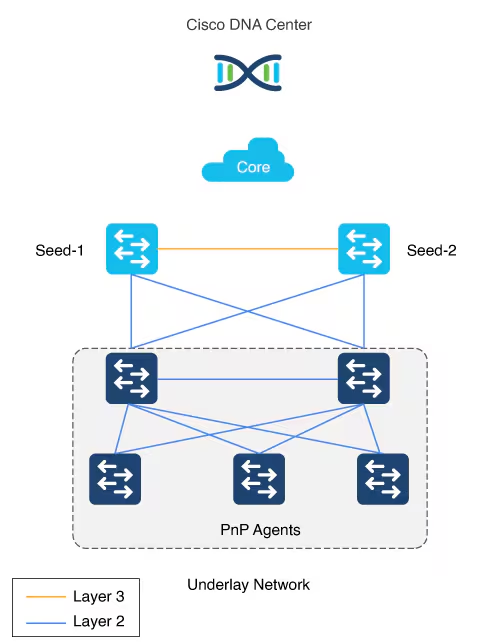
LAN automation in Catalyst Center supports a maximum of two hops from the initial automation boundary point device. Any additional network devices beyond two hops might be discovered but cannot be automated, Given that seed devices are core switches from the three tier model:
- Scenario 1: You have a three-tier network and you want to LAN “automate distribution and access layer switches”, both distribution- and access-layer switches will be discovered and LAN automated.
- Scenario 2: You have a three-tier network and you want to LAN automate distribution and access-layer switches. You already LAN automated the distribution layer. Later, you add access-layer switches to your network and you want to LAN automate these switches. “Because the distribution switches are already LAN automated and links converted to Layer 3, Tier 1 or core switches cannot be used as the seed. You must choose distribution as the seed in this scenario“.
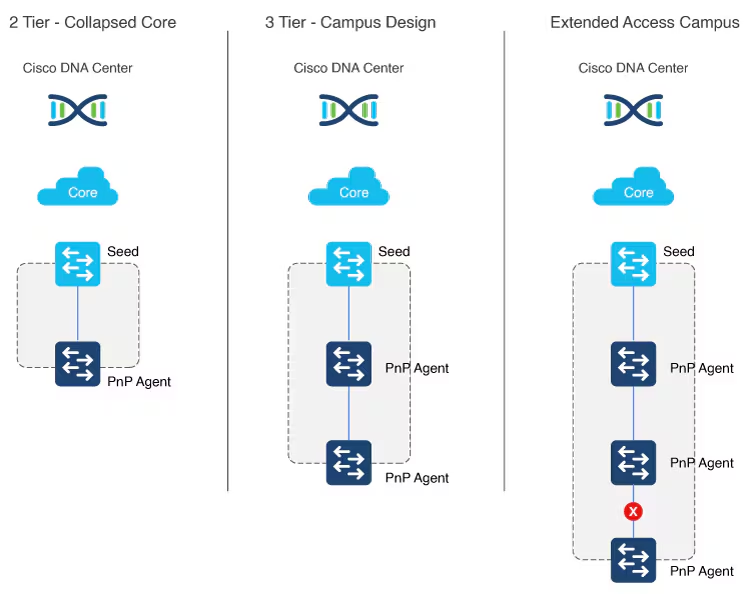
Multistep LAN automation for large topologies: First pass
Large topologies are brought up by performing LAN automation multiple times. During the first pass, core devices are chosen as seed devices to bring up the “distribution” switches as new devices.
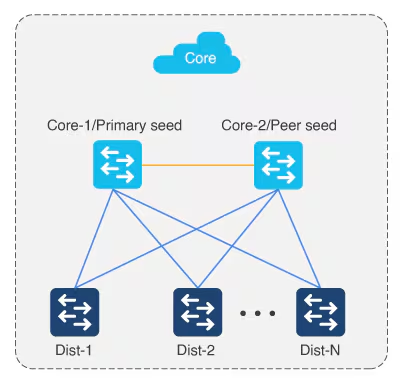
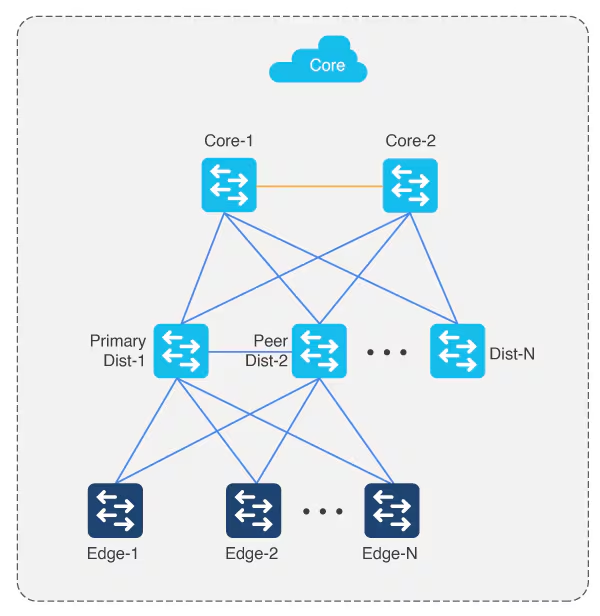
Multistep LAN automation for large topologies: Second pass with first group
During the second pass, two of the distribution switches act as seed devices to bring up the edge devices as new devices. All new devices in this session must connect directly to the two distribution switches that act as new seed devices. Repeat this process for the remaining set of distribution switches, two at a time (in pair).
Connect uplinks from edges to the primary and peer distribution switches only.
Always connect new devices to the primary seed device. Connection to the peer seed device is optional.
There can be two tiers of devices below the seeds.
Perform stacking before hand
Layer 3 link configuration after LAN Automation
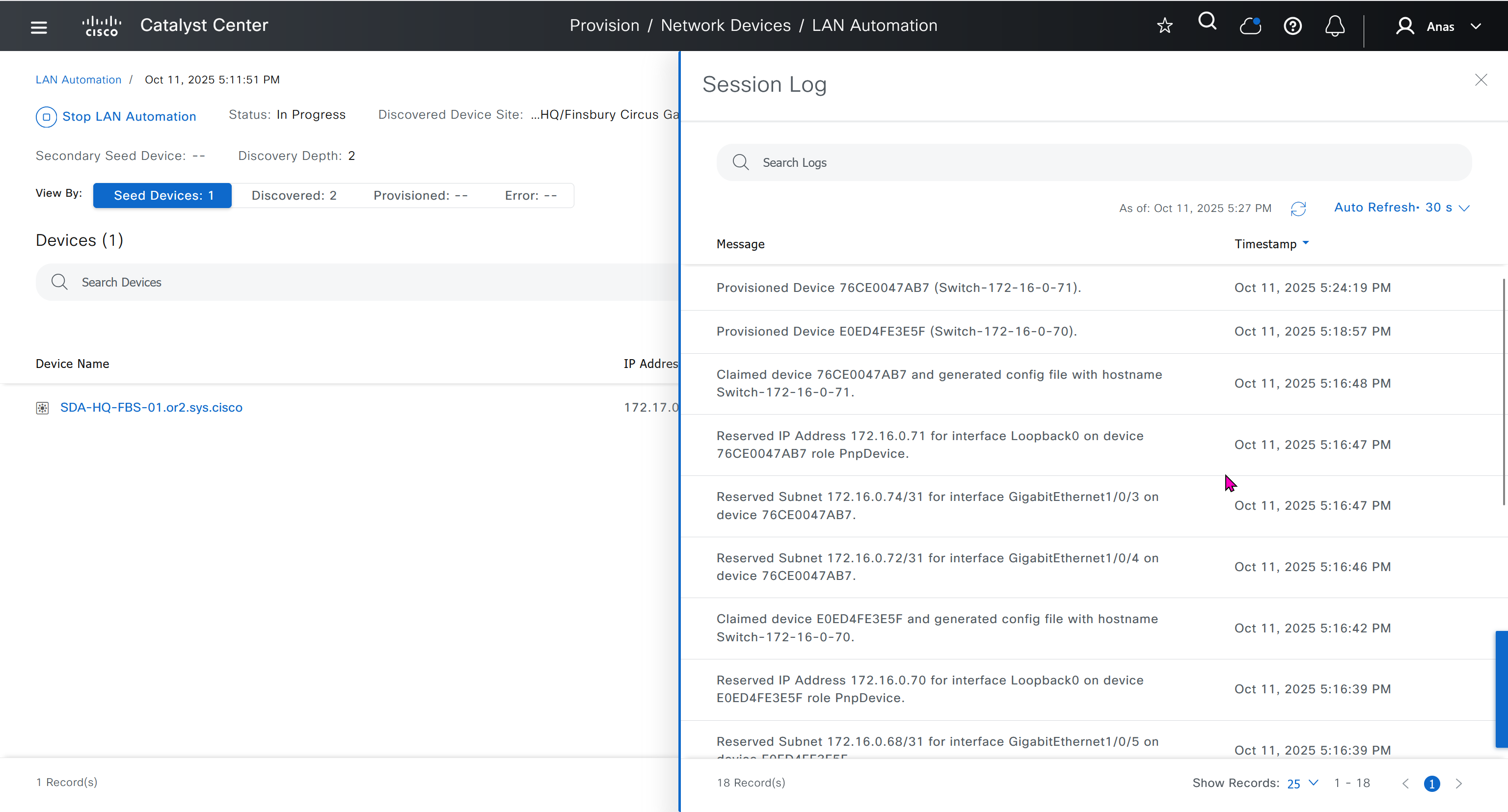
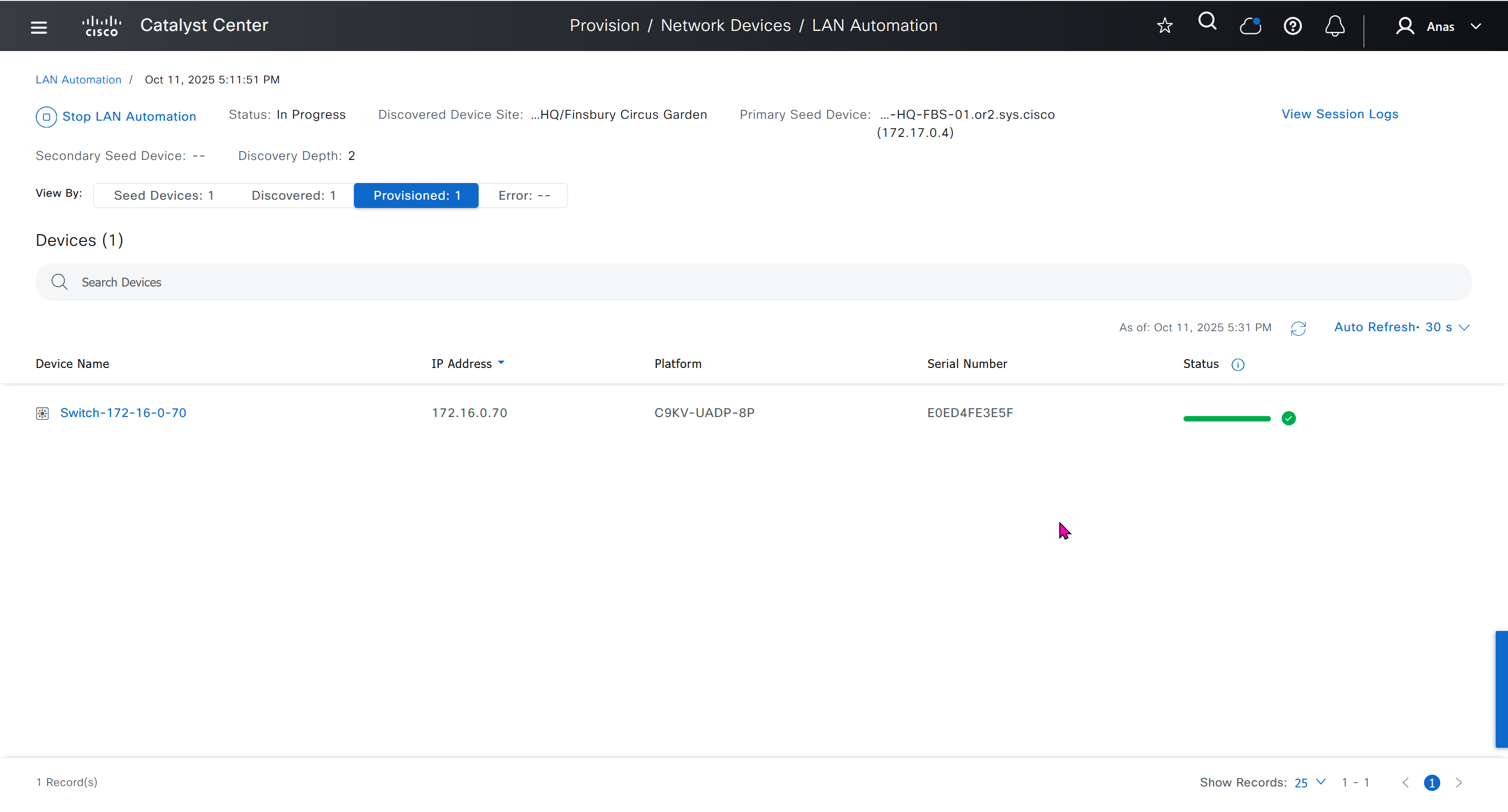
After all devices are added to the Catalyst Center inventory, you can stop the LAN automation session on the GUI to begin the Layer 3 link configuration process.
If you accidentally stop the LAN automation process before all PnP devices are added to the Catalyst Center inventory, You must bring the in-progress devices to the factory-default state in order to do LAN automation again.
Catalyst Center Release 2.3.5 and later provide the support for day-n link configurations (add and delete link). For more information, see Create a link between interfaces.
Supported switches for each role at different layers
Site planning
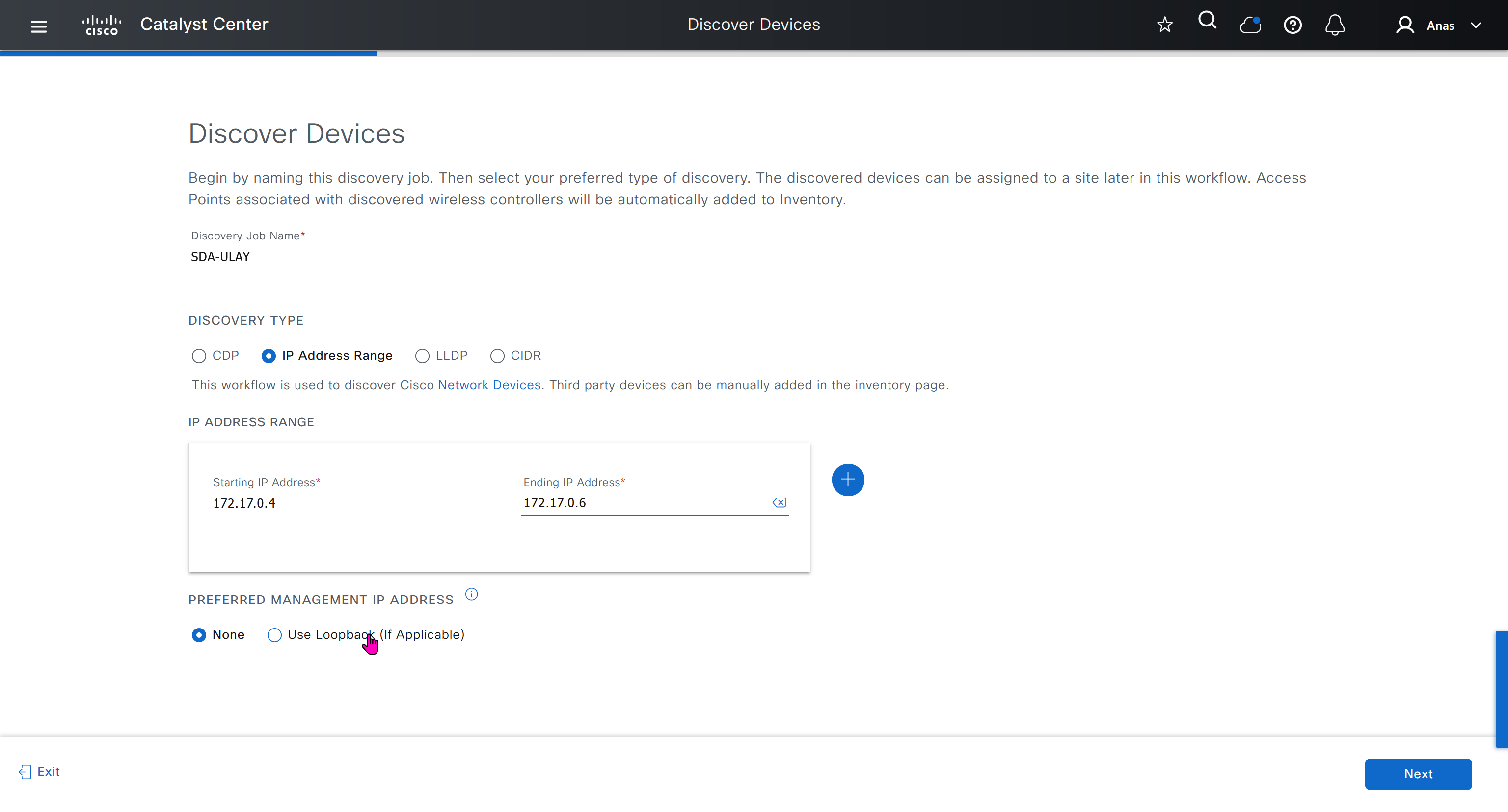
Use the Catalyst Center Design feature to create the required sites, buildings, and floors.
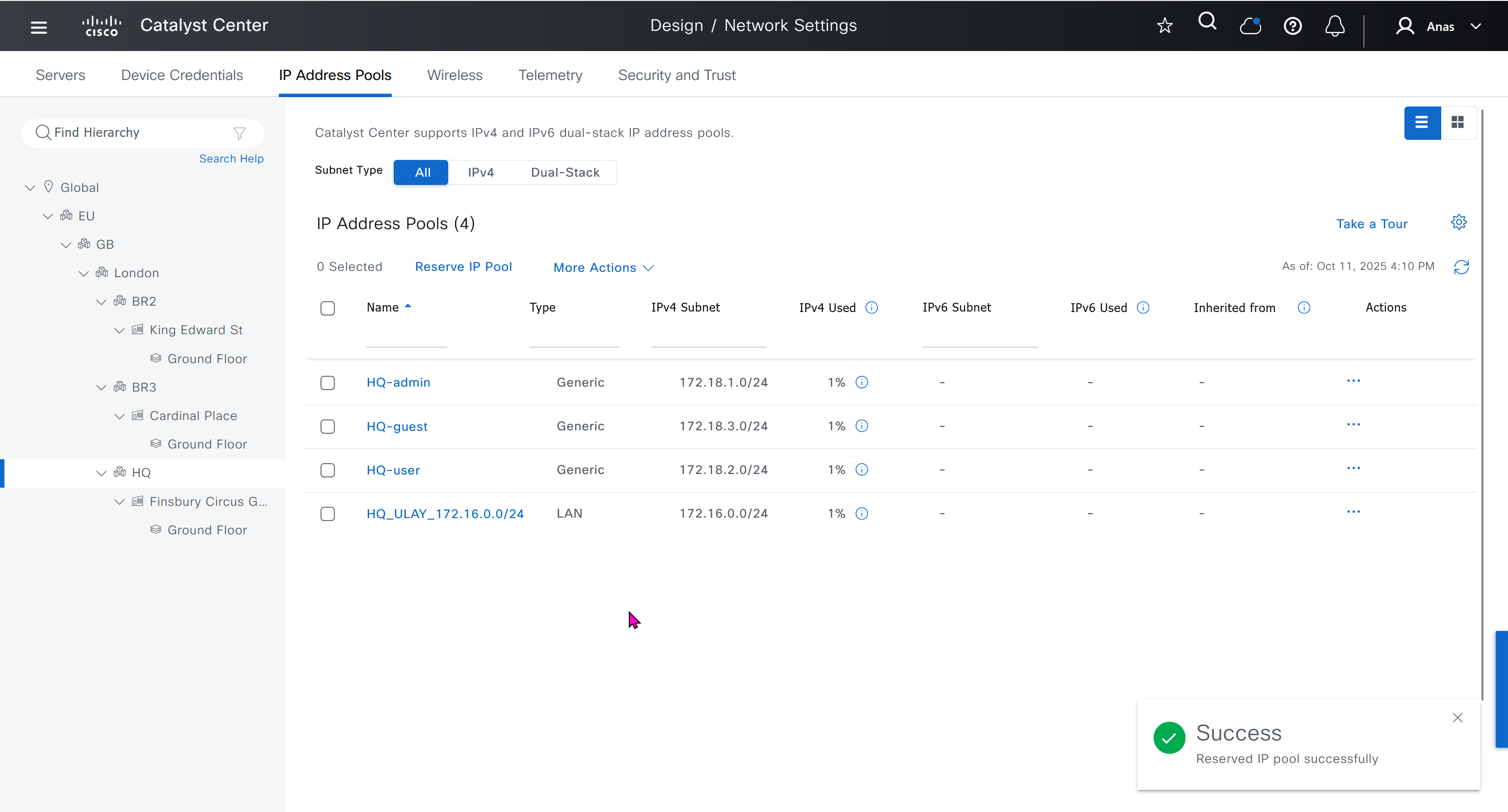
Create a global pool in DNAC, reserve IP Pool specific per site
Different types of IP address assignments used:
- Temporary DHCP pool assigns IP to factory default pnp agents or new switches
- /31 L3 interswitch links
- Loopback IP
- Underlay multicast IP
Temporary DHCP pool so new device can get IP and speak to DNAC
One part of the IP pool per site, is reserved for a temporary DHCP server,
this DHCP server runs on DNAC itself and seed devices are used as relay to relay DHCP request from PnP agent or new switch without IP towards DNAC,
Temporary DHCP server (running on Catalyst Center) leases IP addresses from this temporary DHCP subpool.
Those IPs allow the new device to:
- Boot up with a valid IP address.
- Contact Catalyst Center over the network.
- Be discovered and provisioned automatically
Once the LAN automation session is finished:
- The DHCP service stops.
- The temporary subpool is released.
- All those IP addresses go back to the main LAN pool.
- The switches now have permanent IPs assigned by the automation process (usually from a different IP pool).
The size of this pool depends on the size of the parent LAN pool. For example, if the parent pool is 192.168.10.0/”24″, a /”26″ subpool is allocated for the DHCP server, Therefore, a /”24″ pool reserves /”26″ 64 hosts so we can think of this temporary DHCP pool size with the -2 rule
A /23 pool reserves /”25″ 128 hosts, a /22 pool reserves /24 256 hosts, and larger pools reserve (max) 512 IP addresses for the DHCP server, it steps up in this way and max pool size is 512 addresses for even bigger parent pools
for example initial blocks of 192.168.10.0/24 can be used since site is not operational and LAN automation is being run to deploy the site, once LAN automation is complete these chunks are released back in order for them to be reserved in site and used
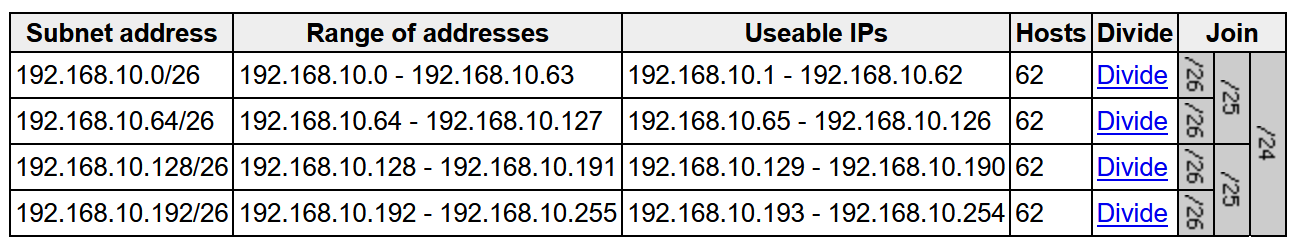
To start LAN automation, the pool size must be atleast /25, which reserves a /27 pool or 32 IP addresses for the DHCP pool.
This IP pool is reserved temporarily for the duration of the LAN automation discovery session. After the LAN automation discovery session completes, the DHCP pool is released, and the IPs are returned to the LAN pool
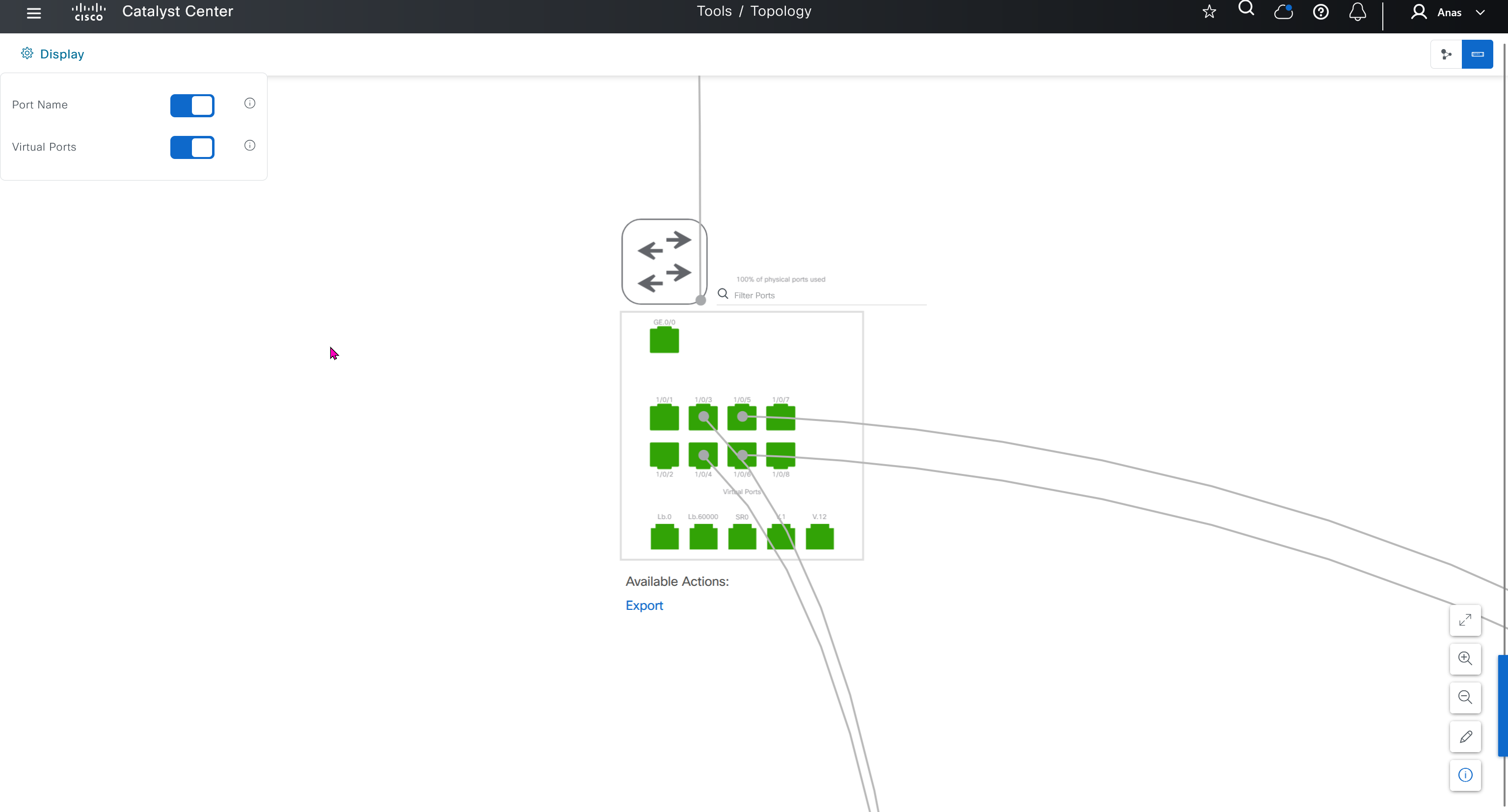
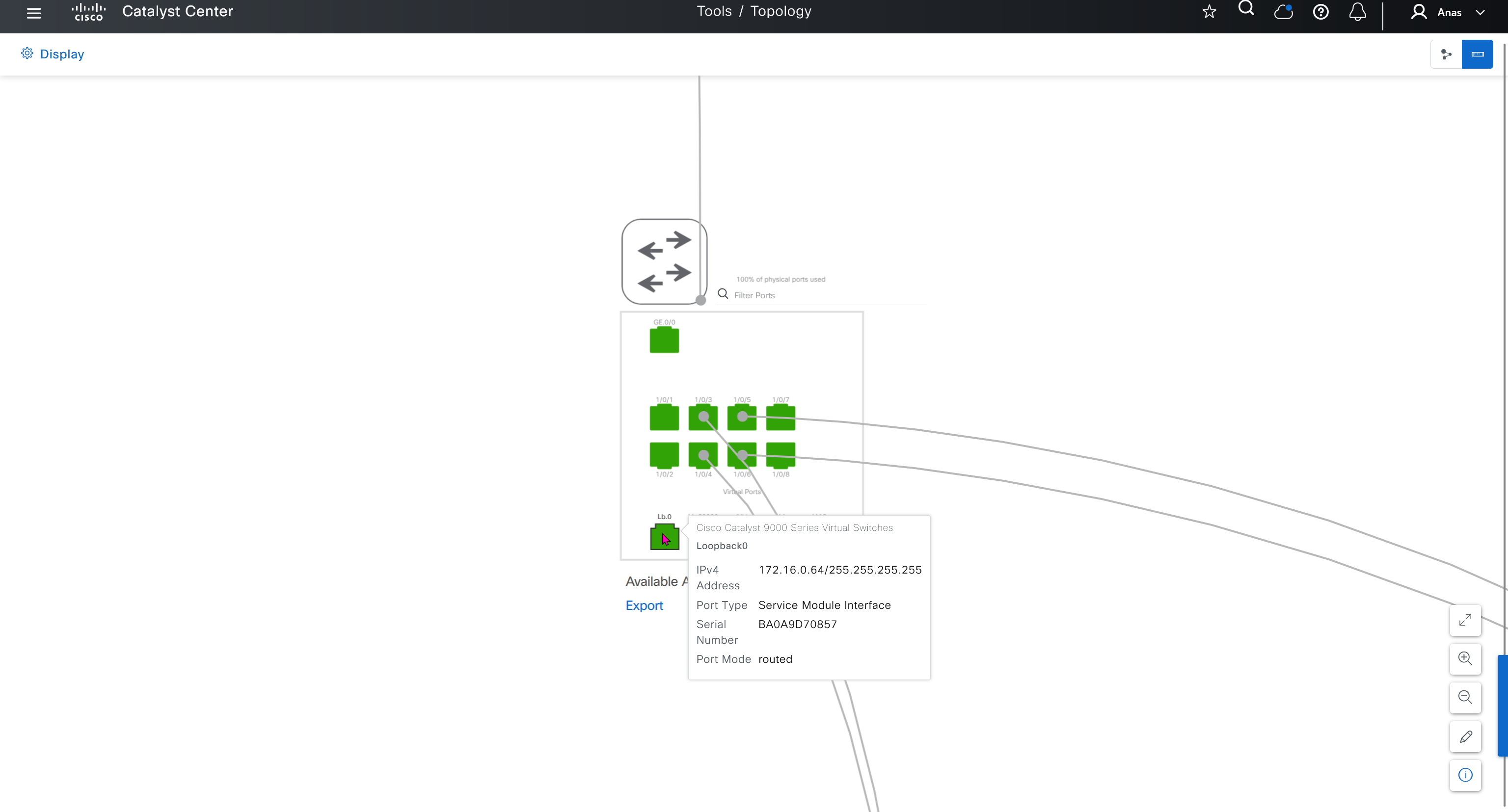
IP pool for loopback and /31 interswitch links
Another part of the IP pool is reserved internally with a subpool of fixed size /27. This subpool is for allocating single IPs for Loopback0 and Loopback60000 always. Also, two consecutive IPs for point-to-point L3 /31 links are allocated from this subpool also, if this pool is exhausted a new /27 subpool is created for allocating IPs
the subpools remain throughout the process and are not allowed to be removed. Due to this internal subpool allocation logic, the IP pool usage in IPAM counts the subpools as allocated.
When a dedicated (single) IP pool is used to build the underlay networks, each of the devices discovered via LAN automation gets a unique /31 per interface for point-to-point connection, and a unique /32 for Loopback0 and the underlay multicast.
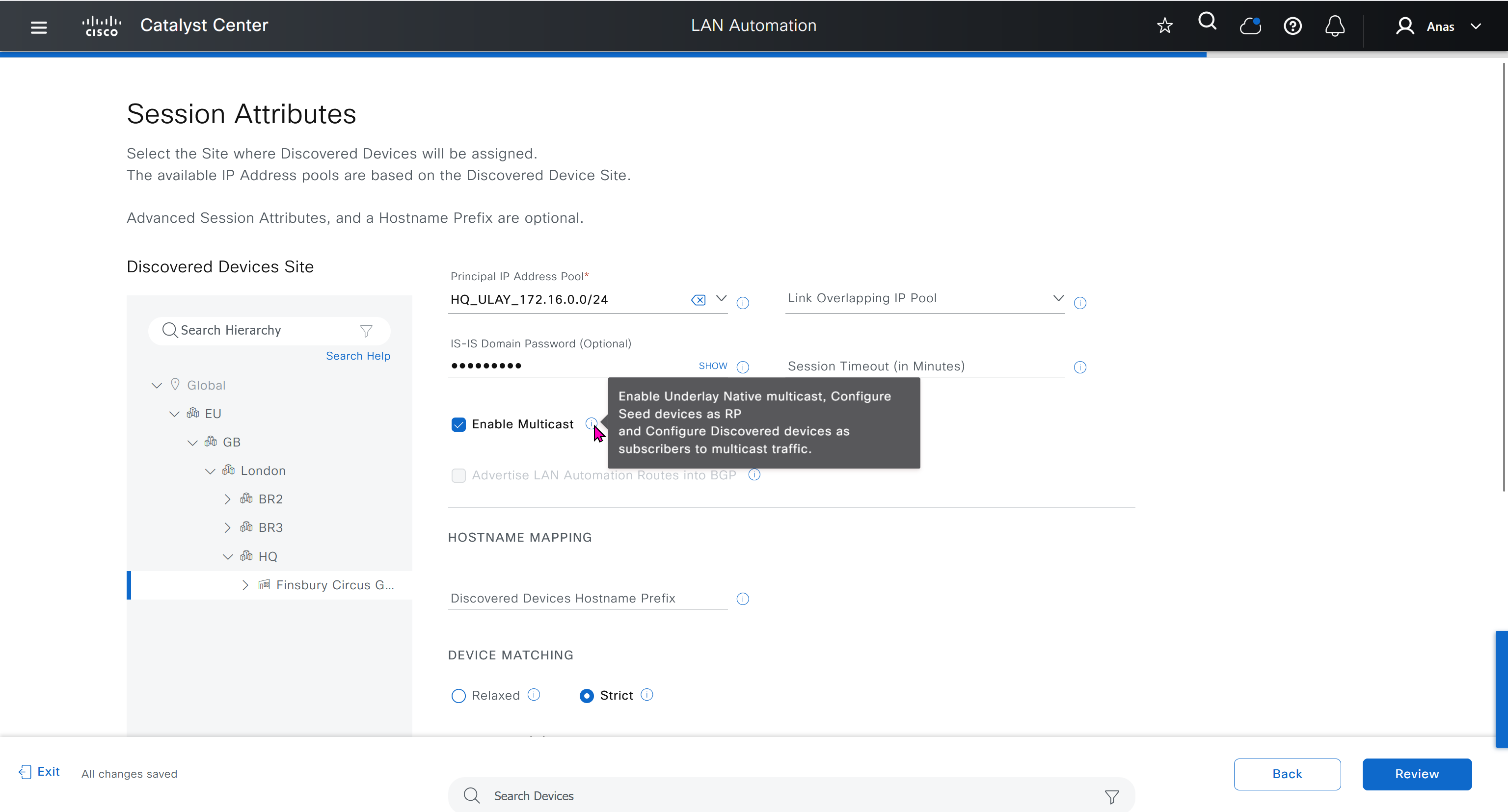
Single Site vs Shared IP pool (overlaps between sites)
When a dedicated (single) IP pool is used to build the underlay networks, each device discovered via LAN automation gets a unique /31 per interface for point-to-point connection, and a unique /32 for Loopback0 and the underlay multicast.
A link overlapping IP pool (only for /31 interswitch links) or shared IP pool is used to optimize the IPv4 addressing in the underlay network by allowing overlapping /31 IP addresses for a multisite deployment. Hosts in different sites can get duplicate IP addresses on the /31 links. The /31s in the underlay are not advertised outside of the fabric site and hence there is no need for them to be unique. However, the /32 loopback needs to be unique to every device, and should be advertised to the global routing table to identify the device in the entire network.
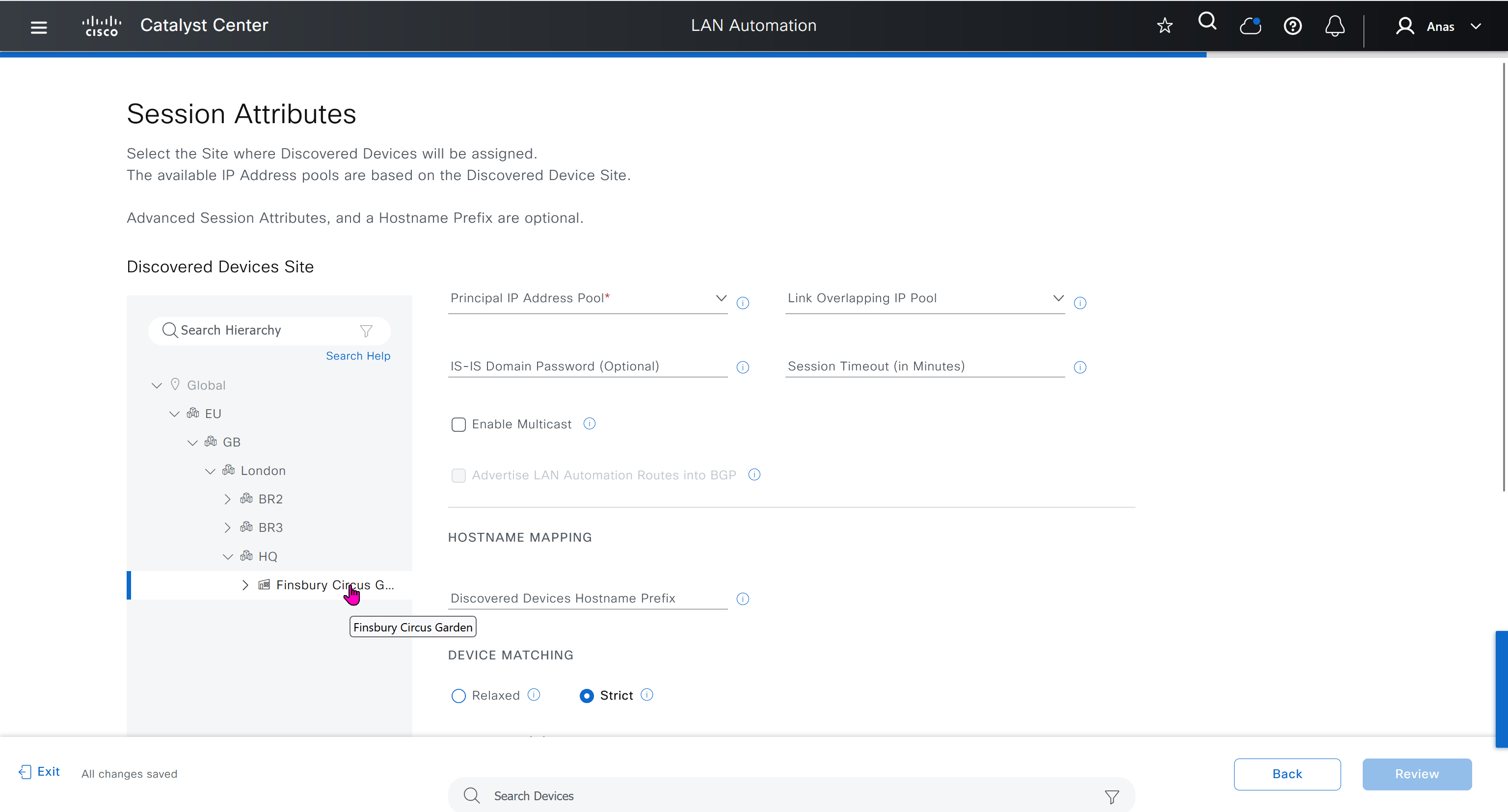
IP pool roles
The LAN IP pool can have these two roles:
- Link Overlapping IP Pool: This pool role is optional for a LAN automation session. If provided, the allocation of IP addresses is only on the /31 point-to-point Layer 3 links, and can be same through out different sites, hence overlapping is in the name.
- Main IP Pool (Principal IP Address Pool in Catalyst Center Release 2.3.5 and later): This pool role is mandatory for every LAN automation session. This is the pool that is used for all management-related IP addressing such as loopbacks, multicast, and DHCP. If the Link Overlapping IP Pool is not provided, then the Main IP Pool is the default fallback pool for the /31 Layer 3 links IP addressing also.

Configuration on seed devices
- Ensure that the system MTU (maximum transmission unit) value is at least 9100 or jumbo frame –
show sys mtu - Turn on IP routing on the seed devices.
- Enable DNA advantage license
- Enable CLI credentials from DNAC
- Enable SNMP strings from DNAC
- Enable ssh
- Enable local authentication
- Enable netconf-yang
- Enable privilege level 15 on vty lines
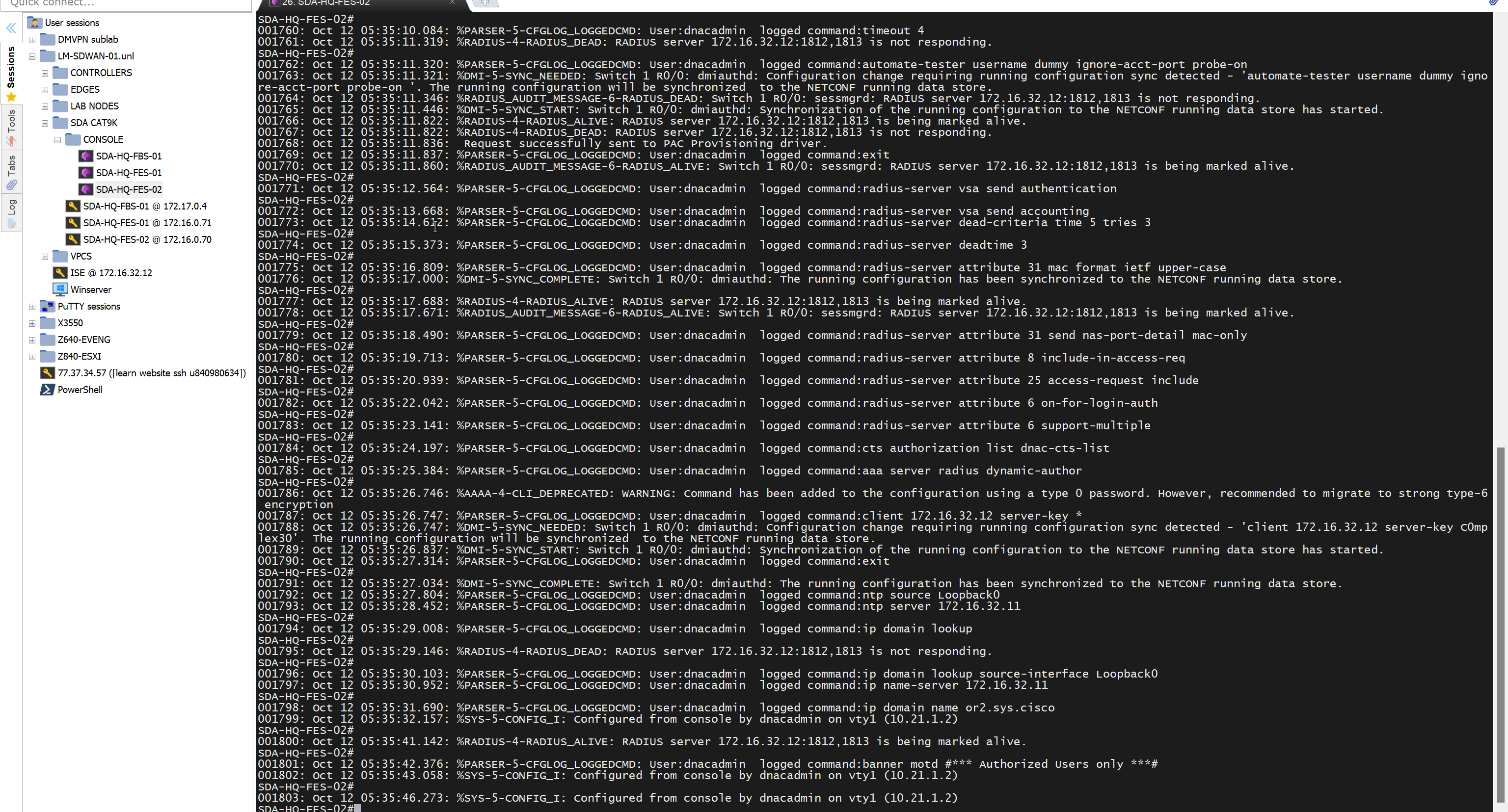
- ip name-server 172.16.32.11
- ip domain name or2.sys.cisco
IP address allocation in Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.x and later
In Catalyst Center Release 2.3.7.x and later, IP address allocation from LAN pool is based on IP address range instead of subnet allocation. This approach helps in minimizing the issue of IP address loss during subnet creation and in effective management of the IP addresses. Instead of creating a subnet, IP address range is blocked for both DHCP pool allocation and IP address assignment for point-to-point links, loopback, and multicast.
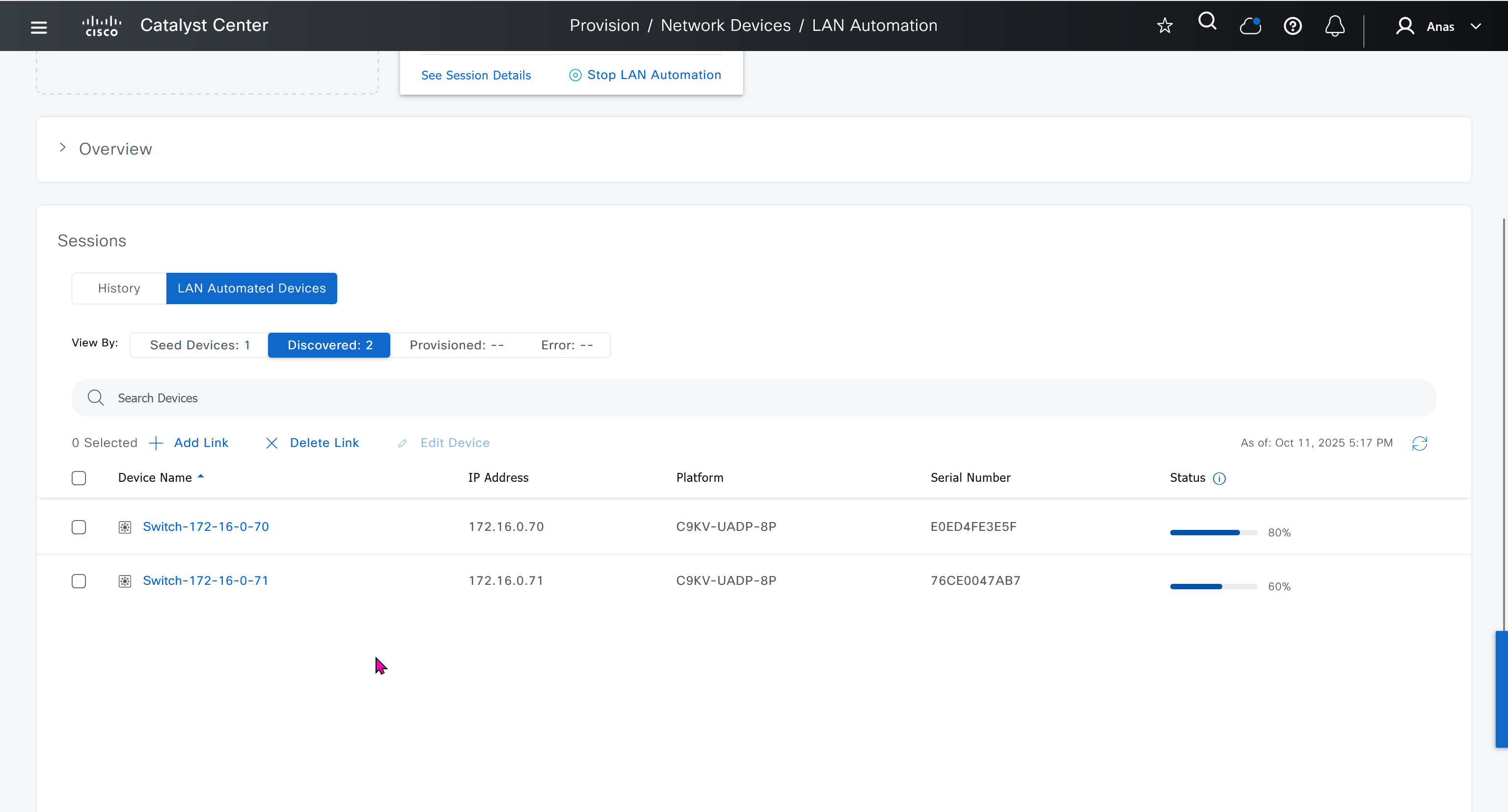
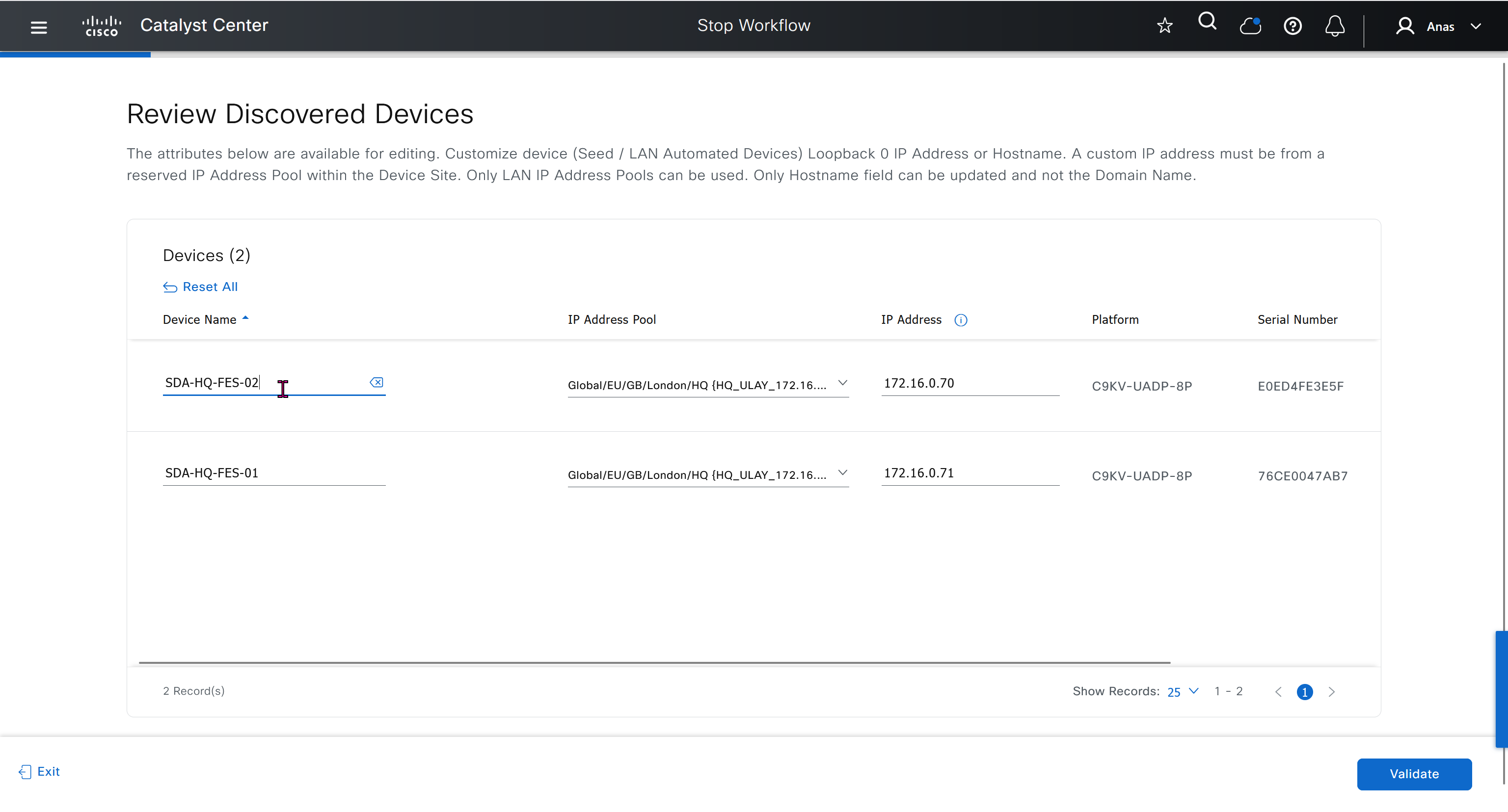
LAN Automation Example
Imagine you want to LAN automate 10 devices in a site using the same pool, where each device has one link to the primary seed and another link to the secondary.
Consider a 192.168.199.0/24 as an example pool. When LAN automation starts,
a first /26 pool is reserved for the DHCP addresses. In this example, 192.168.199.”1″ to 192.168.199.”63″ are reserved and assigned to VLAN 1 for the 10 devices.
Next, a “/27” pool is reserved for loopback addresses.
If there is no shared IP pool, then this pool is used for point-to-point links as well.
Because there are 10 devices with two links each, a total of 40 IP addresses are reserved for point-to-point links,
40 addresses because each switch needs 4 IP addressess (2 assigned on switch’s uplinks itself and 1 assigned on primary seed device and 1 assigned on peer seed device)
In total, 60 IP addresses are reserved for the 10 devices: 10 for each VLAN 1, 10 for each loopback, and 40 for the point-to-point links between devices and seeds.
After LAN automation stops, the VLAN 1 IP addresses are released back to the pool
We recommend that you use the default interfaces connected to PnP agents. If the peer seed device has IP interfaces configured on the interfaces connected to PnP agents, those links are not configured. Default the interfaces connected to ono agents and perform an inventory synchronization on the peer seed device. LAN automation works only when the ports are Layer 2. The ports on the Cisco Catalyst 6000 Series Switches are Layer 3 by default. Convert the ports to Layer 2 before starting LAN automation.
LAN automation configures loopback on the seed devices if they are not configured.
If you change configuration on the seed devices before running LAN automation, synchronize the seed devices with the Catalyst Center inventory.
If you plan to run multiple discovery sessions to onboard devices across different buildings and floors connected to the same seed devices, we recommend that you block the ports for PnP agents that do not participate in the upcoming discovery session yet.
For example, imagine seed devices in Building-23 connected to PnP agents on Floor-1 and Floor-2. Floor-1 devices are connected on interfaces Gig 1/0/10 through Gig 1/0/15. Floor-2 devices are connected on interfaces Gig 1/0/16 through Gig 1/0/20. For the discovery session on Floor-1, we recommend that you shut down ports connected to Gig 1/0/16 through Gig 1/0/20. Otherwise, the PnP agents connected to Floor-2 might also get DHCP IPs from the server running on the primary seed device. Because these interfaces aren’t selected for the discovery session, they remain as stale entries in the PnP database. When you run the discovery session for Floor-2, the discovery doesn’t function correctly until these devices are deleted from the PnP application and write erase/reloaded. Therefore, we recommend that you shut down other discovery interfaces
For Catalyst Center Release 1.2.8 and earlier, if clients are connected to a switch being discovered, they may contend for DHCP IP and exhaust the pool, causing LAN automation to fail. Therefore, we recommend that you connect the client after LAN automation is complete. but that is for older DNAC versions
This endpoint/client integration restriction does not apply to Catalyst Center Release 1.2.10 and later. Clients can remain connected while the switch is undergoing LAN automation.
on the edge nodes add license and then reset pnpa so pnp wizard becomes active after putting license
otherwise LAN Automation commands will fail as there is no dna-advantage
license boot level network-advantage addon dna-advantage
end
write mem
reload pnpa service reset no-promptSteps for LAN Automation
- Default the interfaces connected to agents and perform an inventory synchronization on the peer seed device
- LAN automation configures loopback on the seed devices if they are not configured.
- If you change configuration on the seed devices before running LAN automation, synchronize the seed devices with the Catalyst Center inventory.
- Add Site > Add Area
- Add Site > Add Building
- Add Site > Add Floor
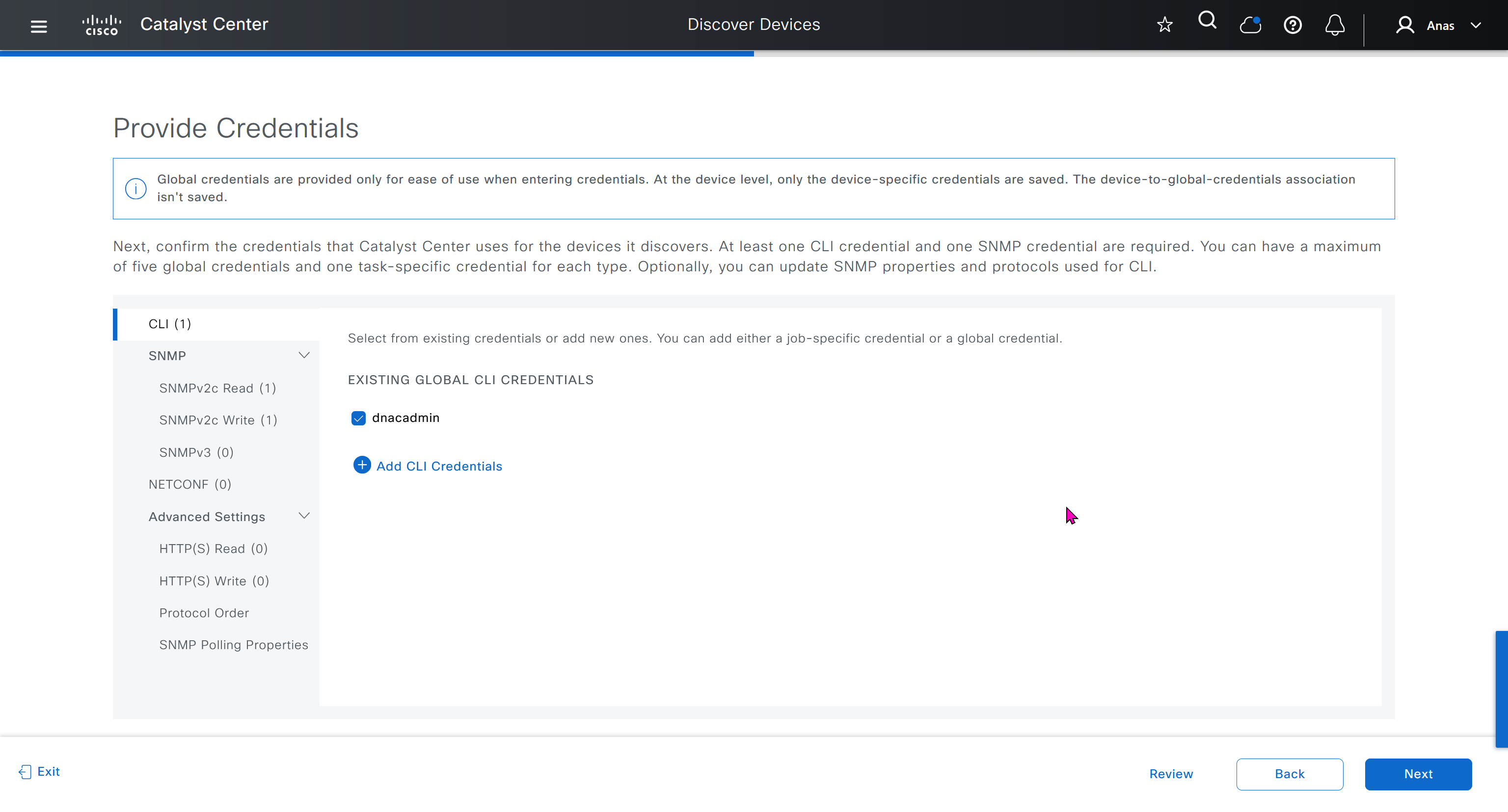
- Design > Network Settings > Device Credentials
- Manage Credentials
- CLI
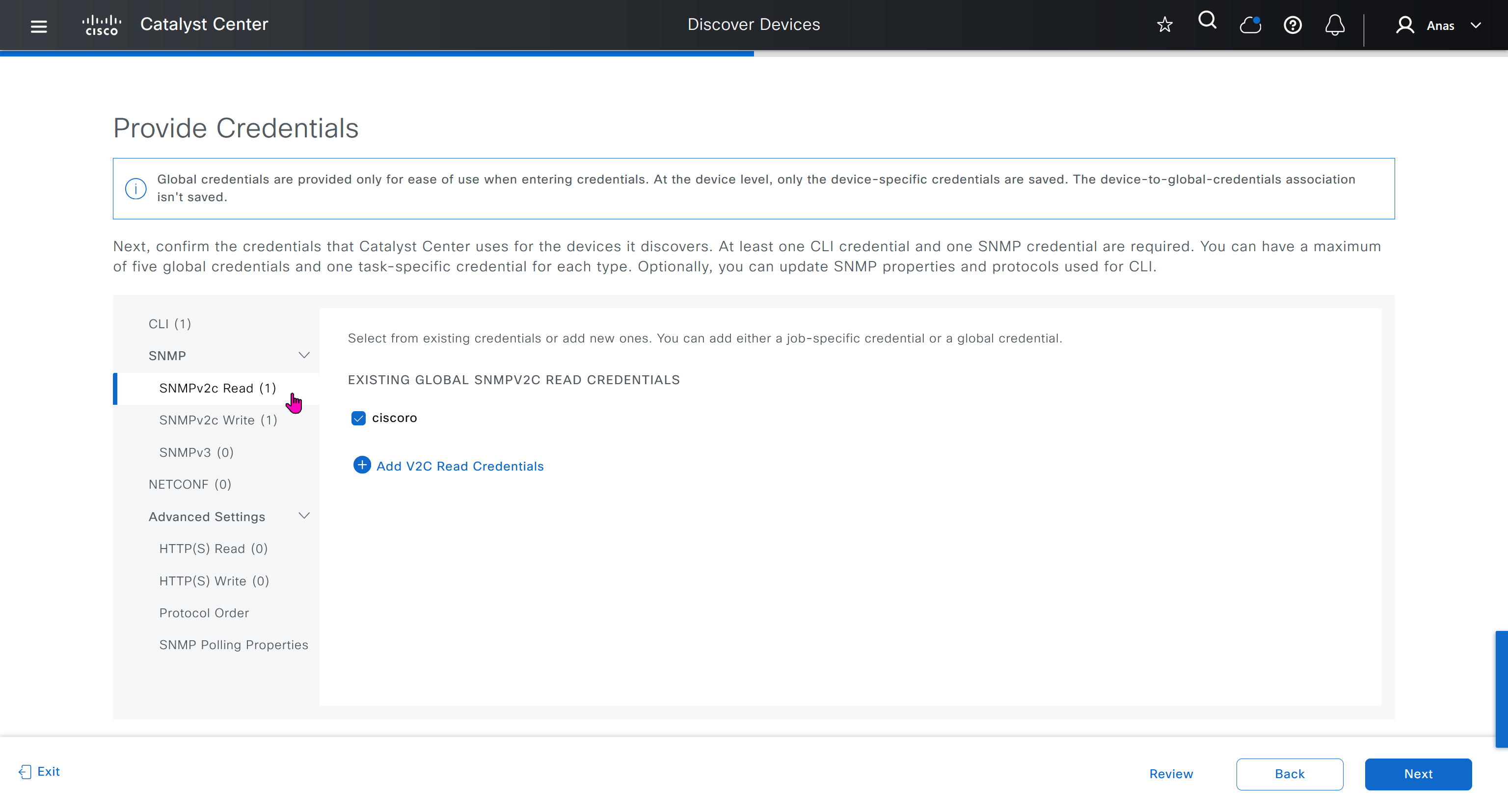
- SNMPV2C Read
- Netconf
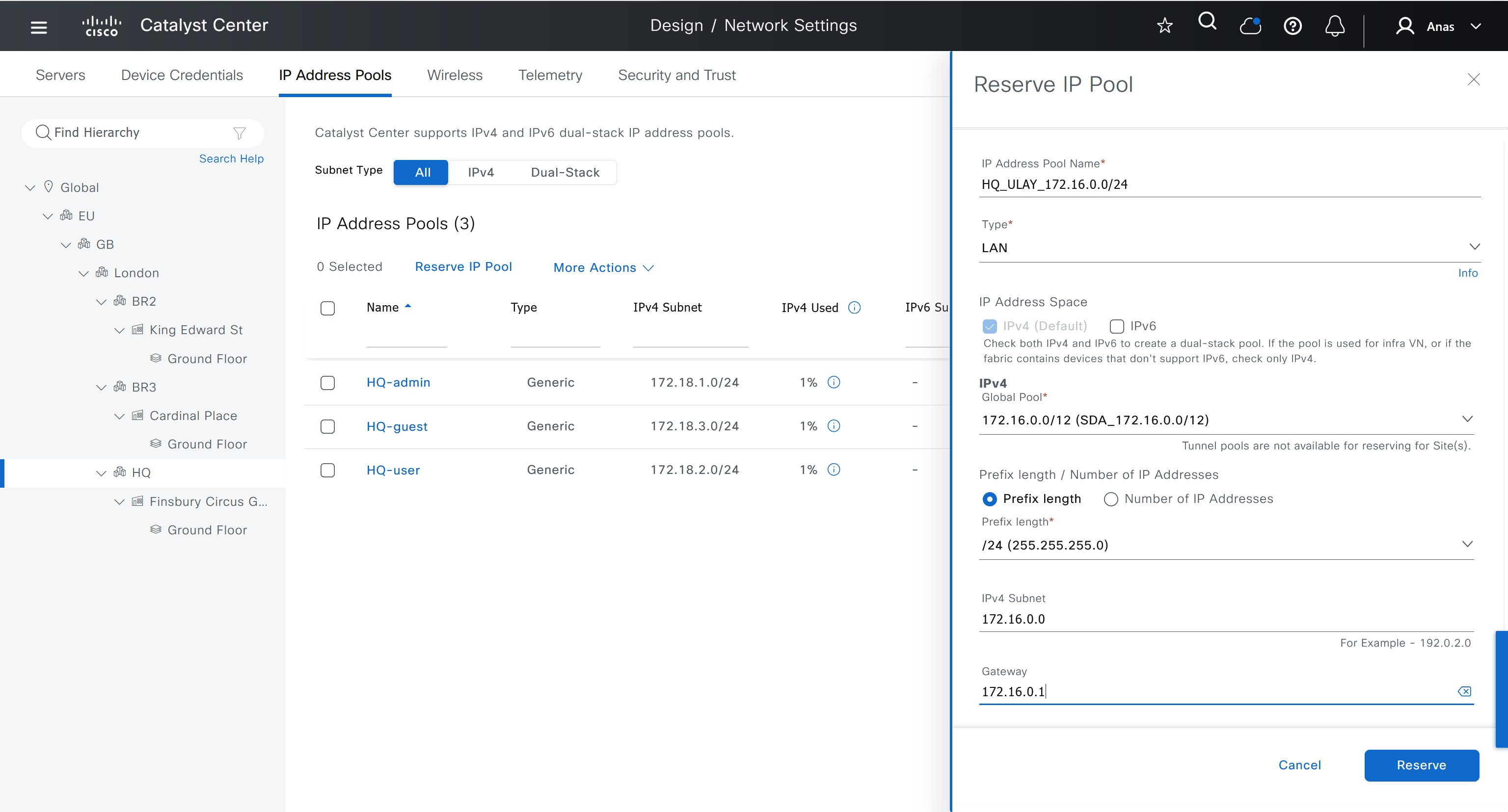
- Create an underlay pool that is not used any where in the network
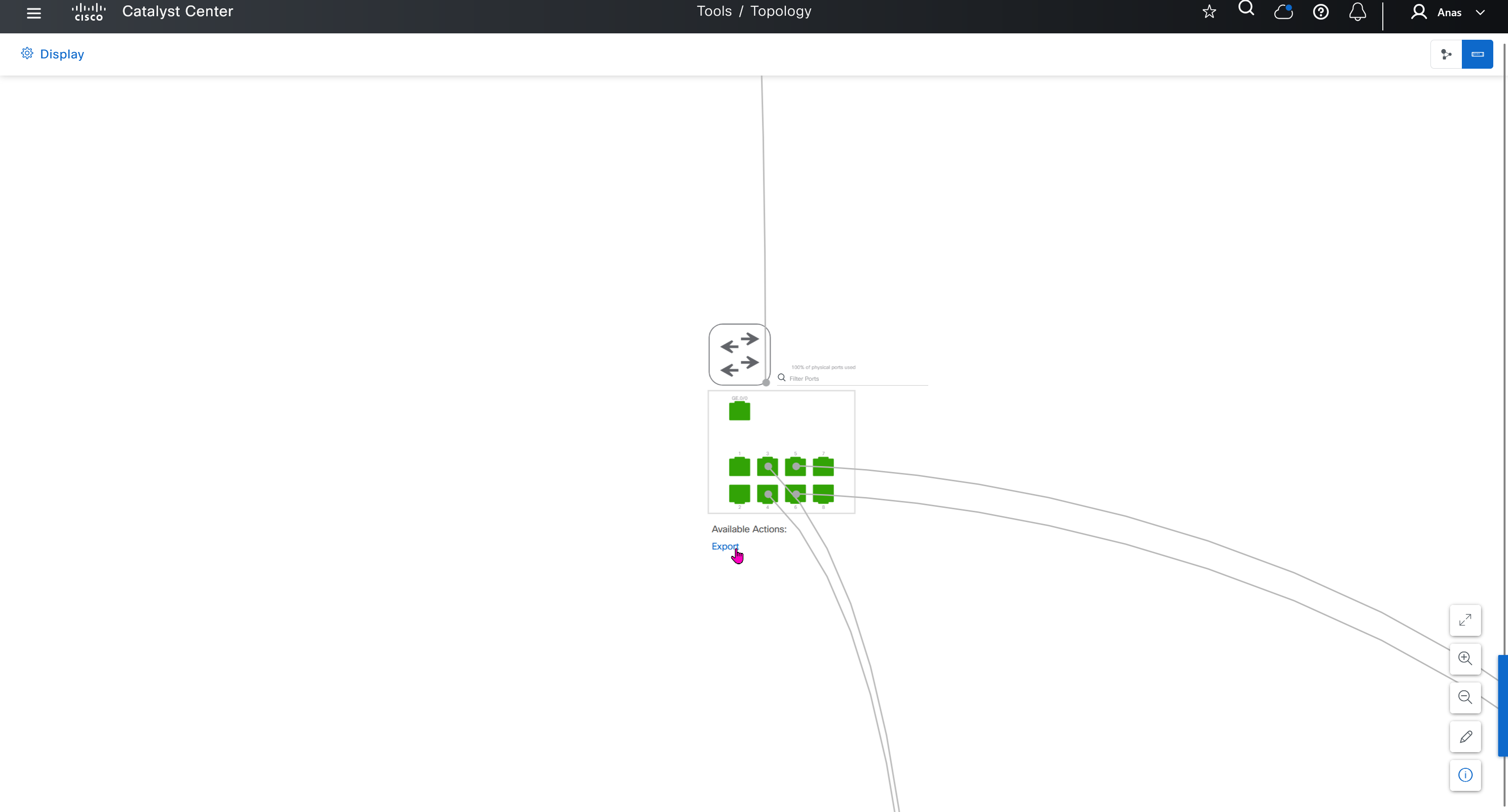
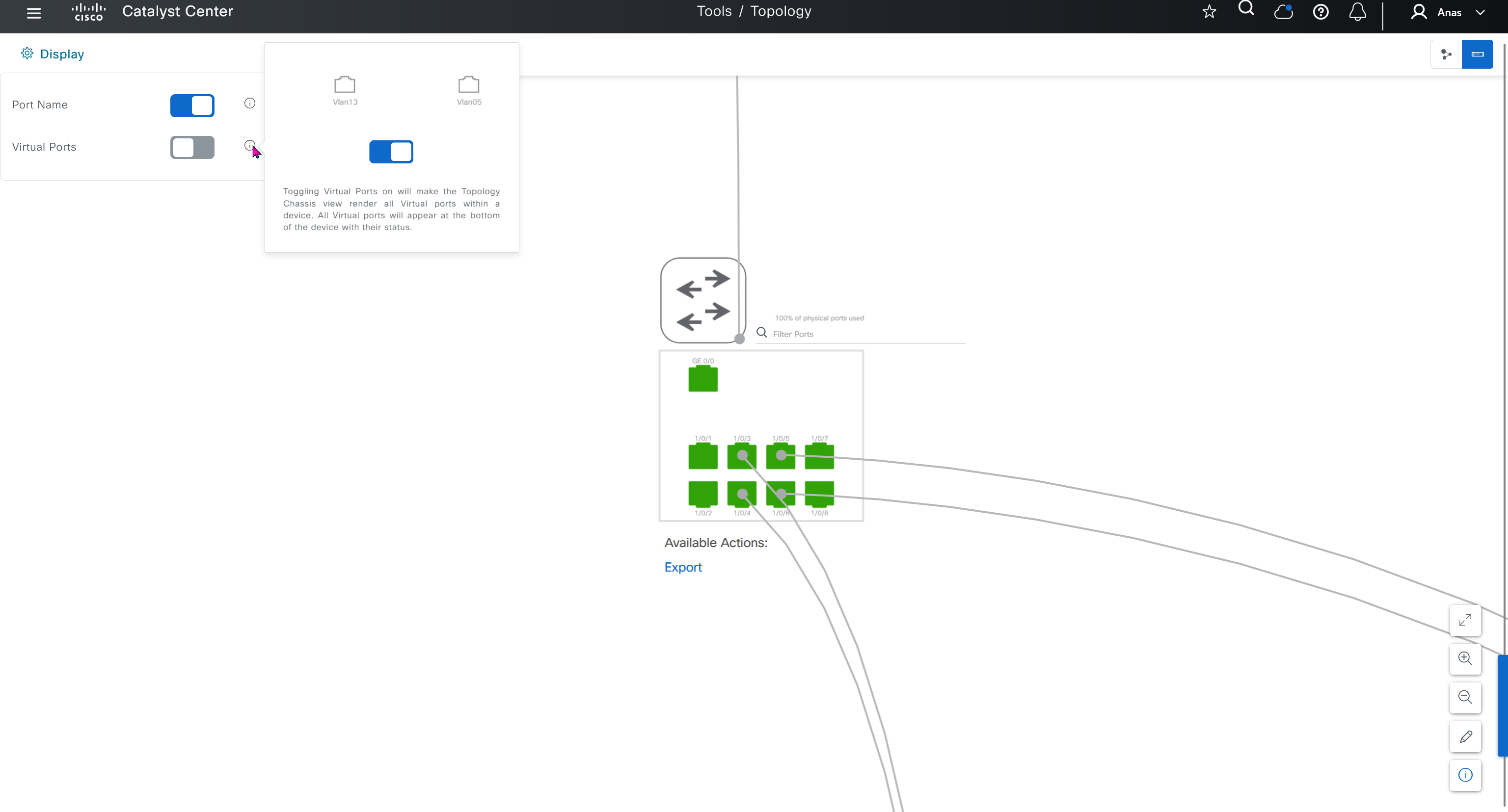
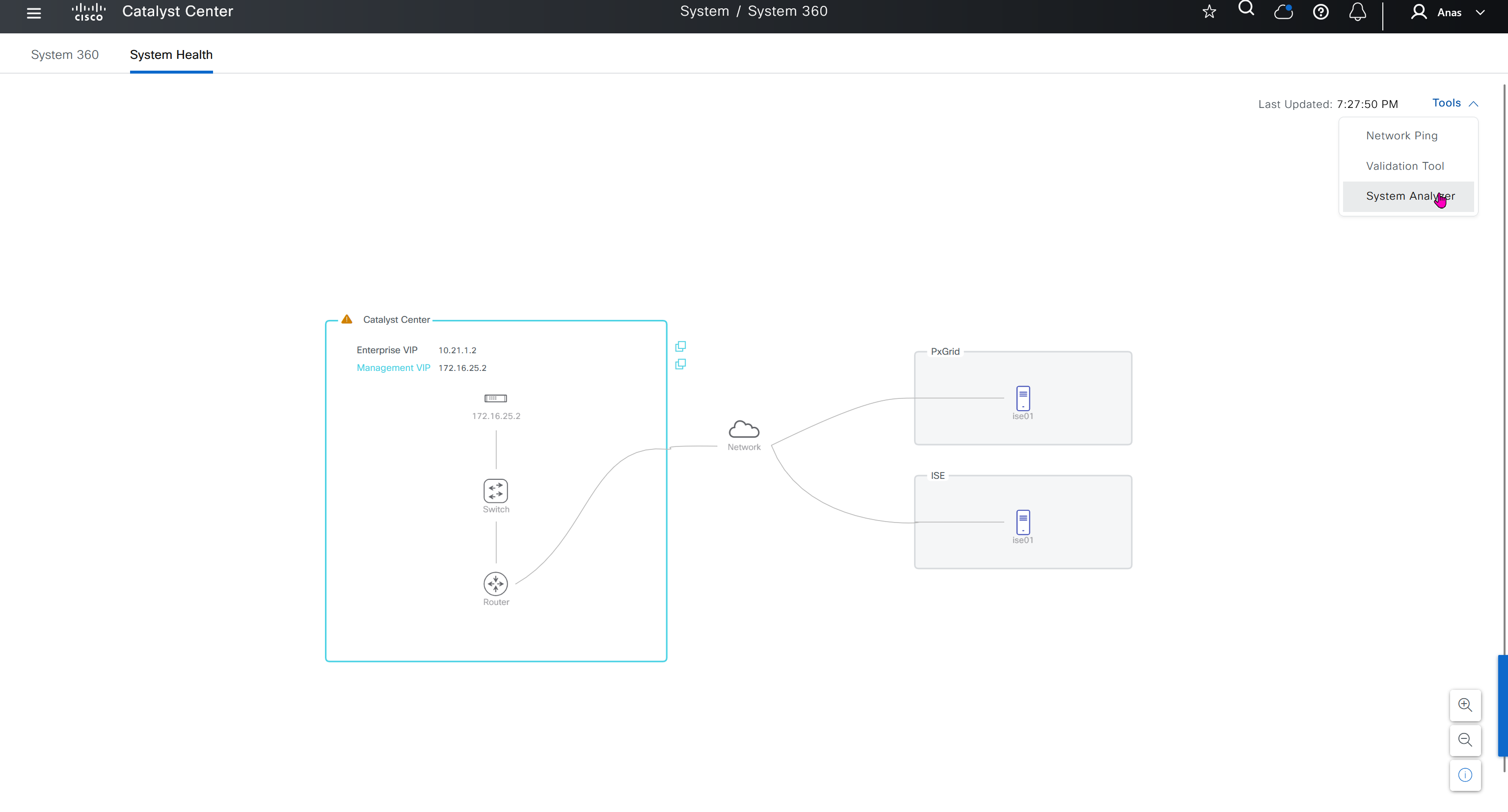
See how the gateway address is set 172.16.0.1 and you ask why is that needed?
This is the address that will be assigned to FBS on vlan 1 interface (which is removed later on once LAN automation ends)
- Discover seed devices with discovery
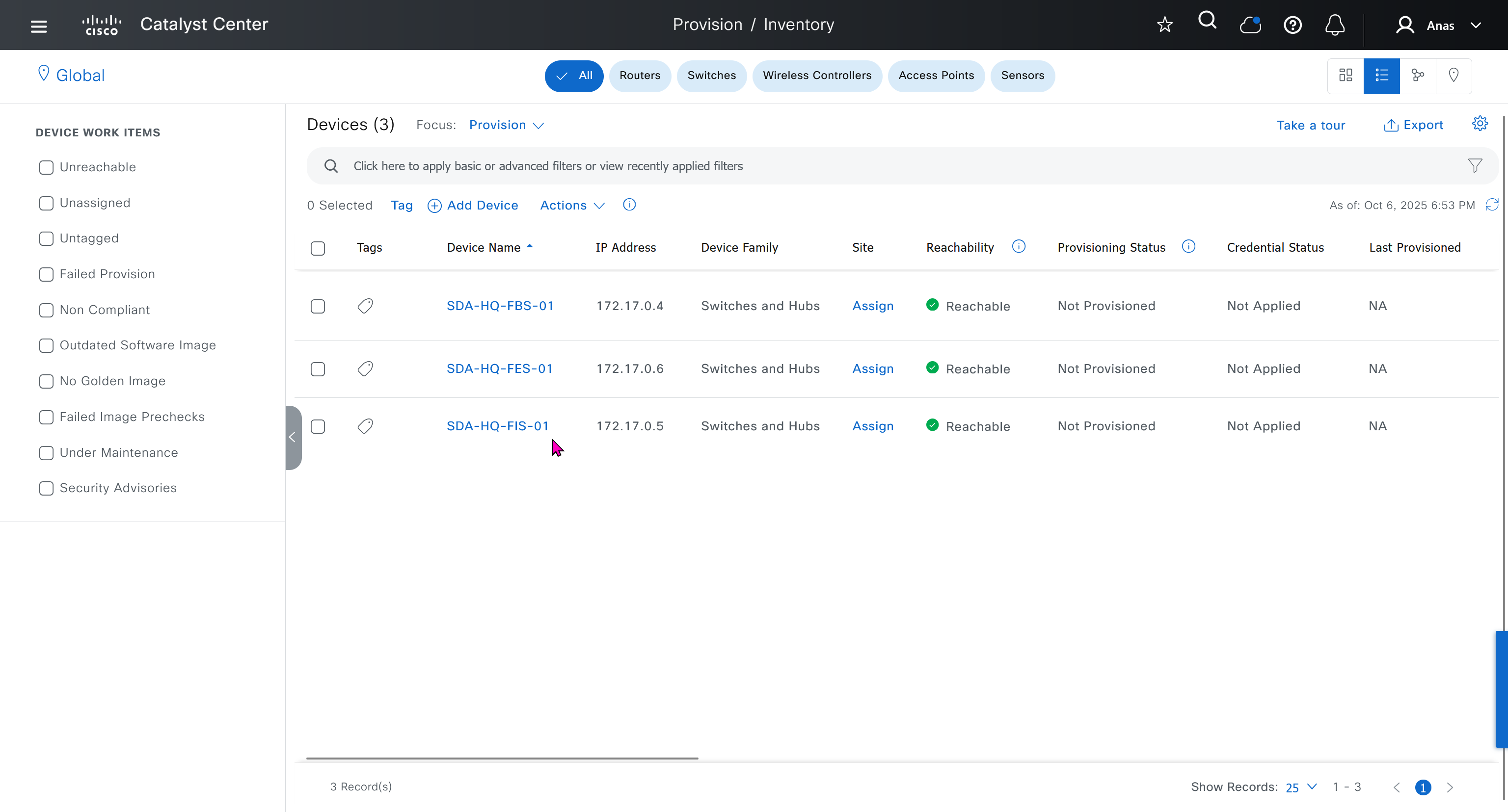
- Make sure that discovered devices are in Reachable + Managed state
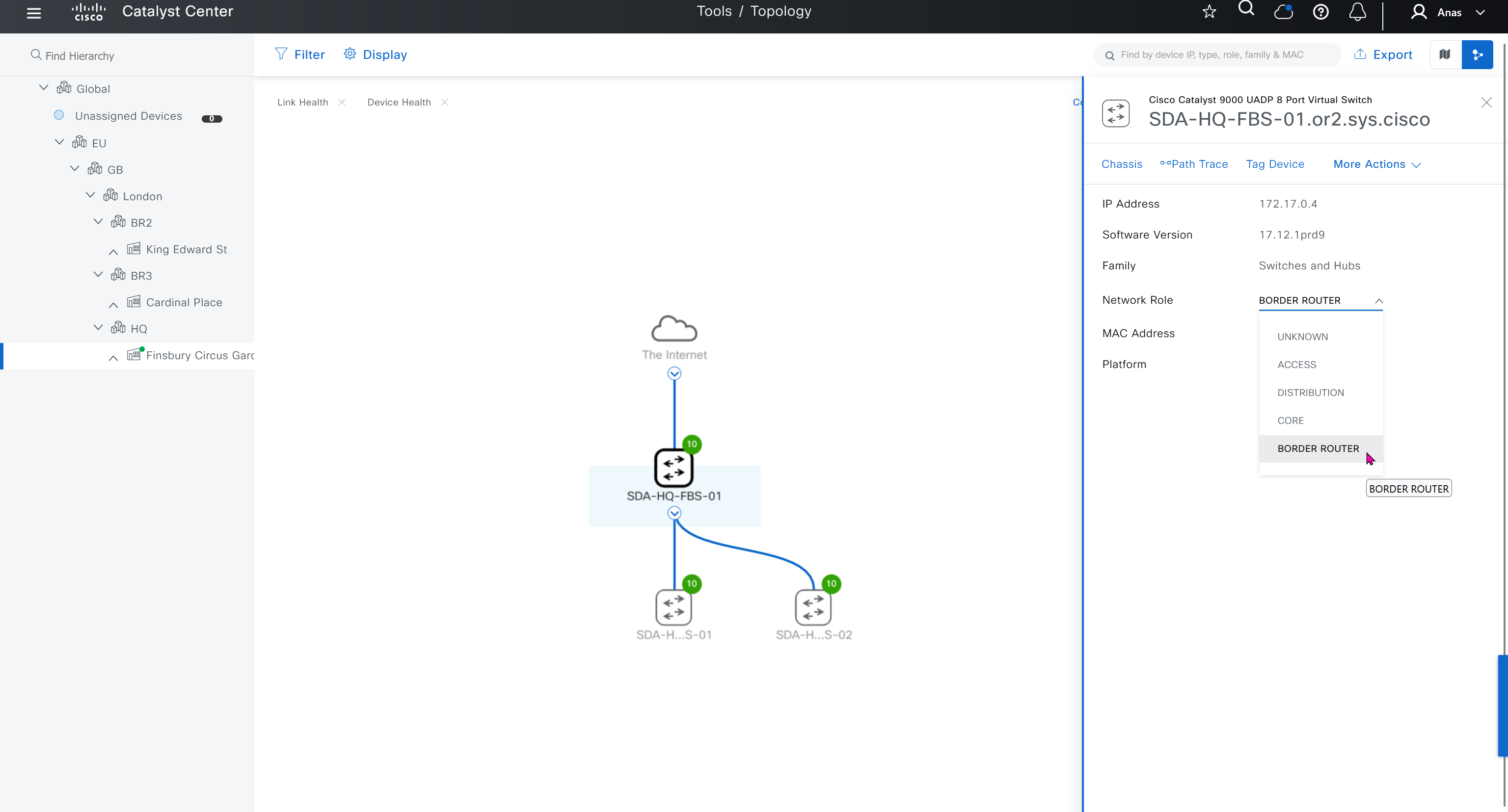
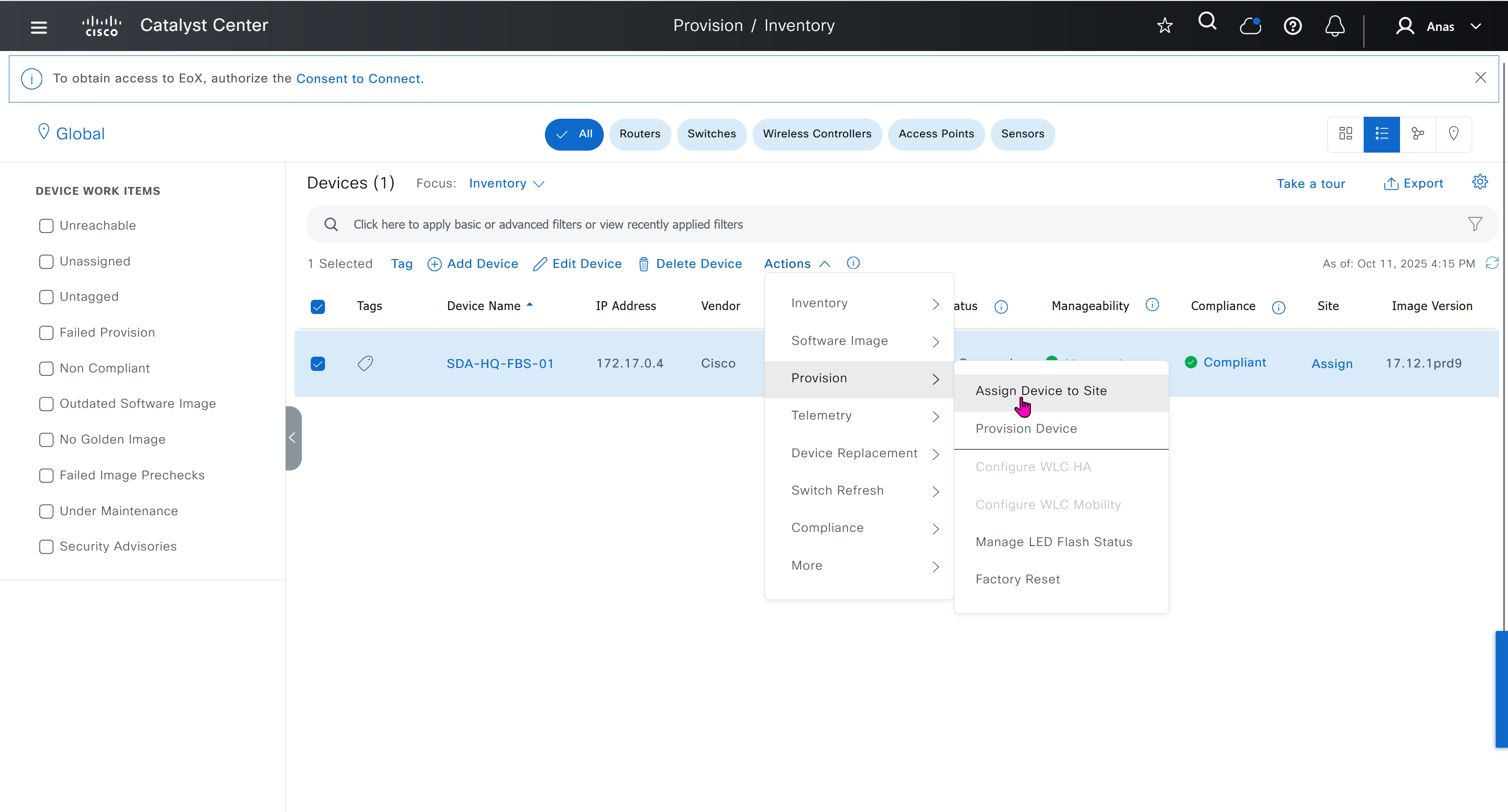
- Actions > Provision > Assign Device to Site to assign the device to a site.

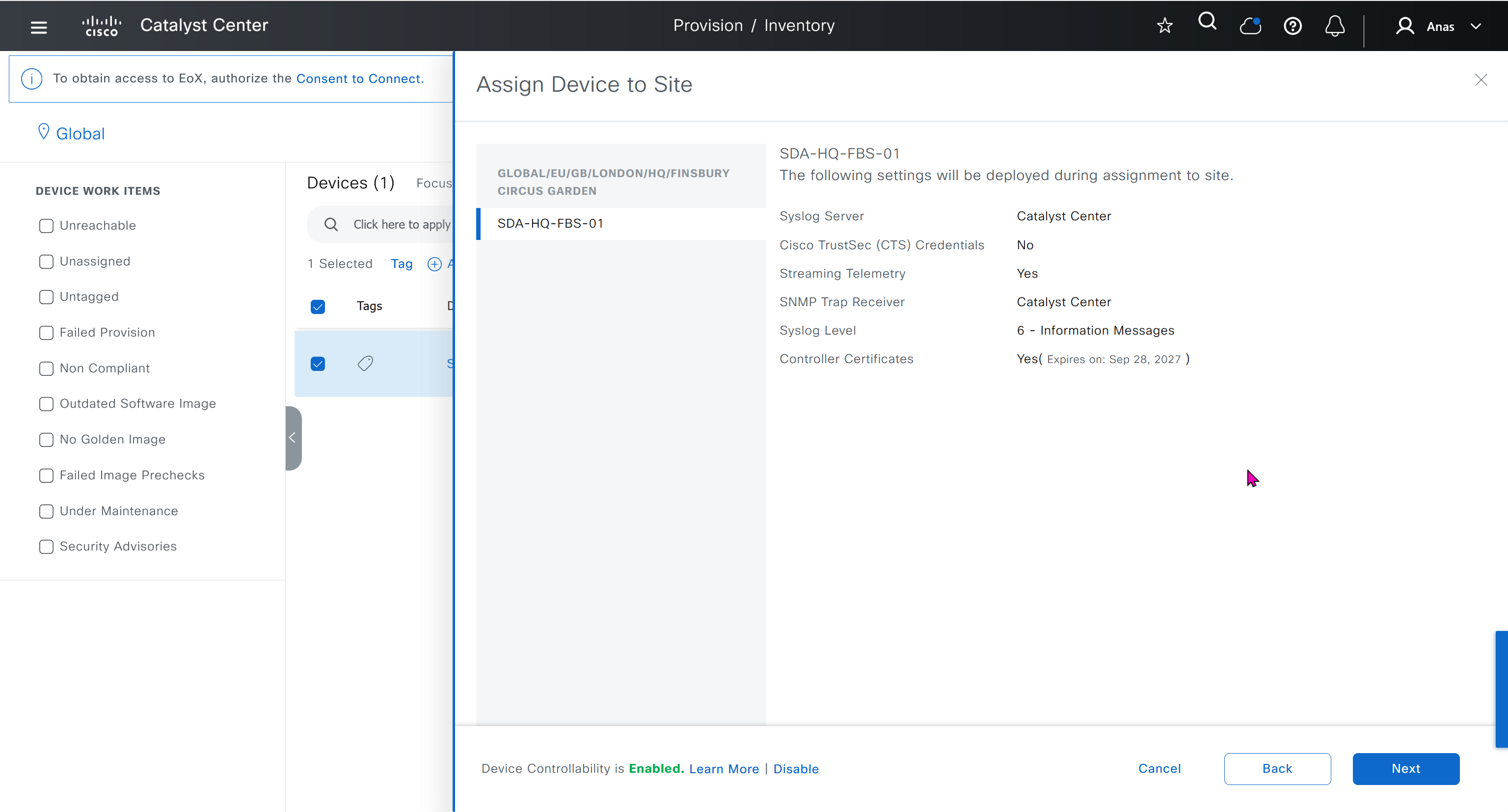



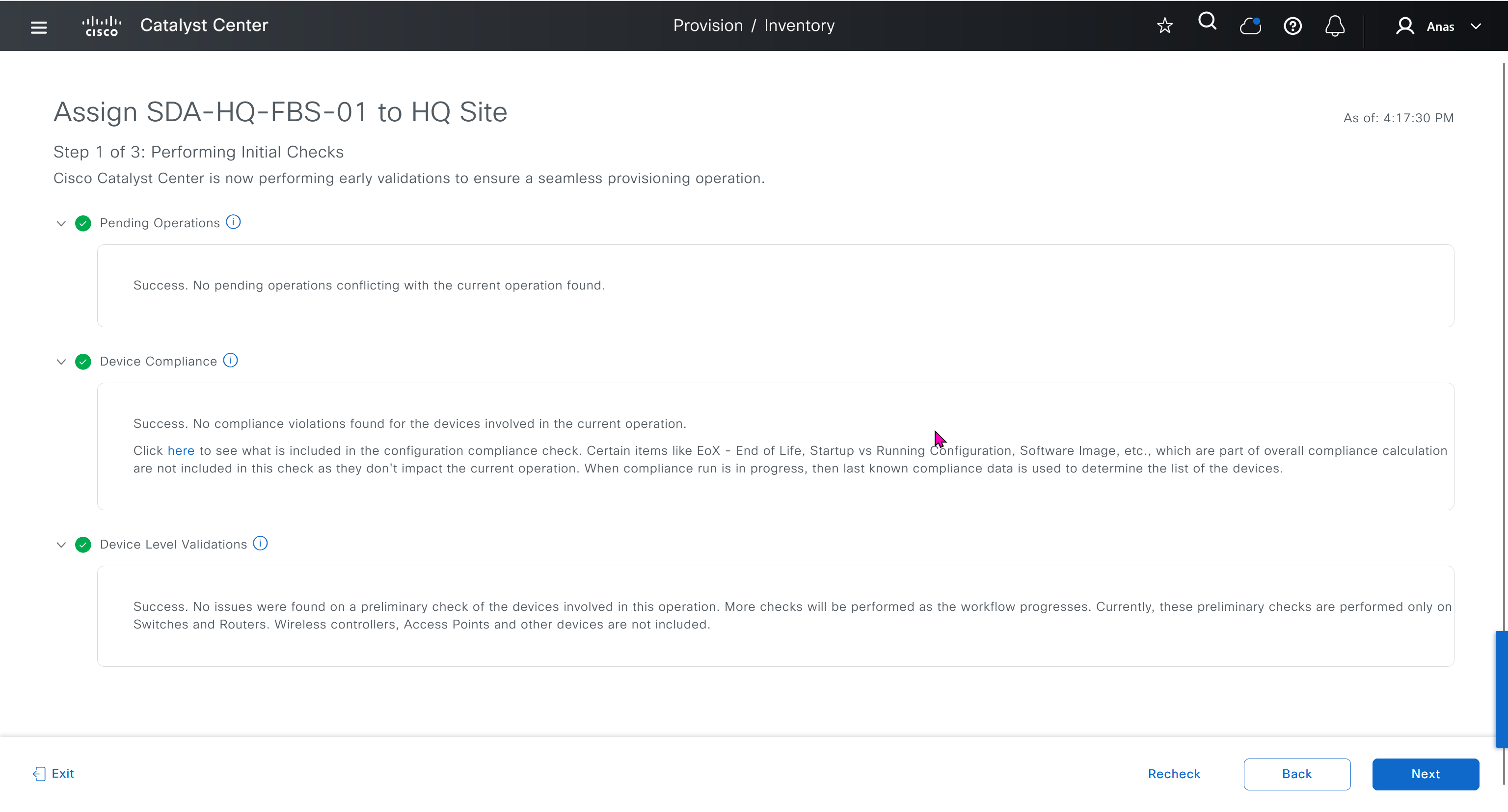
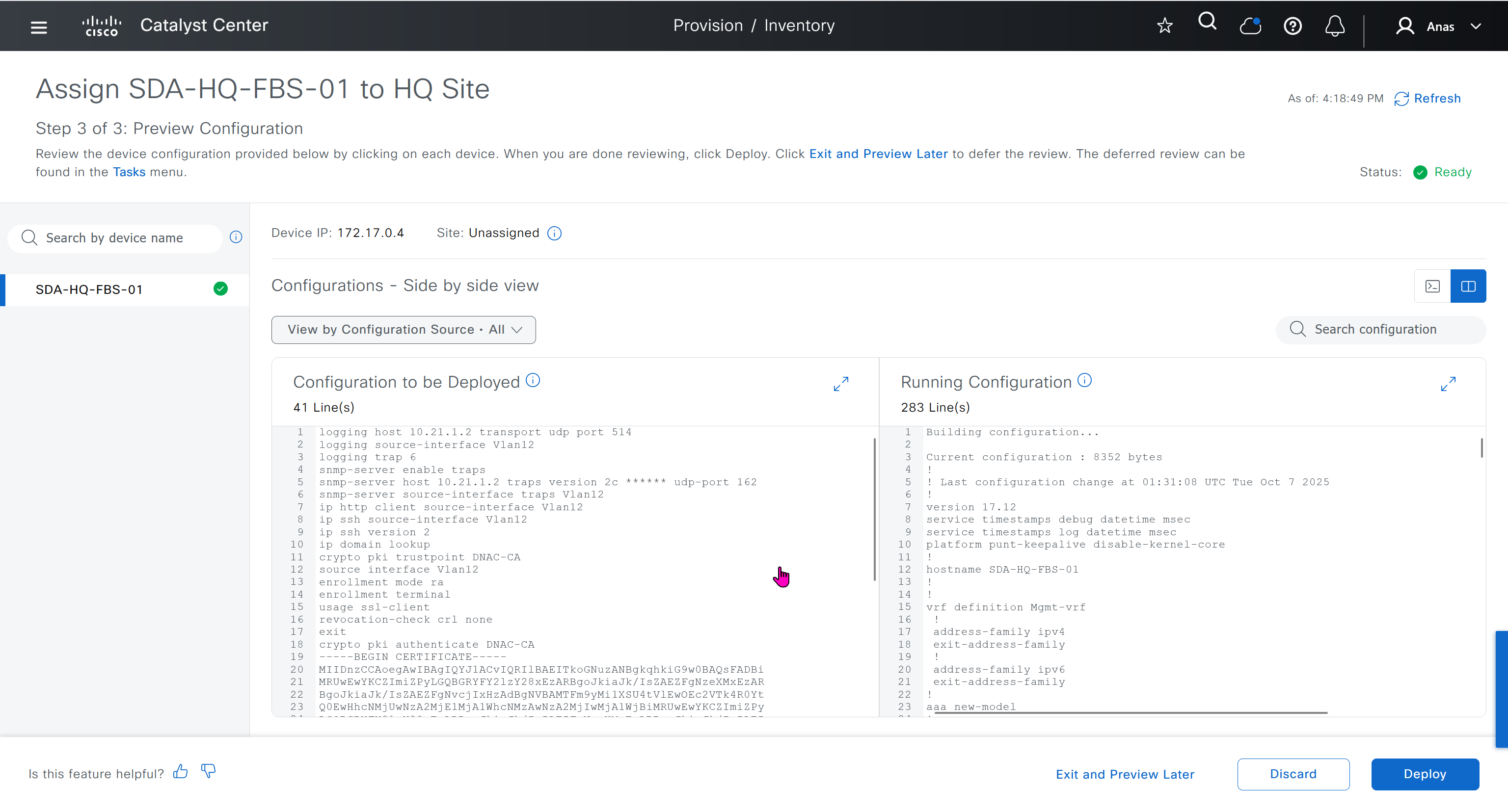
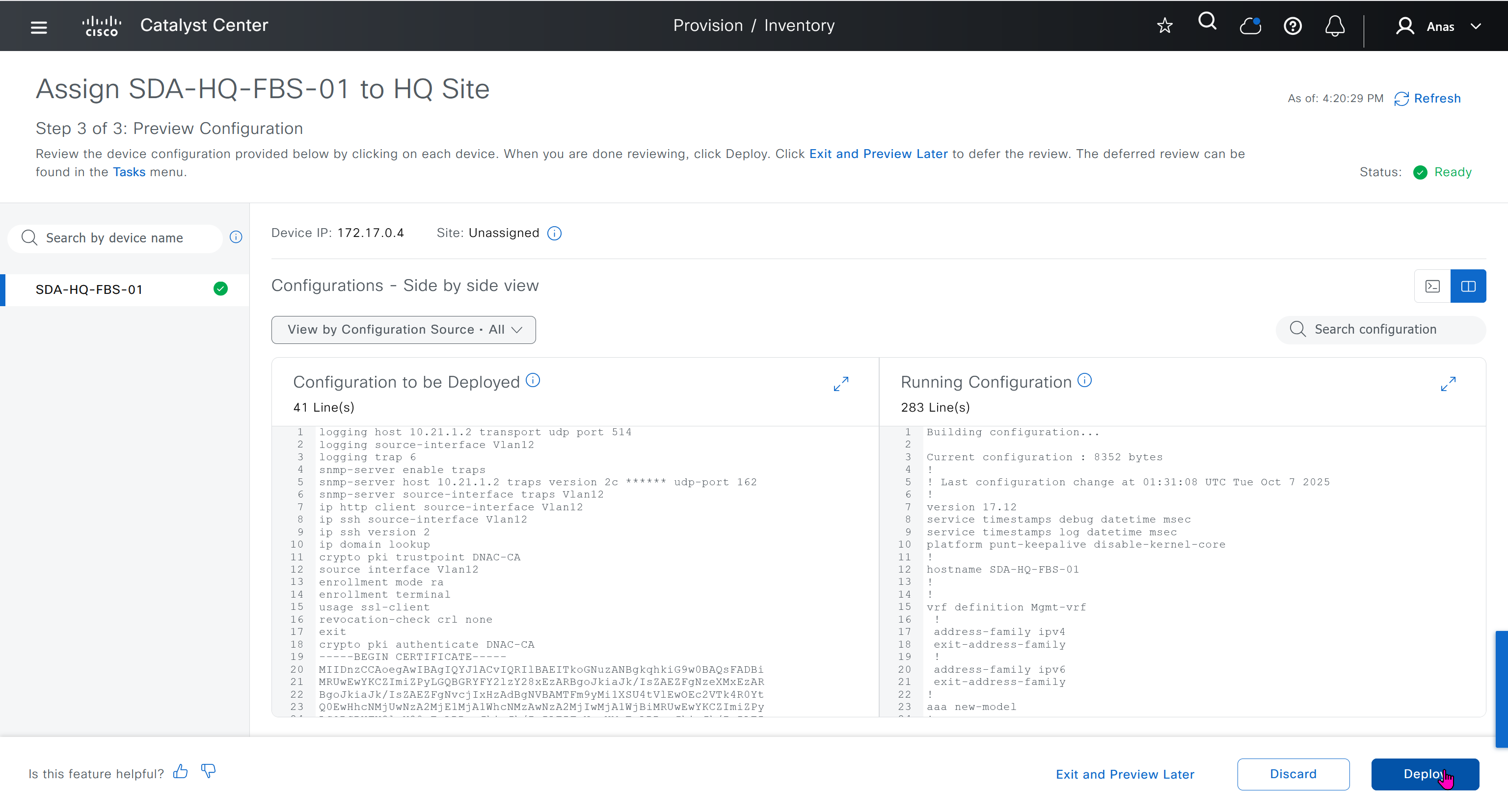
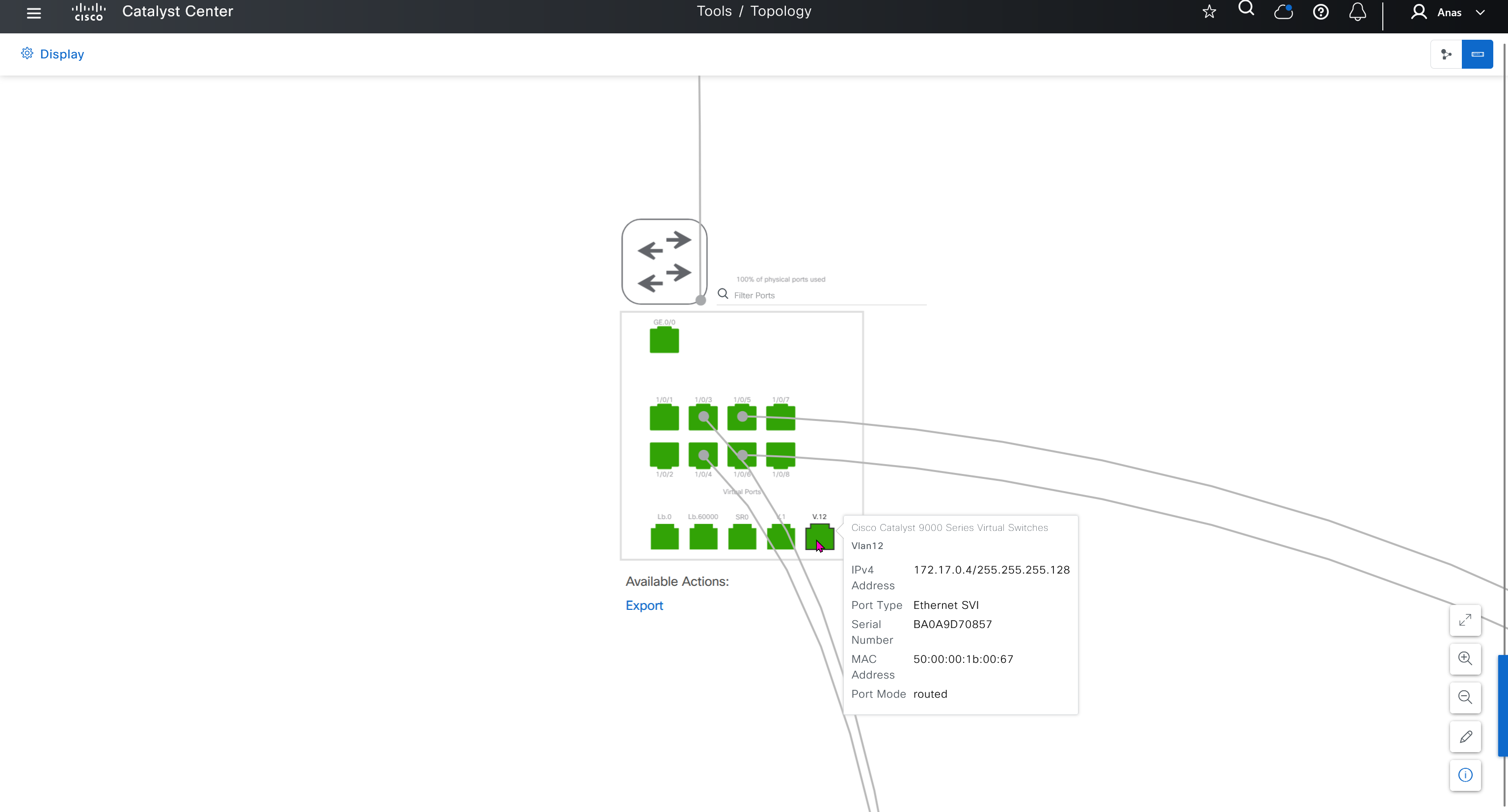
This is the configuration that will go on the seed device after only addign it to the site
logging host 10.21.1.2 transport udp port 514
logging source-interface Vlan12
logging trap 6
snmp-server enable traps
snmp-server host 10.21.1.2 traps version 2c ****** udp-port 162
snmp-server source-interface traps Vlan12
ip http client source-interface Vlan12
ip ssh source-interface Vlan12
ip ssh version 2
ip domain lookup
crypto pki trustpoint DNAC-CA
source interface Vlan12
enrollment mode ra
enrollment terminal
usage ssl-client
revocation-check crl none
exit
crypto pki authenticate DNAC-CA
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----
MIIDnzCCAoegAwIBAgIQYJ1ACvIQRIlBAEITkoGNuzANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFADBi
MRUwEwYKCZImiZPyLGQBGRYFY2lzY28xEzARBgoJkiaJk/IsZAEZFgNzeXMxEzAR
BgoJkiaJk/IsZAEZFgNvcjIxHzAdBgNVBAMTFm9yMi1XSU4tVlEwOEc2VTk4R0Yt
Q0EwHhcNMjUwNzA2MjE1MjA1WhcNMzAwNzA2MjIwMjA1WjBiMRUwEwYKCZImiZPy
LGQBGRYFY2lzY28xEzARBgoJkiaJk/IsZAEZFgNzeXMxEzARBgoJkiaJk/IsZAEZ
FgNvcjIxHzAdBgNVBAMTFm9yMi1XSU4tVlEwOEc2VTk4R0YtQ0EwggEiMA0GCSqG
SIb3DQEBAQUAA4IBDwAwggEKAoIBAQCr6cjaoJz3vzgHlQ1hzhuy5WfIL/Ao0isM
ltIaGL+Z+9WftM1hNh10YECbxR71+lIpQKyBQTXQz8Of4nycxHjoI3dQdUvEYb8H
fysDXh4lYjQ60x82e5c7f1KPbD+AOhC31Zw1dgReMlPIuaa9LK903+z0FRnuCHaI
EG/Z9uCmv3JC22NgL69hscZc+NUGymMy1iBPN8G4EBkgqNVZ+zlRf/adW0JxEdc6
Sy53bp586/fXziRTW++jgdnhvfpn+VJ+BdG88/rEgMl7PUQE95lq4dih7qx0+OXu
ihFwQQvFxvi3dyqWWc0C1RKHPHtYQFz8rRuBJrR+uzgc0lVhrNHdAgMBAAGjUTBP
MAsGA1UdDwQEAwIBhjAPBgNVHRMBAf8EBTADAQH/MB0GA1UdDgQWBBQ/bI8yZeKD
fgjmmeWorjGo25t5hzAQBgkrBgEEAYI3FQEEAwIBADANBgkqhkiG9w0BAQsFAAOC
AQEAdtt6aiABkDDg/mAlcZfFPHcqmEEvQaMPeBaUqvfZKNrFVO8GMb9kingZJ62n
K05x5wE3tHy3jBmAl6eHZ/nUjXS11C06NwZMHpcDhty5BcDN08oEYdLF24upisNA
aRLOBhyEtKI9VKLAWfMkpWYEd/dqgVWs67GjAFT0Osgva9QHbz24iT6/c09jbZMt
41opmxacw8FFZcHMH9Afv1fIW9PwscrdlgjSSHR4XQLyDbyuDGsolzeh9PUVyPOd
f+/LYkLwH9jVcHlxl4Oy7MHRPtcbG9T3+vQGLjSAXu3Ybrl2R9Tn/sz5lYs44EEB
mqCxT00LxB3et6jAxJlEyE5vCw==
-----END CERTIFICATE-----
do cts credentials id 7c71627623014c0a83668477604a0c57 password ******
SDA-HQ-FBS-01# conf t
SDA-HQ-FBS-01# ! for reachability testing only
SDA-HQ-FBS-01# interface vlan 1
SDA-HQ-FBS-01# ip address 172.16.0.1 255.255.255.0
SDA-HQ-FBS-01# end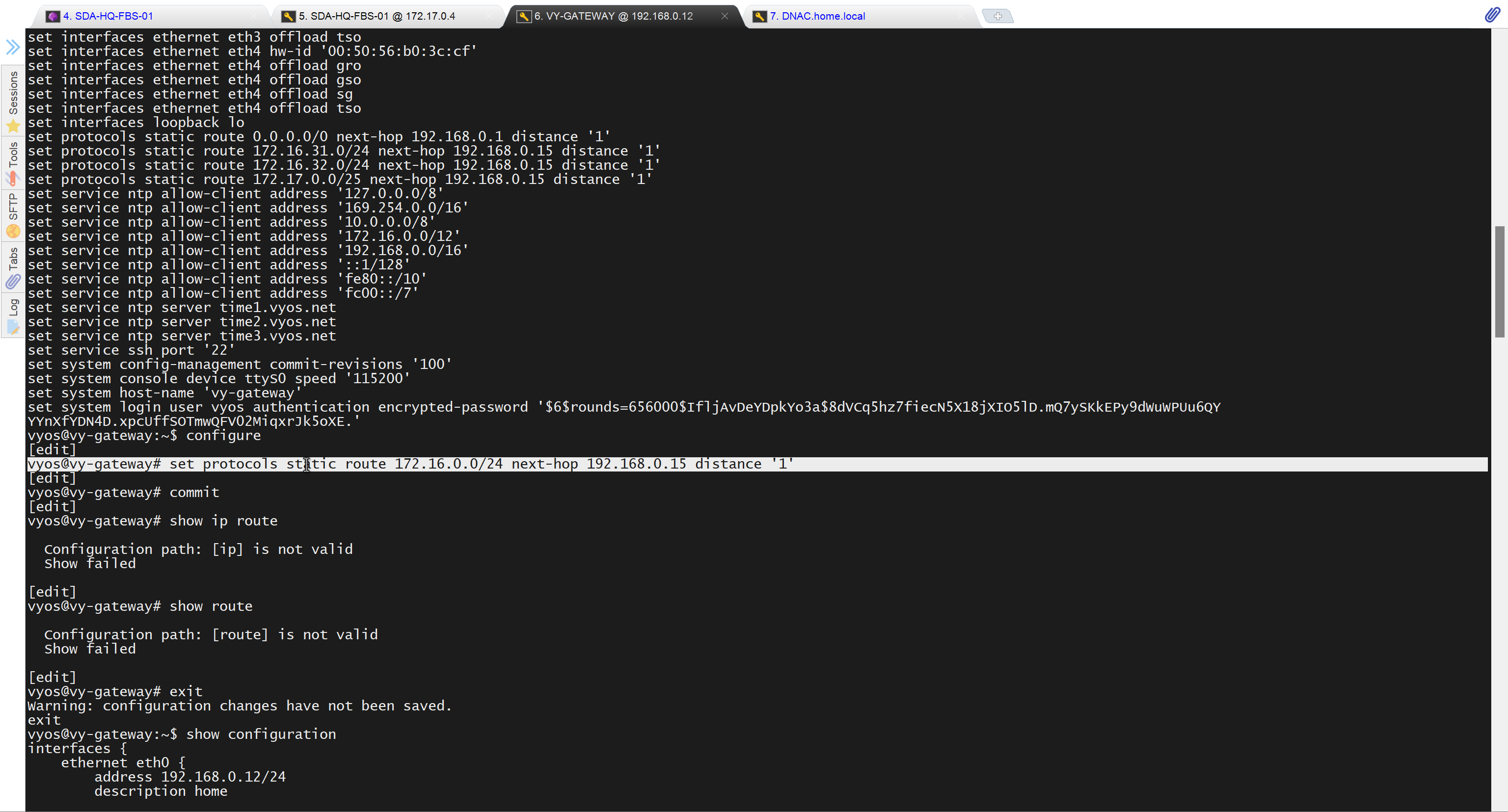
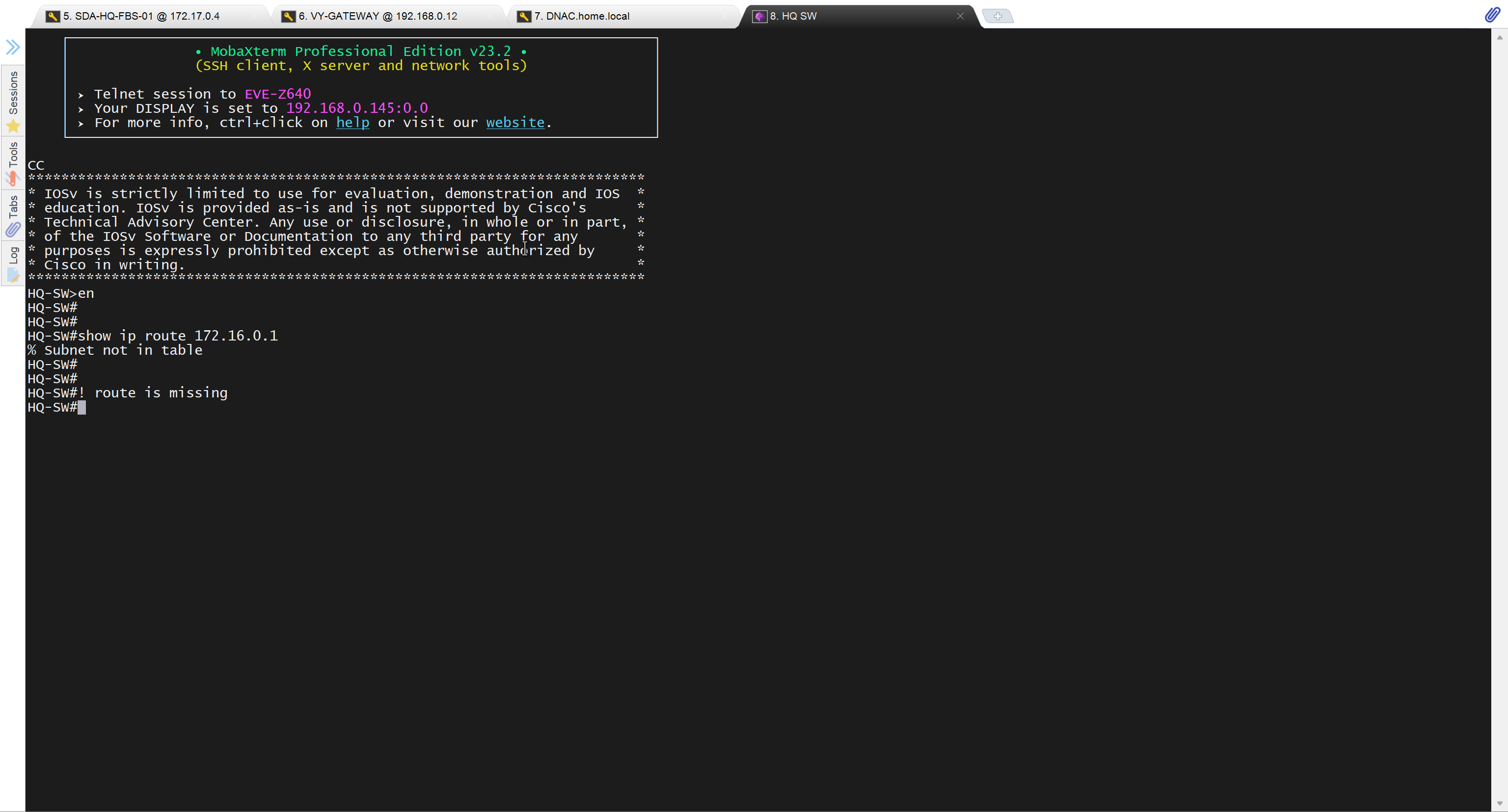
unable to reach
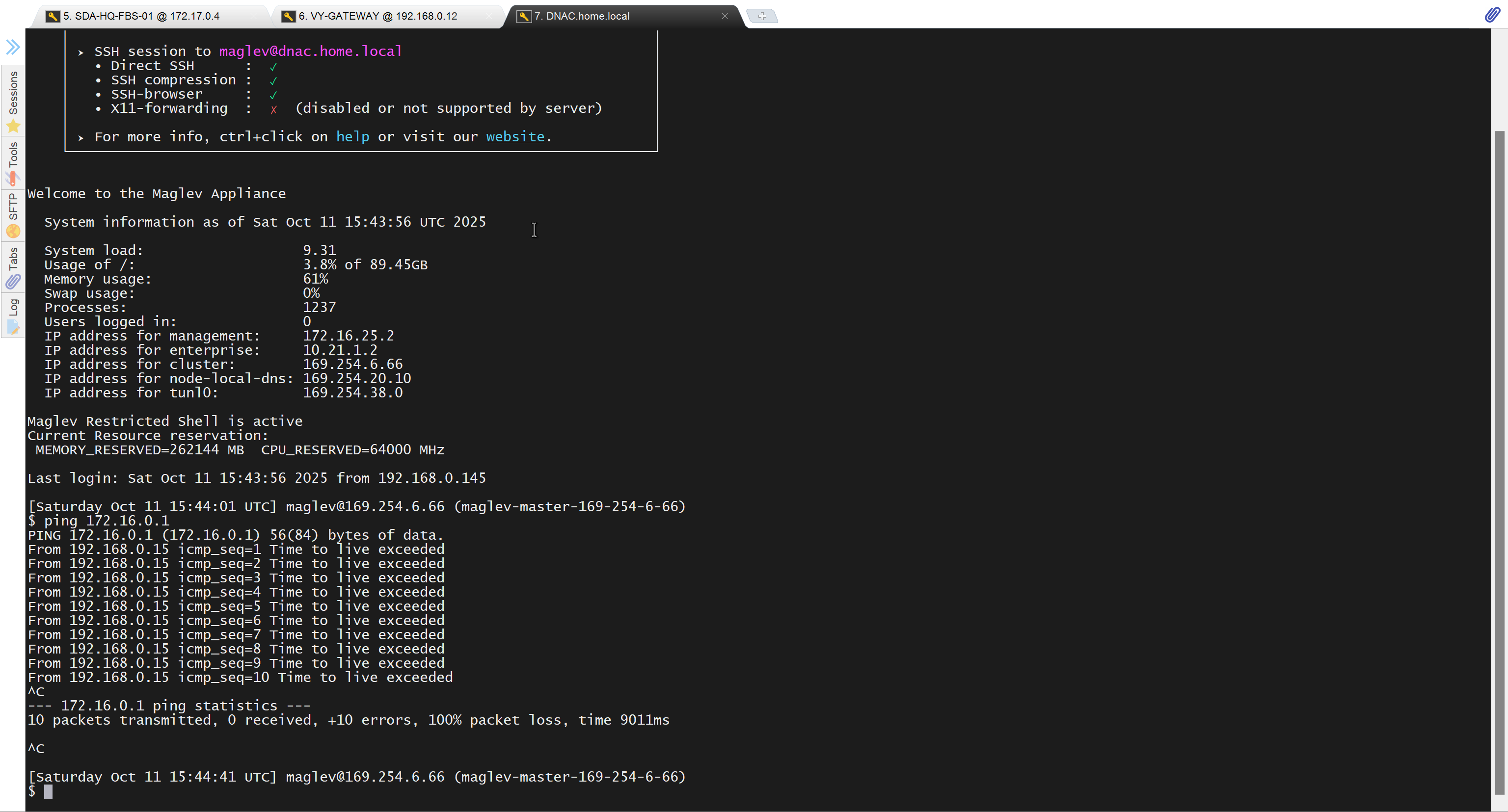
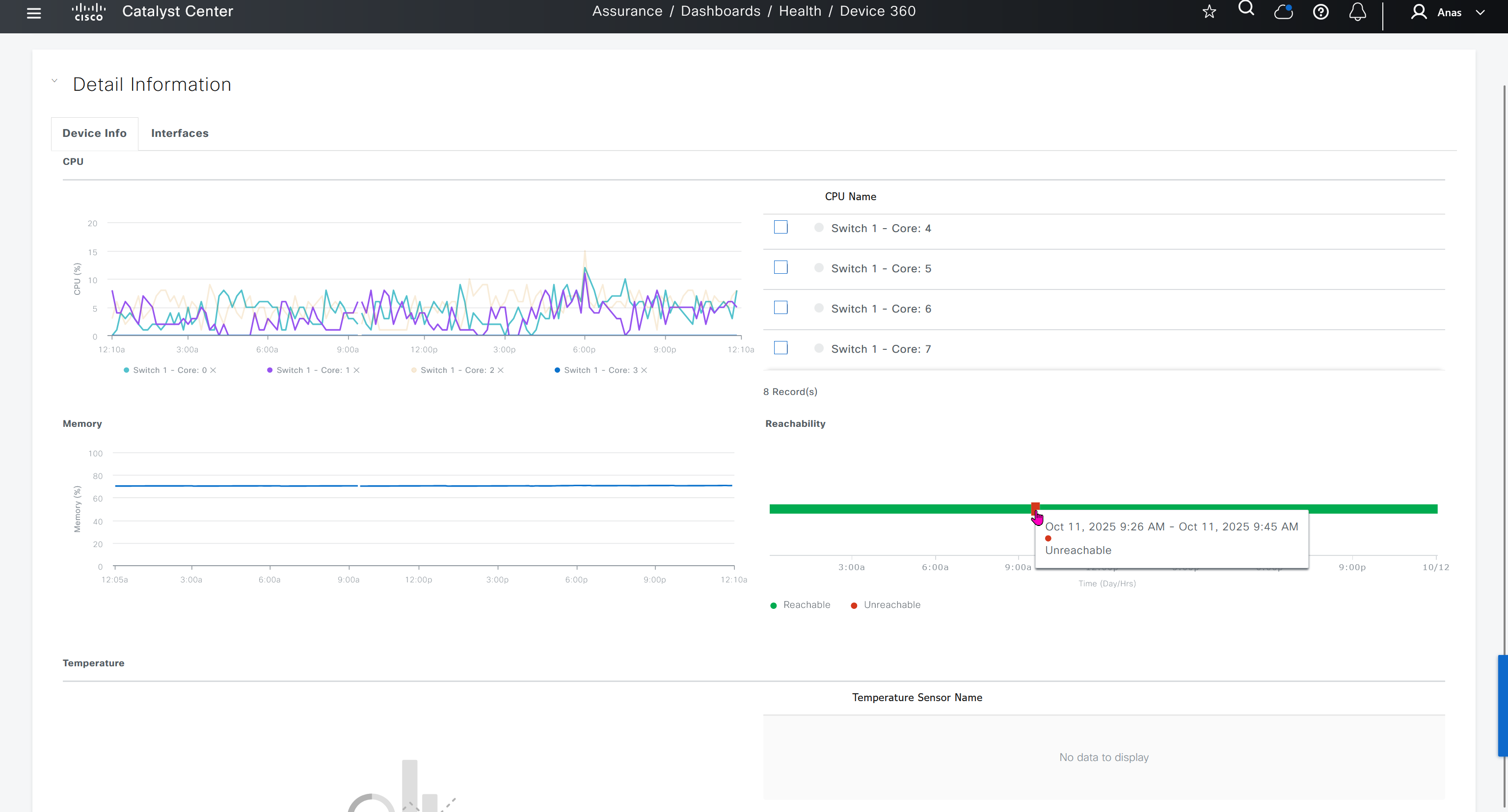
because missing route on HQ-SW in lab
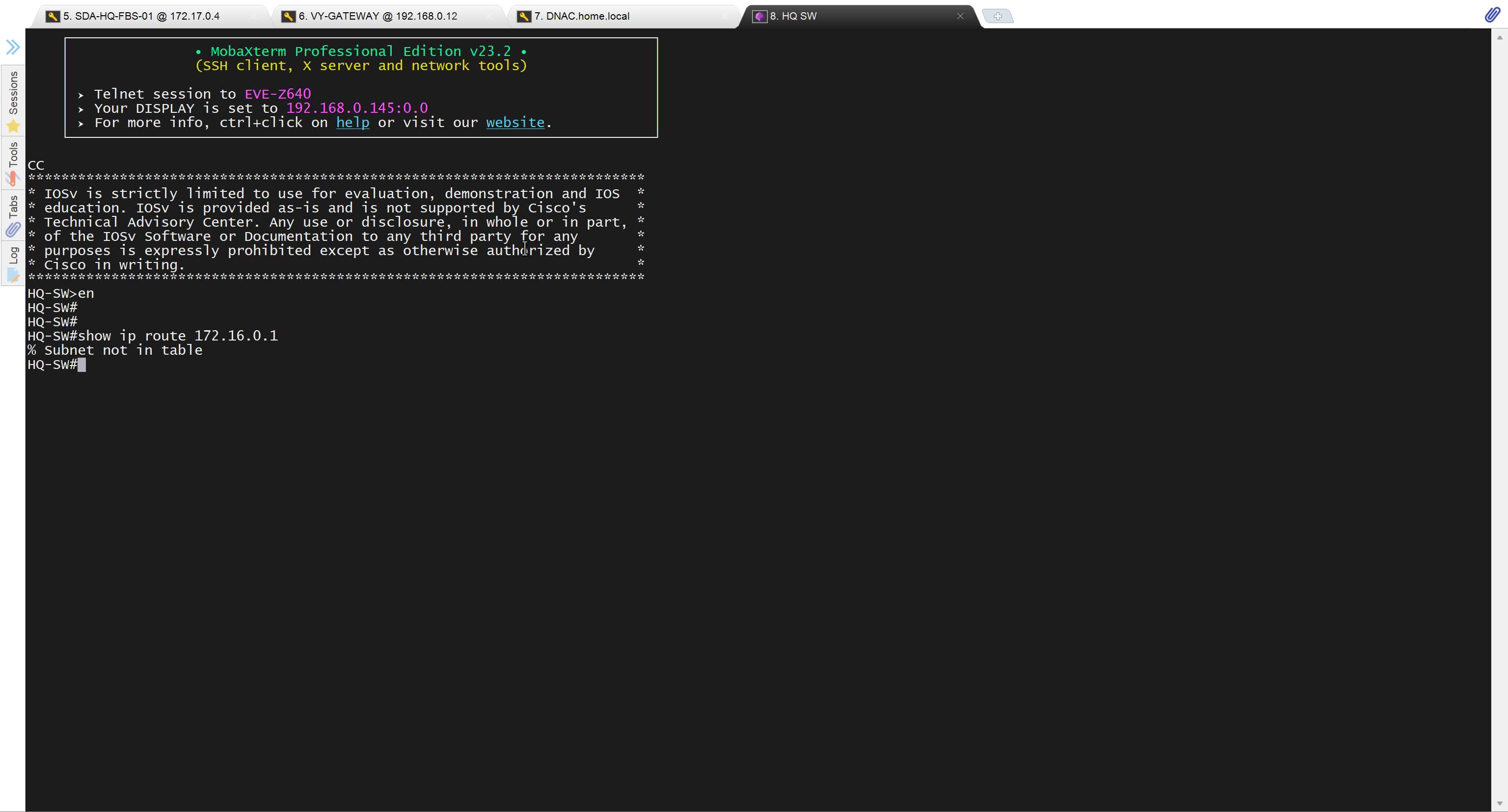
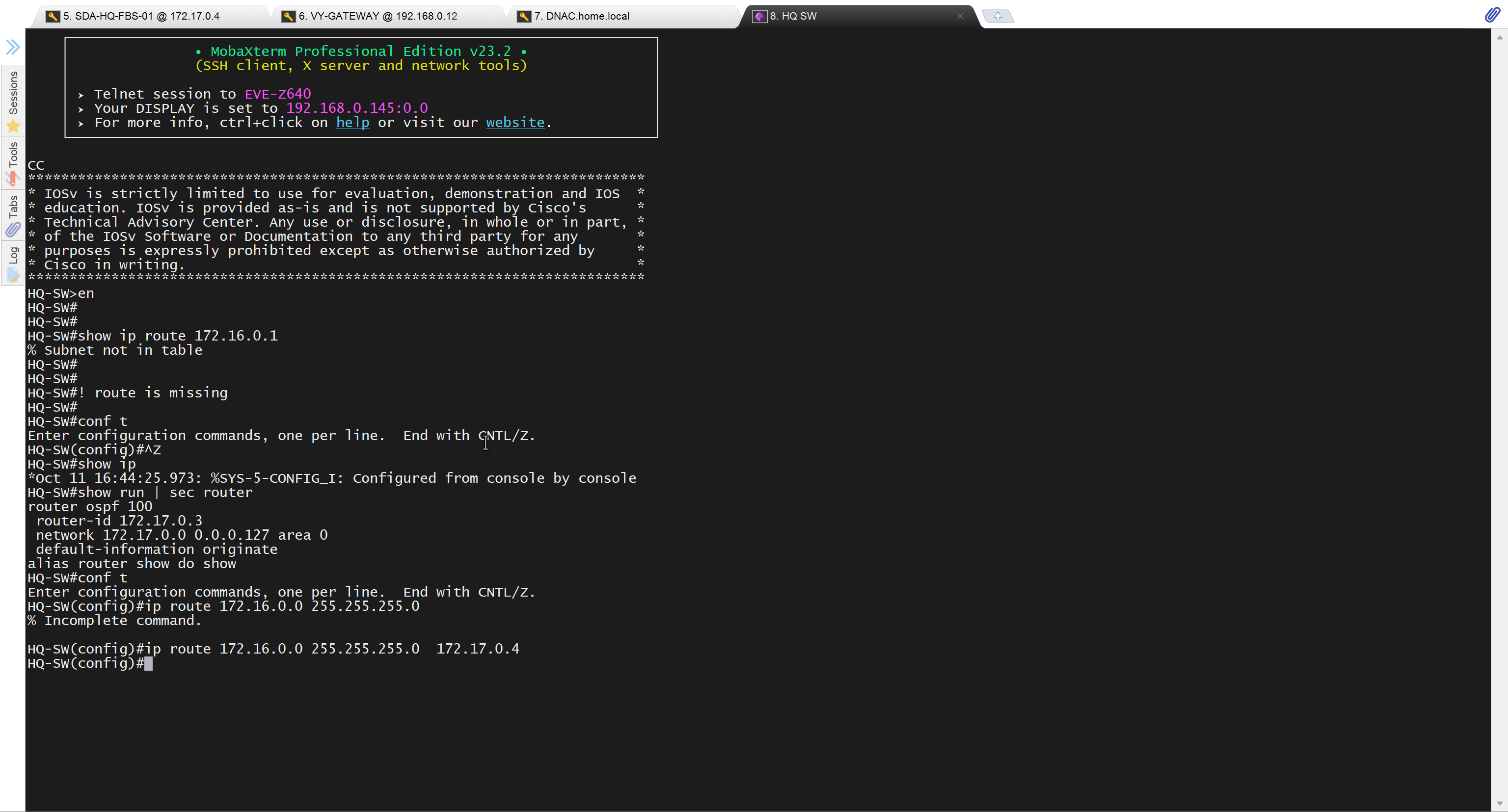
after adding route now we can reach
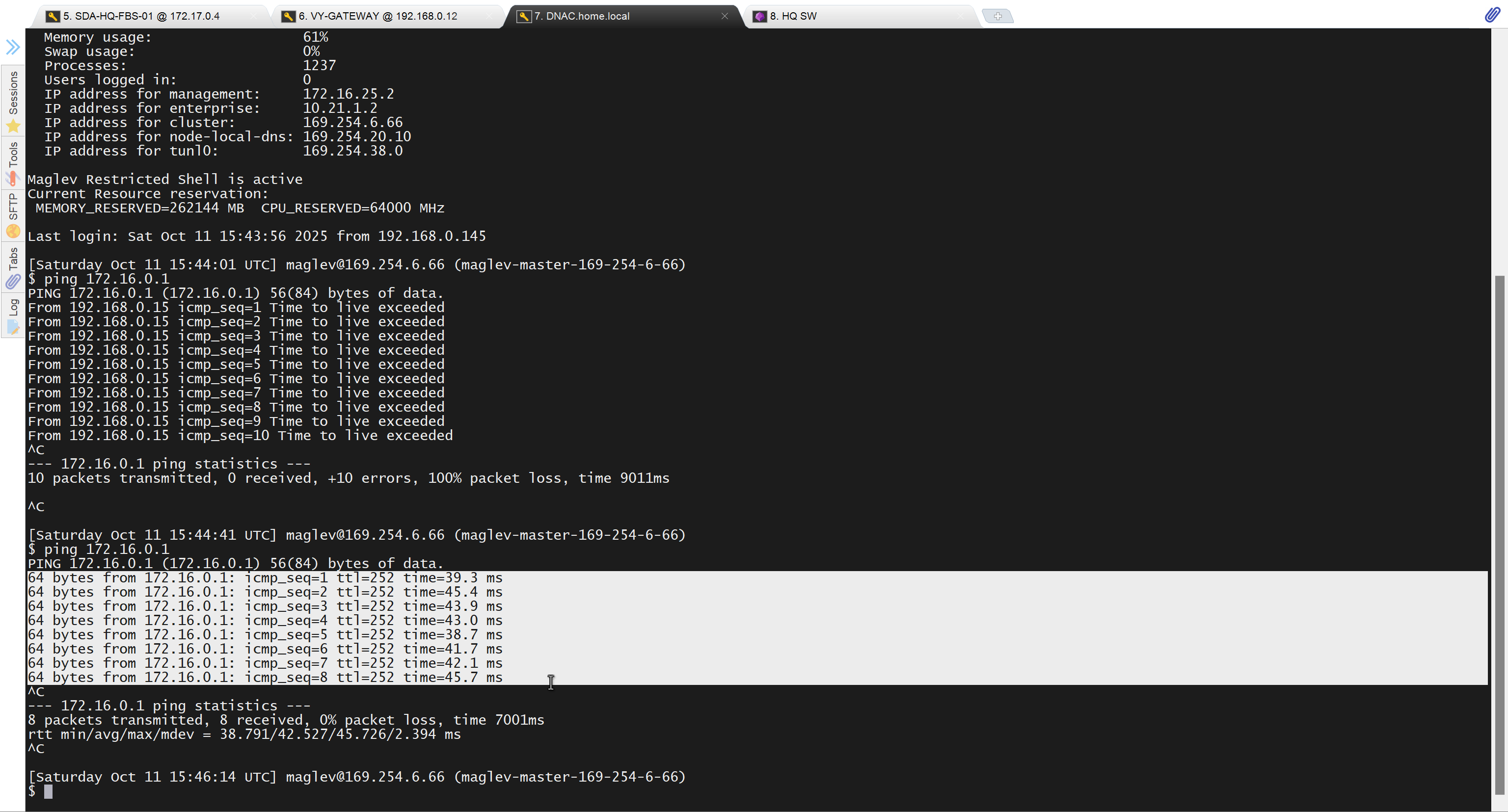
because it was only for testing, we will now remove it
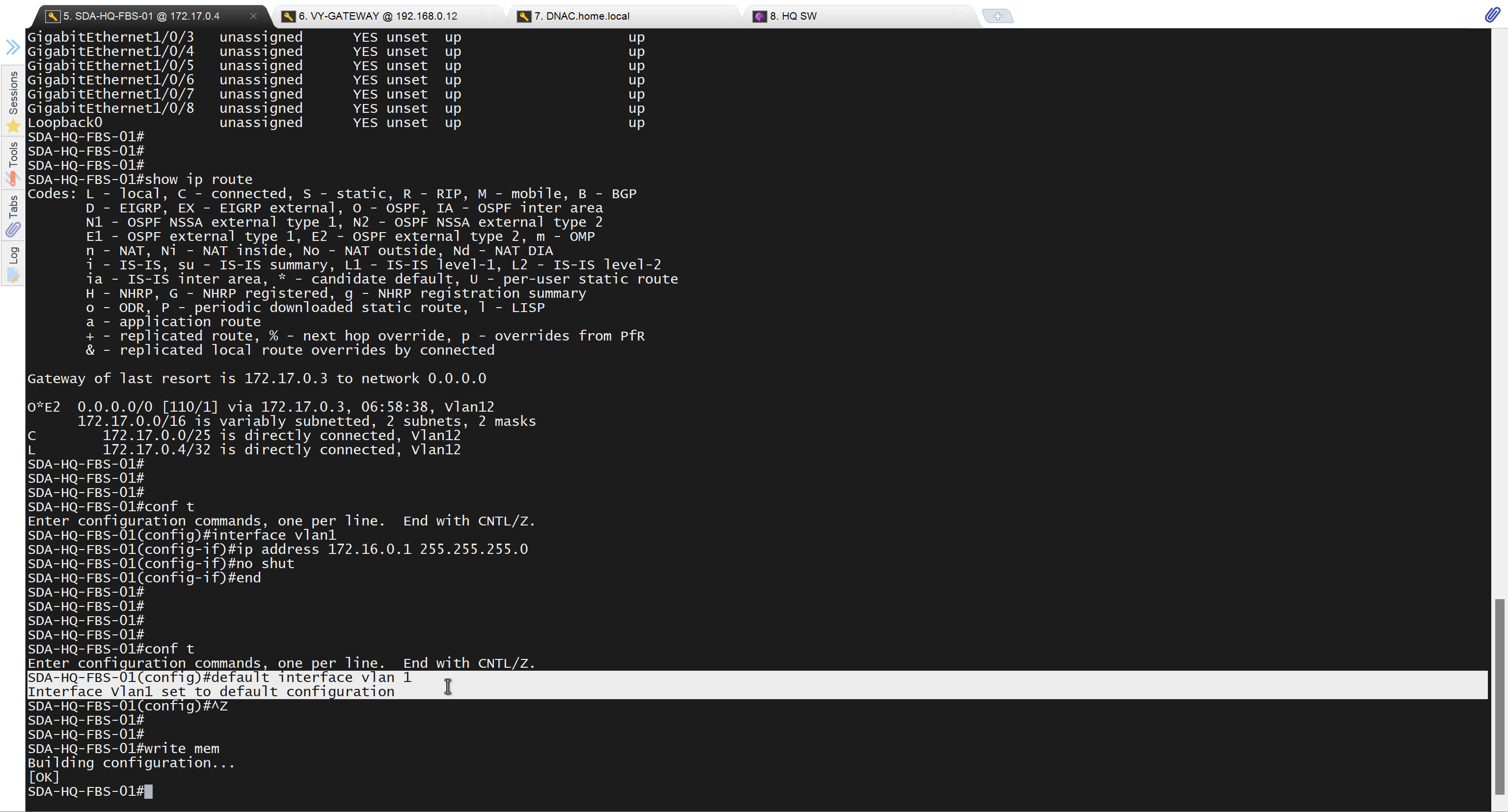
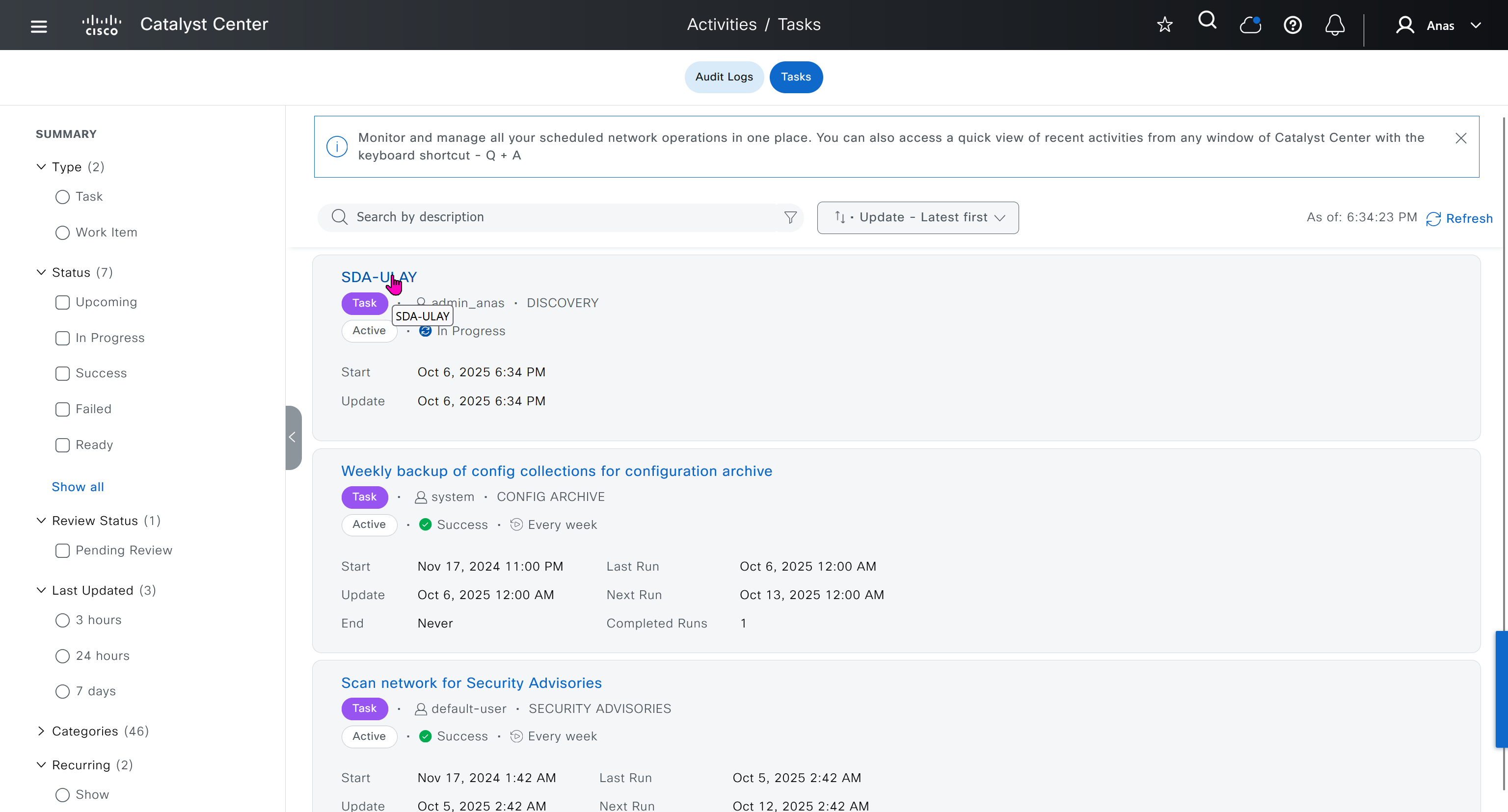
Now lets LAN Automate
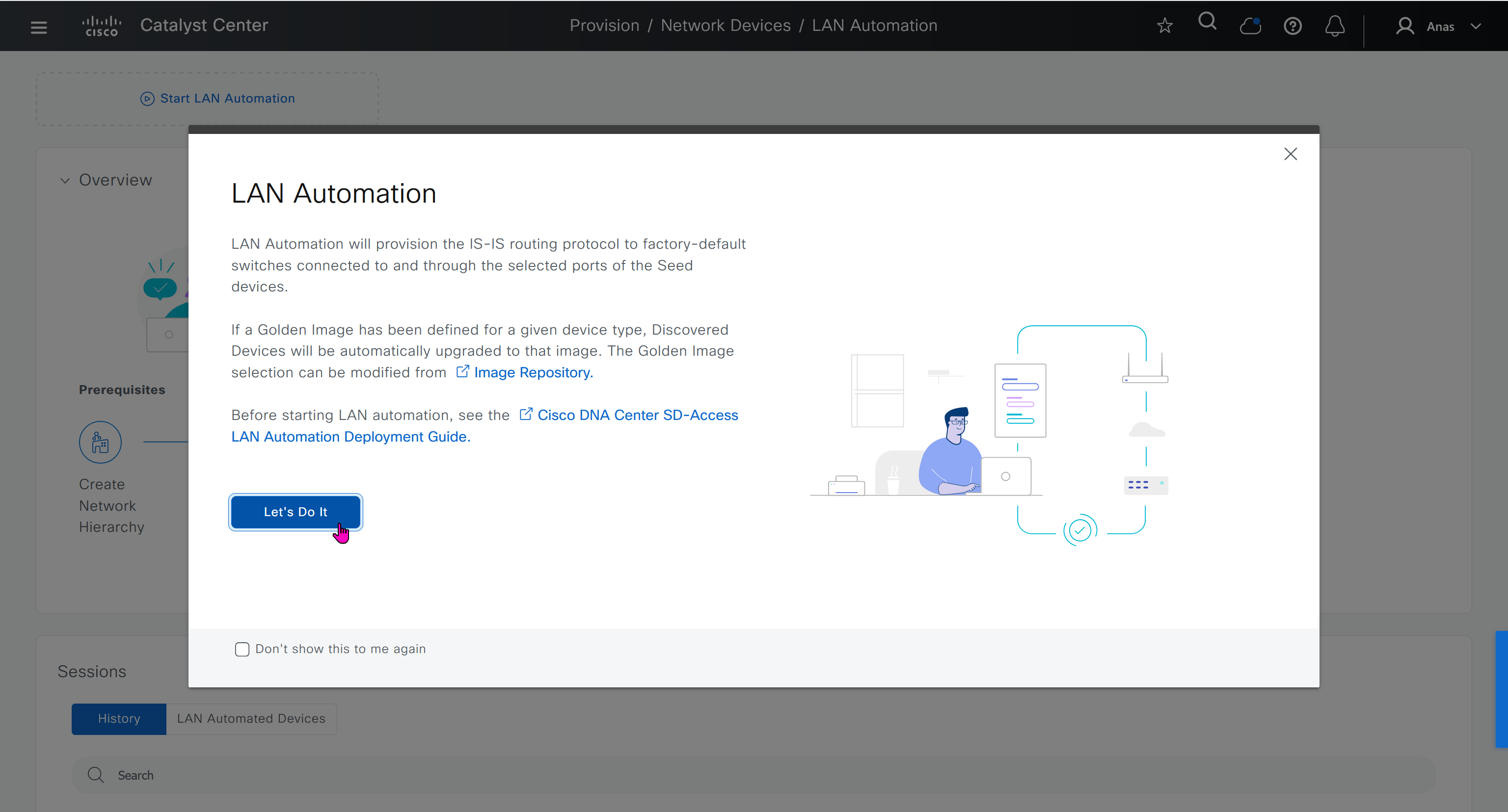
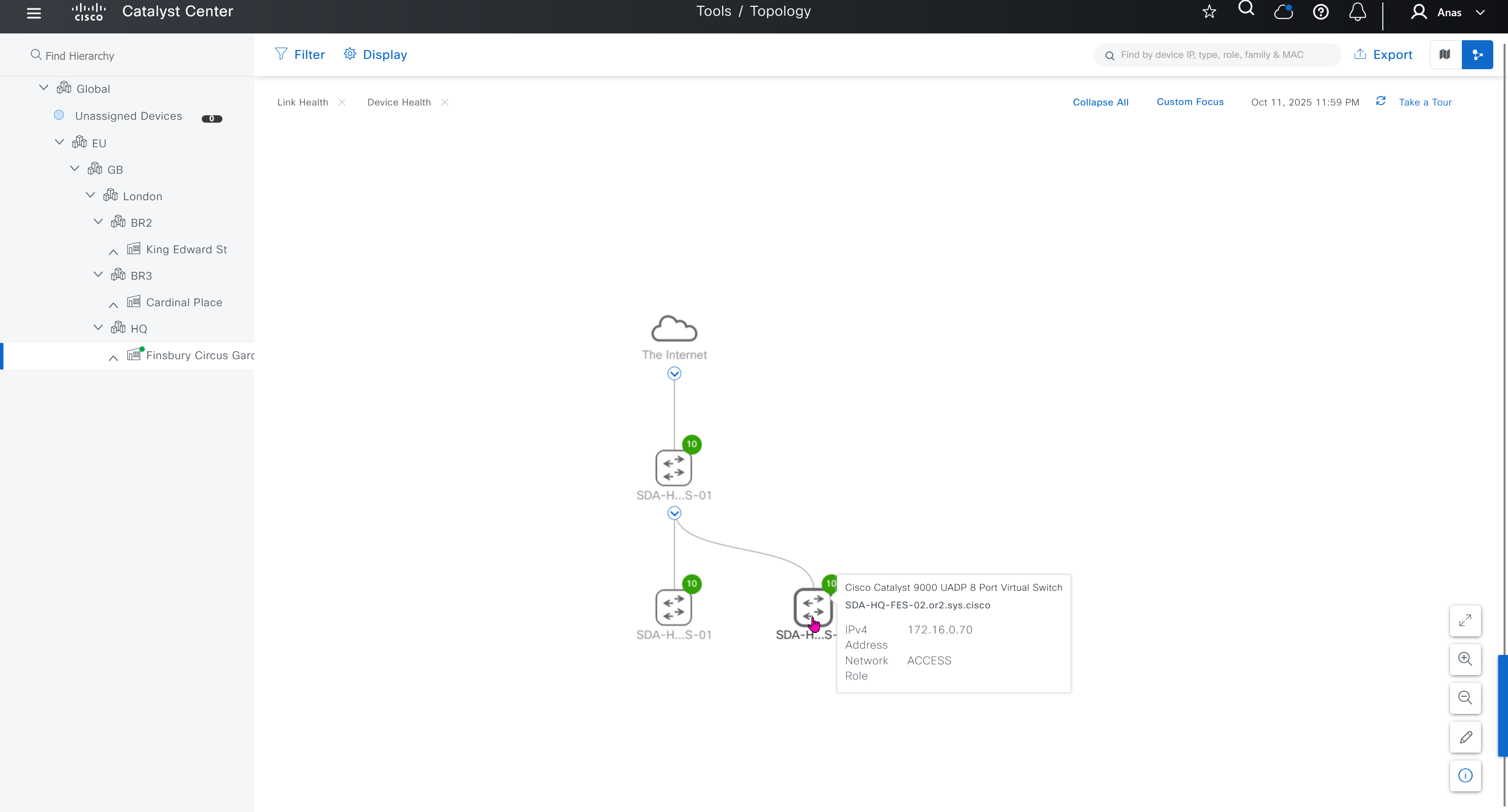
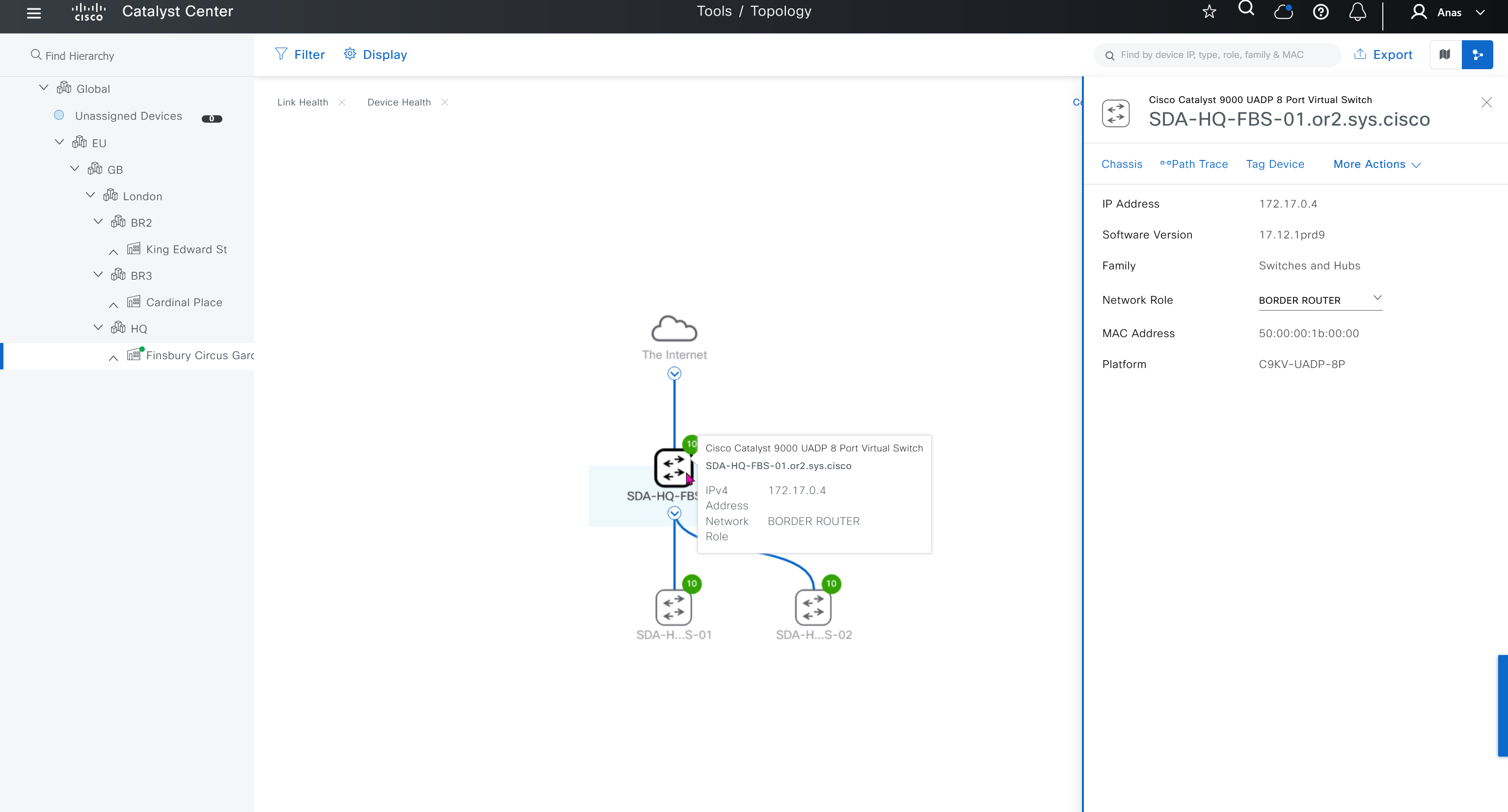
When LAN automation starts, Catalyst Center
pushes the loopback and IS-IS configuration to the primary and peer seed devices and the temporary configuration to the primary seed device
Catalyst Center Release 2.3.3 and later support is-type level-2-only as part of IS-IS configurations.
discovers new devices.
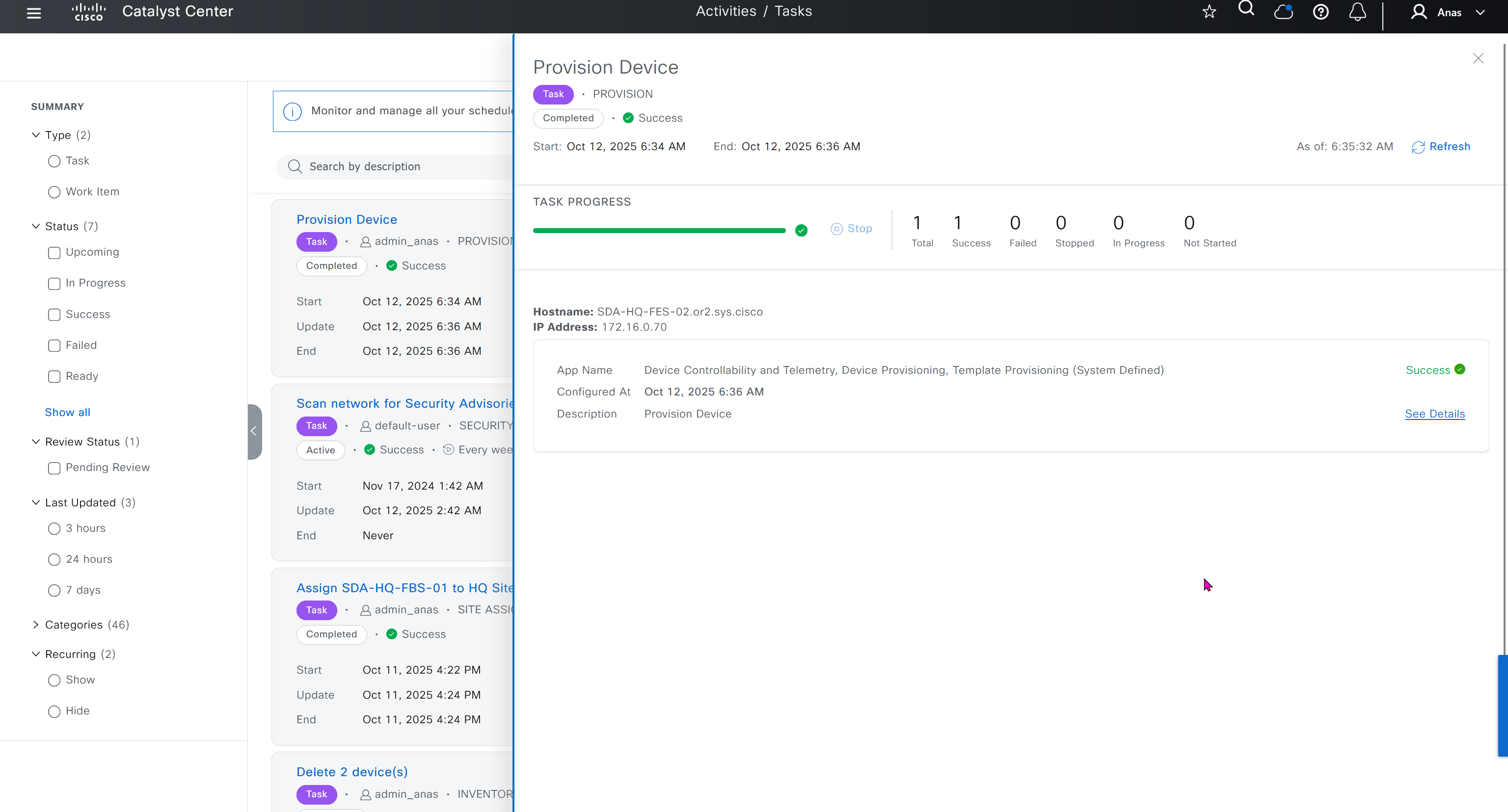
upgrades the device software image and pushes the configuration to discovered devices.
The image is updated only if a golden image is marked for that switch type in Catalyst Center under Design > Image repository.
When LAN automation starts, the temporary configuration is pushed to the primary seed device. This allows the device to discover and onboard the PnP agent. Next, the PnP agent image is upgraded and basic configurations such as loopback address, system MTU, and IP routing are pushed to the PnP agent.
- on PnP agent, Do not press Yes or No. Leave the device in the same state.
- Allow extra time to make sure that all members in the stack are up. Do not start LAN automation until all switches are up.
- LAN automation always begins on the active switch. When all switches in a stack are booted together, the switch with the lowest MAC address (assuming no switch priority is configured) becomes active. The switch with the second lowest MAC address becomes the standby, and so on. Some customers require the first switch to always be active. In this case, if all the switches are booted together and the first switch does not have the lowest MAC address, it does not become the active switch. To ensure that the first switch is active, boot the switches in a staggered manner: boot Switch 1; after 120 seconds, boot Switch 2, and so on. This approach ensures that the switch becomes active in the correct order—Switch 1 is active, Switch 2 is standby, and so on. However, after a reload, the order may change because switches obtain their role based on their MAC address.
- To make sure that the switches maintain their order after reload, it is a good practice to assign switch priorities to ensure that the switches always come up in the same order. The highest priority is 15. During LAN automation, the priority of active switch is set to 15 by default. The priority of other switches is not altered. When priorities are assigned, they take precedence over the switch MAC address. Assigning switch priorities does not change the NVRAM configuration. The values are written to ROMMON and persist after reload or write erase. Refer to this sample code:
3850_edge_2#switch 1 priority ? <1-15> Switch Priority 3850_edge_2#switch 1 priority 14 WARNING: Changing the switch priority may result in a configuration change for that switch. Do you want to continue?[y/n]? [yes]: y- You might have to clean up the switch after assigning priorities using “
pnpa service reset no-prompt“ - Connect PnP agents directly to seed devices. Do not connect PnP agents to any other network (for example, even the management network)
Interface Selection
consider four directly connected PnP agents: device 1 is connected through Gig1/0/10, device 2 through Gig 1/0/11, device 3 through Gig 1/0/12, and device 4 through Gig 1/0/13. If you choose Gig 1/0/11 and Gig 1/0/12 as discovery interfaces, LAN automation discovers only device 1 and device 2. If device 3 and device 4 try to initiate the PnP flow, LAN automation filters them because they connect through unselected interface.
You can also choose interfaces between the primary seed and the peer seed to configure with Layer 3 links. If there are multiple interfaces between the primary and peer seeds, you can choose to configure any set of these interfaces with Layer 3 links. If no interfaces are chosen, they aren’t configured with Layer 3 links.
You can reuse the same LAN pool for multiple LAN automation sessions. For example, you can run a discovery session to find the initial set of devices. After the session completes, you can provide the same IP pool for subsequent LAN automation sessions. Similarly, you can choose a different LAN pool for other discovery sessions. Make sure the LAN pool you select has enough capacity.



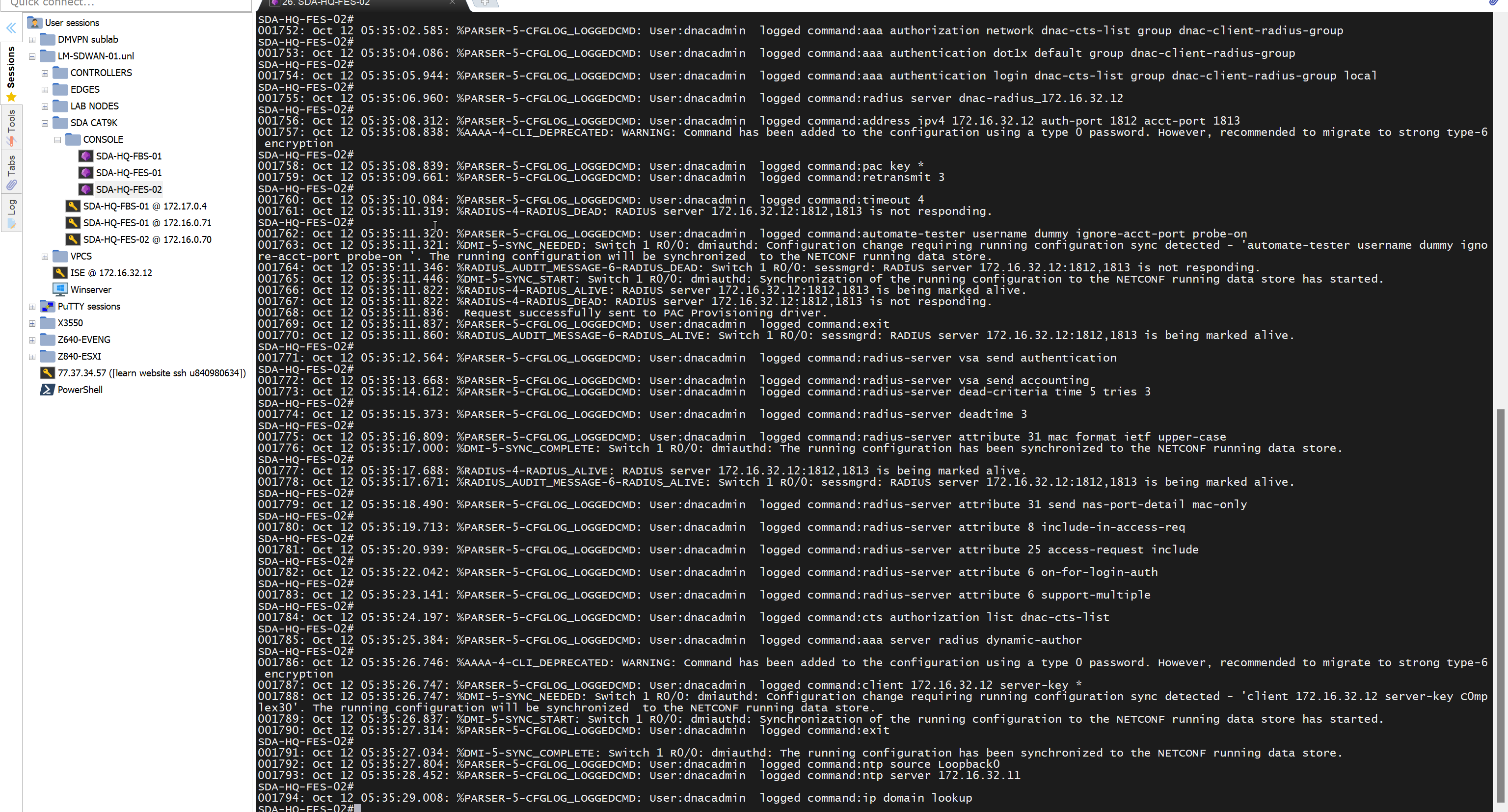
in order to catch all commands pushed by LAN automation to switches add below config and sync with DNAC
conf t
!
! Enable the archive feature
archive
log config
logging enable
notify syslog contenttype plaintext
hidekeys
!
! Optional: Set up where the archived configs are stored
path flash:config-archive
write-memory
!
end
!
! Ensure syslog logging is enabled (optional but recommended)
conf t
logging buffered 64000
service timestamps log datetime msec
!
end
write mem who
show user
! to see if DNAC is logged in and running commands
! to see commands
show logg | inc CFGLOG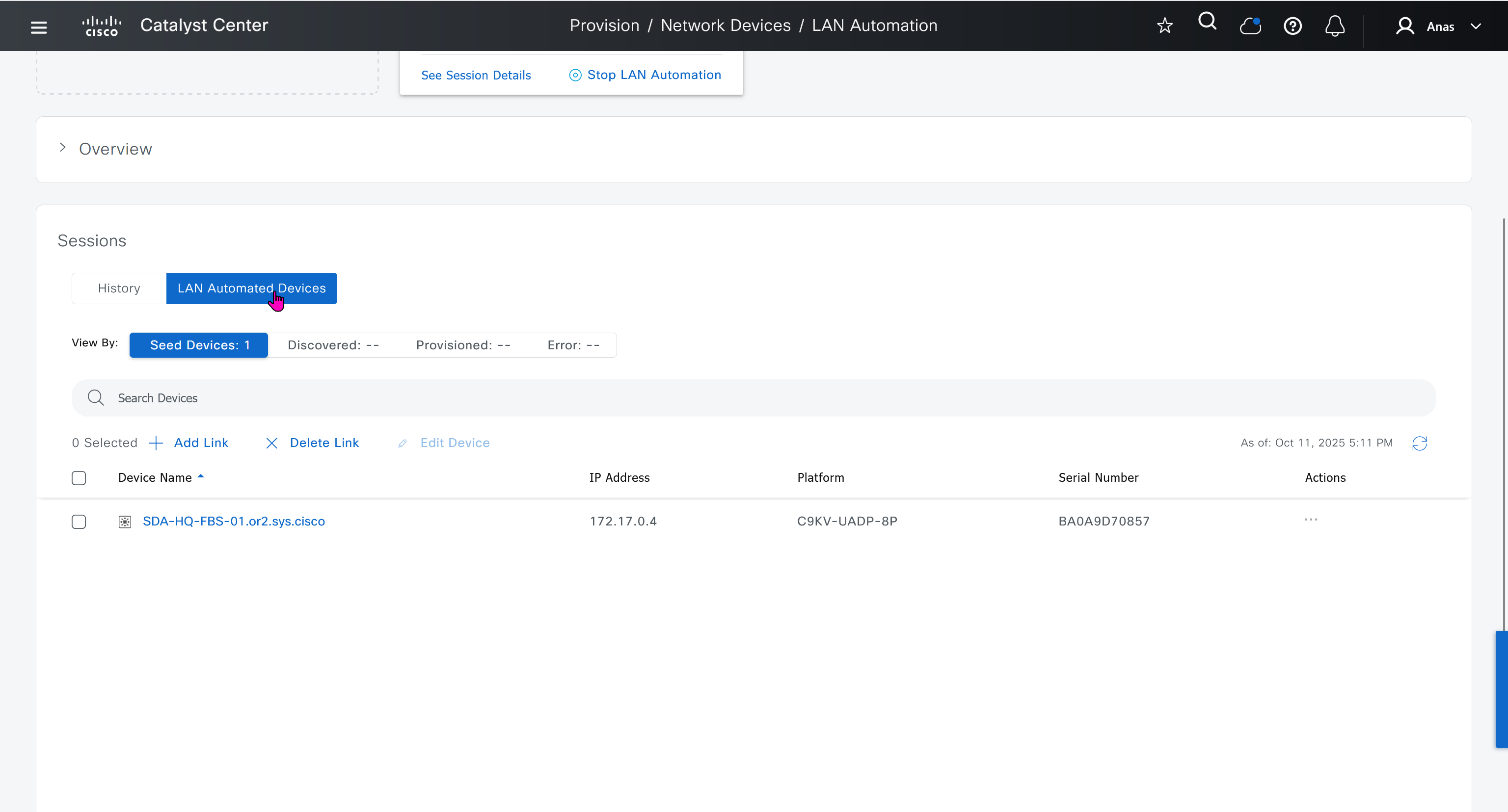
- Quickly as confiiguration is being deployed, intervene and remove using “no” following part of the configuration from “all” switches / routers
- router isis
net 49.0000.280e.ab15.fa02.00
is-type level-2-only
domain-password C0mplex30
metric-style wide
log-adjacency-changes
nsf ietf
bfd all-interfaces




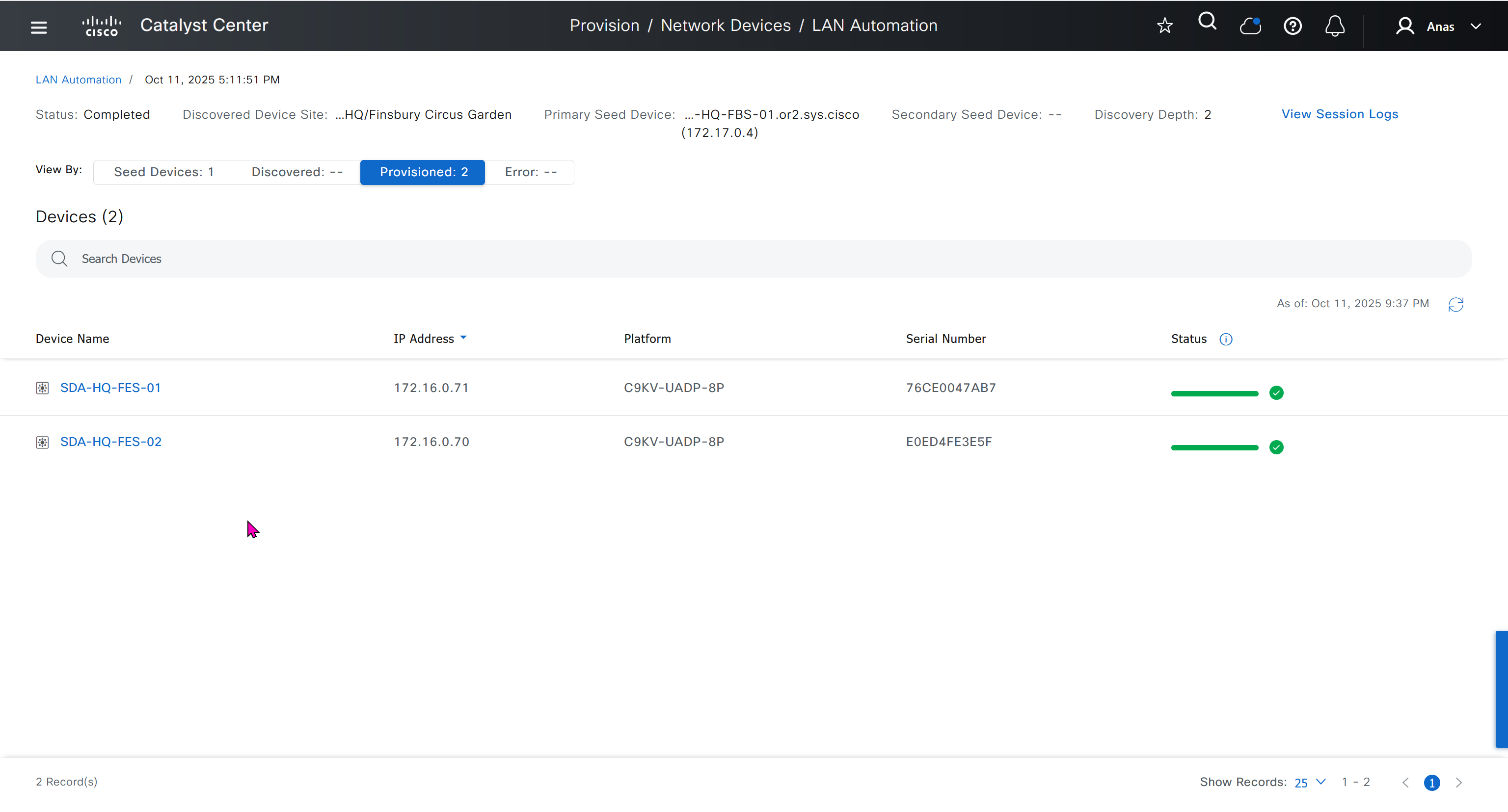
It takes long time to stop LAN automation
When the LAN automation process stops,
the discovery phase ends, and all point-to-point links between the seed and discovered devices and between the discovered devices (maximum of two hops) are converted to Layer 3.








Add a static route for LAN pool on DNAC through Enterprise facing interface
Skipped but complete it for CCIE LAB
next post
SDA LM 2 – Network Design
Videos
Network Design
An area represents the geographical location such as country, city or campus (regardless of the size of area), next level is building which represents physical structure, there cannot be buidling inside a building
Cisco recommends the hierarchy as Continent > Country > City > Campus > Buildings
This is how you are on safe side and covered for any future locations and changes with flexibility built in as it can difficult to adjust the hierarchy later on once everything is configured
For example, today you are domestic but tomorrow you might go international and open new offices in new country / continent

We will create 3 sites in EU > GB > London
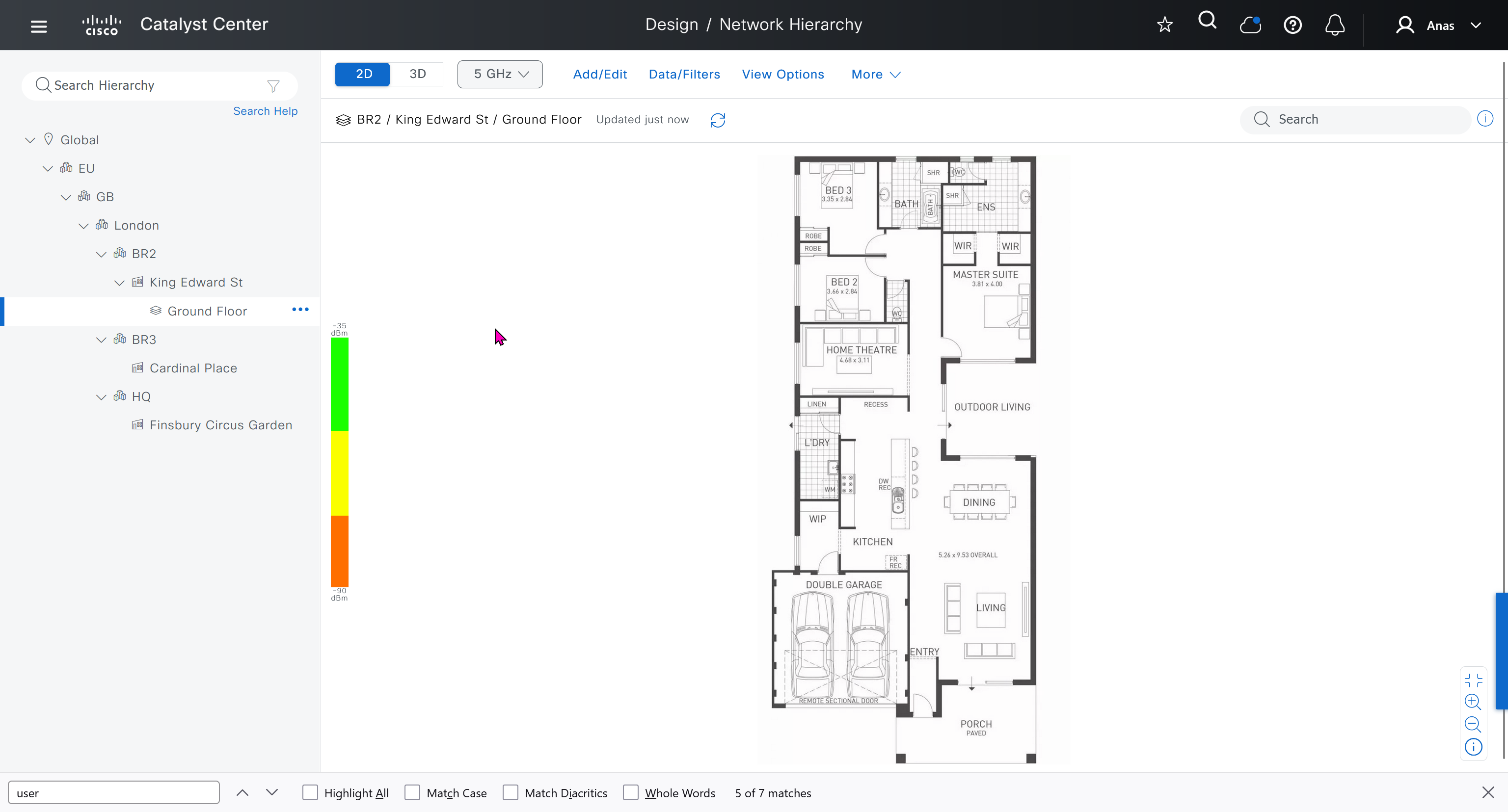
- Finsbury Circus Garden, 14 Finsbury Circus, London EC2M 7EB
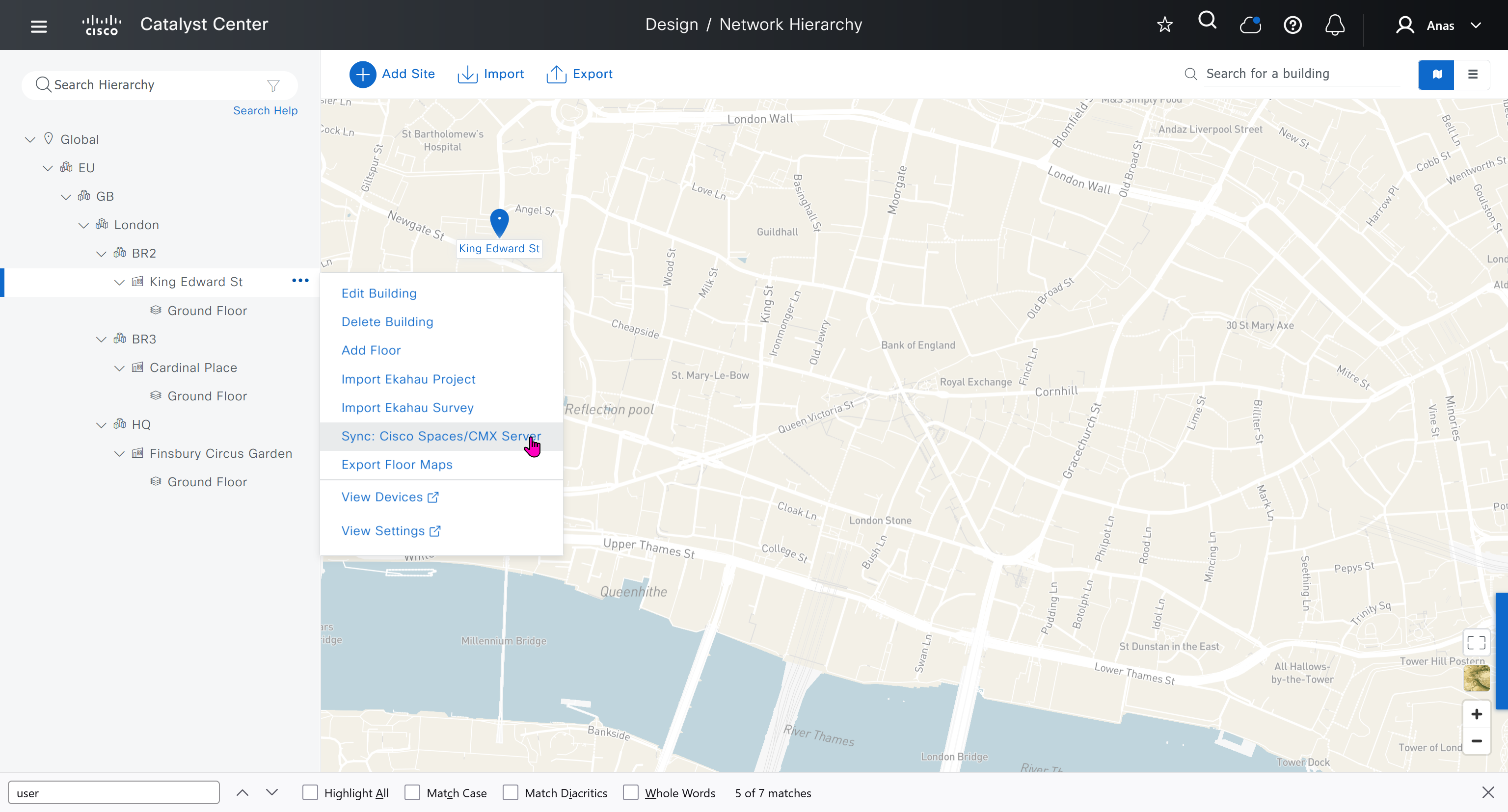
- 2, 7 King Edward St, London EC1A 1HQ
- Cardinal Place, 84 Victoria St, London SW1E 5JL
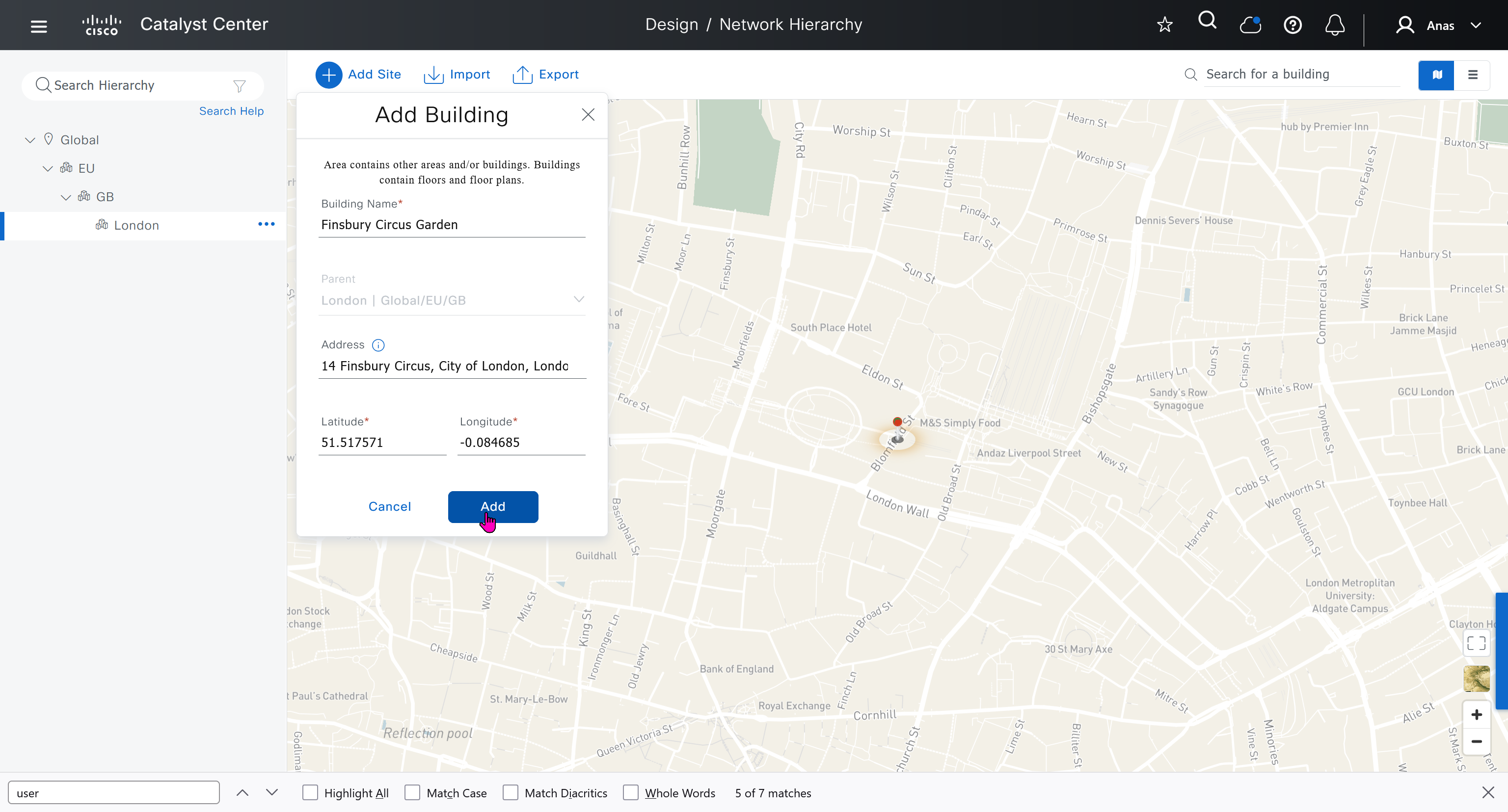
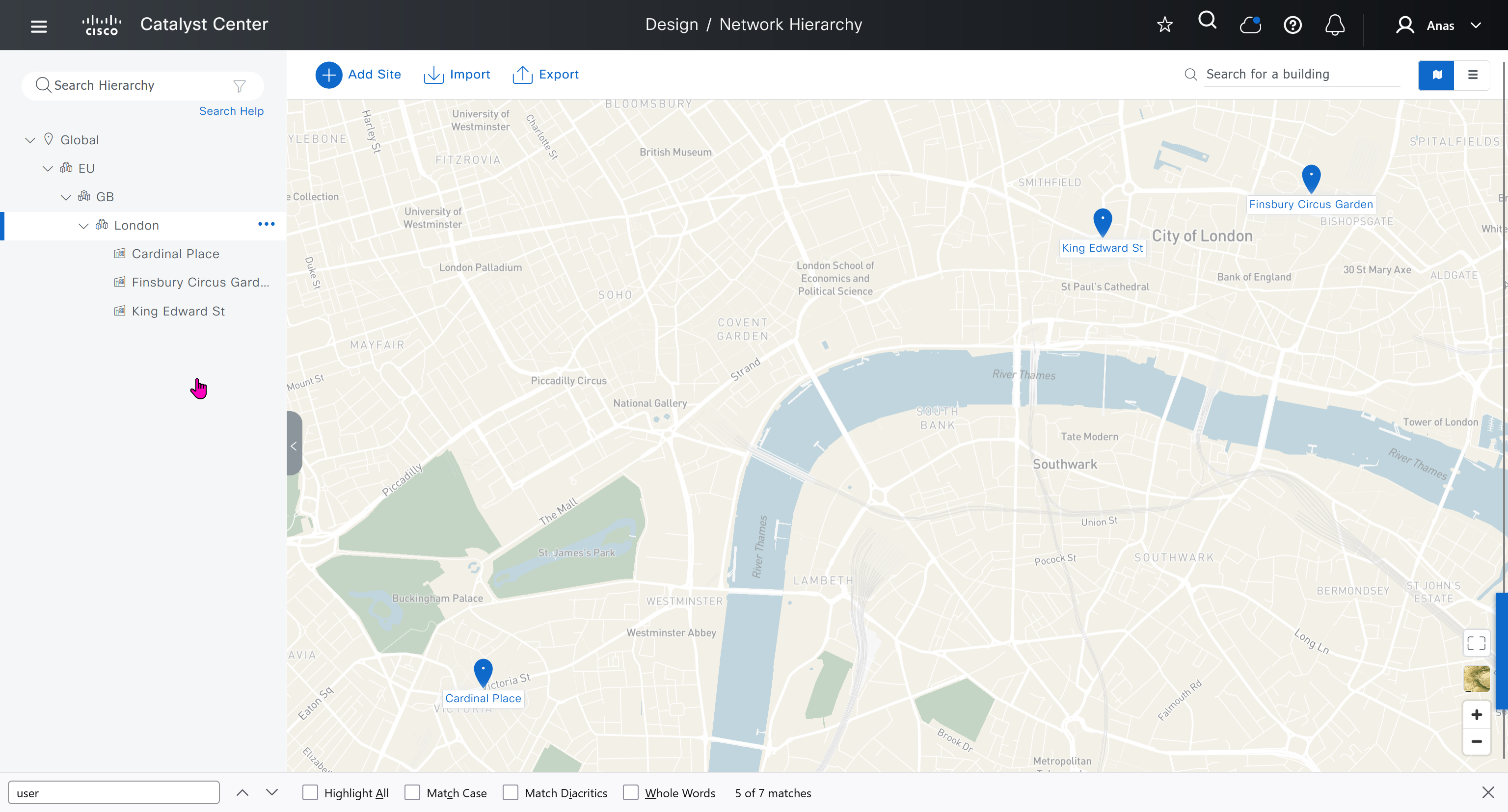

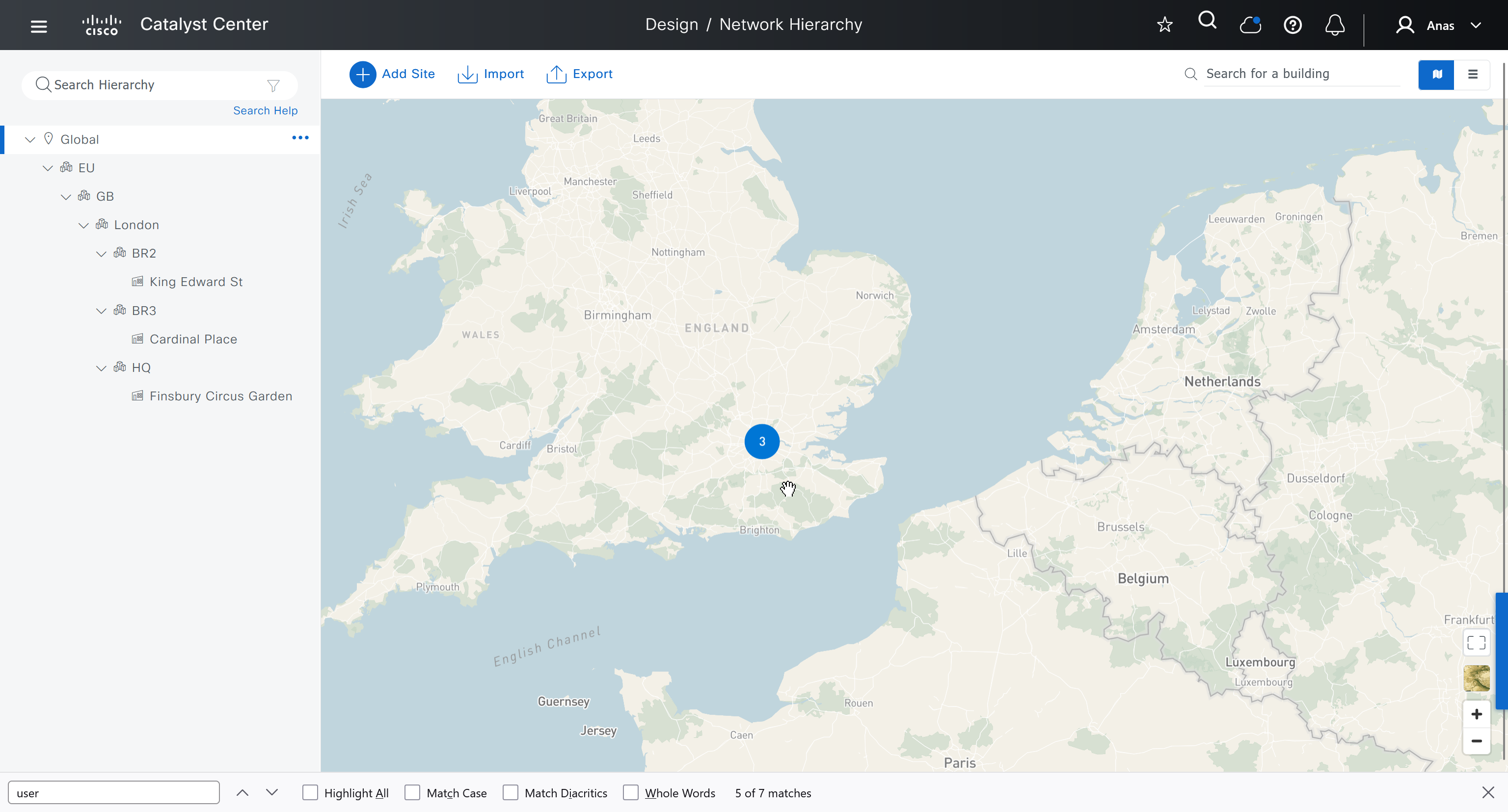
We should add HQ, BR2 and BR3

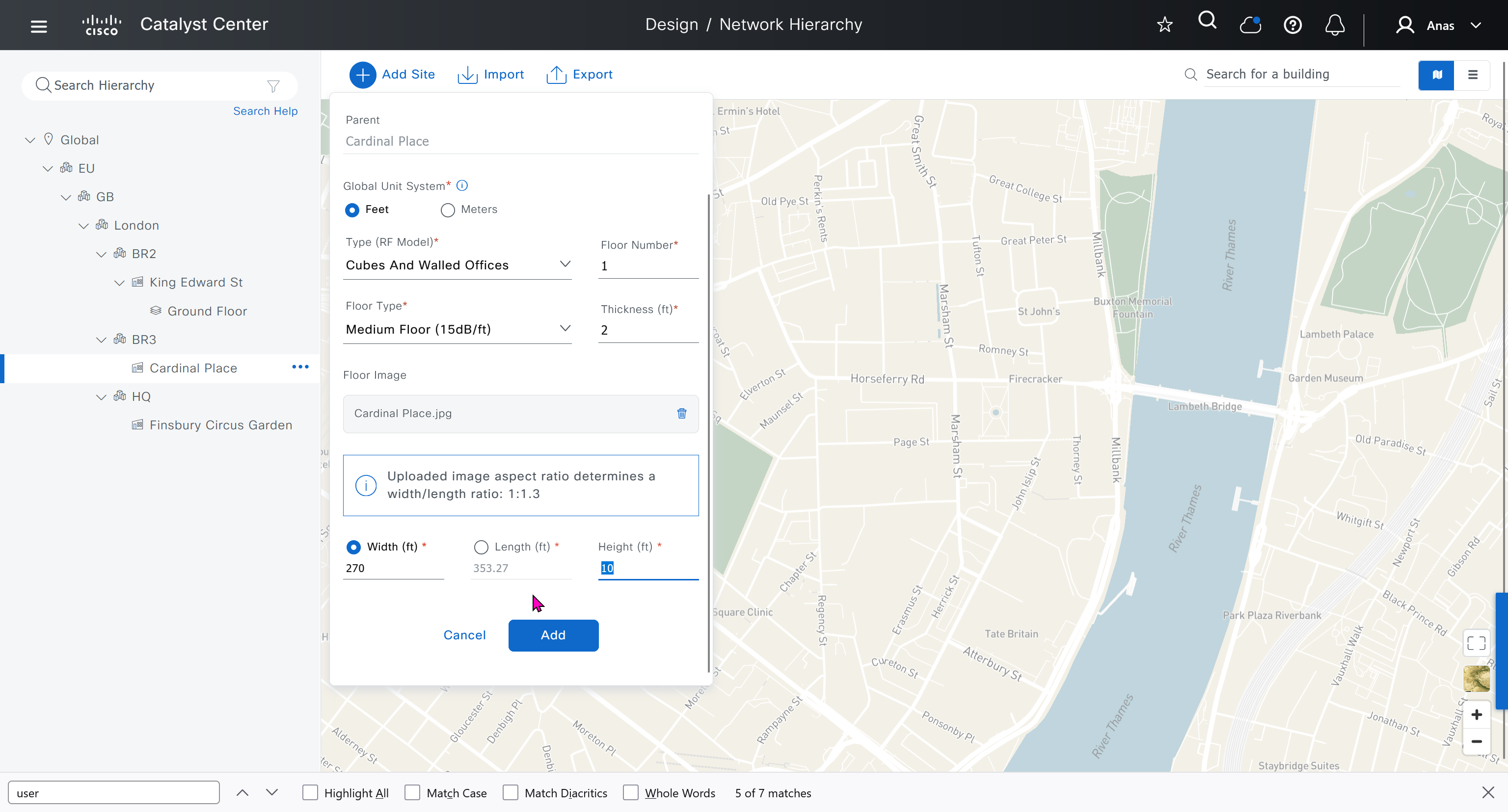
We can add floors and floors are mostly used for placing wireless access points but for SDA we can add ground floor, if customer had prime we can import APs on floor plans already from prime
for RF model on the floor just stick with default of “Cubes And Walled Offices”
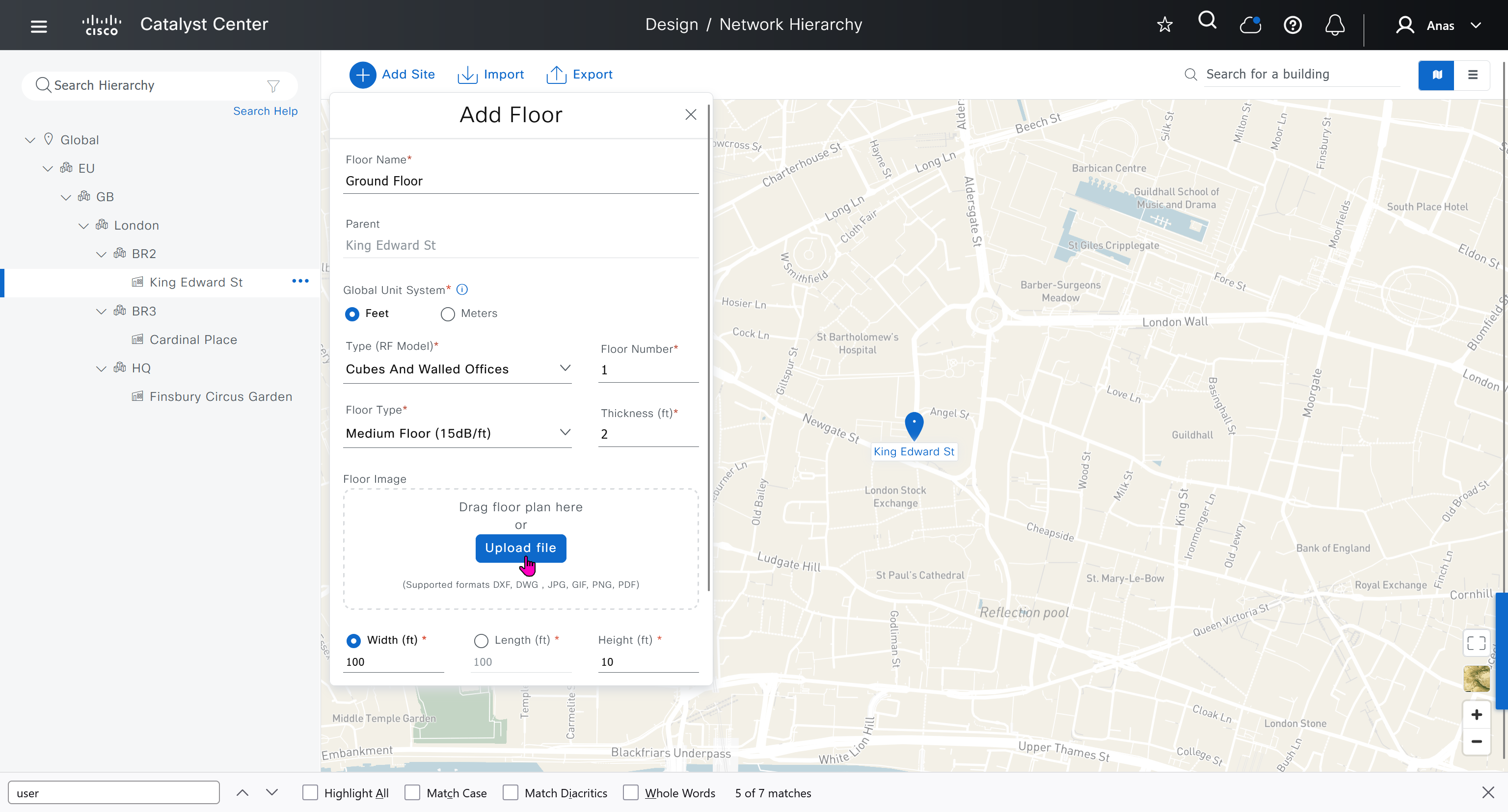
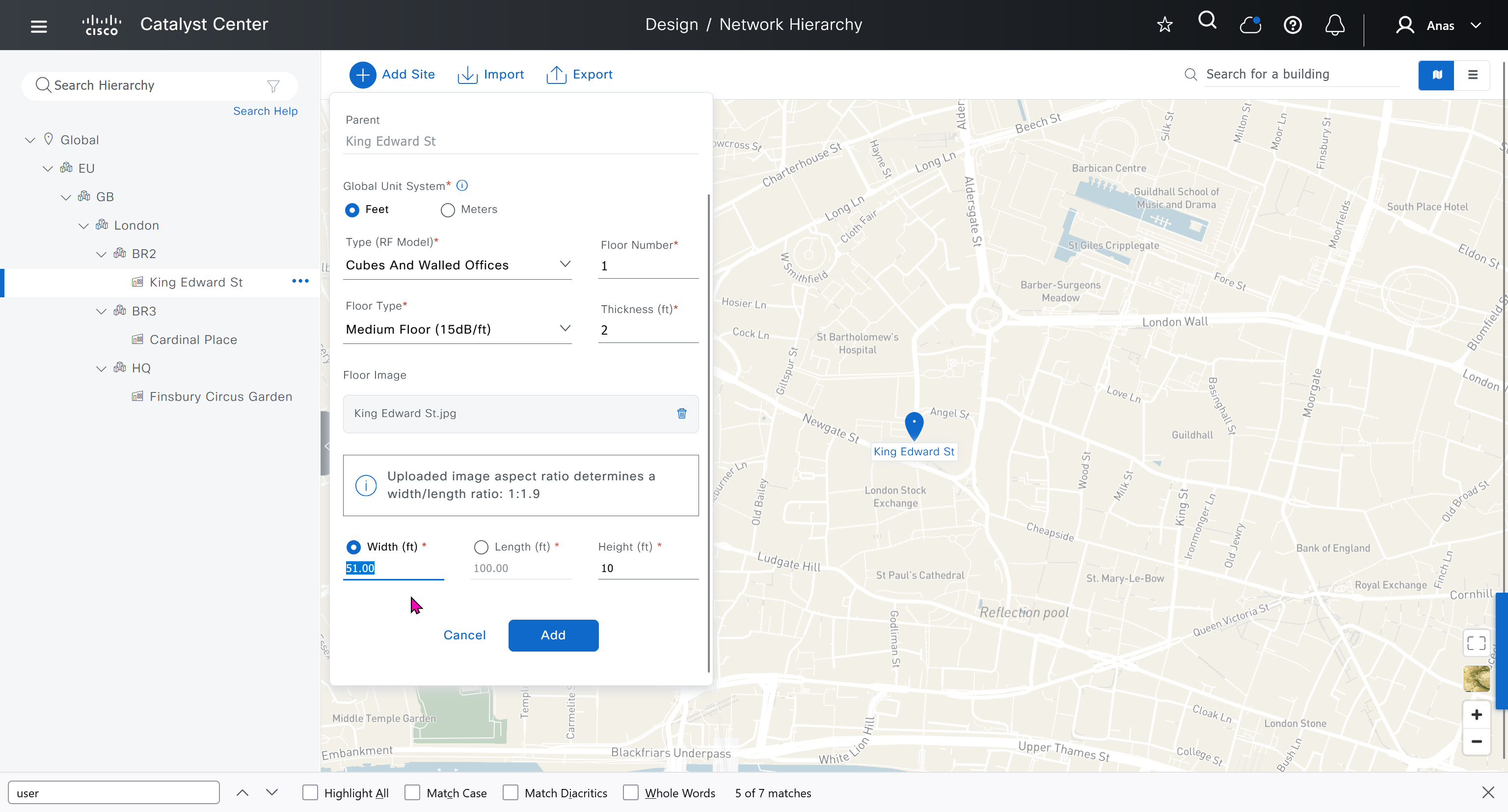
see that when I changed width, dnac maintained the aspect ratio from the image I uploaded
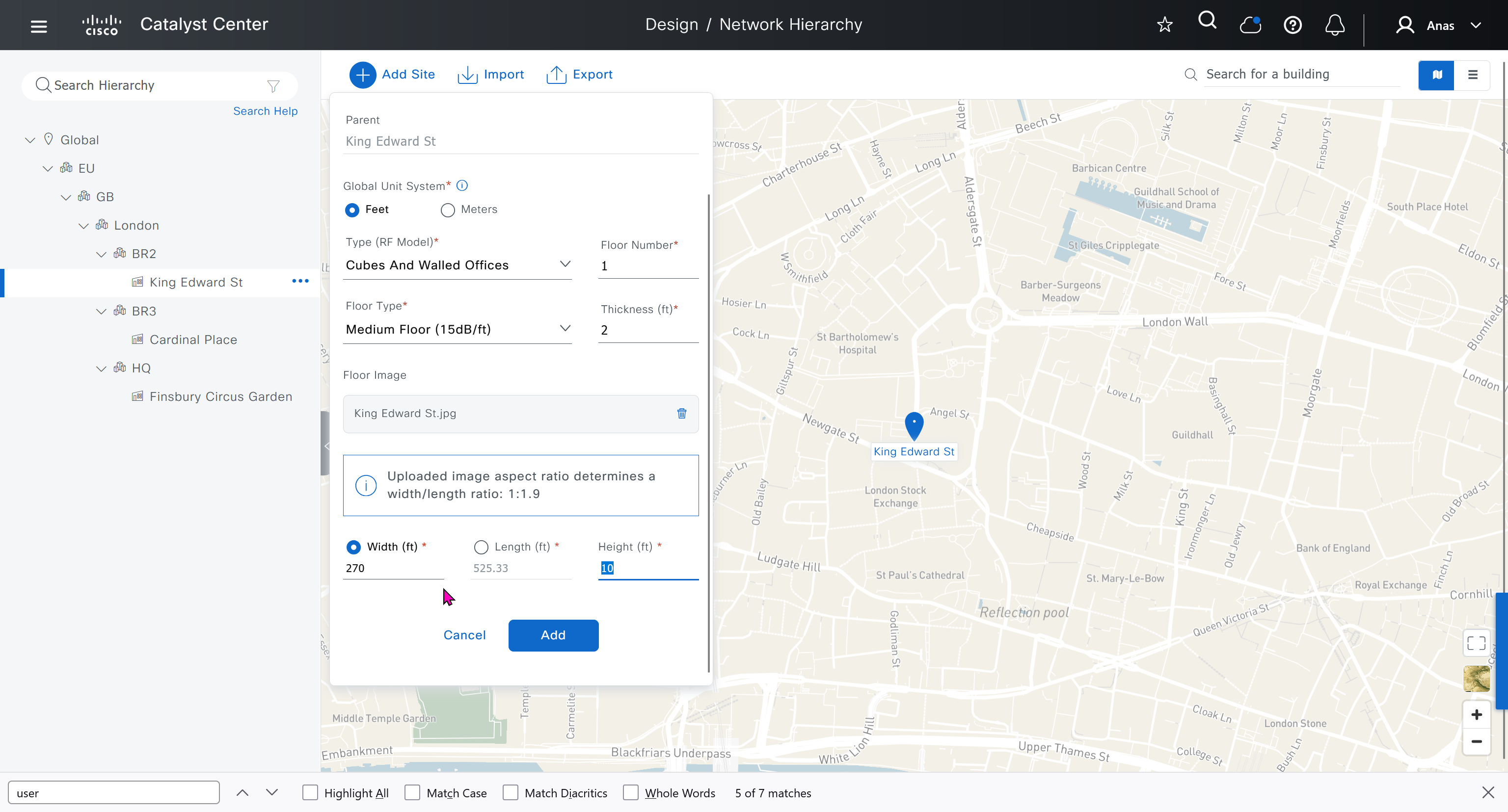

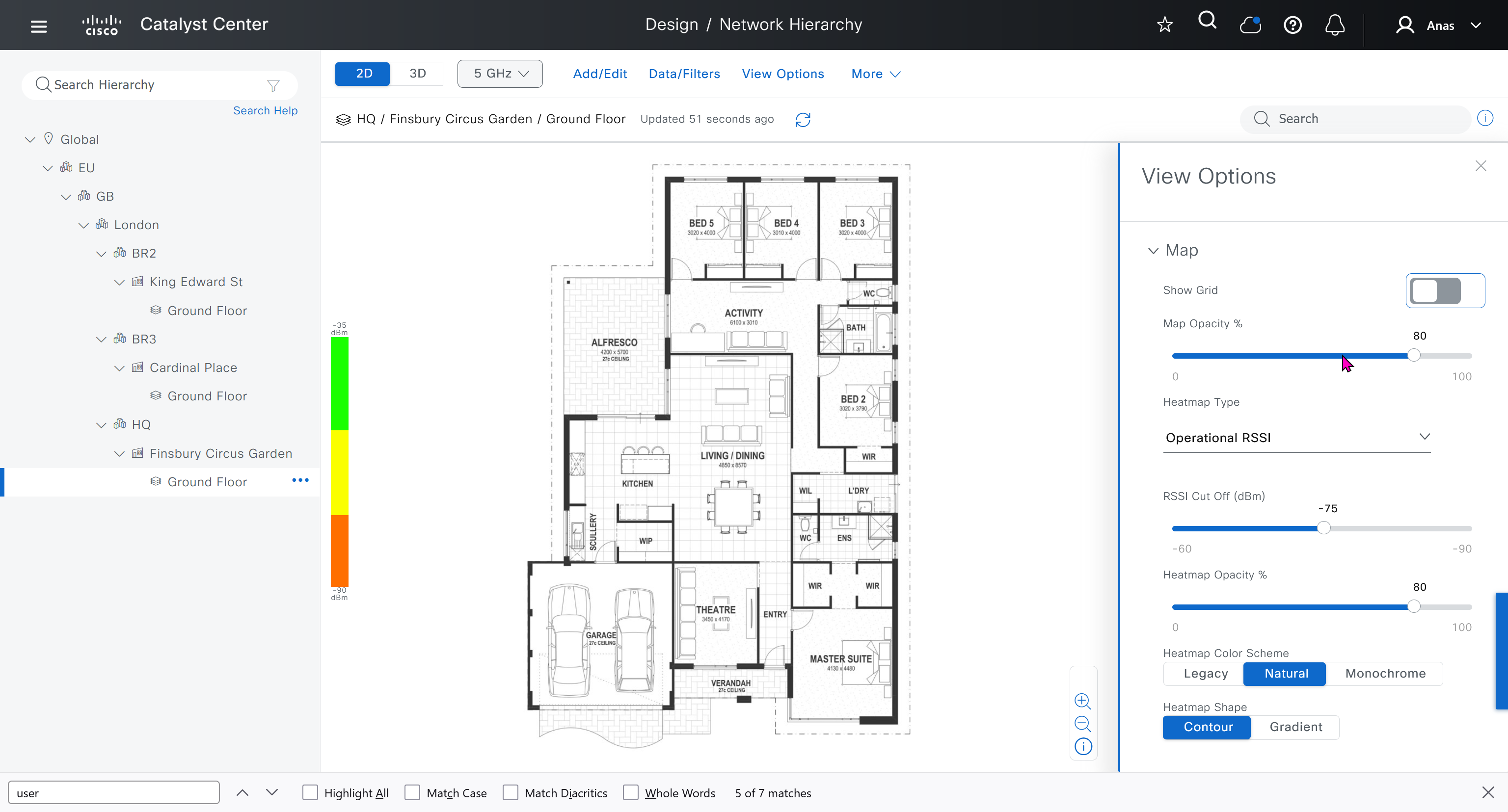
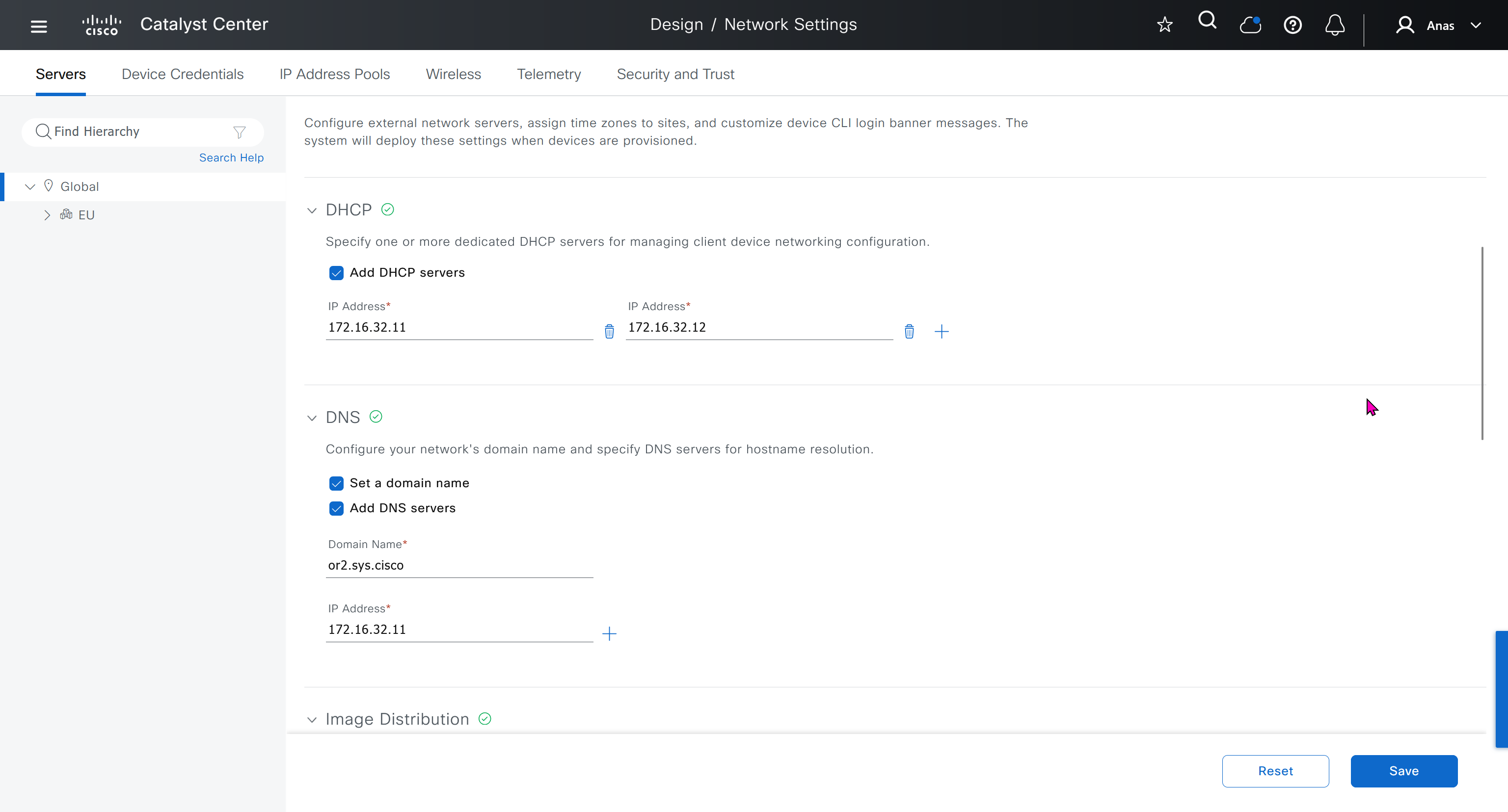
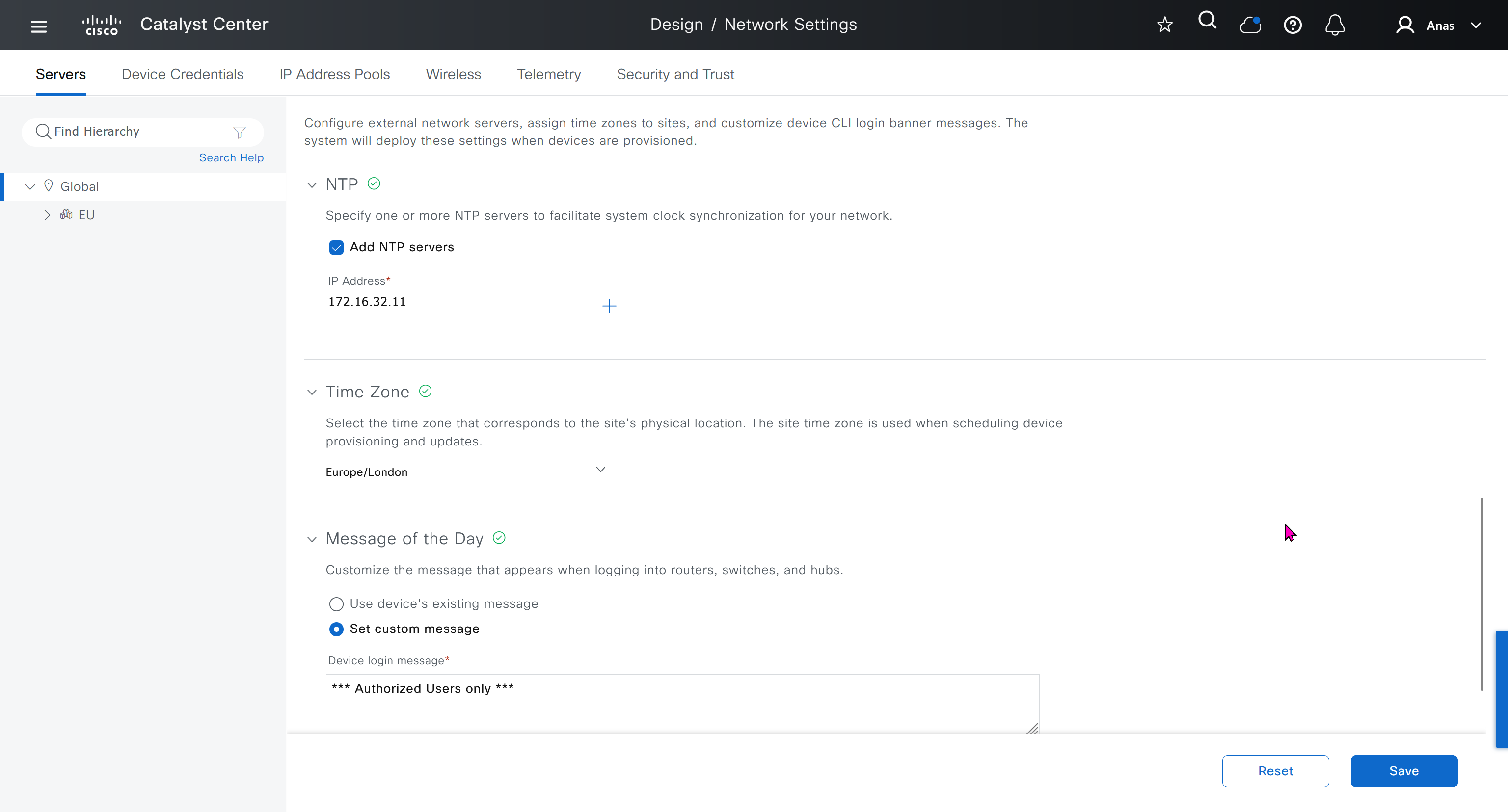
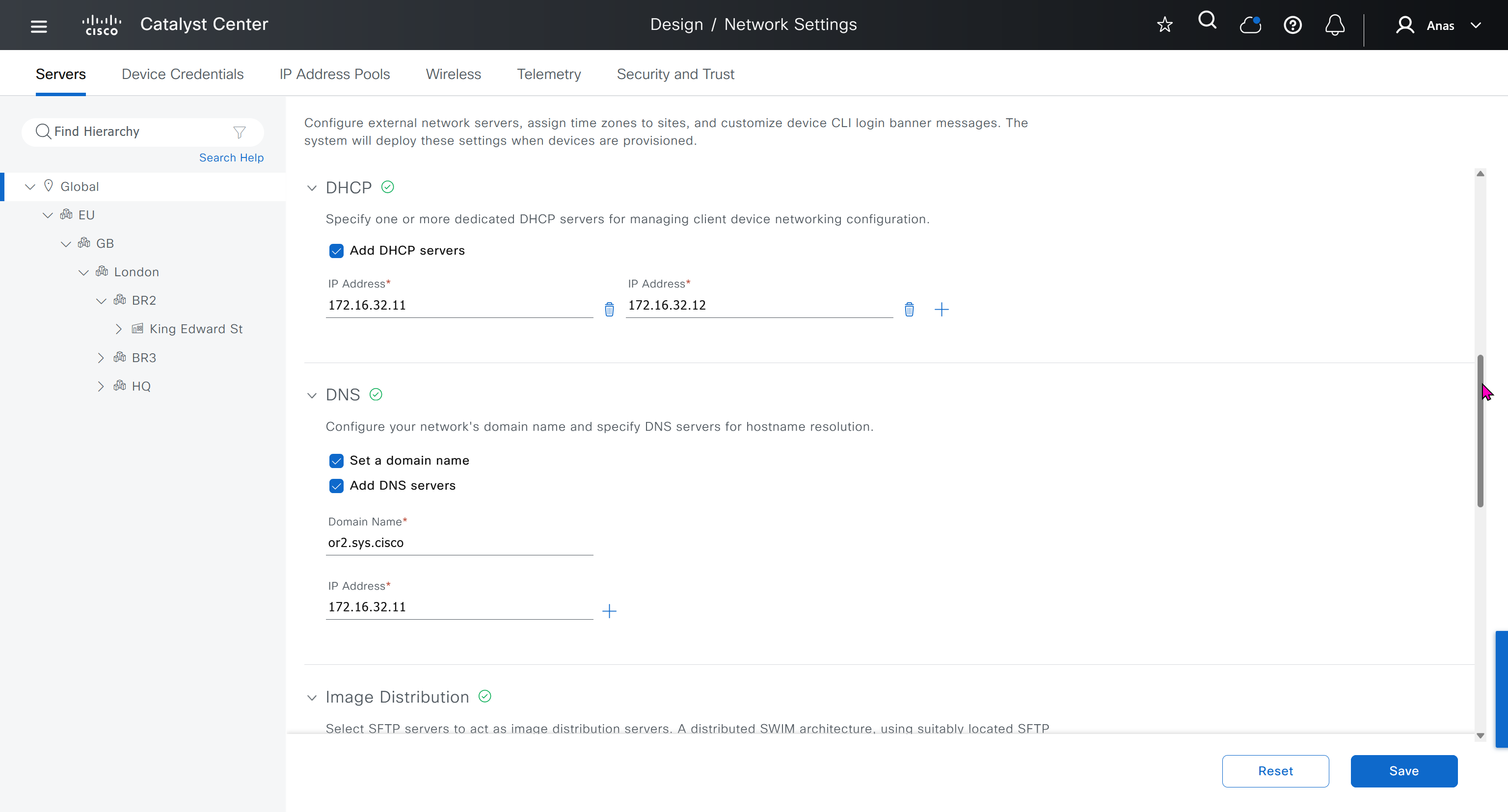
Network contains common settings similar to what DHCP contains but more such as AAA server, DHCP server, DNS server, Image Distribution (used to download the Catalyst IOS XE image), NTP server, Time Zone and Message of the day but looking at it feels like that this configuration is for the switches because this is the configuration that will be pushed to devices as they get provisioned into DNAC
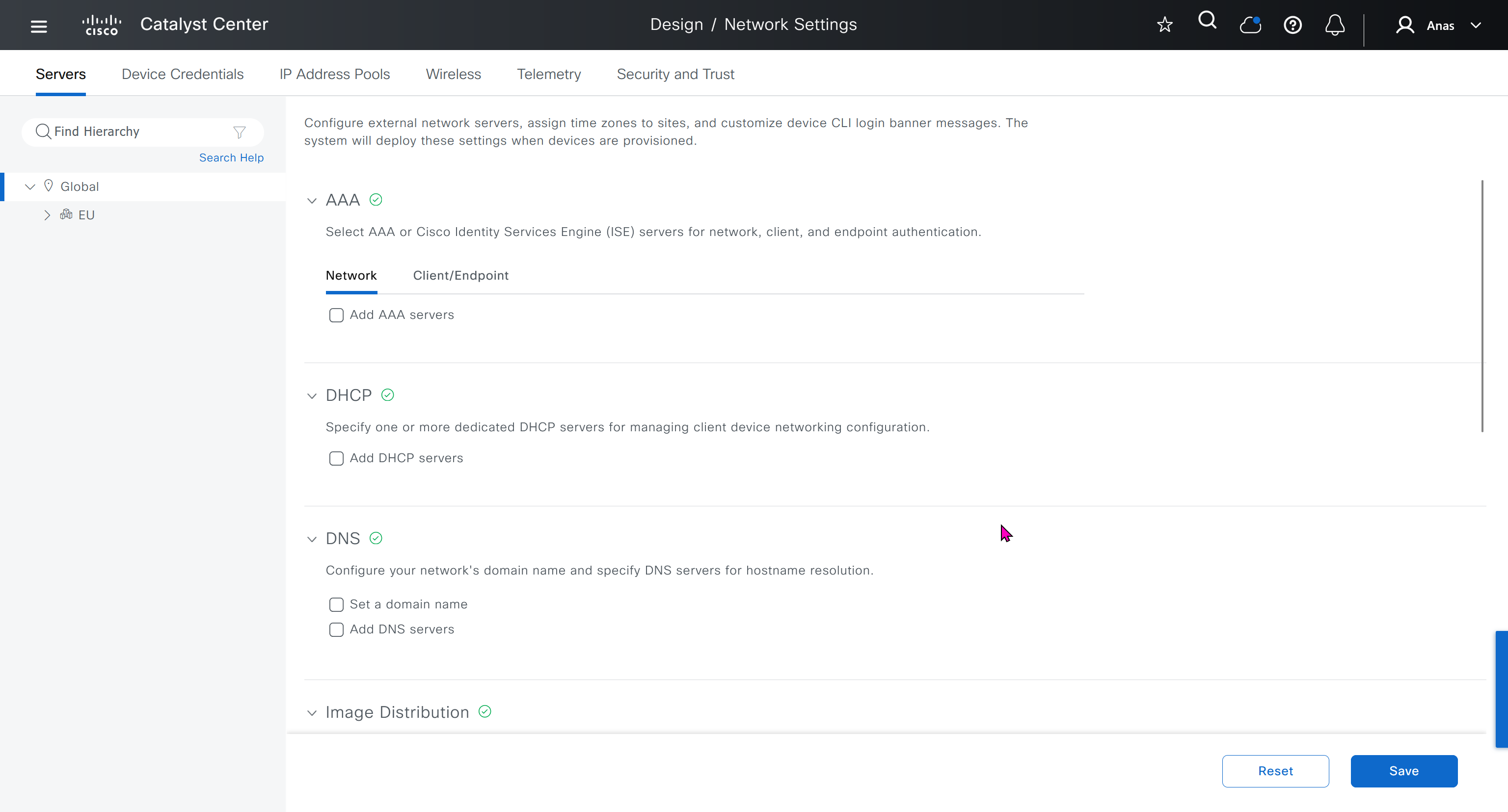
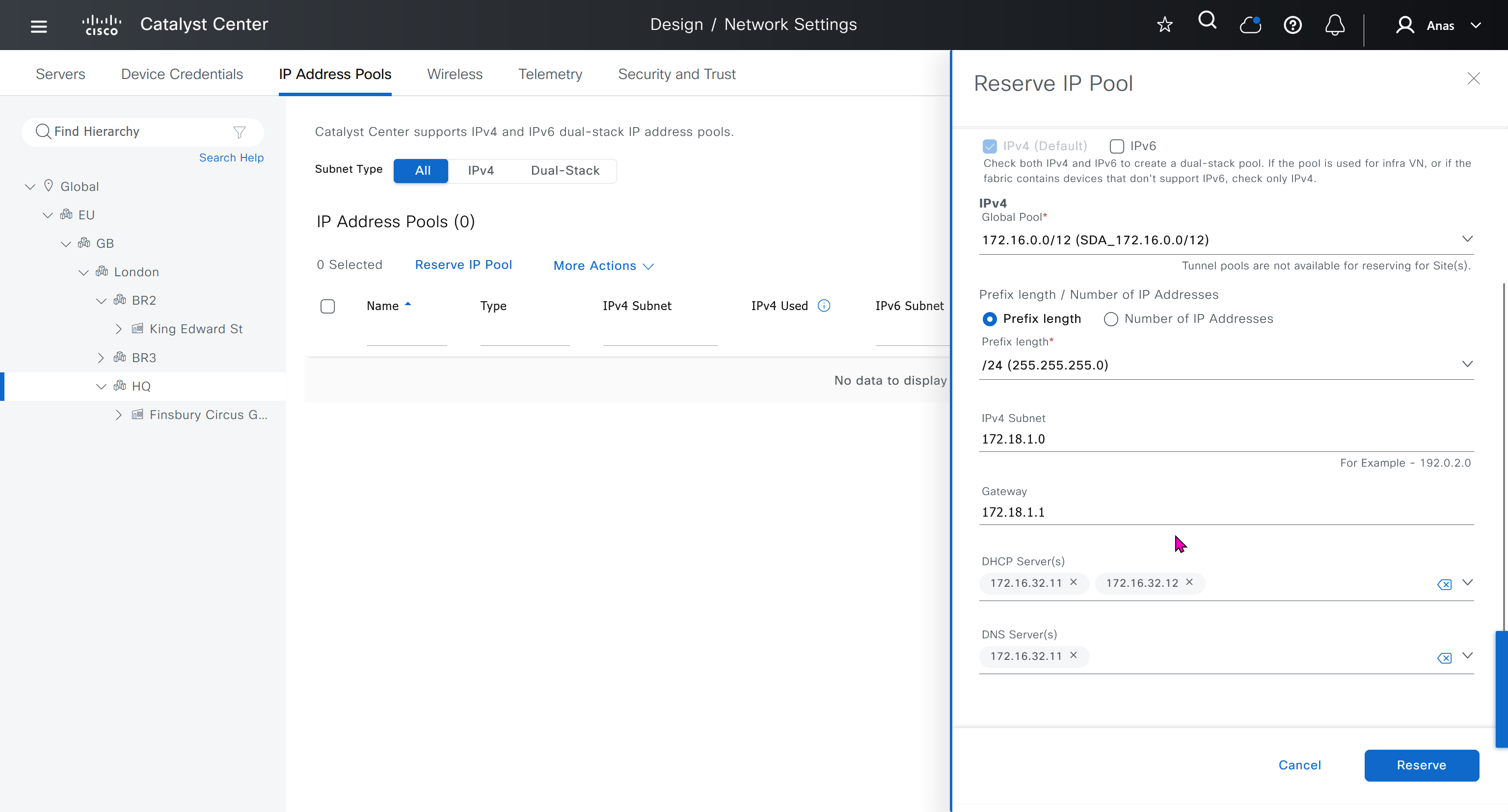
In DHCP servers section we will also specify ISE IP address because it is one of the ways for ISE to perform profiling based on DHCP request from device
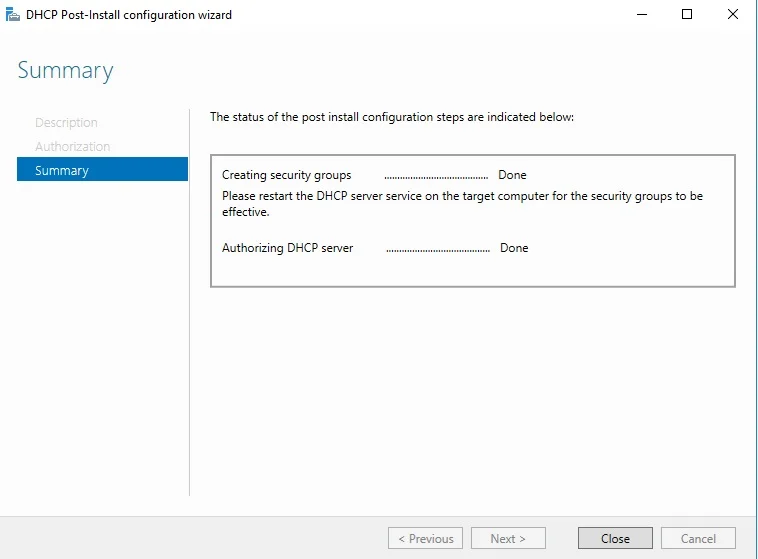
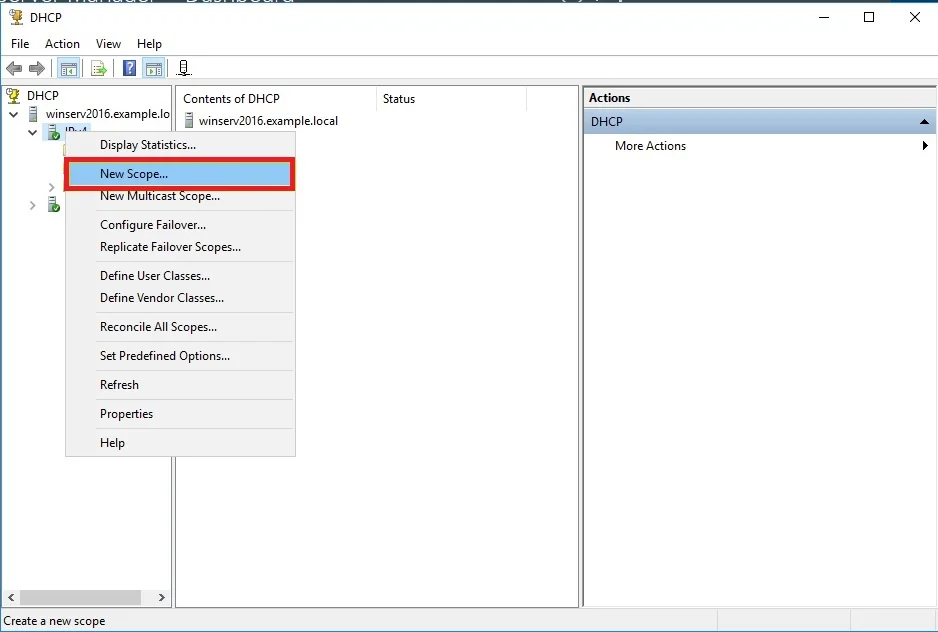
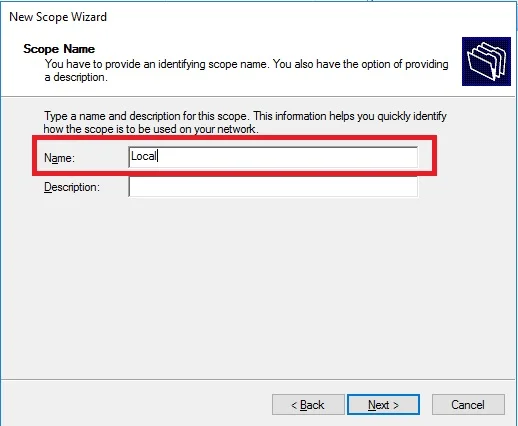
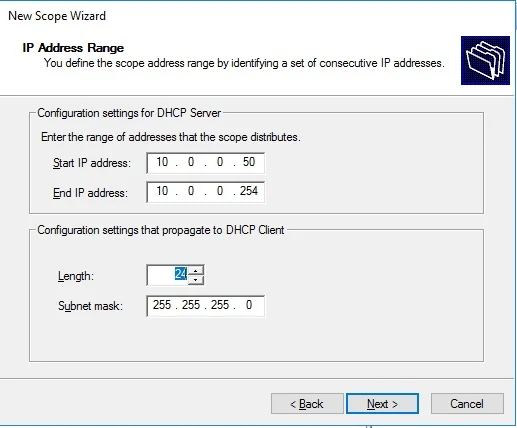
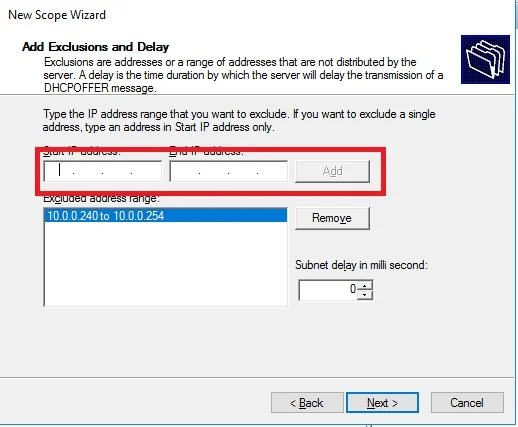
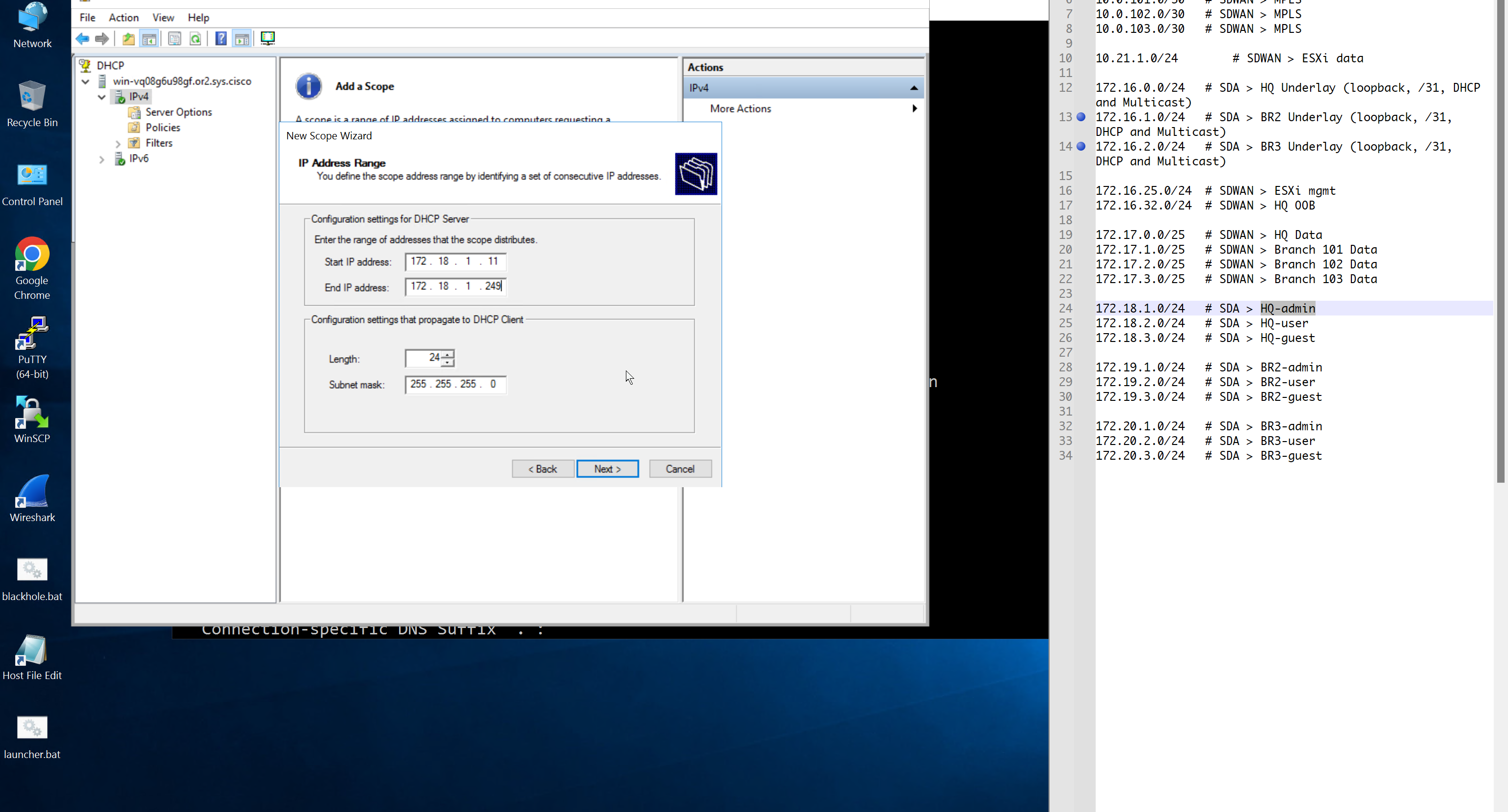
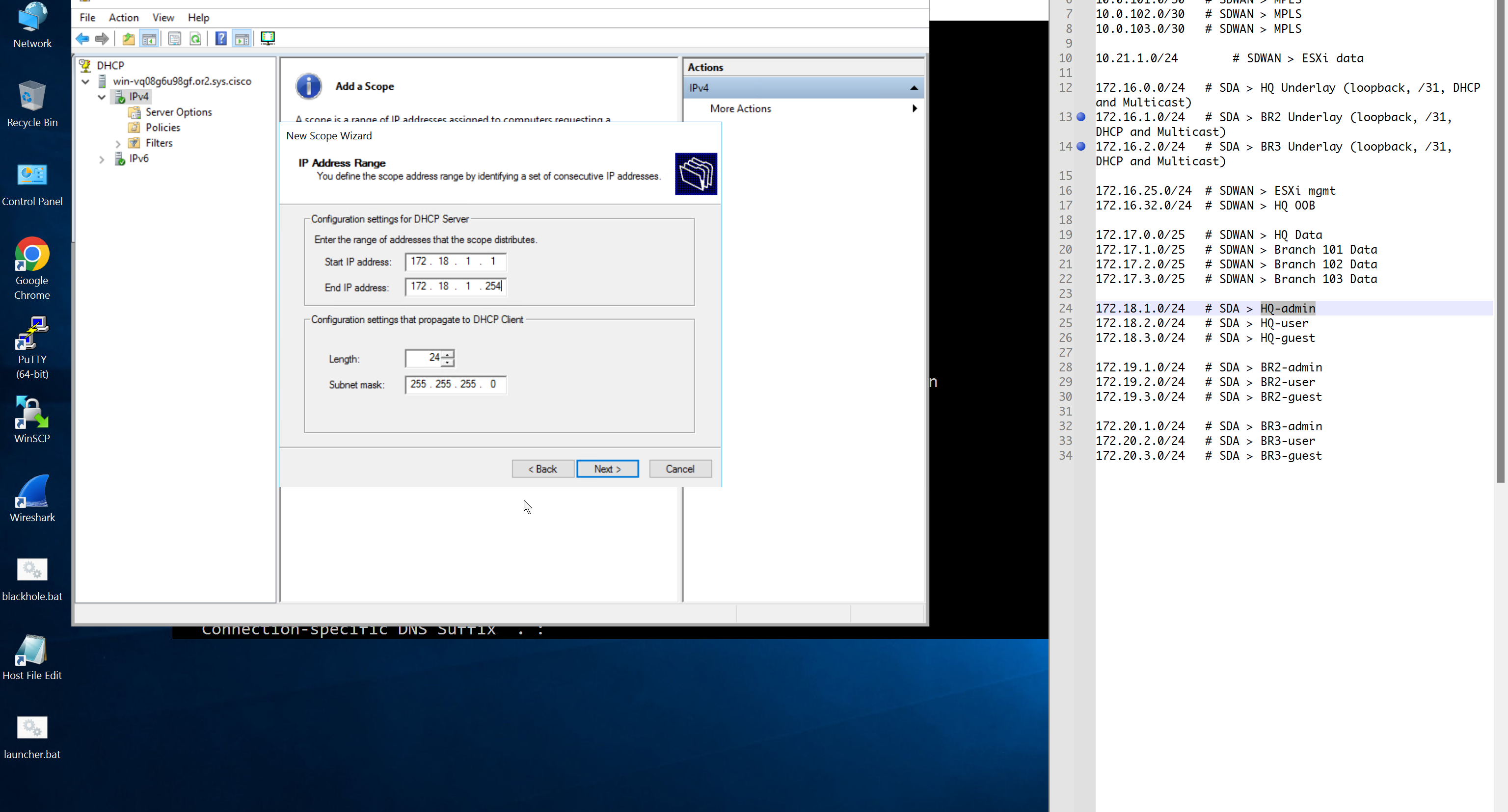
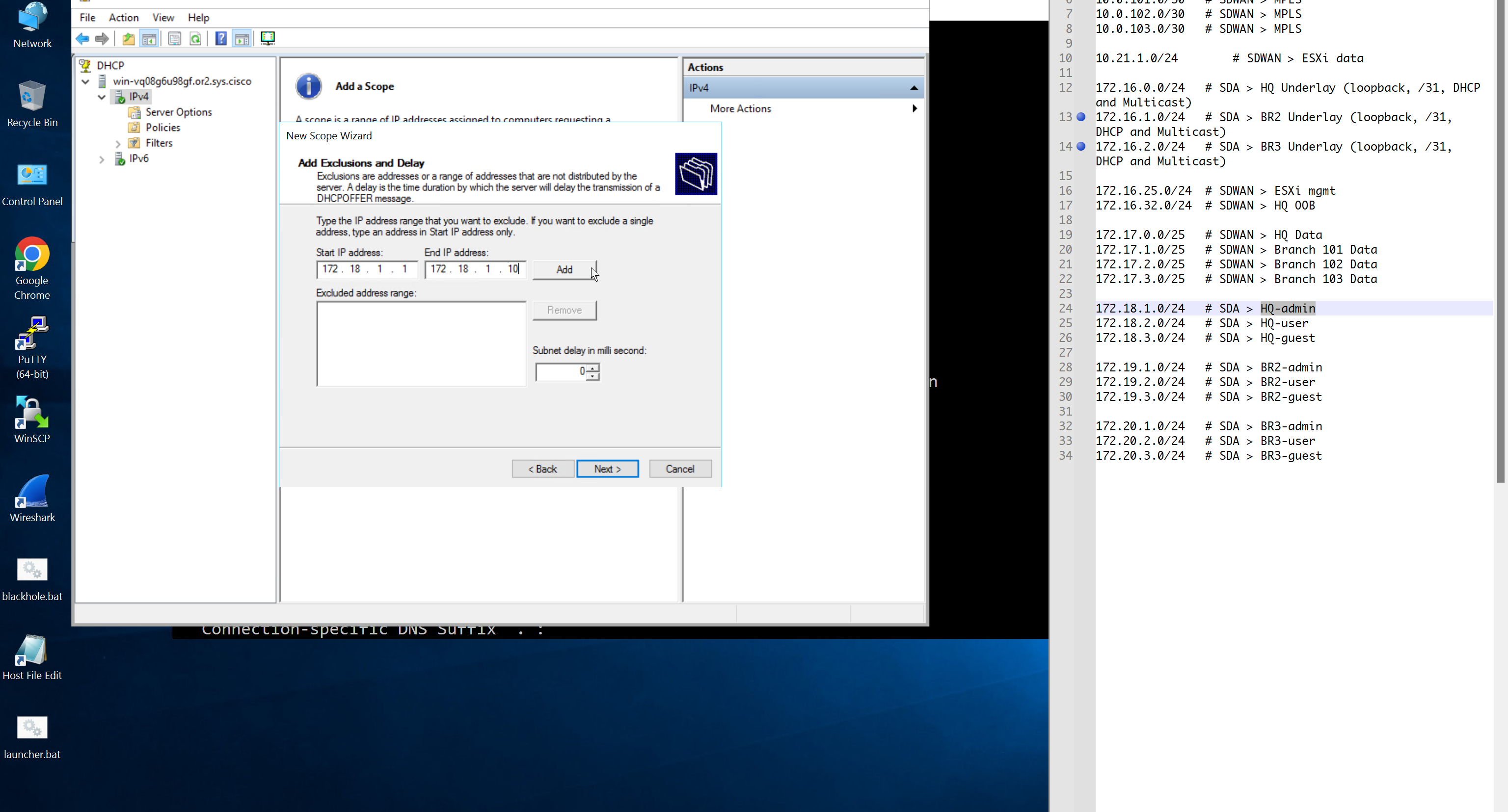
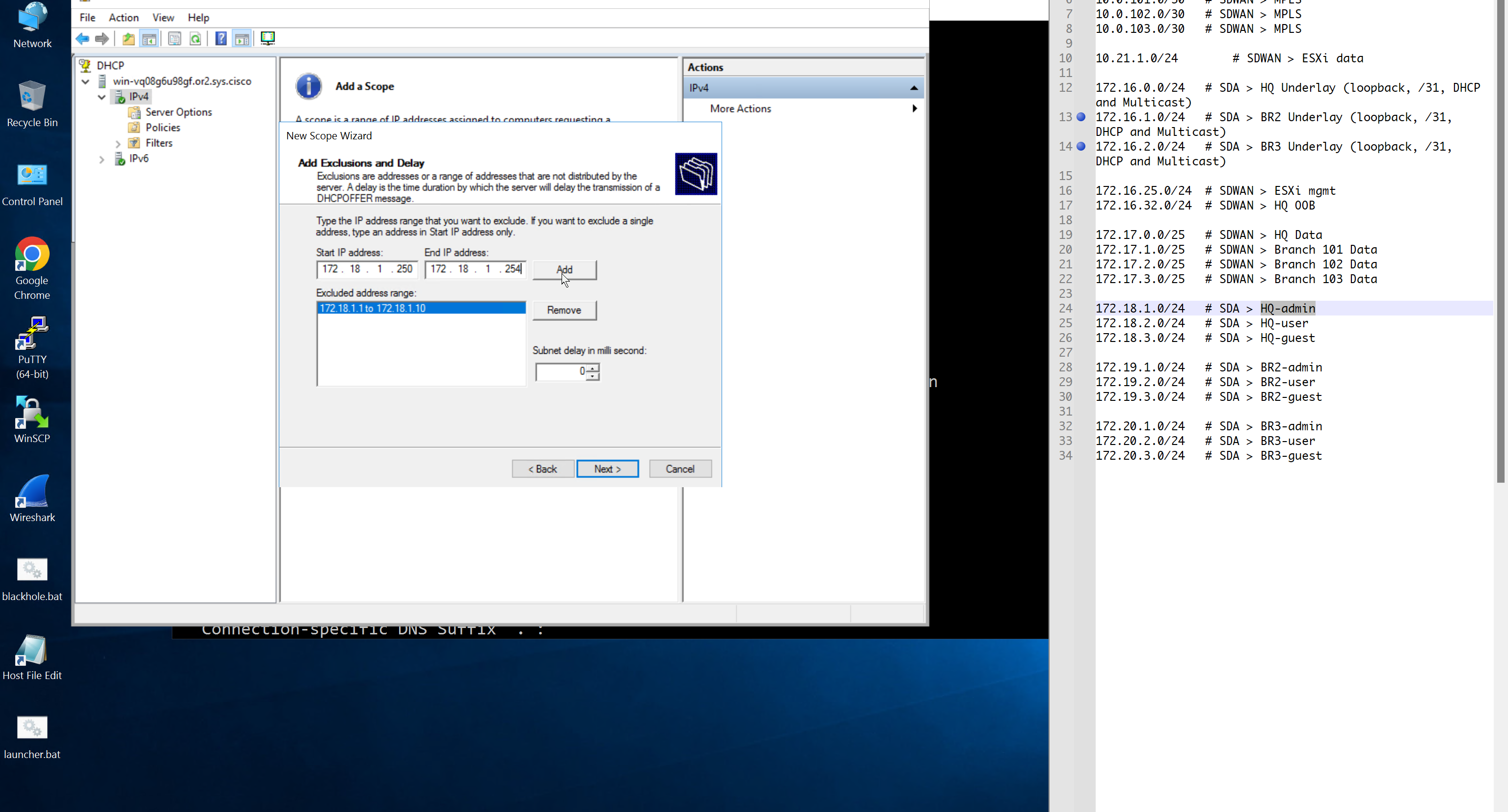
Create DHCP scopes as shown below



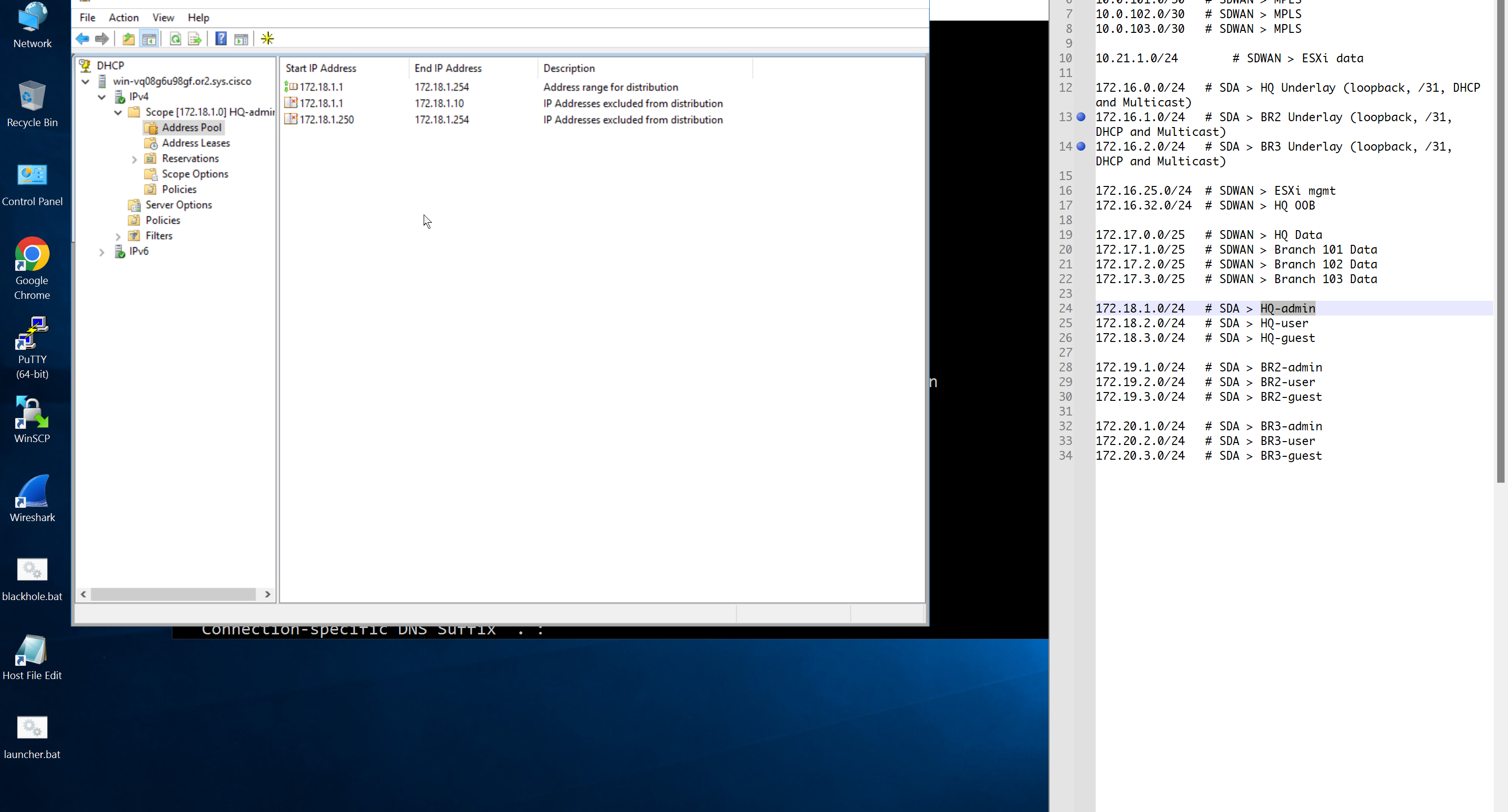
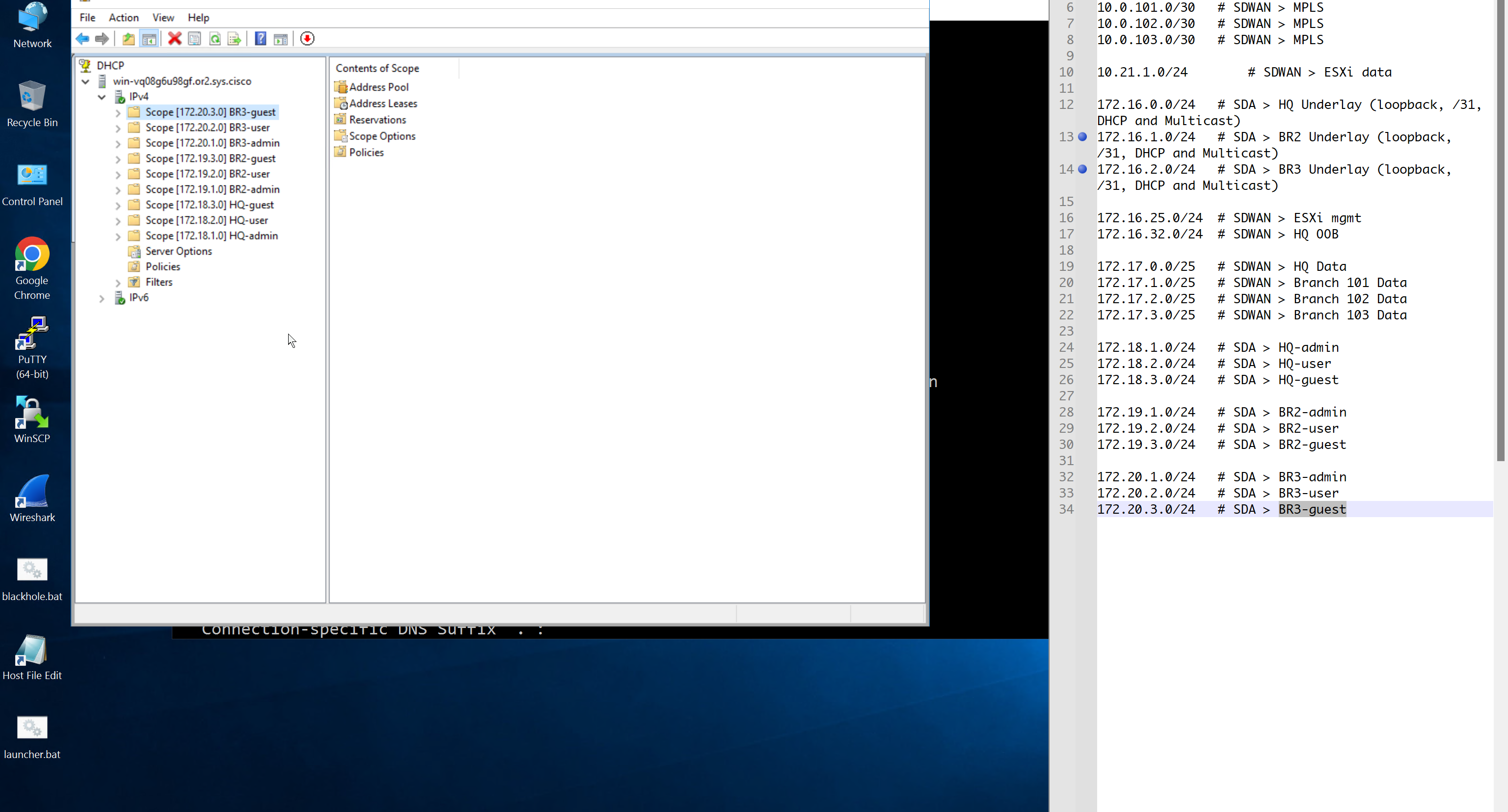
AAA “Network” is for network device administration
and AAA “Client/Endpoint” is 802.1x, we will only configure 802.1x for now


When we click on lower network in hierarchy, for first time we see this symbol which when used in GUI means that configuration is being inherited but they can be overwritten on lower levels


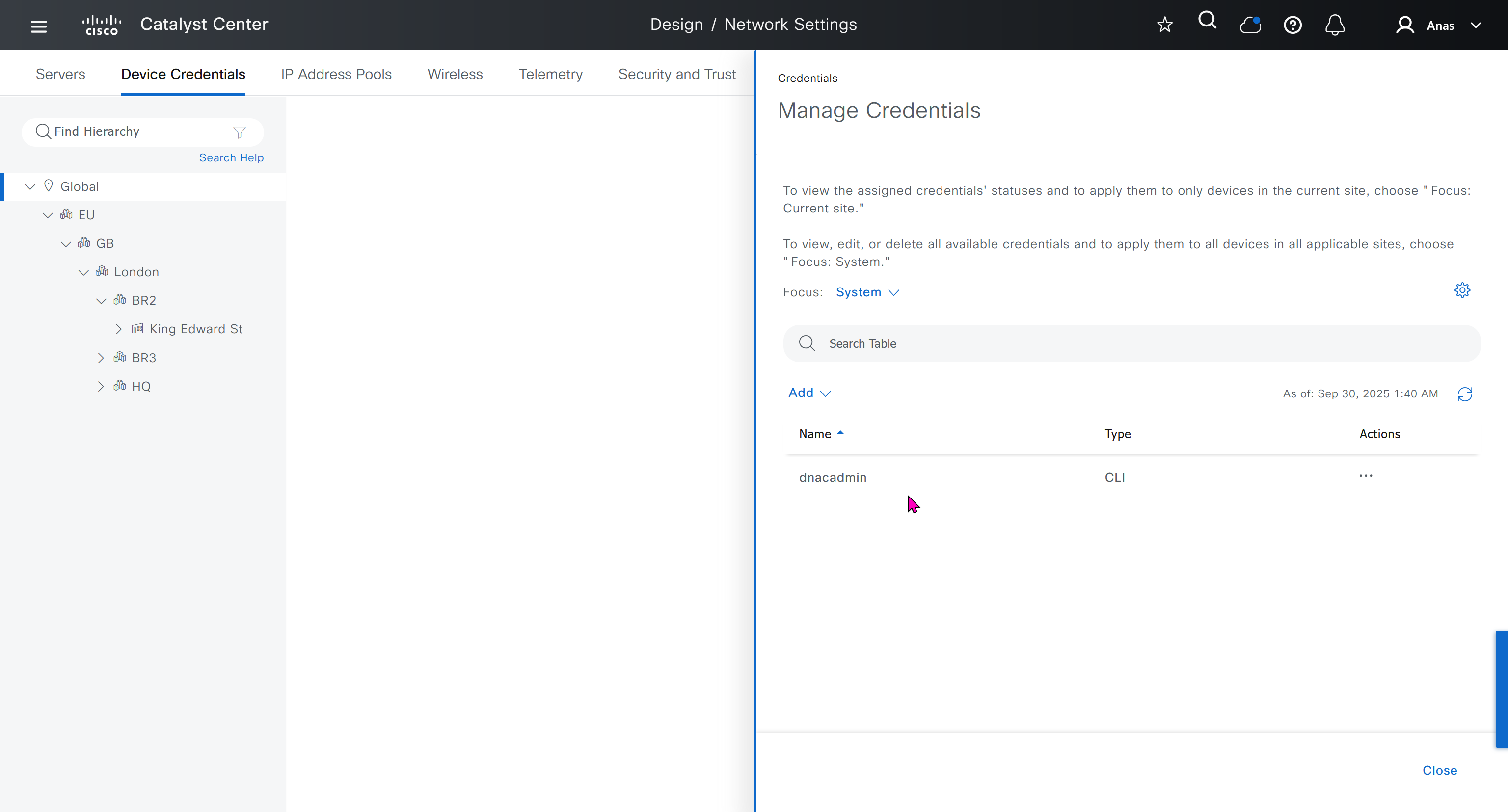
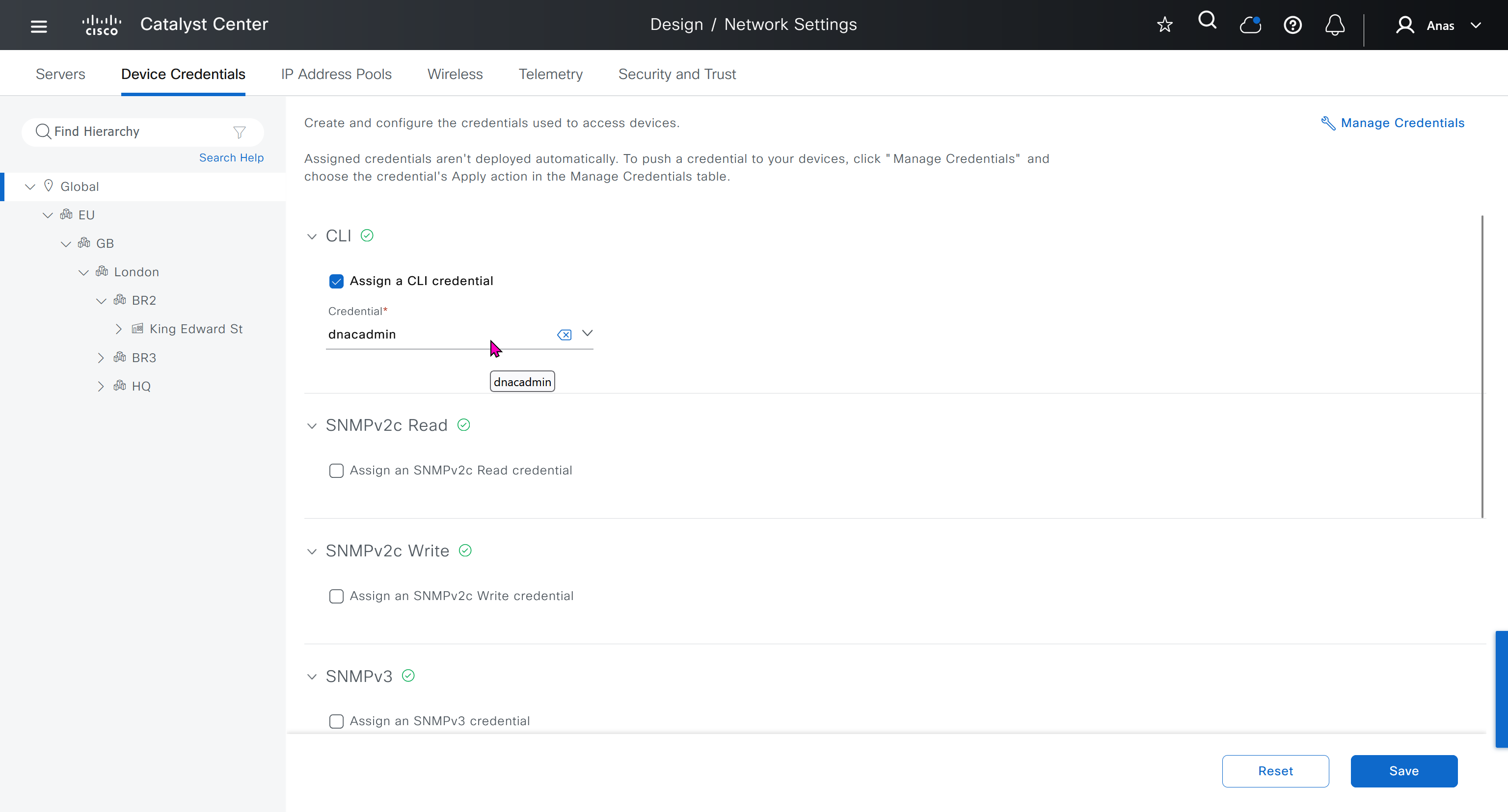
Device credentials is where we feed DNAC with device login details for SSH, SNMPv3 and HTTPS (usually not used

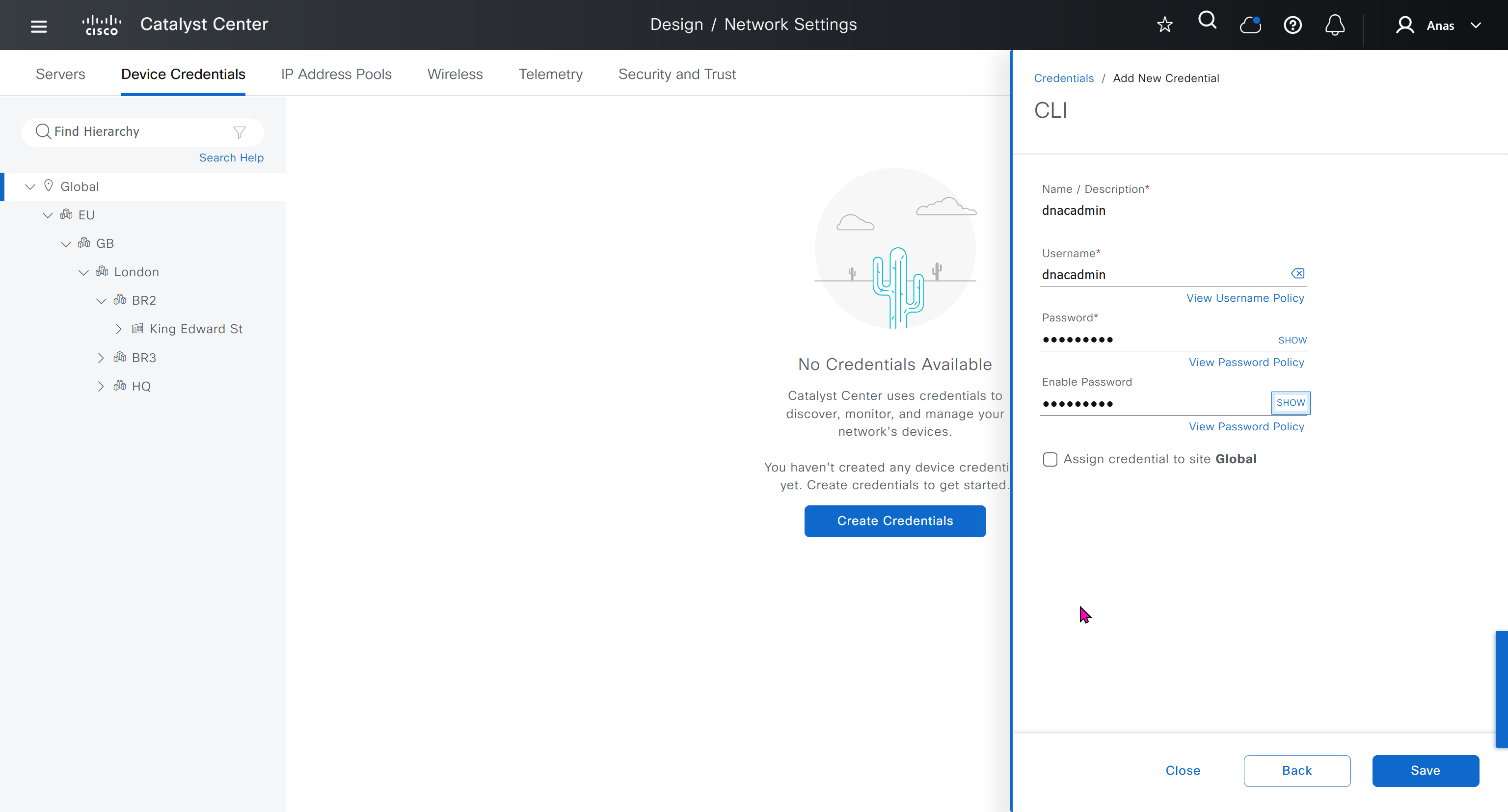
for dnac credentials, try not to use admin as it can cause conflict instead use dnacadmin
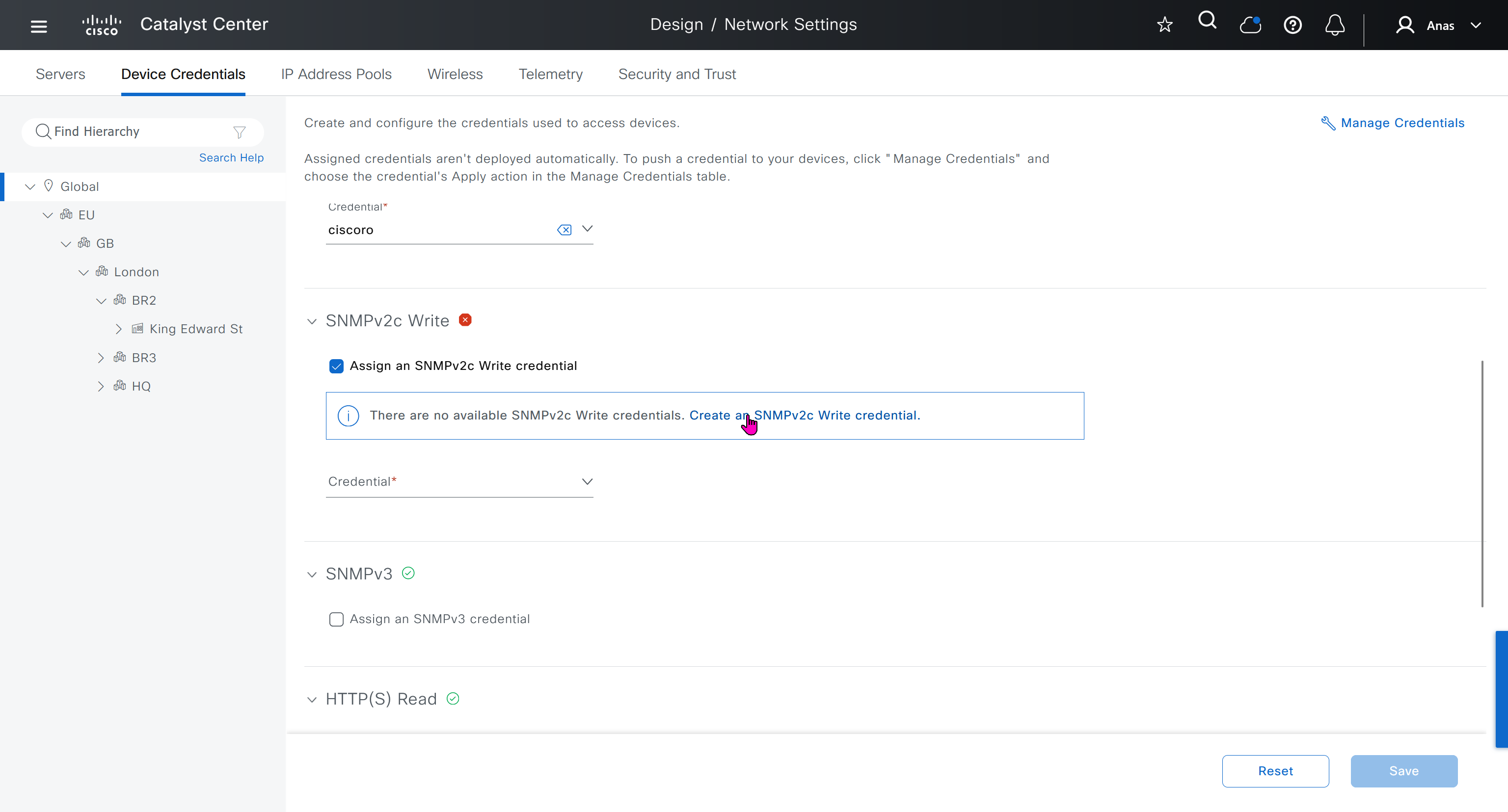
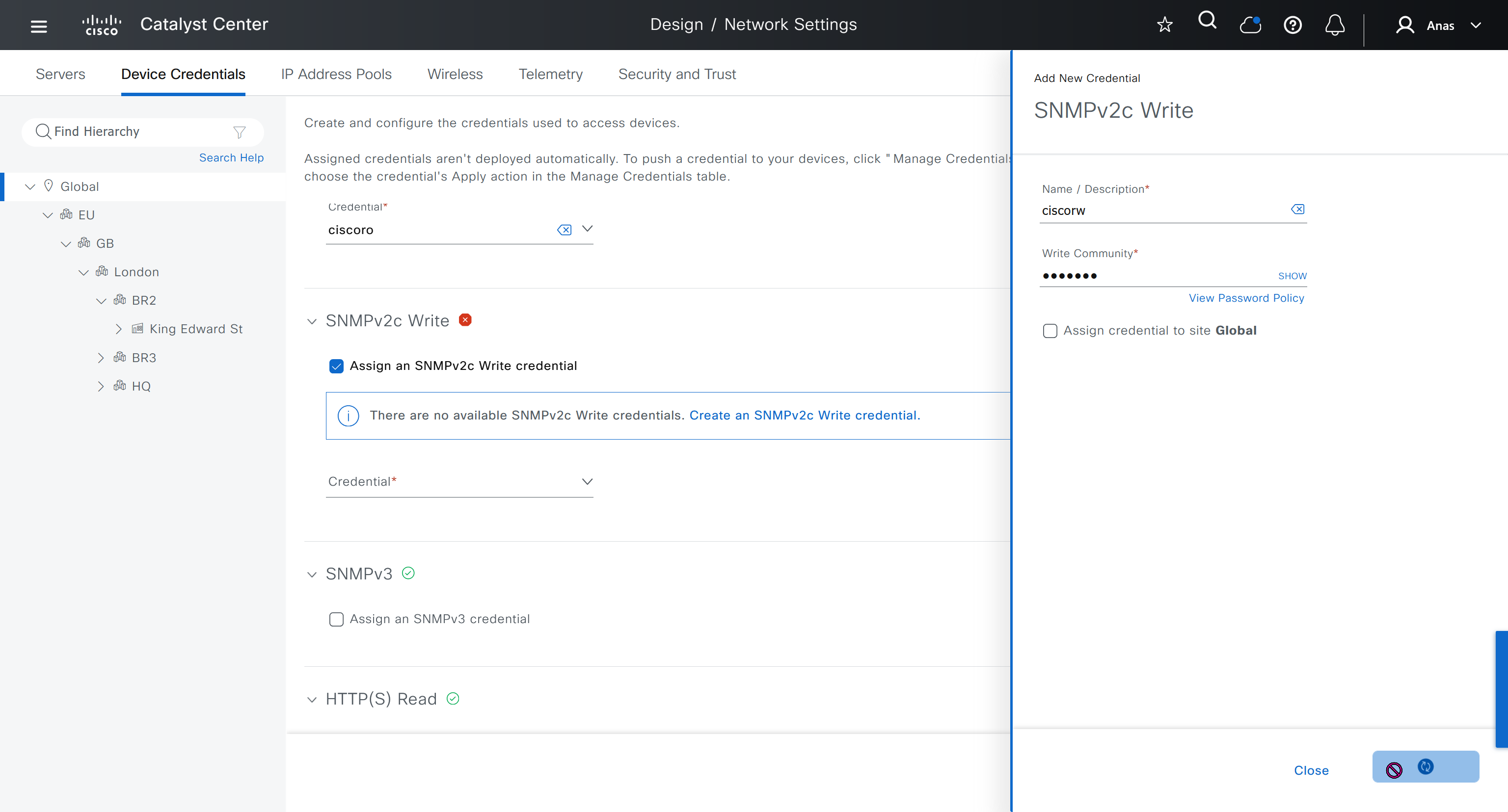
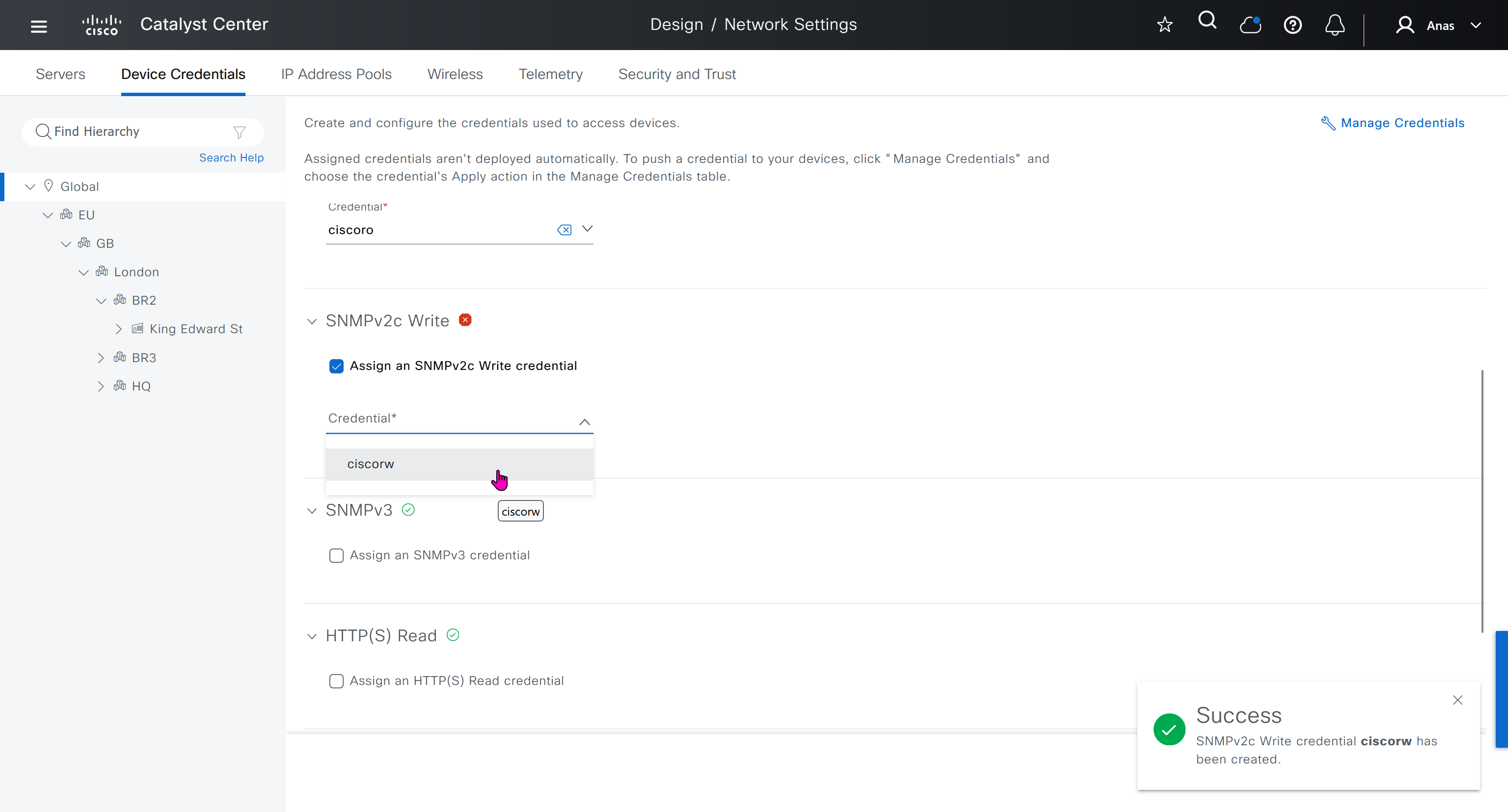
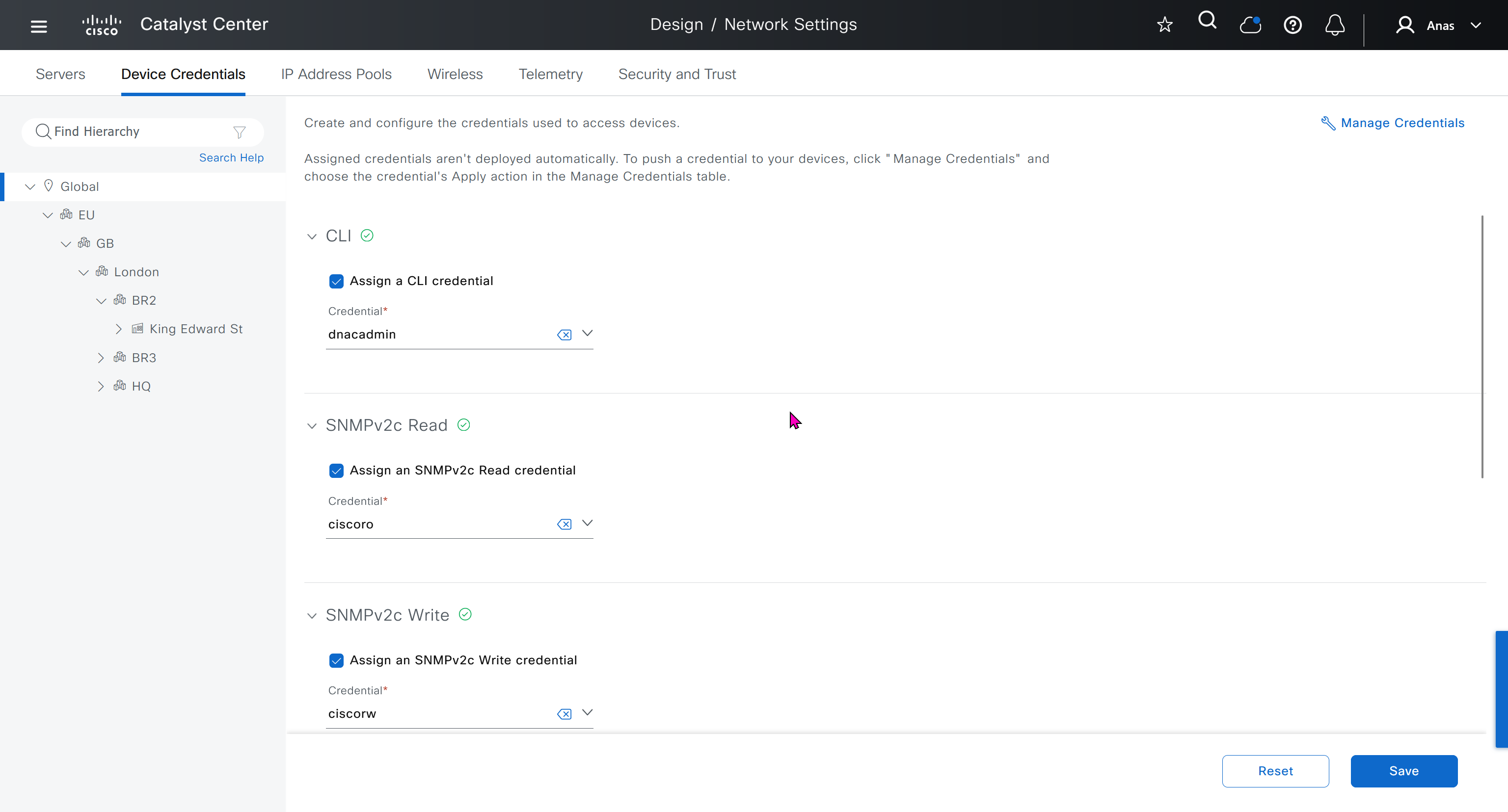
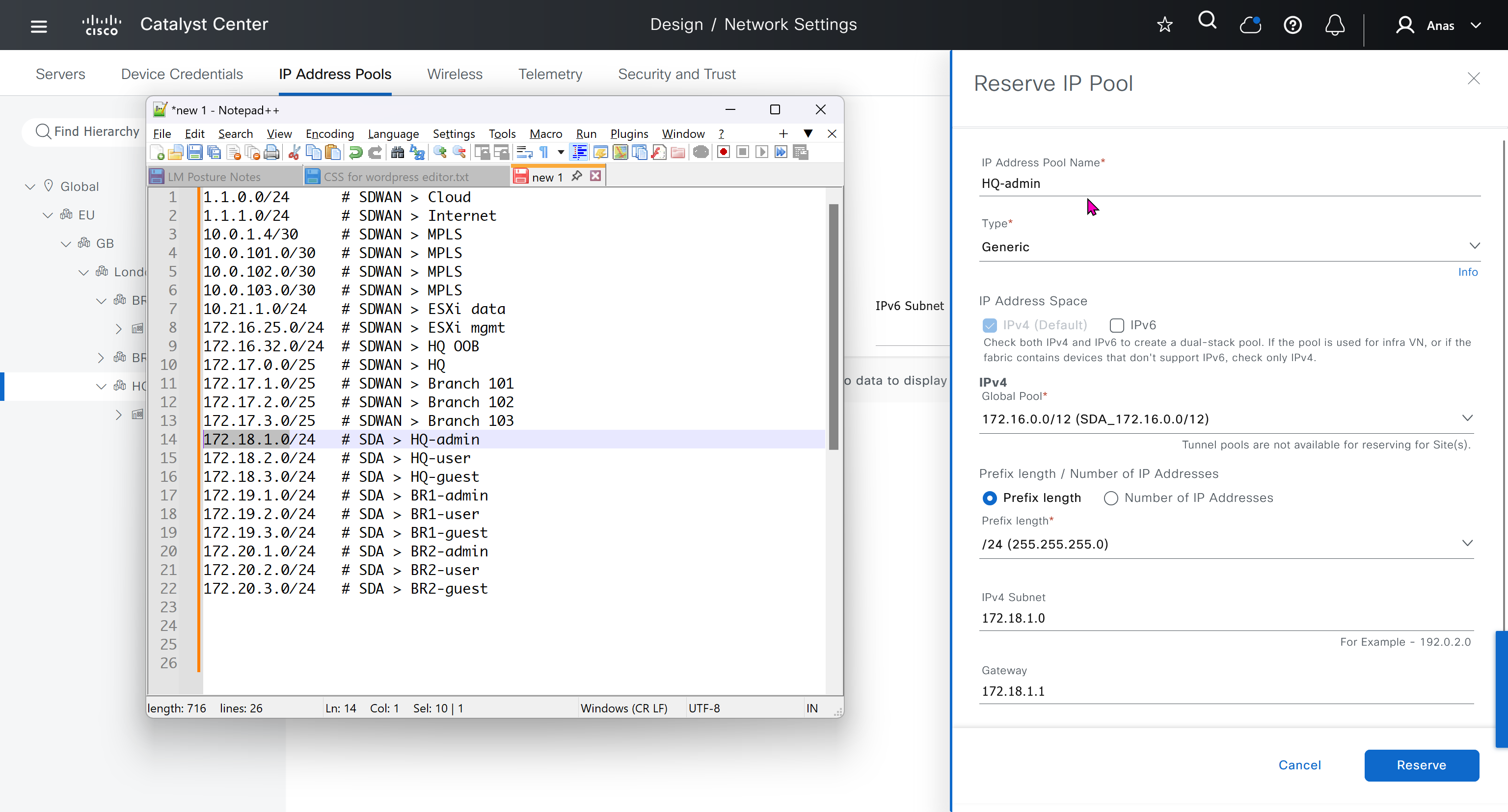
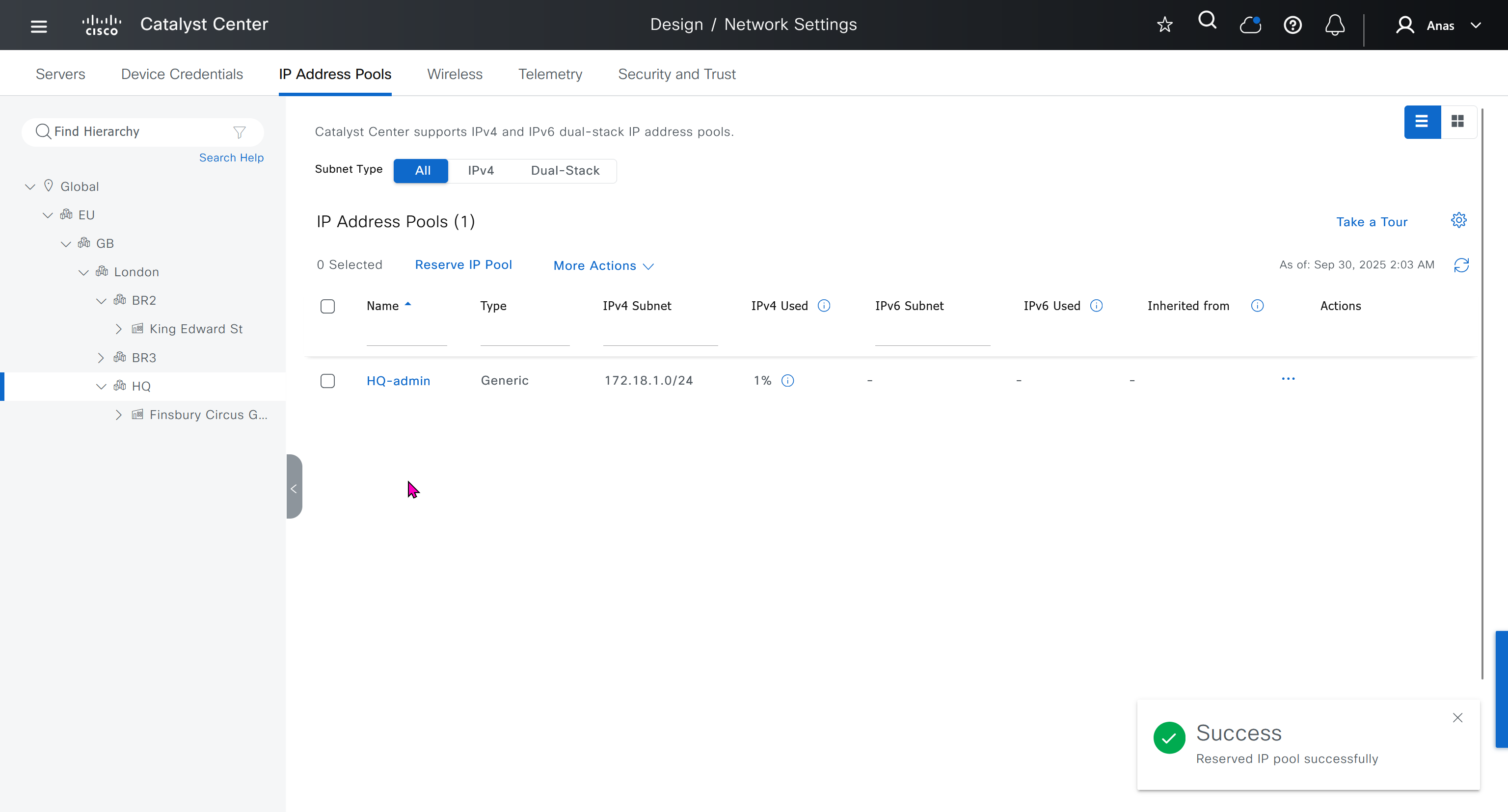
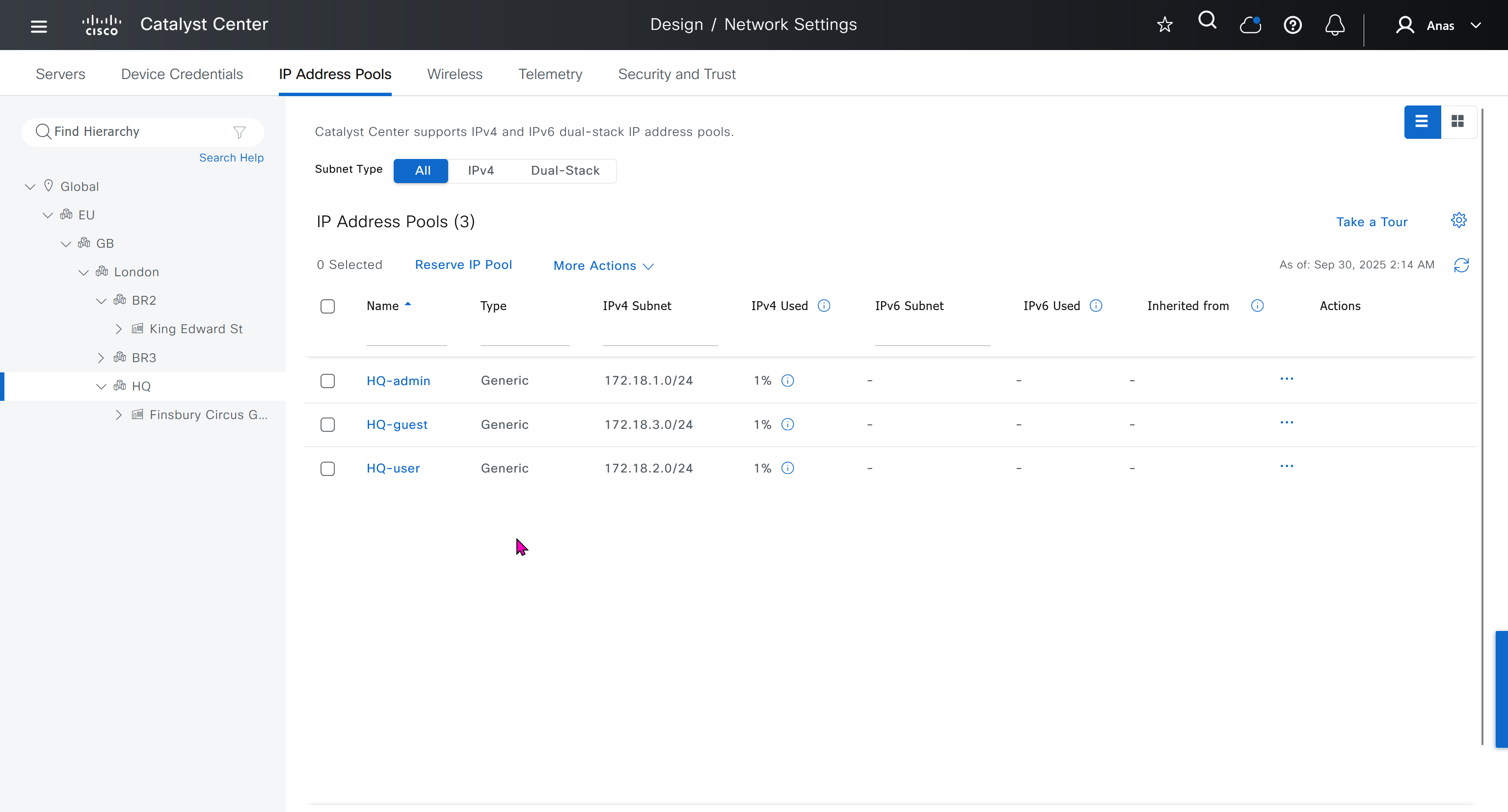
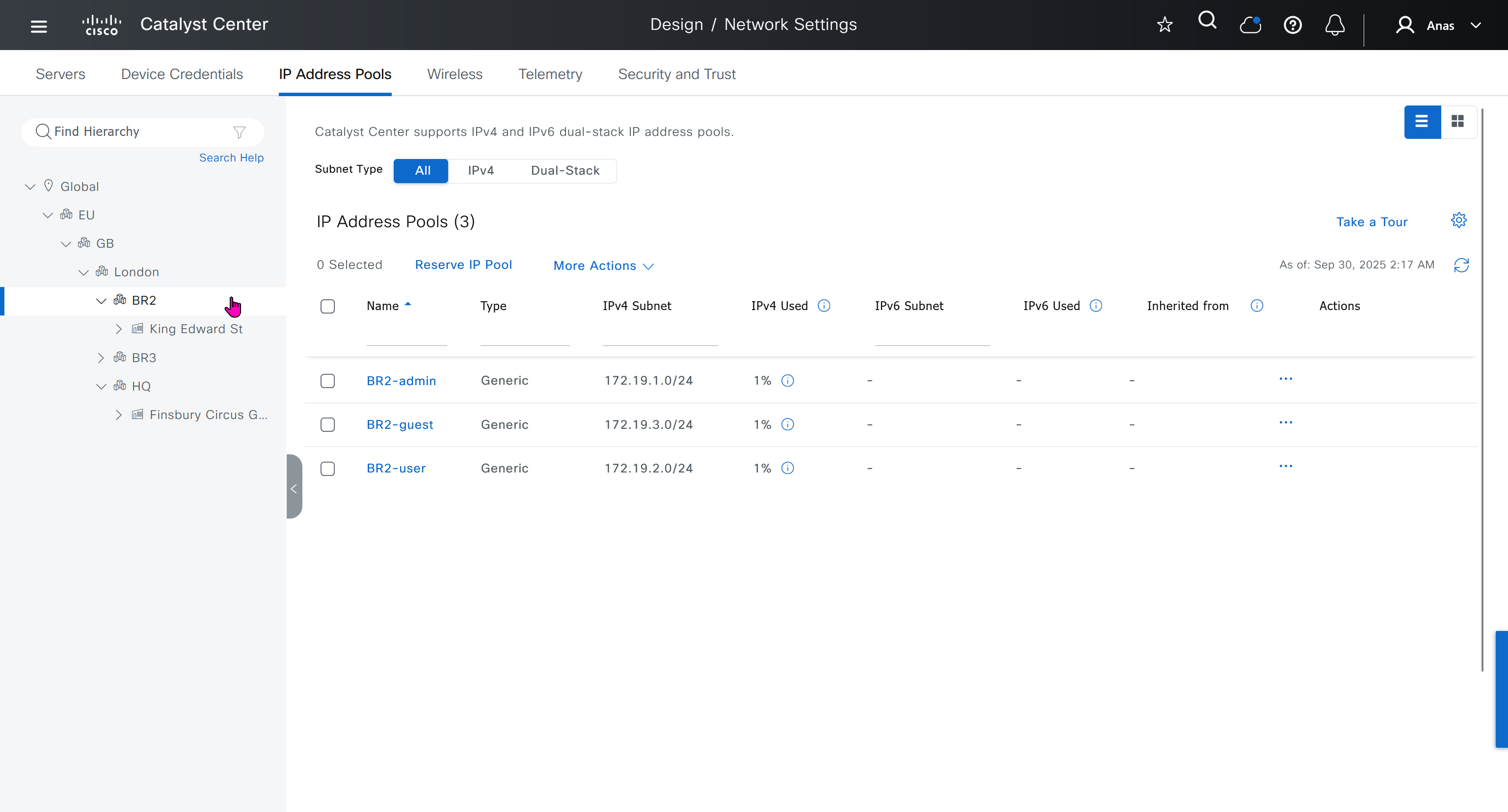
IP address pool is where you define all the subnets that we need to deploy all across SDA, make sure to reserve the supernet at global level
Make sure that we carefully plan and deploy subnets because once it becomes part of SDA, it can be hard to remove it
You can only create IP pools at the global level, Add button is only available at global level and at lower hierarchy you simply reserve IP pools for use
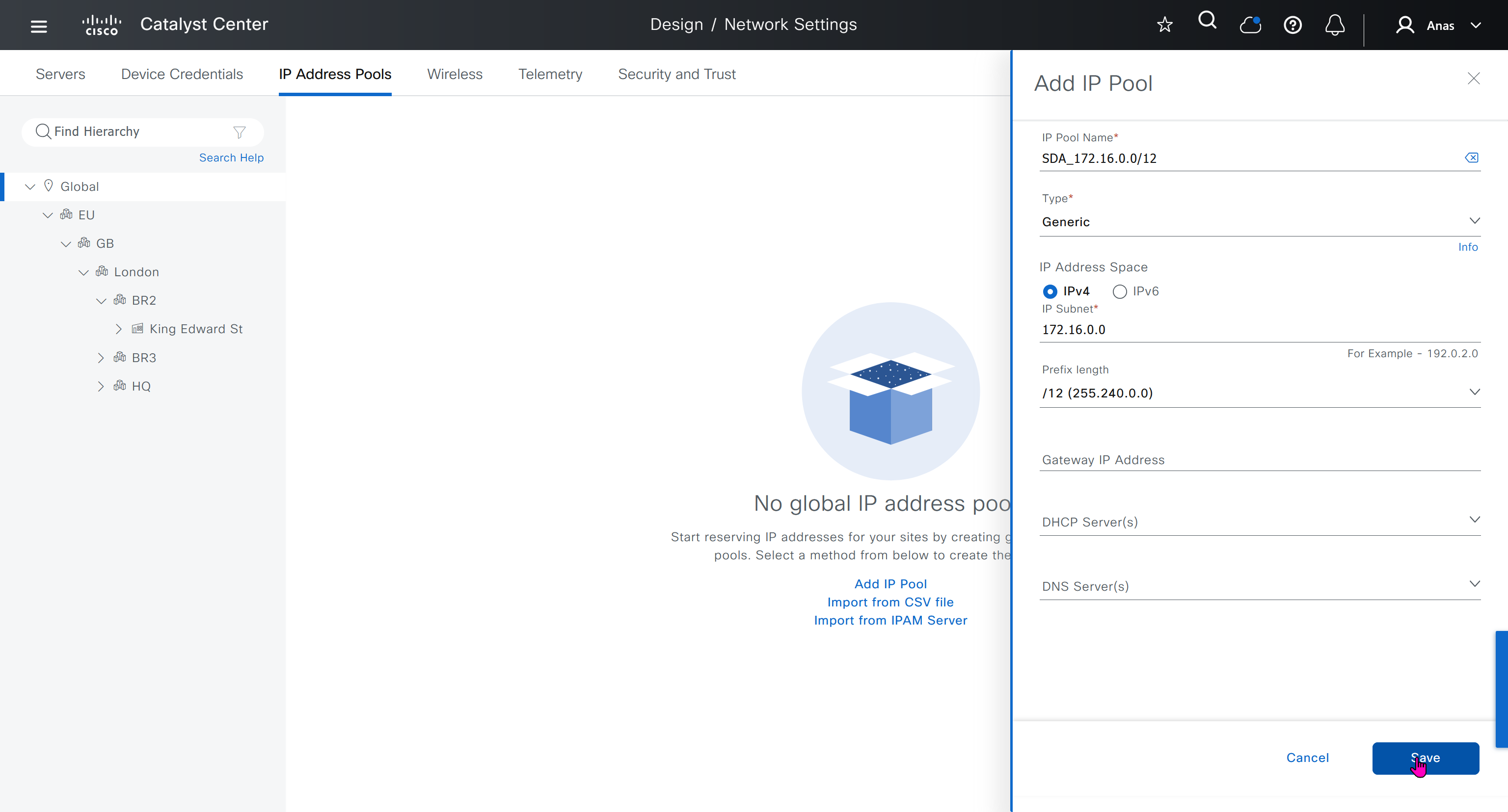
IP address pool type for SDA will be generic
When defining IP address pools at Global level then we don’t need to define the gateway IP address, DHCP server and DNS server
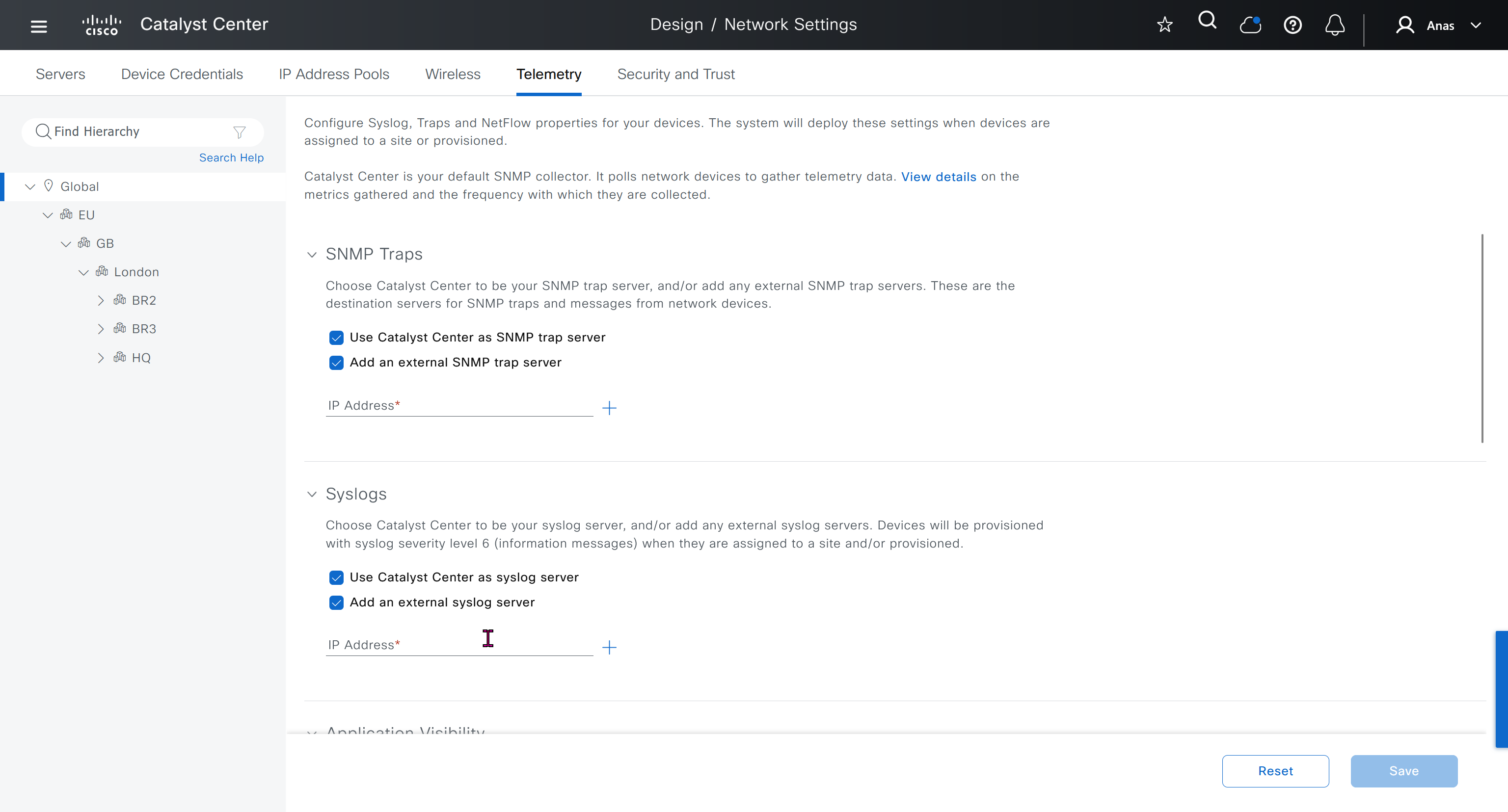
Telemetry section is where DNAC configured devices to uses SNMP, netflow and Syslog to send telemetry information to DNAC
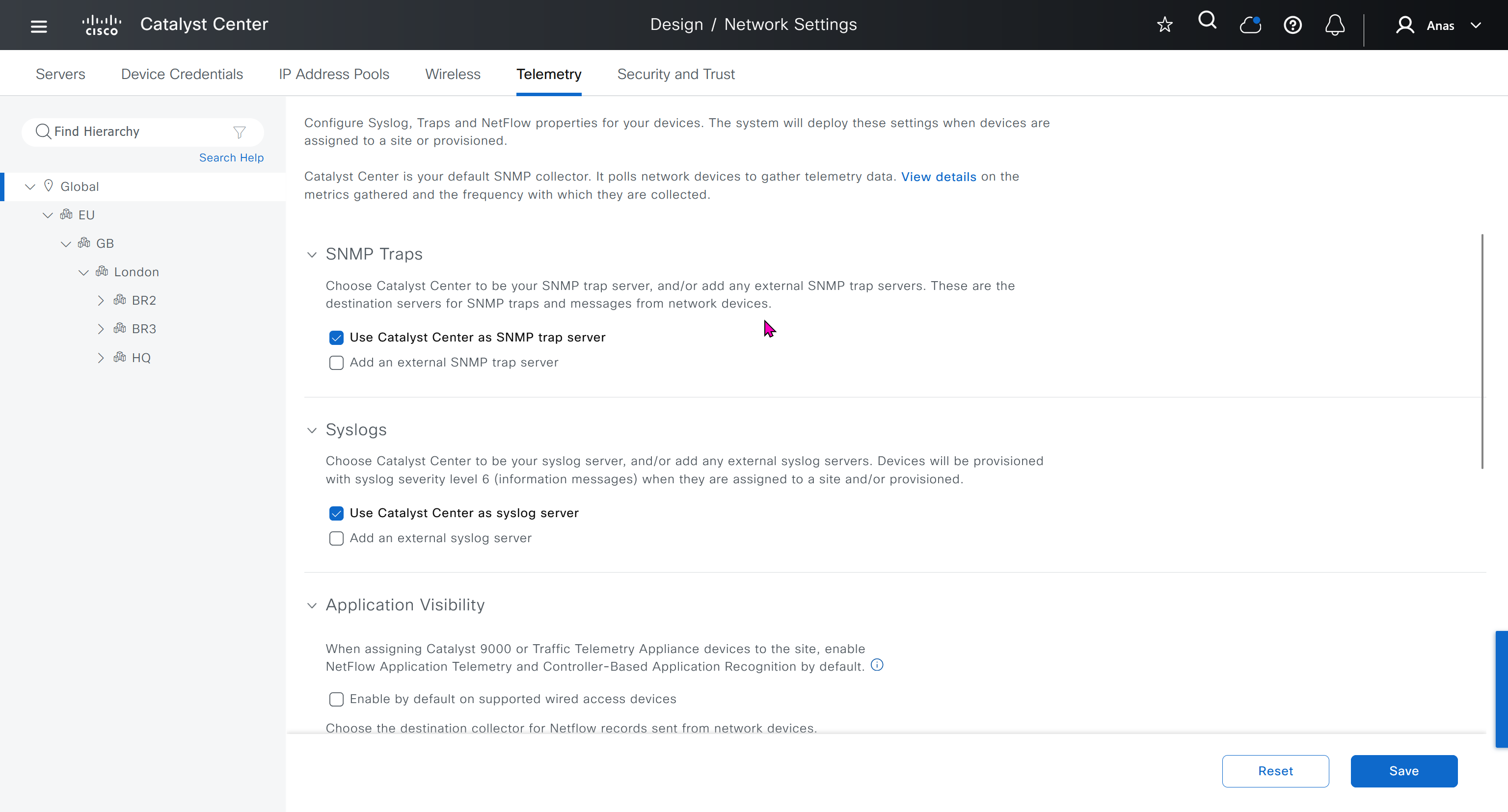

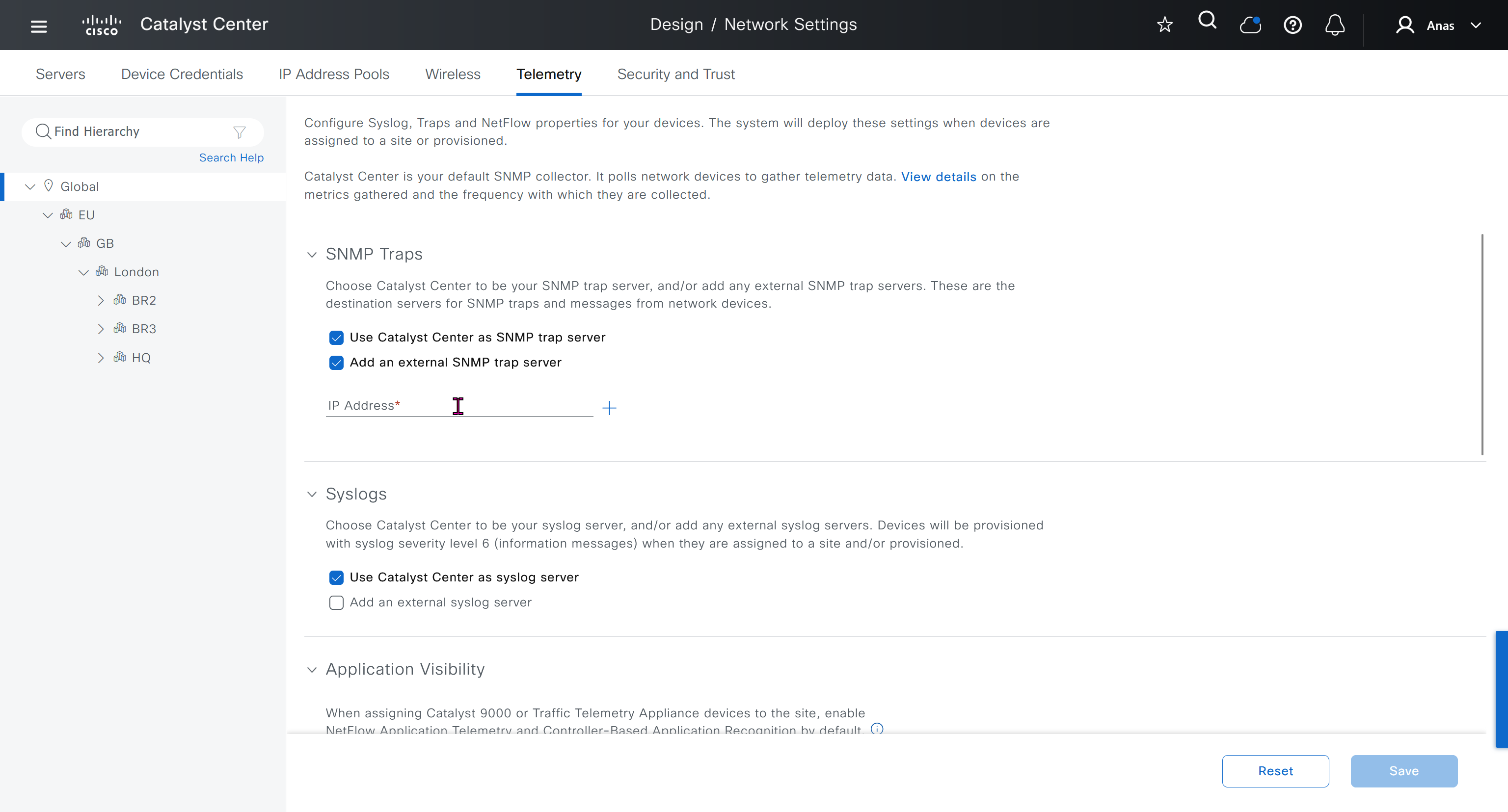
While configuring the Telemetry section, there are options to configure DNAC as SNMP Trap server, Syslog server and netflow collector also but under all these option there is an option also by dnac to configure other syslog and snmp trap server if desired such as SolarWinds
- Enable DNA advantage license
- Enable ip routing
- Enable jumbo frame
- Enable ospf on single vlan between switches (as configured below)
- Enable CLI credentials from DNAC
- Enable SNMP strings from DNAC
- Enable ssh
- Enable local authentication
- Enable netconf-yang
- Enable privilege level 15 on vty lines
conf t
license boot level network-advantage addon dna-advantage
end
write memory
reload
conf t
!
snmp-server community ciscoro RO
snmp-server community ciscorw RW
!
aaa new-model
!
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authorization exec default local
!
aaa session-id common
!
ip routing
!
license boot level network-advantage addon dna-advantage
!
system mtu 8978
!
enable secret 9 $9$WsbGbEnlY7ZnOE$8Y5qUmOgCatKFC2M/Kpmov7Dbd08QBhQlA8nlOXjnfA
!
username cisco privilege 15 secret 9 $9$K2c68lctCCR3v.$SgFneM9tcIGiIKFFsAsZDcBT/DX0ty2rJ01pQSVW5LU
username dnacadmin privilege 15 secret 9 $9$ss2NT8jXdGqUGU$QVfZV.IgKGnzd8GNy5oCLpfZvamjwuusTVNBK61XPMQ
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/x
description SDA-HQ-FXX-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/x
description SDA-HQ-FXX-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
!
interface Vlan12
ip address 172.17.0.x 255.255.255.128
ip ospf mtu-ignore
!
router ospf 100
router-id 172.17.0.x
network 172.17.0.0 0.0.0.127 area 0
!
snmp-server community ciscoro RO
snmp-server community ciscorw RW
!
alias router show do show
alias interface show do show
alias configure show do show
!
line vty 0 98
privilege level 15
transport input ssh
!
netconf-yang
end
write memHQ-SW config
HQ-SW#show run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 3914 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 03:22:03 UTC Mon Oct 6 2025
!
version 15.2
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
no service password-encryption
service compress-config
!
hostname HQ-SW
!
boot-start-marker
boot-end-marker
!
!
!
username cisco privilege 15 secret 5 $1$SACq$2ExGwHsqUe3mKfho1B3AQ1
no aaa new-model
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
ip cef
no ipv6 cef
!
!
!
spanning-tree mode pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
vlan internal allocation policy ascending
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
description INTERNET
no switchport
ip address 1.1.1.11 255.255.255.0
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/1
description WINSERVER
media-type rj45
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/2
description home.local network
switchport access vlan 11
media-type rj45
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/3
description ISE01
media-type rj45
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0
description SDA-HQ-FBS-01 HQ-DATA
switchport access vlan 12
switchport mode access
media-type rj45
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/1
media-type rj45
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/2
media-type rj45
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/3
media-type rj45
negotiation auto
!
interface Vlan1
description HQ-OOB network
ip address 172.16.32.1 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan11
description home.local network
ip address 192.168.0.15 255.255.255.0
!
interface Vlan12
ip address 172.17.0.3 255.255.255.128
ip ospf mtu-ignore
!
router ospf 100
router-id 172.17.0.3
network 172.17.0.0 0.0.0.127 area 0
default-information originate
!
ip forward-protocol nd
!
no ip http server
no ip http secure-server
!
ip route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 192.168.0.1
ip route 1.1.0.0 255.255.255.0 1.1.1.250
ip route 10.21.1.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.12
ip route 172.16.25.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.0.12
!
!
!
!
!
control-plane
!
banner exec ^CCC
**************************************************************************
* IOSv is strictly limited to use for evaluation, demonstration and IOS *
* education. IOSv is provided as-is and is not supported by Cisco's *
* Technical Advisory Center. Any use or disclosure, in whole or in part, *
* of the IOSv Software or Documentation to any third party for any *
* purposes is expressly prohibited except as otherwise authorized by *
* Cisco in writing. *
**************************************************************************^C
banner incoming ^CCC
**************************************************************************
* IOSv is strictly limited to use for evaluation, demonstration and IOS *
* education. IOSv is provided as-is and is not supported by Cisco's *
* Technical Advisory Center. Any use or disclosure, in whole or in part, *
* of the IOSv Software or Documentation to any third party for any *
* purposes is expressly prohibited except as otherwise authorized by *
* Cisco in writing. *
**************************************************************************^C
banner login ^CCC
**************************************************************************
* IOSv is strictly limited to use for evaluation, demonstration and IOS *
* education. IOSv is provided as-is and is not supported by Cisco's *
* Technical Advisory Center. Any use or disclosure, in whole or in part, *
* of the IOSv Software or Documentation to any third party for any *
* purposes is expressly prohibited except as otherwise authorized by *
* Cisco in writing. *
**************************************************************************^C
alias router show do show
alias interface show do show
alias configure show do show
!
line con 0
line aux 0
line vty 0 4
login
!
!
netconf-yang
endSDA-HQ-FBS-01 config
SDA-HQ-FBS-01#show run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 8301 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 03:40:18 UTC Mon Oct 6 2025
!
version 17.12
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname SDA-HQ-FBS-01
!
!
vrf definition Mgmt-vrf
!
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6
exit-address-family
!
aaa new-model
!
!
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authorization exec default local
!
!
aaa session-id common
switch 1 provision c9kv-uadp-8p
!
!
!
!
ip routing
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
login on-success log
vtp version 1
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
crypto pki trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint
enrollment pkcs12
revocation-check crl
hash sha256
!
crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed-2070352050
enrollment selfsigned
subject-name cn=IOS-Self-Signed-Certificate-2070352050
revocation-check none
rsakeypair TP-self-signed-2070352050
hash sha256
!
!
crypto pki certificate chain SLA-TrustPoint
certificate ca 01
30820321 30820209 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050030
32310E30 0C060355 040A1305 43697363 6F312030 1E060355 04031317 43697363
6F204C69 63656E73 696E6720 526F6F74 20434130 1E170D31 33303533 30313934
3834375A 170D3338 30353330 31393438 34375A30 32310E30 0C060355 040A1305
43697363 6F312030 1E060355 04031317 43697363 6F204C69 63656E73 696E6720
526F6F74 20434130 82012230 0D06092A 864886F7 0D010101 05000382 010F0030
82010A02 82010100 A6BCBD96 131E05F7 145EA72C 2CD686E6 17222EA1 F1EFF64D
CBB4C798 212AA147 C655D8D7 9471380D 8711441E 1AAF071A 9CAE6388 8A38E520
1C394D78 462EF239 C659F715 B98C0A59 5BBB5CBD 0CFEBEA3 700A8BF7 D8F256EE
4AA4E80D DB6FD1C9 60B1FD18 FFC69C96 6FA68957 A2617DE7 104FDC5F EA2956AC
7390A3EB 2B5436AD C847A2C5 DAB553EB 69A9A535 58E9F3E3 C0BD23CF 58BD7188
68E69491 20F320E7 948E71D7 AE3BCC84 F10684C7 4BC8E00F 539BA42B 42C68BB7
C7479096 B4CB2D62 EA2F505D C7B062A4 6811D95B E8250FC4 5D5D5FB8 8F27D191
C55F0D76 61F9A4CD 3D992327 A8BB03BD 4E6D7069 7CBADF8B DF5F4368 95135E44
DFC7C6CF 04DD7FD1 02030100 01A34230 40300E06 03551D0F 0101FF04 04030201
06300F06 03551D13 0101FF04 05300301 01FF301D 0603551D 0E041604 1449DC85
4B3D31E5 1B3E6A17 606AF333 3D3B4C73 E8300D06 092A8648 86F70D01 010B0500
03820101 00507F24 D3932A66 86025D9F E838AE5C 6D4DF6B0 49631C78 240DA905
604EDCDE FF4FED2B 77FC460E CD636FDB DD44681E 3A5673AB 9093D3B1 6C9E3D8B
D98987BF E40CBD9E 1AECA0C2 2189BB5C 8FA85686 CD98B646 5575B146 8DFC66A8
467A3DF4 4D565700 6ADF0F0D CF835015 3C04FF7C 21E878AC 11BA9CD2 55A9232C
7CA7B7E6 C1AF74F6 152E99B7 B1FCF9BB E973DE7F 5BDDEB86 C71E3B49 1765308B
5FB0DA06 B92AFE7F 494E8A9E 07B85737 F3A58BE1 1A48A229 C37C1E69 39F08678
80DDCD16 D6BACECA EEBC7CF9 8428787B 35202CDC 60E4616A B623CDBD 230E3AFB
418616A9 4093E049 4D10AB75 27E86F73 932E35B5 8862FDAE 0275156F 719BB2F0
D697DF7F 28
quit
crypto pki certificate chain TP-self-signed-2070352050
certificate self-signed 01
30820330 30820218 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050030
31312F30 2D060355 04030C26 494F532D 53656C66 2D536967 6E65642D 43657274
69666963 6174652D 32303730 33353230 3530301E 170D3235 30393231 32313439
32315A17 0D333530 39323132 31343932 315A3031 312F302D 06035504 030C2649
4F532D53 656C662D 5369676E 65642D43 65727469 66696361 74652D32 30373033
35323035 30308201 22300D06 092A8648 86F70D01 01010500 0382010F 00308201
0A028201 0100BE6B 15431B3C C2F339F8 E68ED232 38C6D054 26256330 1860898B
3427C857 6F821274 0C5B8B21 D2B908B2 71205F22 E9E2D9EF CCCEF719 CB65D798
620546BE 724EFEE4 B7D9026F E94D9B0C A1B7755C 33C13A5B 5803DE7F DABC513B
17181601 AE98D442 44694CF2 57D1505F 3A119649 E0F7C524 A2C544D1 8C986BC2
89C8FAF7 0E72811A AC4FDC69 D0A4DE17 BE69A40F F83E5BFD B16E894B 18830516
06726E02 3E6F1A7F 3A202286 600059F0 CF9EC6A8 420946BD A0F70AFF CE386017
44CB8032 55B22C27 E240440C 39D3EEF3 B887DF4B ECECD738 76C531B7 DC43AC1F
38AAE8C1 A12B5574 0DCA1A63 88E12E80 62411882 573FBF7A 85DD348B 425A477E
9AF7DAB7 D9EF0203 010001A3 53305130 1D060355 1D0E0416 0414864F 5DC3AA3D
570D29AC 614578D3 7BCFD3AF 76D5301F 0603551D 23041830 16801486 4F5DC3AA
3D570D29 AC614578 D37BCFD3 AF76D530 0F060355 1D130101 FF040530 030101FF
300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050003 82010100 3037A0B0 4EE53529 F17F5DAF
A4B8BF4C 1B0B63D3 2F5785E9 4A2FFE10 46890D5C 3A50C253 6AF15B6F 13FA2AC8
EBF67CBD CFA8D7AE 756B2596 B554A972 40F4E277 98310DC0 9EA3EB9A B8CCD9BE
C5332F30 4C6A7F5B D76CF4DF 69E29977 745B232E EC606EB5 CD6CA542 A425C5CC
D307EE95 FBF9FE6A F0561077 83079168 0DEA031B 00D4D850 EFED9136 607A5F2F
FB848029 6C2457A0 1AD24EBB A915E9DE F0F4BFD5 DA125681 55183EE5 D62333F9
97EA23F6 F2925C1E 440888B7 34A5F17D 66245CF7 3D4C53EB 1E364B3F 9861630D
31F4E67F 05F58704 E4D4238D 539144CC 70F0A6AB F51BAFE9 F47D3E14 72AABFB8
F44C060A BE7D007B DA1DF7FB B73C8E9D 1B24F792
quit
!
!
license boot level network-advantage addon dna-advantage
memory free low-watermark processor 74862
!
system mtu 8978
diagnostic bootup level minimal
!
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
!
!
enable secret 9 $9$WsbGbEnlY7ZnOE$8Y5qUmOgCatKFC2M/Kpmov7Dbd08QBhQlA8nlOXjnfA
!
username cisco privilege 15 secret 9 $9$K2c68lctCCR3v.$SgFneM9tcIGiIKFFsAsZDcBT/DX0ty2rJ01pQSVW5LU
username dnacadmin privilege 15 secret 9 $9$ss2NT8jXdGqUGU$QVfZV.IgKGnzd8GNy5oCLpfZvamjwuusTVNBK61XPMQ
!
redundancy
mode sso
!
!
!
!
!
!
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control
description Topology control
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward
description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING
class-map match-any system-cpp-default
description EWLC control, EWLC data, Inter FED
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data
description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFL SAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth
description Punt Webauth
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control
description L2 LVX control packets
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus
description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station
description MCAST END STATION
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast
description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control
description L2 control
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth
description DOT1X Auth
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data
description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control
description Stackwise Virtual
class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control
description Routing control and Low Latency
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping
description Protocol snooping
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping
description DHCP snooping
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical
description System Critical and Gold Pkt
!
policy-map system-cpp-policy
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
interface Loopback0
no ip address
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf
ip address dhcp
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
description HQ-SW
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
!
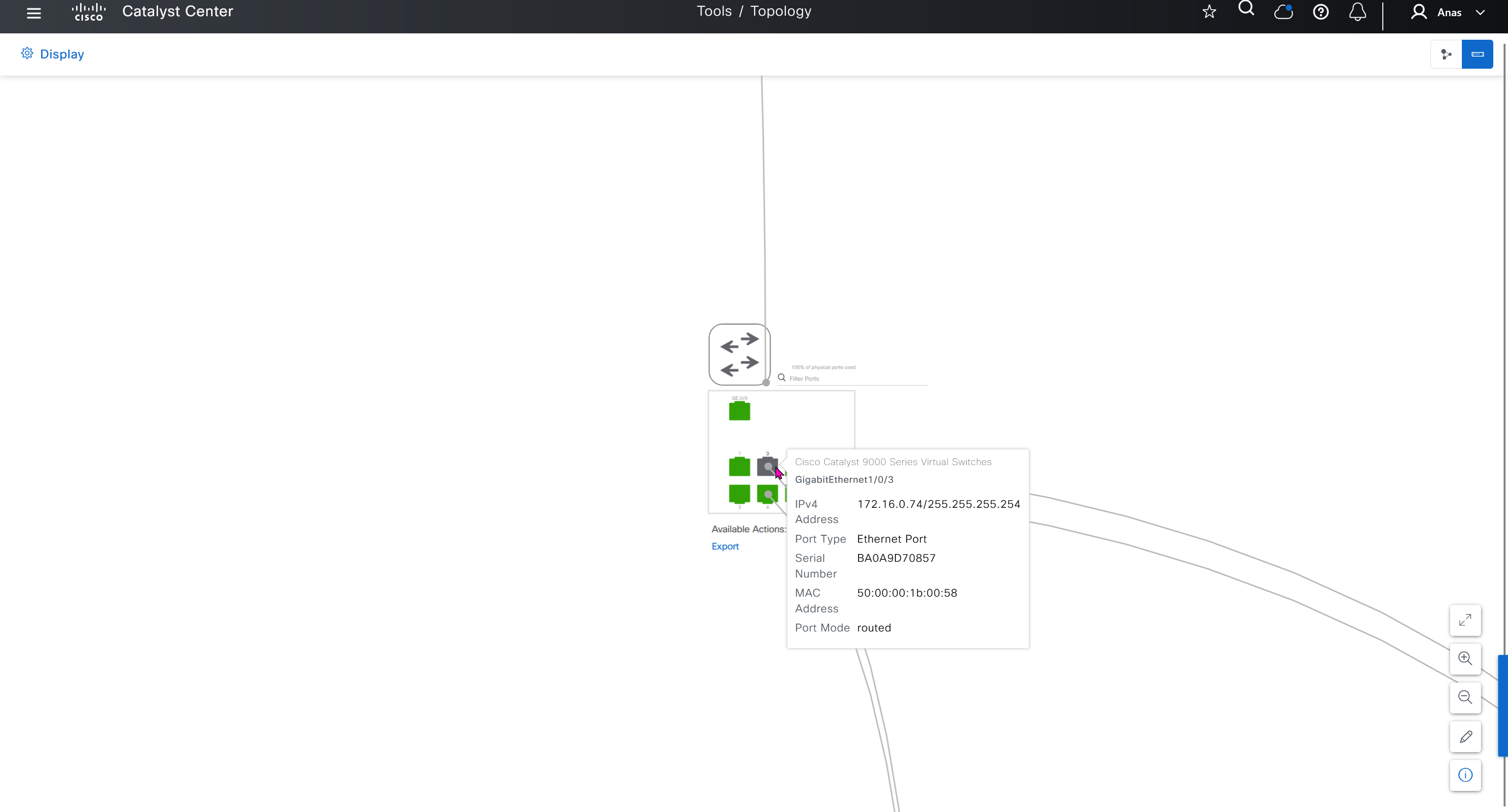
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7
description SDA-HQ-FIS-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8
description SDA-HQ-FIS-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
!
interface Vlan12
ip address 172.17.0.4 255.255.255.128
ip ospf mtu-ignore
!
router ospf 100
router-id 172.17.0.4
network 172.17.0.0 0.0.0.127 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
ip tcp mss 1280
ip tcp window-size 212000
ip http server
ip http authentication local
ip http secure-server
ip ssh bulk-mode 131072
!
!
!
!
snmp-server community ciscoro RO
snmp-server community ciscorw RW
!
!
!
!
control-plane
service-policy input system-cpp-policy
!
!
alias router show do show
alias interface show do show
alias configure show do show
!
line con 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
privilege level 15
transport input ssh
line vty 5 98
privilege level 15
transport input ssh
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
netconf-yang
endSDA-HQ-FES-01 config
SDA-HQ-FES-01#show run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 8213 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 03:42:50 UTC Mon Oct 6 2025
!
version 17.12
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname SDA-HQ-FES-01
!
!
vrf definition Mgmt-vrf
!
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6
exit-address-family
!
aaa new-model
!
!
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authorization exec default local
!
!
aaa session-id common
switch 1 provision c9kv-uadp-8p
!
!
!
!
ip routing
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
login on-success log
vtp version 1
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
crypto pki trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint
enrollment pkcs12
revocation-check crl
hash sha256
!
crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed-4128105830
enrollment selfsigned
subject-name cn=IOS-Self-Signed-Certificate-4128105830
revocation-check none
rsakeypair TP-self-signed-4128105830
hash sha256
!
!
crypto pki certificate chain SLA-TrustPoint
certificate ca 01
30820321 30820209 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050030
32310E30 0C060355 040A1305 43697363 6F312030 1E060355 04031317 43697363
6F204C69 63656E73 696E6720 526F6F74 20434130 1E170D31 33303533 30313934
3834375A 170D3338 30353330 31393438 34375A30 32310E30 0C060355 040A1305
43697363 6F312030 1E060355 04031317 43697363 6F204C69 63656E73 696E6720
526F6F74 20434130 82012230 0D06092A 864886F7 0D010101 05000382 010F0030
82010A02 82010100 A6BCBD96 131E05F7 145EA72C 2CD686E6 17222EA1 F1EFF64D
CBB4C798 212AA147 C655D8D7 9471380D 8711441E 1AAF071A 9CAE6388 8A38E520
1C394D78 462EF239 C659F715 B98C0A59 5BBB5CBD 0CFEBEA3 700A8BF7 D8F256EE
4AA4E80D DB6FD1C9 60B1FD18 FFC69C96 6FA68957 A2617DE7 104FDC5F EA2956AC
7390A3EB 2B5436AD C847A2C5 DAB553EB 69A9A535 58E9F3E3 C0BD23CF 58BD7188
68E69491 20F320E7 948E71D7 AE3BCC84 F10684C7 4BC8E00F 539BA42B 42C68BB7
C7479096 B4CB2D62 EA2F505D C7B062A4 6811D95B E8250FC4 5D5D5FB8 8F27D191
C55F0D76 61F9A4CD 3D992327 A8BB03BD 4E6D7069 7CBADF8B DF5F4368 95135E44
DFC7C6CF 04DD7FD1 02030100 01A34230 40300E06 03551D0F 0101FF04 04030201
06300F06 03551D13 0101FF04 05300301 01FF301D 0603551D 0E041604 1449DC85
4B3D31E5 1B3E6A17 606AF333 3D3B4C73 E8300D06 092A8648 86F70D01 010B0500
03820101 00507F24 D3932A66 86025D9F E838AE5C 6D4DF6B0 49631C78 240DA905
604EDCDE FF4FED2B 77FC460E CD636FDB DD44681E 3A5673AB 9093D3B1 6C9E3D8B
D98987BF E40CBD9E 1AECA0C2 2189BB5C 8FA85686 CD98B646 5575B146 8DFC66A8
467A3DF4 4D565700 6ADF0F0D CF835015 3C04FF7C 21E878AC 11BA9CD2 55A9232C
7CA7B7E6 C1AF74F6 152E99B7 B1FCF9BB E973DE7F 5BDDEB86 C71E3B49 1765308B
5FB0DA06 B92AFE7F 494E8A9E 07B85737 F3A58BE1 1A48A229 C37C1E69 39F08678
80DDCD16 D6BACECA EEBC7CF9 8428787B 35202CDC 60E4616A B623CDBD 230E3AFB
418616A9 4093E049 4D10AB75 27E86F73 932E35B5 8862FDAE 0275156F 719BB2F0
D697DF7F 28
quit
crypto pki certificate chain TP-self-signed-4128105830
certificate self-signed 01
30820330 30820218 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050030
31312F30 2D060355 04030C26 494F532D 53656C66 2D536967 6E65642D 43657274
69666963 6174652D 34313238 31303538 3330301E 170D3235 31303035 31393137
30325A17 0D333531 30303531 39313730 325A3031 312F302D 06035504 030C2649
4F532D53 656C662D 5369676E 65642D43 65727469 66696361 74652D34 31323831
30353833 30308201 22300D06 092A8648 86F70D01 01010500 0382010F 00308201
0A028201 0100B7B2 70B7BDF4 91177742 63220480 4899E262 C48CF80E B97F5343
5BC116D2 EFE21CC5 7B2C5BDA 8A2A1397 D1BEE9BF 8EB1BF36 82F1AC35 C87B876D
B59424B1 E20EEE3C 1C0B2AC9 B769A6C9 2704BE3F F6C0C75C 2815086C 917819AA
82EF8509 92B044E2 48CA015B B7703328 A60A9DFF 27475FE8 C868CF1E 33037F41
F6B54D71 BB26B172 BB07764C 0805B093 DA0B75CD 0FC332B8 9E421DEB 10EF4640
E43766A7 32B8ACF5 8031B253 26AF5CFB 33520DCA 0E30F1E5 C9A63627 34440ACB
3F0368DD 0B0E3F3A BE744597 4820D2B1 2AF9D788 606318A6 7FCD560B E6DA777B
1EF3CE00 F1B9A366 B6D1D54A AD0388E2 DA333E0D 647E6CCB FF102702 917725FF
2F63BDC2 6DF30203 010001A3 53305130 1D060355 1D0E0416 0414B90C B90FAFDA
1F2782DC 146CA7D0 8D14E721 EF83301F 0603551D 23041830 168014B9 0CB90FAF
DA1F2782 DC146CA7 D08D14E7 21EF8330 0F060355 1D130101 FF040530 030101FF
300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050003 82010100 2C21E6F0 C64F7362 5B29B2FB
B45BCA4D 6A8E2C8E E5EFA844 7D8FC72C 274D3DA4 012F8940 464A1DE5 EA3D0E0D
37D92810 DC75FD6B 7160B76A 4FD75857 2DC18727 E2CFCB55 AA43C8E2 5A9AF302
FABFEF84 BC3D5CD1 4A2AB3AC D42FD4D6 5F588A68 B8F0788B 75634E4F 37F5D64B
33E533F5 79B81E64 D9232BBE 5F7CBB1A 7AF088CA 0BB04ADB 332680A1 E23F22A7
4F39F12F 82A0D7F3 D00F451E 5A247ABB E333C470 3C0A67D9 3D6DD9A3 554A51B8
DA59EEFD 621970F5 4958AB38 92CECECF 7AF08EE2 803B5F2B 3FB7195D BA49B4E0
4EB859F8 366D1A48 74B86593 6812A3E2 27683CA0 7C7045ED FD45961A C888D693
D75AF59C E28965D3 B2B7931B 3CD50C73 1E0D378A
quit
!
!
license boot level network-advantage addon dna-advantage
memory free low-watermark processor 74862
!
system mtu 8978
diagnostic bootup level minimal
!
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
!
!
enable secret 9 $9$WsbGbEnlY7ZnOE$8Y5qUmOgCatKFC2M/Kpmov7Dbd08QBhQlA8nlOXjnfA
!
username cisco privilege 15 secret 9 $9$K2c68lctCCR3v.$SgFneM9tcIGiIKFFsAsZDcBT/DX0ty2rJ01pQSVW5LU
username dnacadmin privilege 15 secret 9 $9$ss2NT8jXdGqUGU$QVfZV.IgKGnzd8GNy5oCLpfZvamjwuusTVNBK61XPMQ
!
redundancy
mode sso
!
!
!
!
!
!
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control
description Topology control
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward
description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING
class-map match-any system-cpp-default
description EWLC control, EWLC data, Inter FED
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data
description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFL SAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth
description Punt Webauth
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control
description L2 LVX control packets
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus
description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station
description MCAST END STATION
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast
description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control
description L2 control
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth
description DOT1X Auth
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data
description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control
description Stackwise Virtual
class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control
description Routing control and Low Latency
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping
description Protocol snooping
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping
description DHCP snooping
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical
description System Critical and Gold Pkt
!
policy-map system-cpp-policy
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf
ip address dhcp
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
description SDA-HQ-FIS-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
description SDA-HQ-FIS-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
!
interface Vlan12
ip address 172.17.0.6 255.255.255.128
ip ospf mtu-ignore
!
router ospf 100
router-id 172.17.0.6
network 172.17.0.0 0.0.0.127 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
ip tcp mss 1280
ip tcp window-size 212000
ip http server
ip http authentication local
ip http secure-server
ip ssh bulk-mode 131072
!
!
!
!
snmp-server community ciscoro RO
snmp-server community ciscorw RW
!
!
!
!
control-plane
service-policy input system-cpp-policy
!
!
alias router show do show
alias interface show do show
alias configure show do show
!
line con 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
privilege level 15
transport input ssh
line vty 5 98
privilege level 15
transport input ssh
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
netconf-yang
endSDA-HQ-FIS-01 config
SDA-HQ-FIS-01#show run
Building configuration...
Current configuration : 8321 bytes
!
! Last configuration change at 03:43:50 UTC Mon Oct 6 2025
!
version 17.12
service timestamps debug datetime msec
service timestamps log datetime msec
platform punt-keepalive disable-kernel-core
!
hostname SDA-HQ-FIS-01
!
!
vrf definition Mgmt-vrf
!
address-family ipv4
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6
exit-address-family
!
aaa new-model
!
!
aaa authentication login default local
aaa authorization exec default local
!
!
aaa session-id common
switch 1 provision c9kv-uadp-8p
!
!
!
!
ip routing
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
login on-success log
vtp version 1
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
crypto pki trustpoint SLA-TrustPoint
enrollment pkcs12
revocation-check crl
hash sha256
!
crypto pki trustpoint TP-self-signed-3709873604
enrollment selfsigned
subject-name cn=IOS-Self-Signed-Certificate-3709873604
revocation-check none
rsakeypair TP-self-signed-3709873604
hash sha256
!
!
crypto pki certificate chain SLA-TrustPoint
certificate ca 01
30820321 30820209 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050030
32310E30 0C060355 040A1305 43697363 6F312030 1E060355 04031317 43697363
6F204C69 63656E73 696E6720 526F6F74 20434130 1E170D31 33303533 30313934
3834375A 170D3338 30353330 31393438 34375A30 32310E30 0C060355 040A1305
43697363 6F312030 1E060355 04031317 43697363 6F204C69 63656E73 696E6720
526F6F74 20434130 82012230 0D06092A 864886F7 0D010101 05000382 010F0030
82010A02 82010100 A6BCBD96 131E05F7 145EA72C 2CD686E6 17222EA1 F1EFF64D
CBB4C798 212AA147 C655D8D7 9471380D 8711441E 1AAF071A 9CAE6388 8A38E520
1C394D78 462EF239 C659F715 B98C0A59 5BBB5CBD 0CFEBEA3 700A8BF7 D8F256EE
4AA4E80D DB6FD1C9 60B1FD18 FFC69C96 6FA68957 A2617DE7 104FDC5F EA2956AC
7390A3EB 2B5436AD C847A2C5 DAB553EB 69A9A535 58E9F3E3 C0BD23CF 58BD7188
68E69491 20F320E7 948E71D7 AE3BCC84 F10684C7 4BC8E00F 539BA42B 42C68BB7
C7479096 B4CB2D62 EA2F505D C7B062A4 6811D95B E8250FC4 5D5D5FB8 8F27D191
C55F0D76 61F9A4CD 3D992327 A8BB03BD 4E6D7069 7CBADF8B DF5F4368 95135E44
DFC7C6CF 04DD7FD1 02030100 01A34230 40300E06 03551D0F 0101FF04 04030201
06300F06 03551D13 0101FF04 05300301 01FF301D 0603551D 0E041604 1449DC85
4B3D31E5 1B3E6A17 606AF333 3D3B4C73 E8300D06 092A8648 86F70D01 010B0500
03820101 00507F24 D3932A66 86025D9F E838AE5C 6D4DF6B0 49631C78 240DA905
604EDCDE FF4FED2B 77FC460E CD636FDB DD44681E 3A5673AB 9093D3B1 6C9E3D8B
D98987BF E40CBD9E 1AECA0C2 2189BB5C 8FA85686 CD98B646 5575B146 8DFC66A8
467A3DF4 4D565700 6ADF0F0D CF835015 3C04FF7C 21E878AC 11BA9CD2 55A9232C
7CA7B7E6 C1AF74F6 152E99B7 B1FCF9BB E973DE7F 5BDDEB86 C71E3B49 1765308B
5FB0DA06 B92AFE7F 494E8A9E 07B85737 F3A58BE1 1A48A229 C37C1E69 39F08678
80DDCD16 D6BACECA EEBC7CF9 8428787B 35202CDC 60E4616A B623CDBD 230E3AFB
418616A9 4093E049 4D10AB75 27E86F73 932E35B5 8862FDAE 0275156F 719BB2F0
D697DF7F 28
quit
crypto pki certificate chain TP-self-signed-3709873604
certificate self-signed 01
30820330 30820218 A0030201 02020101 300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050030
31312F30 2D060355 04030C26 494F532D 53656C66 2D536967 6E65642D 43657274
69666963 6174652D 33373039 38373336 3034301E 170D3235 31303035 31393137
31335A17 0D333531 30303531 39313731 335A3031 312F302D 06035504 030C2649
4F532D53 656C662D 5369676E 65642D43 65727469 66696361 74652D33 37303938
37333630 34308201 22300D06 092A8648 86F70D01 01010500 0382010F 00308201
0A028201 0100C759 F84AFB37 54B78EFF 9273D1C3 0D6C5070 A83E4D91 FCF8D23C
448032EA 06A19825 5079D281 48A6864B B52DD90F 3B8D38FD A94746E0 2F704FE5
9AEB1C6E 2641C6DE 7D8410A4 E9A7C403 F3C81746 2E68527D 3B7AD8DA 2CD42017
5605E8A7 2F2A9F7B 9BDCC916 A305847B 10338575 99FCB13B C698BC10 0040FC1B
008AC100 0CBE486E 2A3674F6 C3C29501 3225EB05 20948377 C5FB1B80 30B7C775
059FC53D 43CDA2BC 4551028A C92B19AE 26A16499 2D95D48E 7BDD5B2B 499E9825
A3355A37 BC1A0581 E5FAD1CD 9D71ED1F 394DCE1F 48BBB3B8 4B077745 385FE76D
F2B90AC7 9F048D9E 29B83A57 022FBA37 4BADD628 D7DA69BA 9172BEDE 7518F3BB
2E7878D3 A31F0203 010001A3 53305130 1D060355 1D0E0416 0414021D 7AFCBB5E
378C9A0F 5864A7C3 A633ABE1 4517301F 0603551D 23041830 16801402 1D7AFCBB
5E378C9A 0F5864A7 C3A633AB E1451730 0F060355 1D130101 FF040530 030101FF
300D0609 2A864886 F70D0101 0B050003 82010100 95998C49 0D9ABEC9 1E1B1DE8
54C08FCE 536685EB 9E3E8B44 FC13DDA4 658DD6D8 662DF08A 41749F88 891194E9
AF06D23D 0980F173 4DDA2F20 3BC6751F 4BF45821 6C4071BE 9F9B24EA 47B224EB
6E22FDA9 7B57181E 54691EFD DB0EC11D CBB42446 E4728F57 CA901250 A7C69207
36DEDB9A 4B377903 92FC2684 AF2EAC79 5E45EB4C 29F8F083 77099D29 3877C84D
CC7A28D8 2C1E8B2F 4E1361EE 2ABA2D60 A6DD101F 12560715 29439D98 AA1F3167
404629FA D6CB1F8F 5A5A4C6E 181178BF 9500A404 1F3D13C8 22FE5BEA 8E8F247E
BBCAE461 365EA67E DFF2F9F1 97AD52D2 8269E54F B4E63F25 797C2720 258F8505
4ACCE8A9 6CC78BDA 532508B4 9D74C3A0 BE6F2A7B
quit
!
!
license boot level network-advantage addon dna-advantage
memory free low-watermark processor 74862
!
system mtu 8978
diagnostic bootup level minimal
!
spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst
spanning-tree extend system-id
!
!
!
enable secret 9 $9$WsbGbEnlY7ZnOE$8Y5qUmOgCatKFC2M/Kpmov7Dbd08QBhQlA8nlOXjnfA
!
username cisco privilege 15 secret 9 $9$K2c68lctCCR3v.$SgFneM9tcIGiIKFFsAsZDcBT/DX0ty2rJ01pQSVW5LU
username dnacadmin privilege 15 secret 9 $9$ss2NT8jXdGqUGU$QVfZV.IgKGnzd8GNy5oCLpfZvamjwuusTVNBK61XPMQ
!
redundancy
mode sso
!
!
!
!
!
!
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-topology-control
description Topology control
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sw-forward
description Sw forwarding, L2 LVX data, LOGGING
class-map match-any system-cpp-default
description EWLC control, EWLC data, Inter FED
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-sys-data
description Learning cache ovfl, High Rate App, Exception, EGR Exception, NFL SAMPLED DATA, RPF Failed
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-punt-webauth
description Punt Webauth
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2lvx-control
description L2 LVX control packets
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-forus
description Forus Address resolution and Forus traffic
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast-end-station
description MCAST END STATION
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-multicast
description Transit Traffic and MCAST Data
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-l2-control
description L2 control
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dot1x-auth
description DOT1X Auth
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-data
description ICMP redirect, ICMP_GEN and BROADCAST
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-stackwise-virt-control
description Stackwise Virtual
class-map match-any non-client-nrt-class
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-routing-control
description Routing control and Low Latency
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-protocol-snooping
description Protocol snooping
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-dhcp-snooping
description DHCP snooping
class-map match-any system-cpp-police-system-critical
description System Critical and Gold Pkt
!
policy-map system-cpp-policy
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
interface GigabitEthernet0/0
vrf forwarding Mgmt-vrf
ip address dhcp
negotiation auto
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/1
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/2
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/3
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/4
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/5
description SDA-HQ-FIS-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/6
description SDA-HQ-FIS-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/7
description SDA-HQ-FBS-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface GigabitEthernet1/0/8
description SDA-HQ-FBS-01
switchport access vlan 12
!
interface Vlan1
no ip address
!
interface Vlan12
ip address 172.17.0.5 255.255.255.128
ip ospf mtu-ignore
!
router ospf 100
router-id 172.17.0.5
network 172.17.0.0 0.0.0.127 area 0
!
ip forward-protocol nd
ip tcp mss 1280
ip tcp window-size 212000
ip http server
ip http authentication local
ip http secure-server
ip ssh bulk-mode 131072
!
!
!
!
snmp-server community ciscoro RO
snmp-server community ciscorw RW
!
!
!
!
control-plane
service-policy input system-cpp-policy
!
!
alias router show do show
alias interface show do show
alias configure show do show
!
line con 0
stopbits 1
line vty 0 4
privilege level 15
transport input ssh
line vty 5 98
privilege level 15
transport input ssh
!
!
!
!
!
!
!
netconf-yang
endshow netconf-yang status
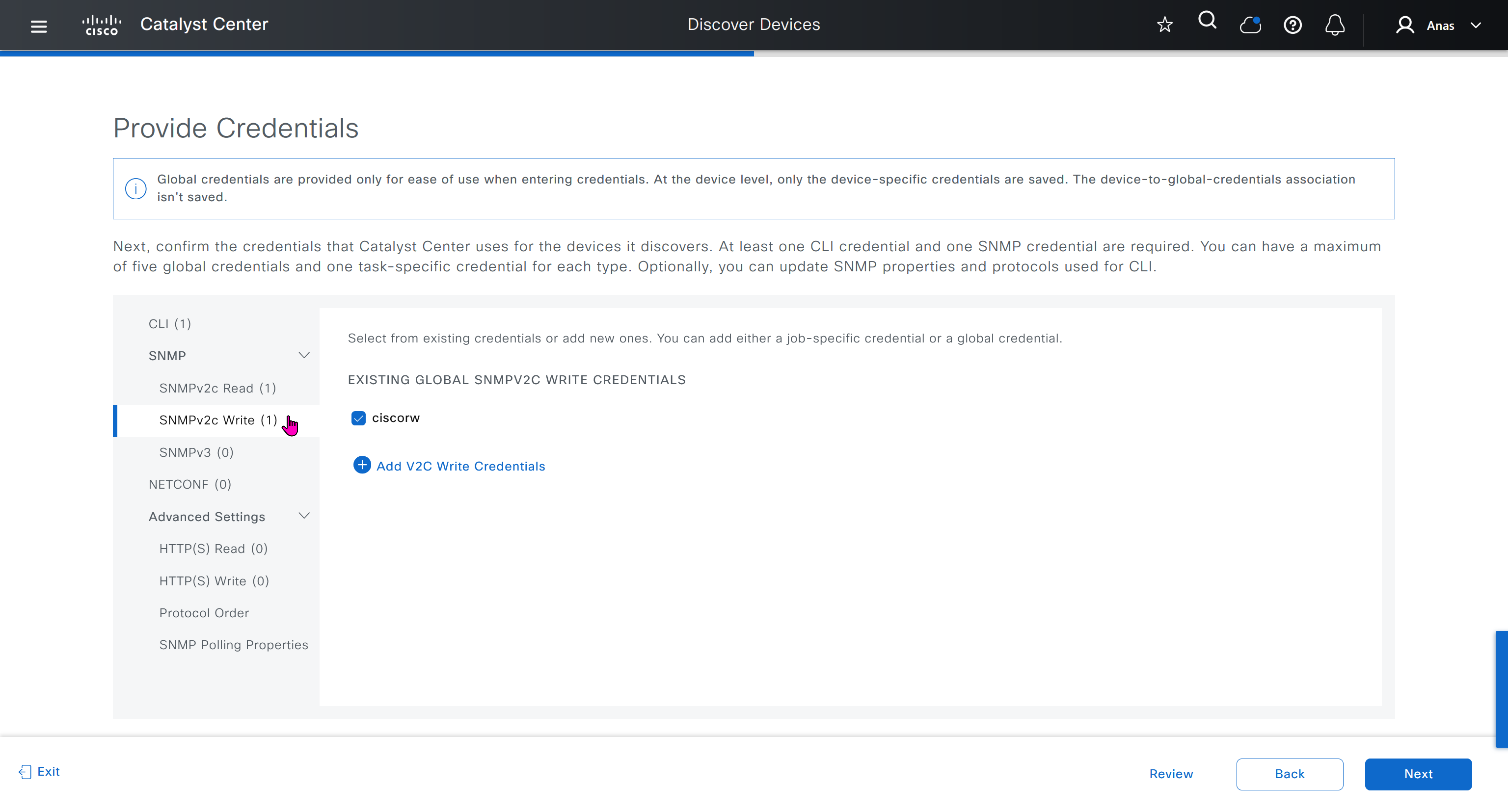
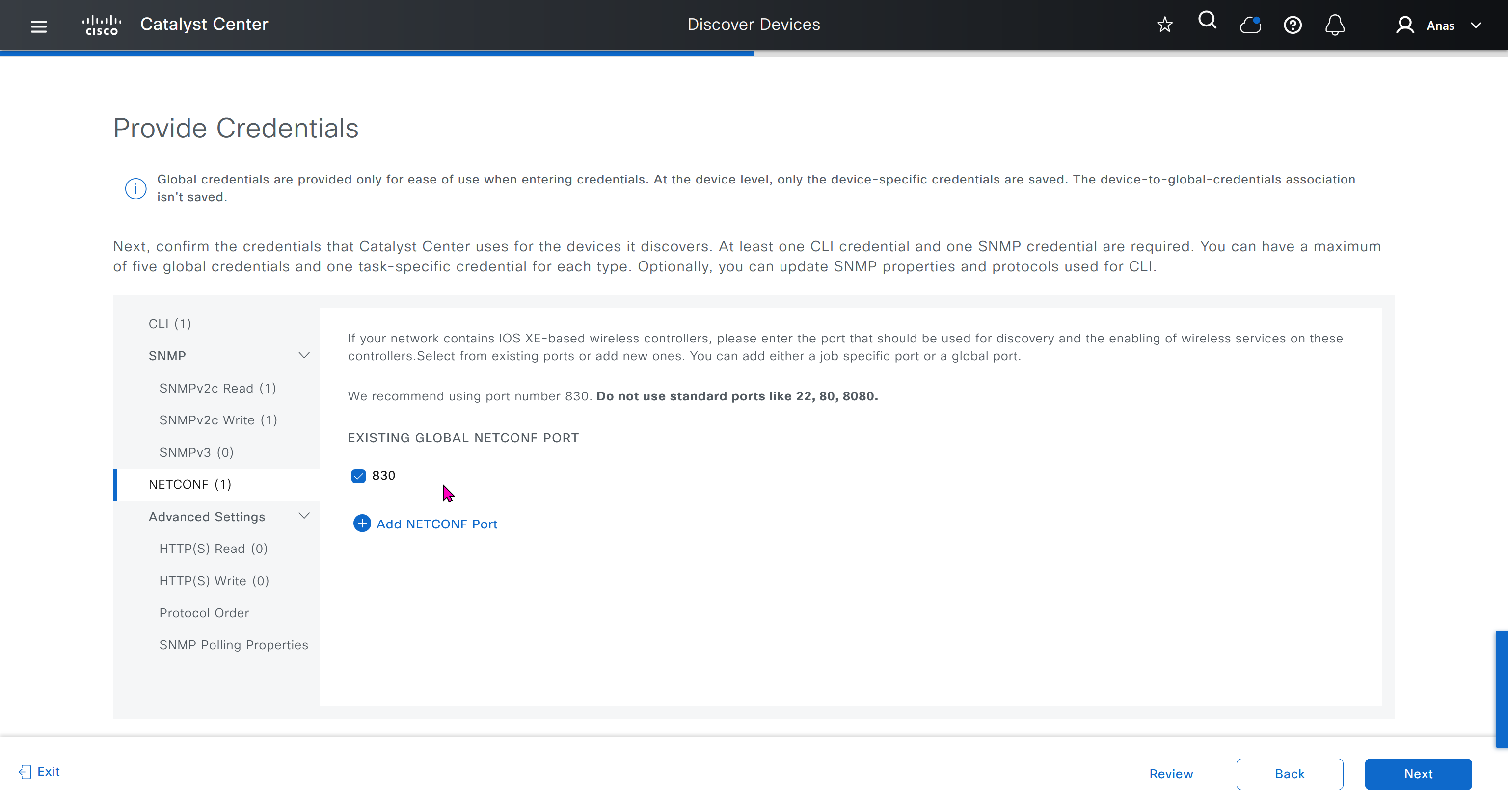
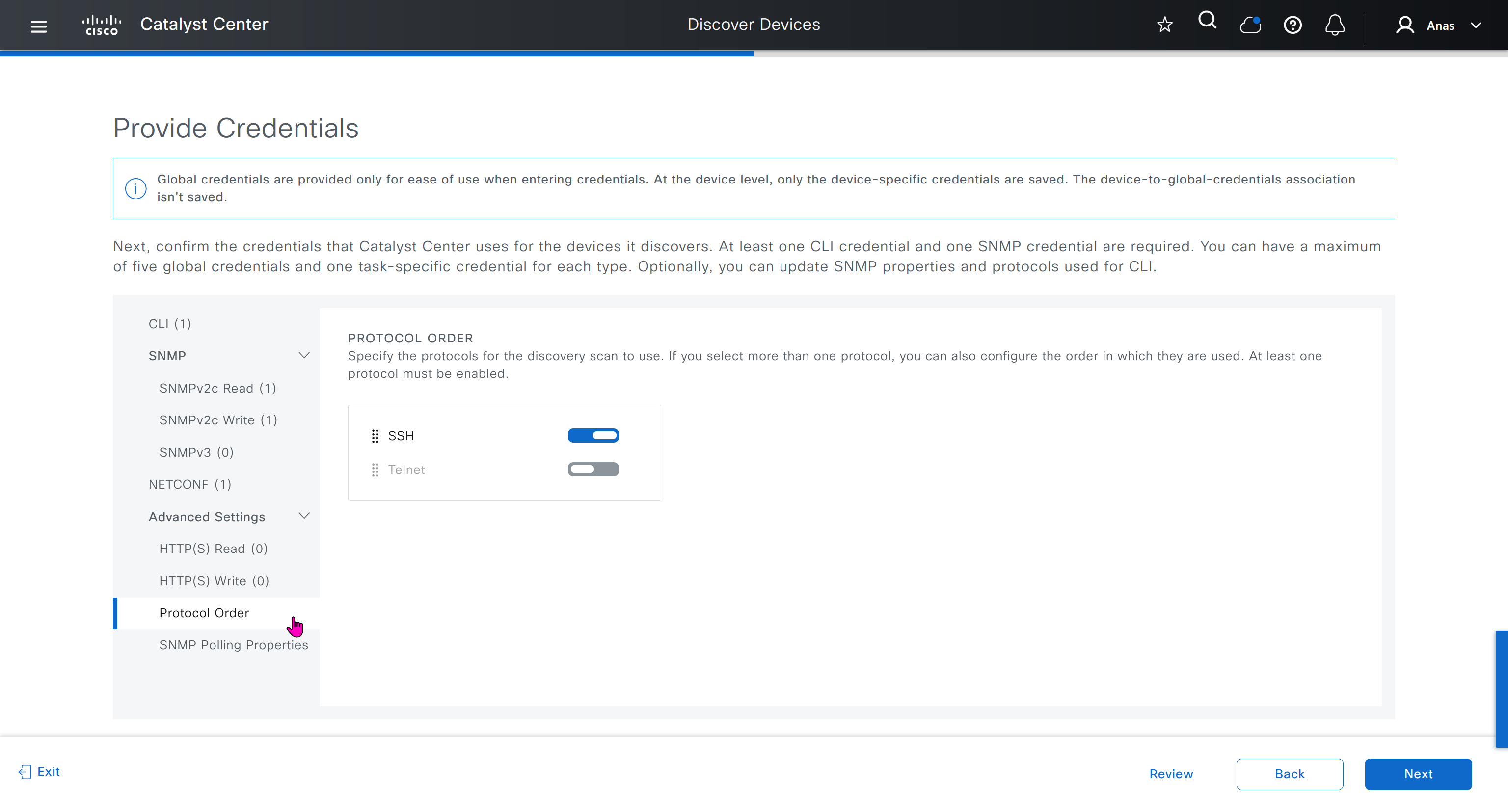
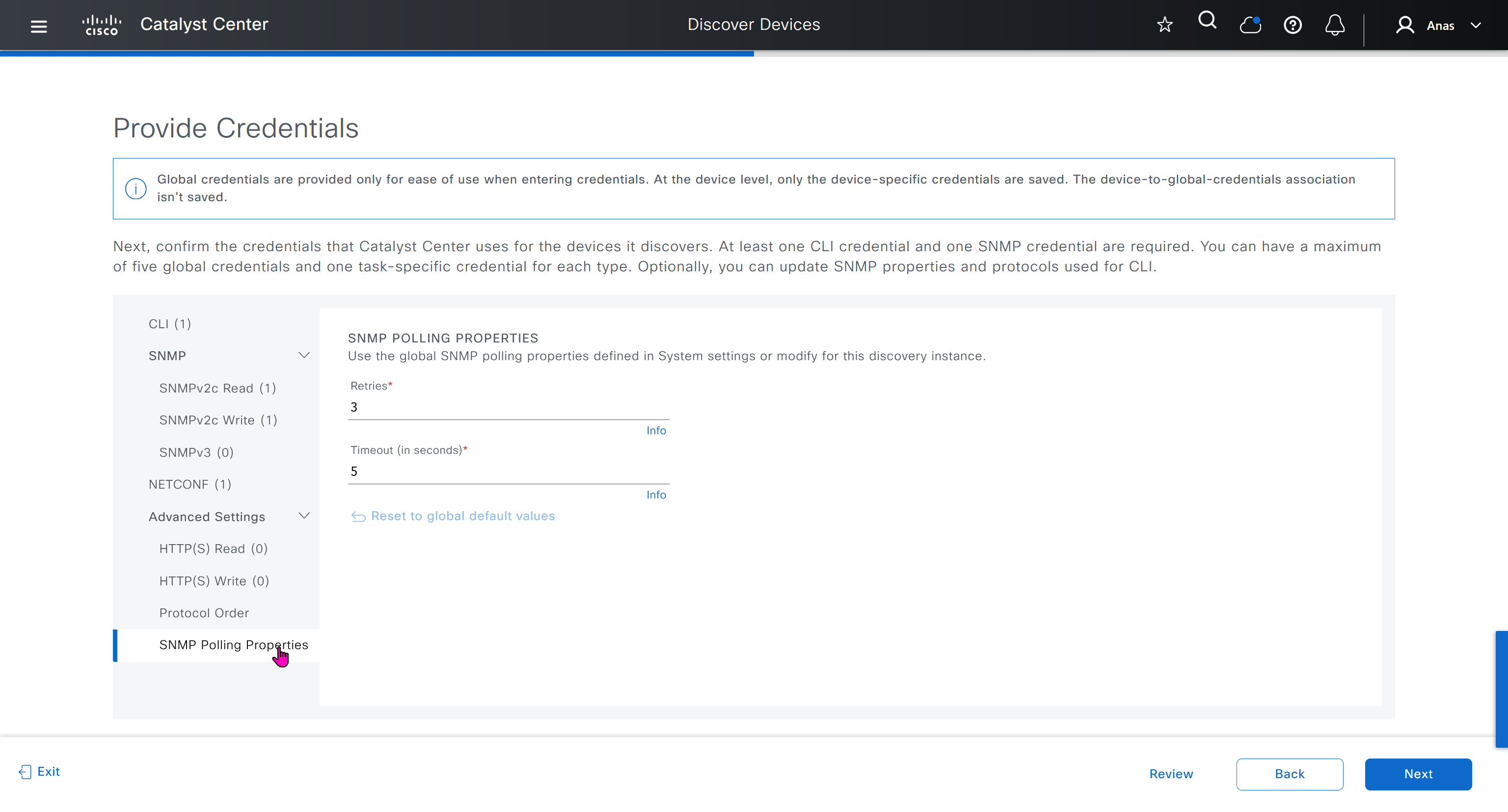
If you just want to use DNAC without SDA and take advantage of things such as image management and telemetry, you can use DNAC, but SDA changes the way LAN operates
one very important point to keep in mind is that we need is the latency requirements for SDA between DNAC and devices is 100ms and 200ms is kind of pushing
From ISE we only have 100ms to play with anyway
latency requirement between WLC and AP is 20ms
within the cluster of DNAC (which includes ISE as policy node) needs to be 10 msec
another requirement is that all devices be configured with SSH access with credentials that were configured in DNAC with full access and not just enable prompt
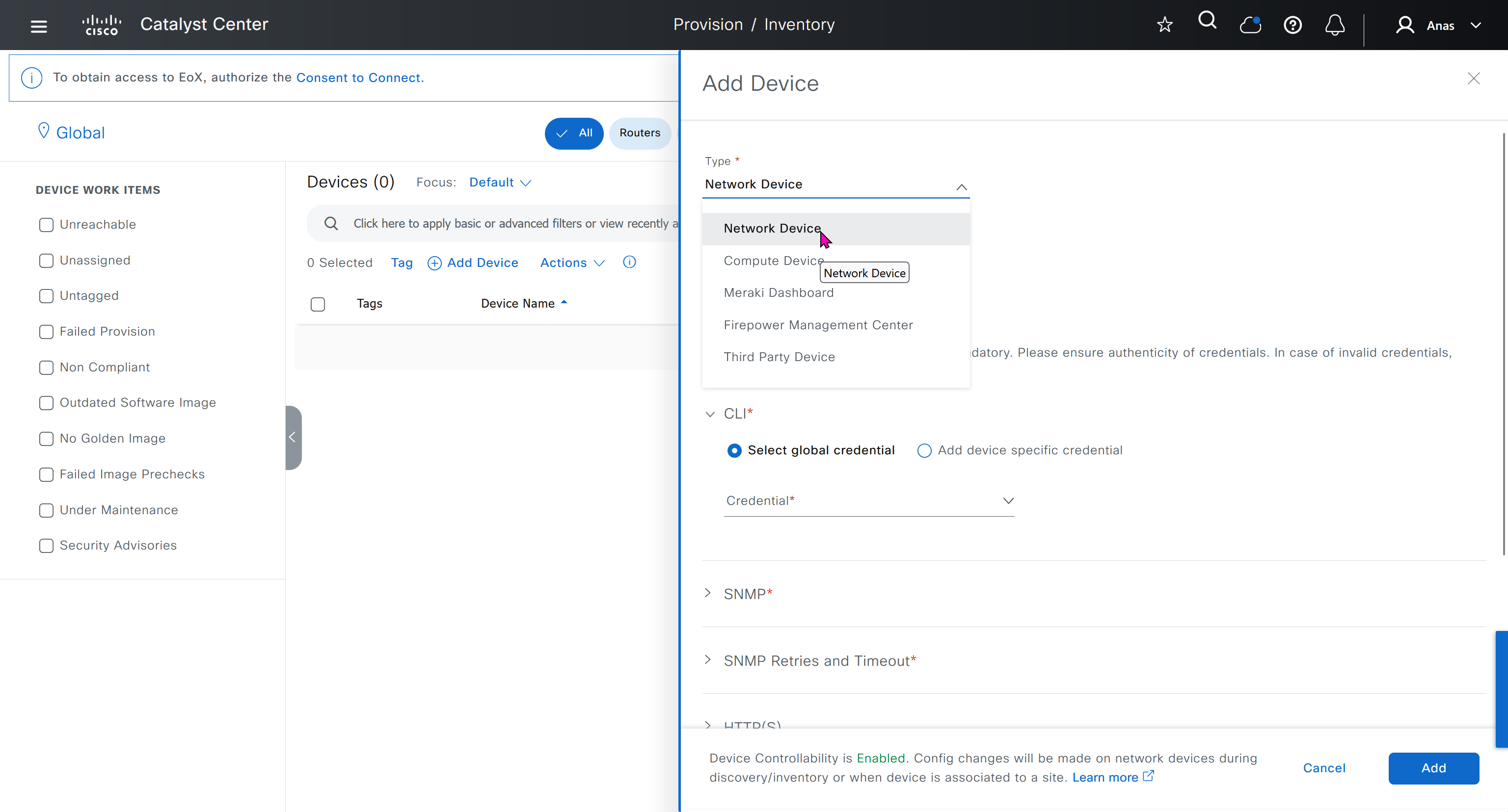
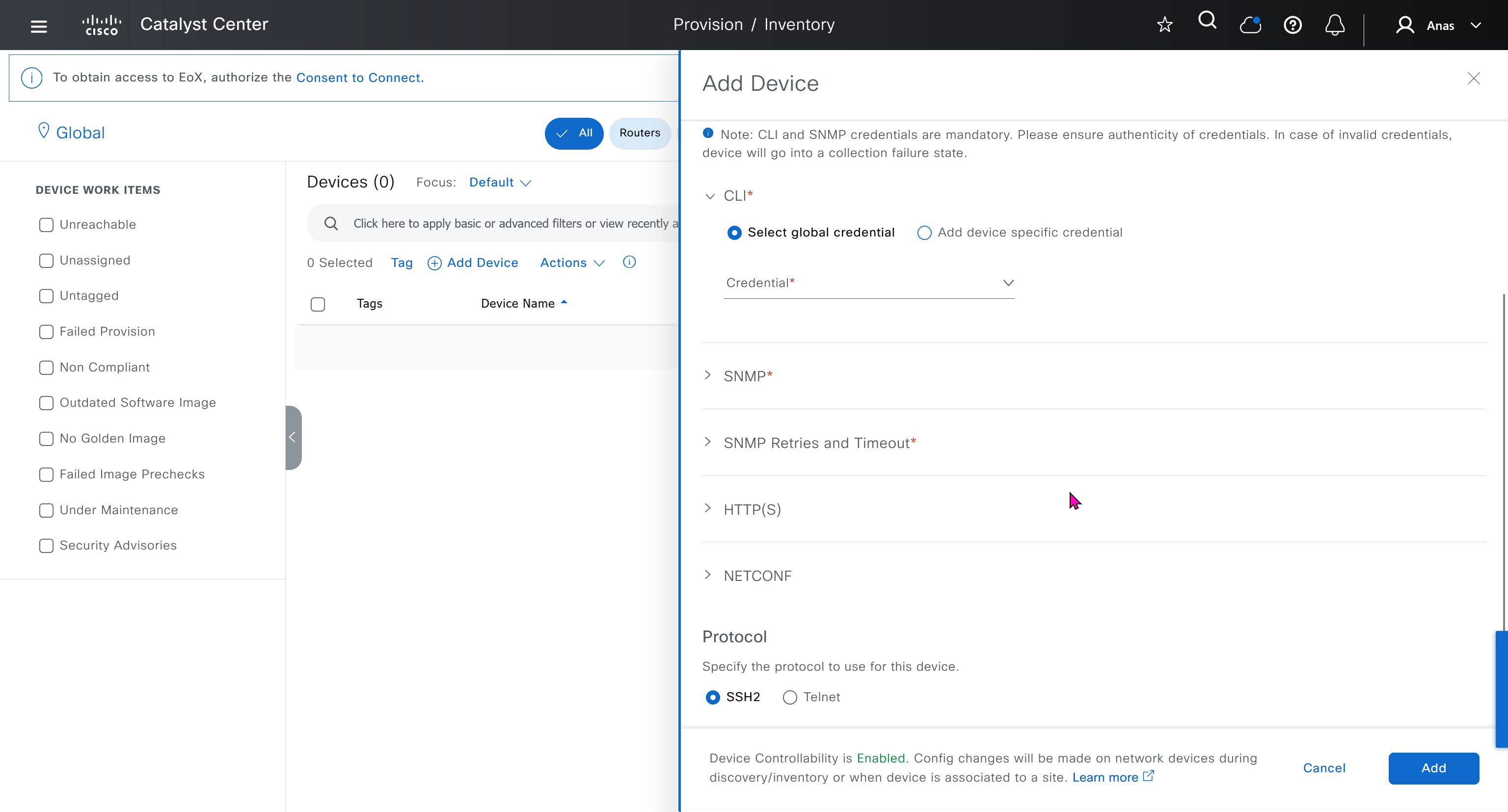
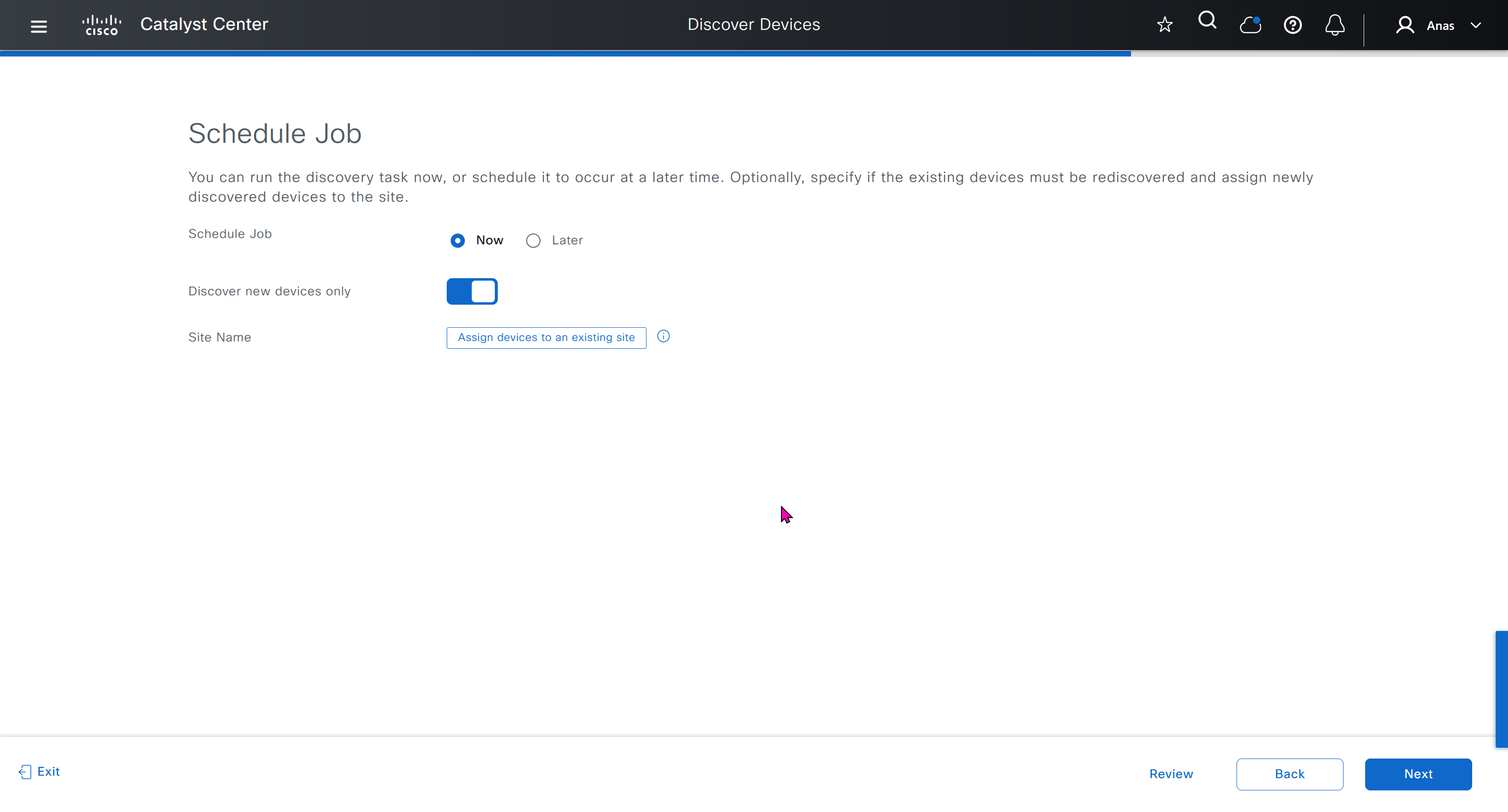
Device controllability during discovery means that configuration changes will be done during inventory / discovery or when device is associated to site, it is enabled by default









next post
SDA LM 1 – Initial Configuration & Setup
Videos
SDA – LISP and Routing introduction
Fabric spans from top of the border nodes (could be routers or switches) and down to the edge switches
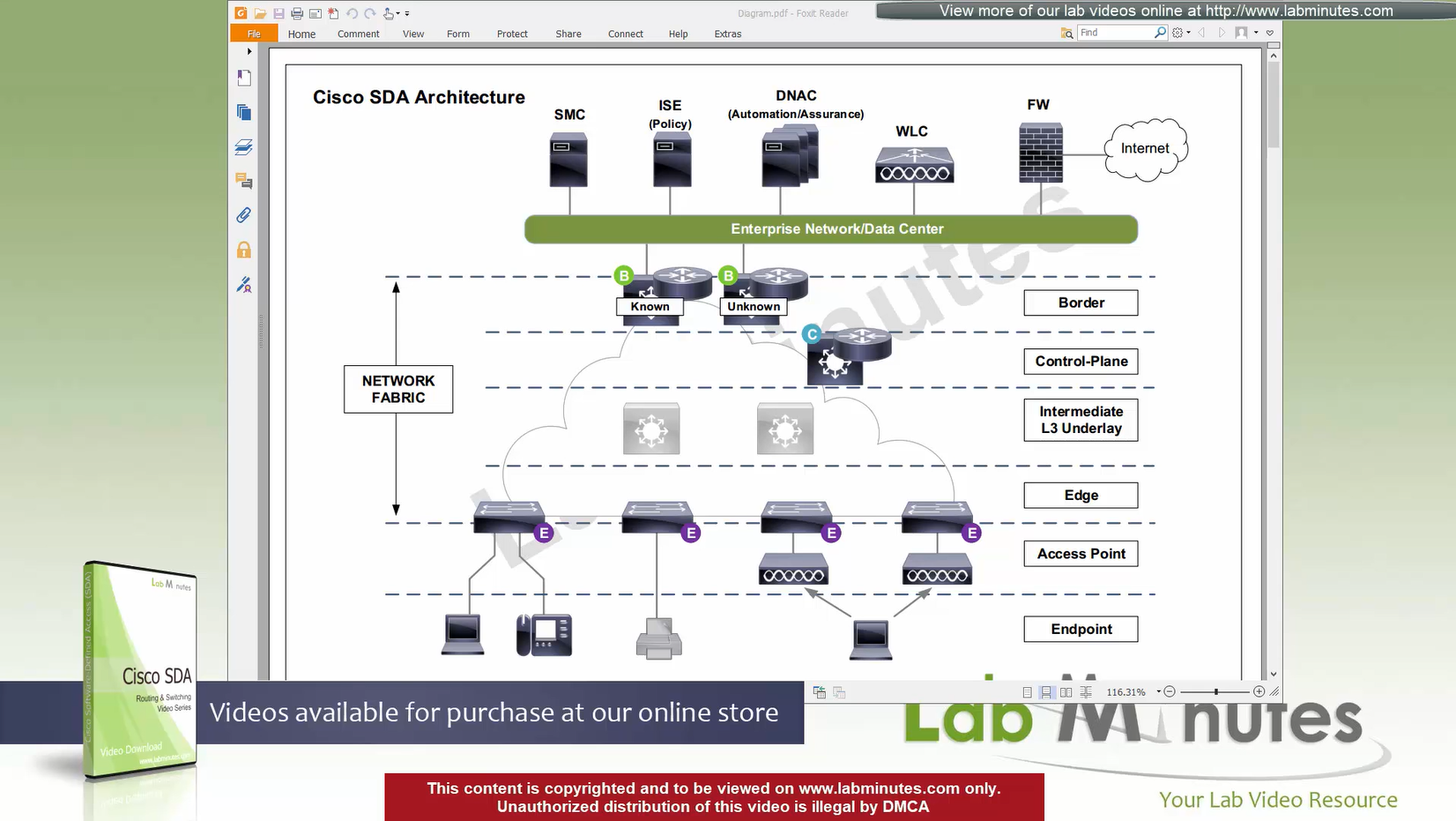
VXLAN (tunnel packets) routed across the point to point L3 (underlay)
Edge and border run L3 eliminating L2
Underlay routing is there for learning loopbacks on all switches in the domain
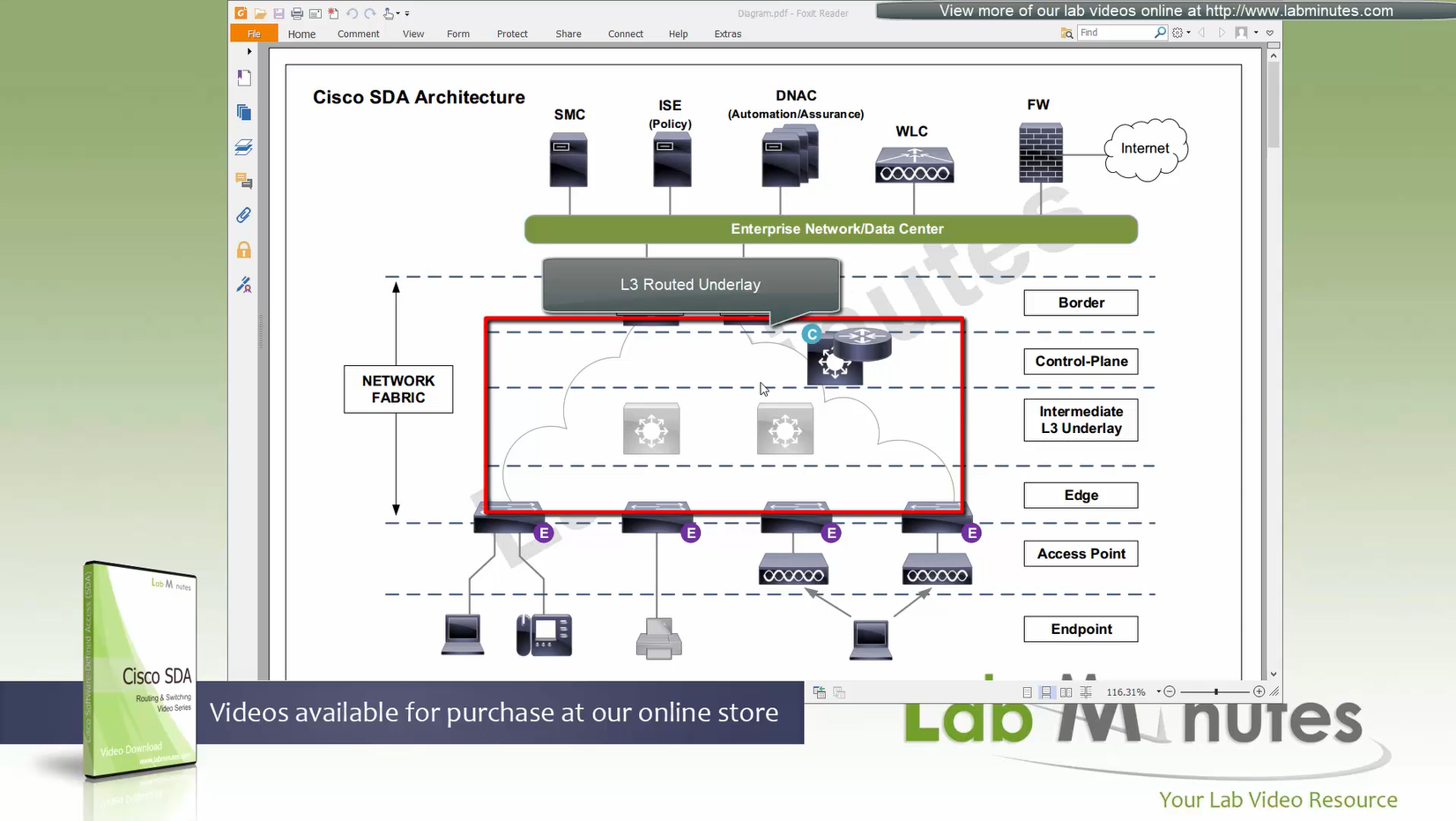
Client data can be vlan tagged or untagged
Edge switches once receive data from clients, if destination of the packet or frame is on another switch
or to outside world via border node then VXLAN encapsulation (tunnel) is created to other switch or border node
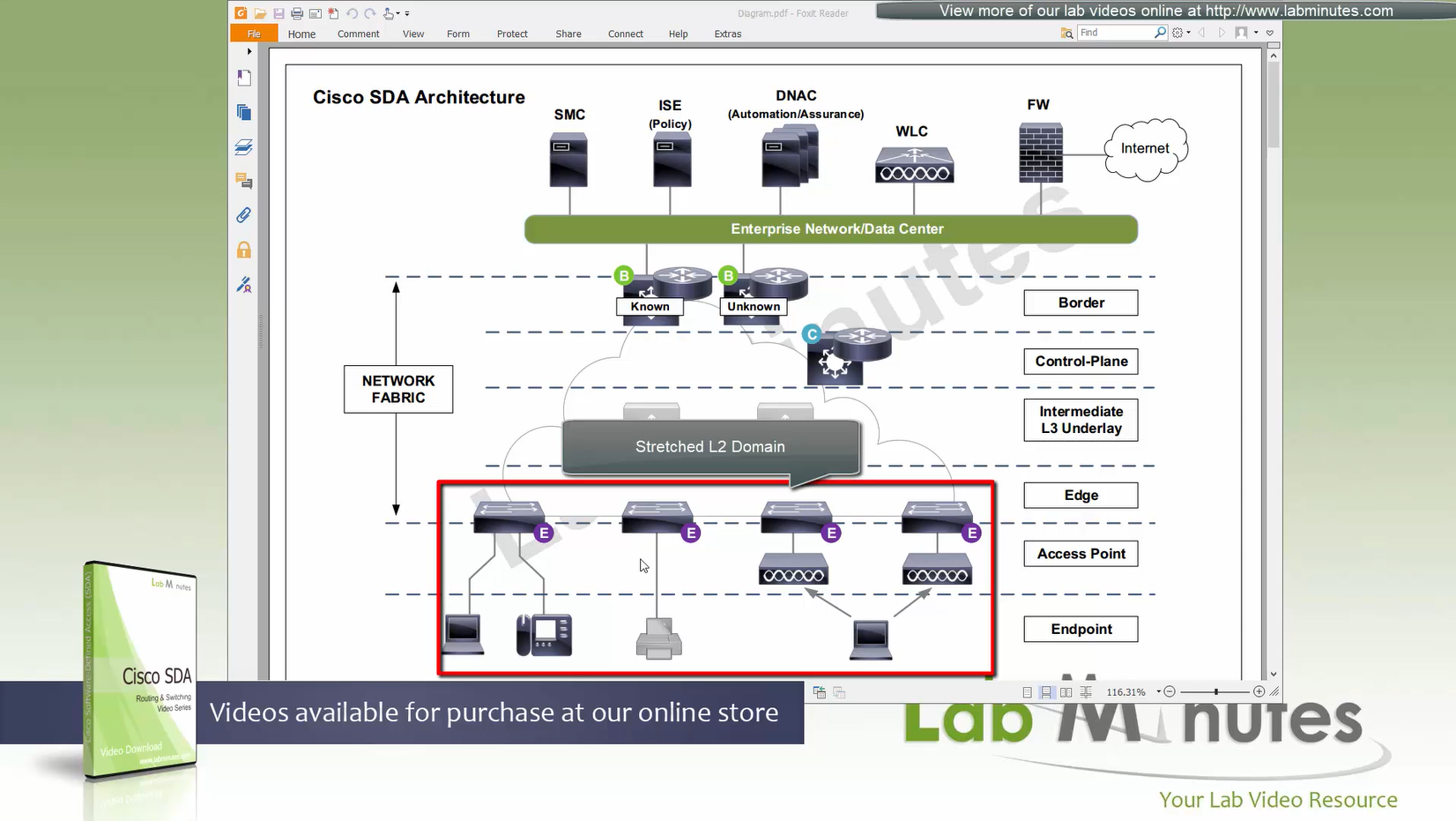
“Stretched” Layer 2 means that a client can roam from one location to another keeping their original IP address and L2 domain,
same subnets (SVIs and also vlans) are available in all edge switches for both wired and wireless
so we can say that SDA does L2 stretch within the fabric site by default
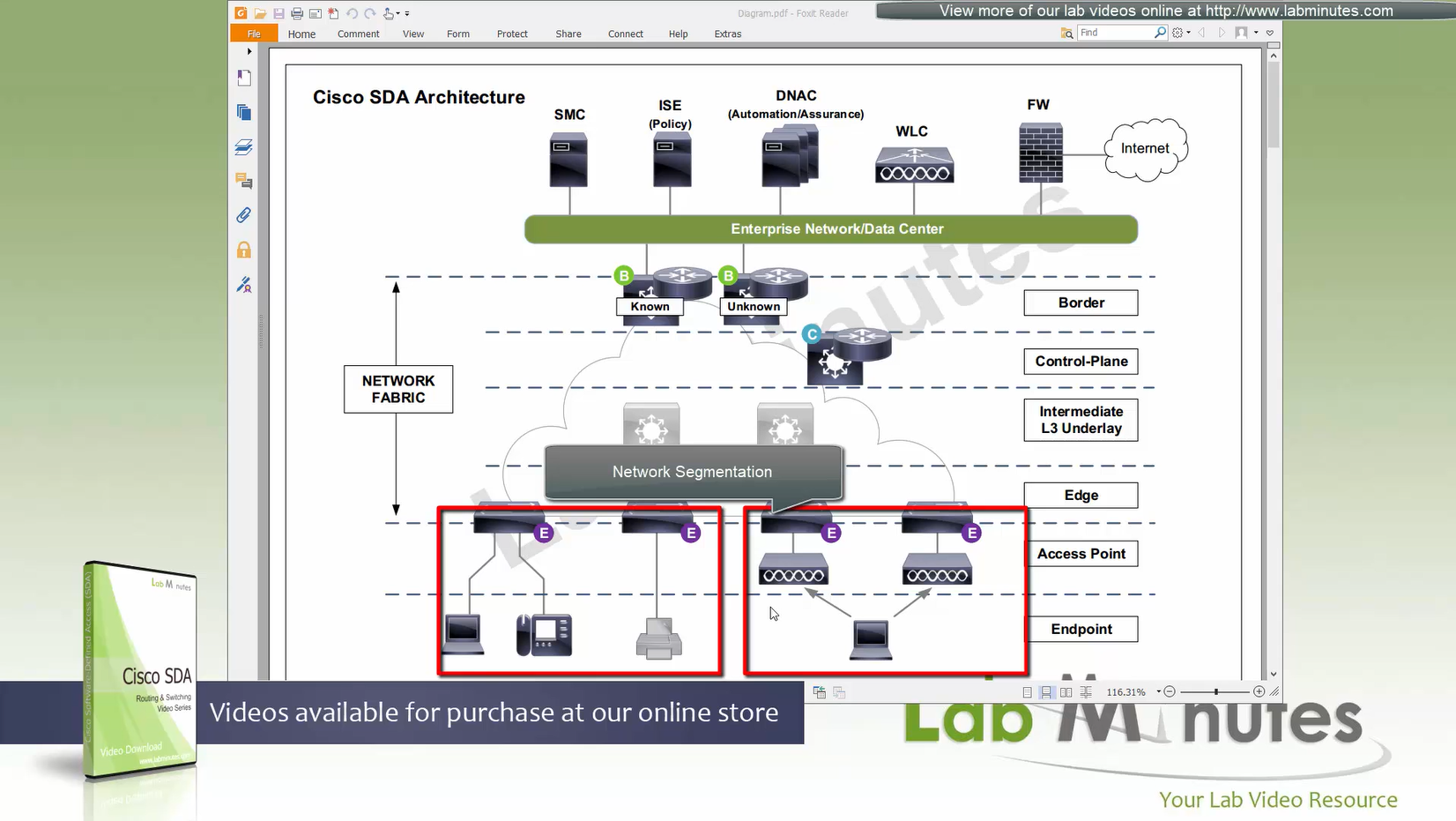
Network segmentation (different virtual networks) or Micro segmentation (using SGT tags and TrustSec)
You can also have “Fabric” enabled WLC and AP, this makes wireless clients consistent policy wise in DNAC same as wired clients policies
Edge nodes detect the endpoints and updates the control plane about endpoints detected
Edge nodes are also responsible for VXLAN encapsulation and decapsulation
Control plane node is the brains of the Fabric and provides “Endpoint to Location mapping” to the edge nodes and border nodes using LISP
in following format:
Ethernet mac address of a PC -> behind this loopback (switch)
/32 IP address of a PC -> behind this loopback (switch)
Control plane node(s) is LISP Map Server (input of endpoint entries) and LISP Map Resolver (resolves them for edge switches like a DNS server – returns the loopback IP of the switch)
VXLAN can carry both Layer 2 frames and also Layer 3 packets also
Control plane node needs to be deployed with redundancy
Control plane nodes dont need to be in the data path, in most deployments this role lives on same device as border nodes.
Border node and control plane node should be deployed in pair (2x) to have redundancy in the network
Border and control nodes are usually combined on single physical device then there should be 2 of those devices in the network
Fabric border node – acts as a gateway to fabric world
Network traffic from Fabric will need to leave the fabric border node to access the rest of the enterprise network and internet
border node peers with external networks via Fusion router and advertise Fabric to fusion and also redistribute external networks into fabric.
Any external routes learned will be registered with control plane “so that those external destinations are reachable by fabric”
By virtue of control plane node “these external routes will be available to edge nodes once registered” and access those destinations.
When packets from edge needs to go out, edge queries the control plane and control plane needs to have that routes information, which will have edge make tunnels to the border node, same logic is for edge to edge packet / frame sending between hosts connected to edge nodes.
so control plane is consulted if any packets need to leave for destination other than local switch
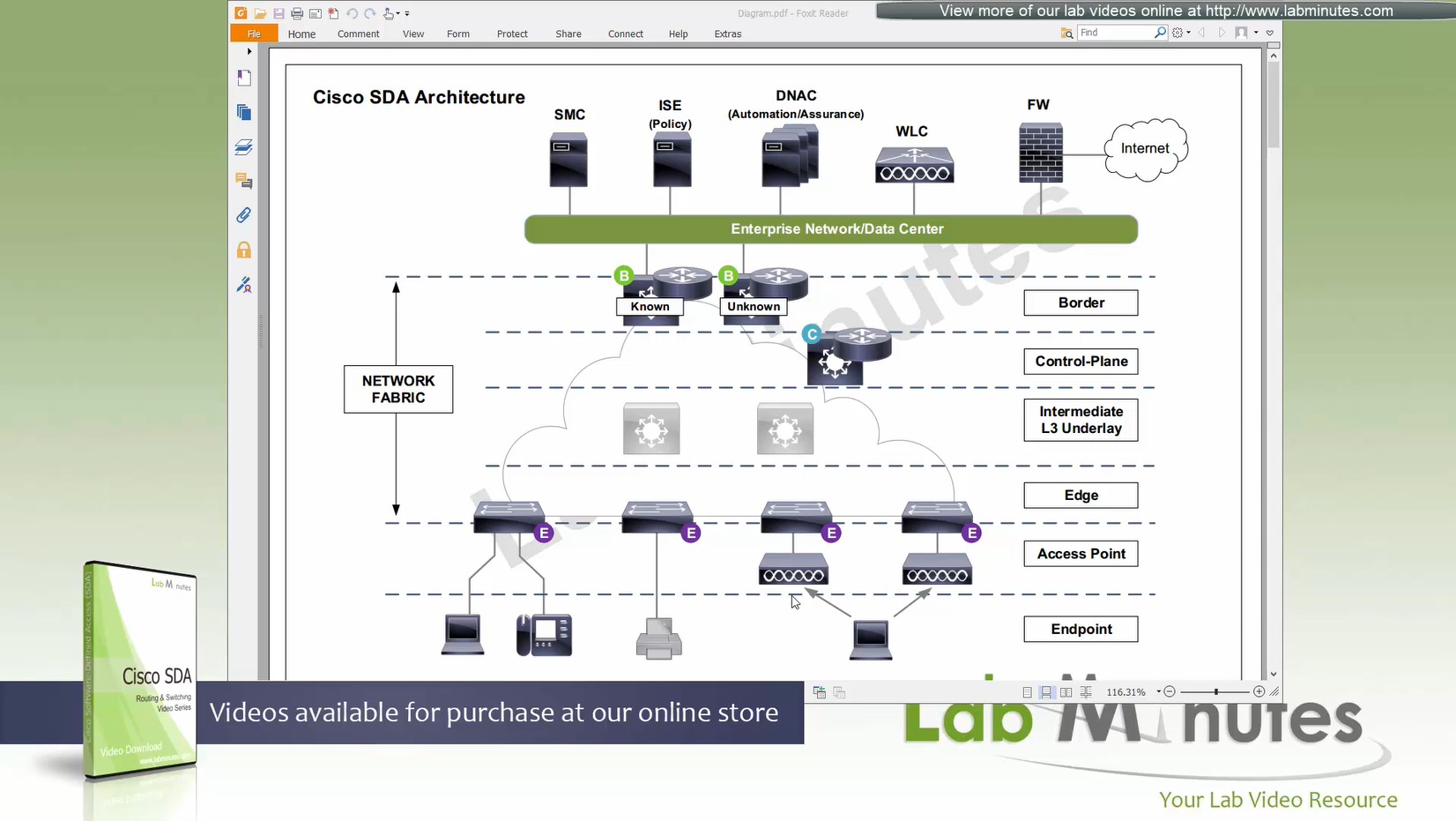
There are 2 types of border nodes
1. Known Border Node
2. “Default Border Node” or “Unknown Border Node”
Border node is for destinations that are known such as “subnets”, “server vlans” etc
Second type of border node is that deals with unknown routes and is also called Default Border, it is used as a last resort if there is no match to specific routes in Known Border, usually this is traffic for default route or internet,
When edge nodes consult control plane and control plane node does not know about the destination, Control plane answers (vxlan IP) loopback IP of default border node
Both Known Border and Unknown Border can live on same device or two different devices
but in this diagram they are shown to be 2 different devices
Now the role separation goes 2 levels on border
- control plane node
- border node
- known border node
- default border node
Intermediate Underlay device:
Intermediate Underlay devices need to be able to support the “Jumbo frame” and use ISIS
Cisco recommends this intermediate devices to participate ISIS (shortest path) with redundant links and there should be no spanning-tree or layer 2 in the “Fabric”.
Underlay Intermediate device has layer 3 interfaces and no spanning-tree or L2 port channels. Intermediate nodes are required to aggregate all the access edge nodes into something and then connect into border switch or router, direct connections to border are supported but should not be done for larger site due to scalability issues
“Fabric mode WLCs” still manages the AP and maintains client connection information also but like edge node
Fabric mode WLC reports to control plane node and lets it know about the client – this the main thing
communicates associations and communicates roamings to control plane, controller sits outside of the fabric and APs sit inside the fabric but at the host connection layer on the edge nodes
WLC can be connected outside the fabric as long as it has reachability to the border and control and APs
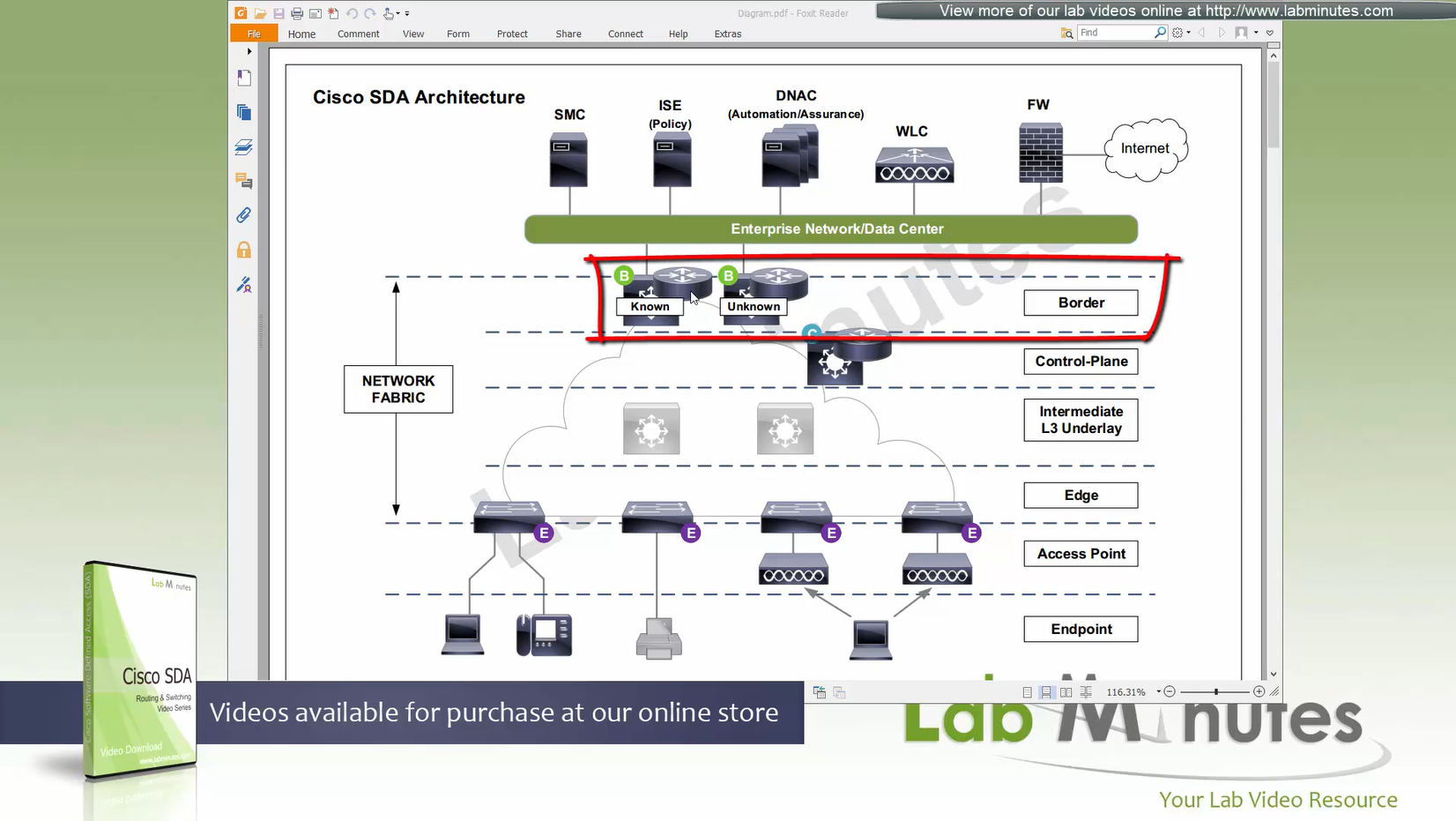
Fabric mode AP, there is one major difference from local mode AP, (Data tunnel) they will not send data to WLC for it to be centrally switched but exit data locally on the fabric via VXLAN tunnel > edge switch
Fabric AP participates in VXLAN encapsulation however they maintain CAPWAP tunnel (Control tunnel only) to the WLC at the same time,
so WLC can learn about the clients and relay same info to the control plane node
This allows wireless clients to be treated within the same system and policies of the fabric.
AP <–CAPWAP CONTROL–> WLC <–LISP–> Control node
AP <–VXLAN–> edge node
AP must connect to edge node “directly”, there should be no switches in between AP and Edge node
So WLC sites outside the fabric or Fabric border node and APs sits directly under the edge nodes
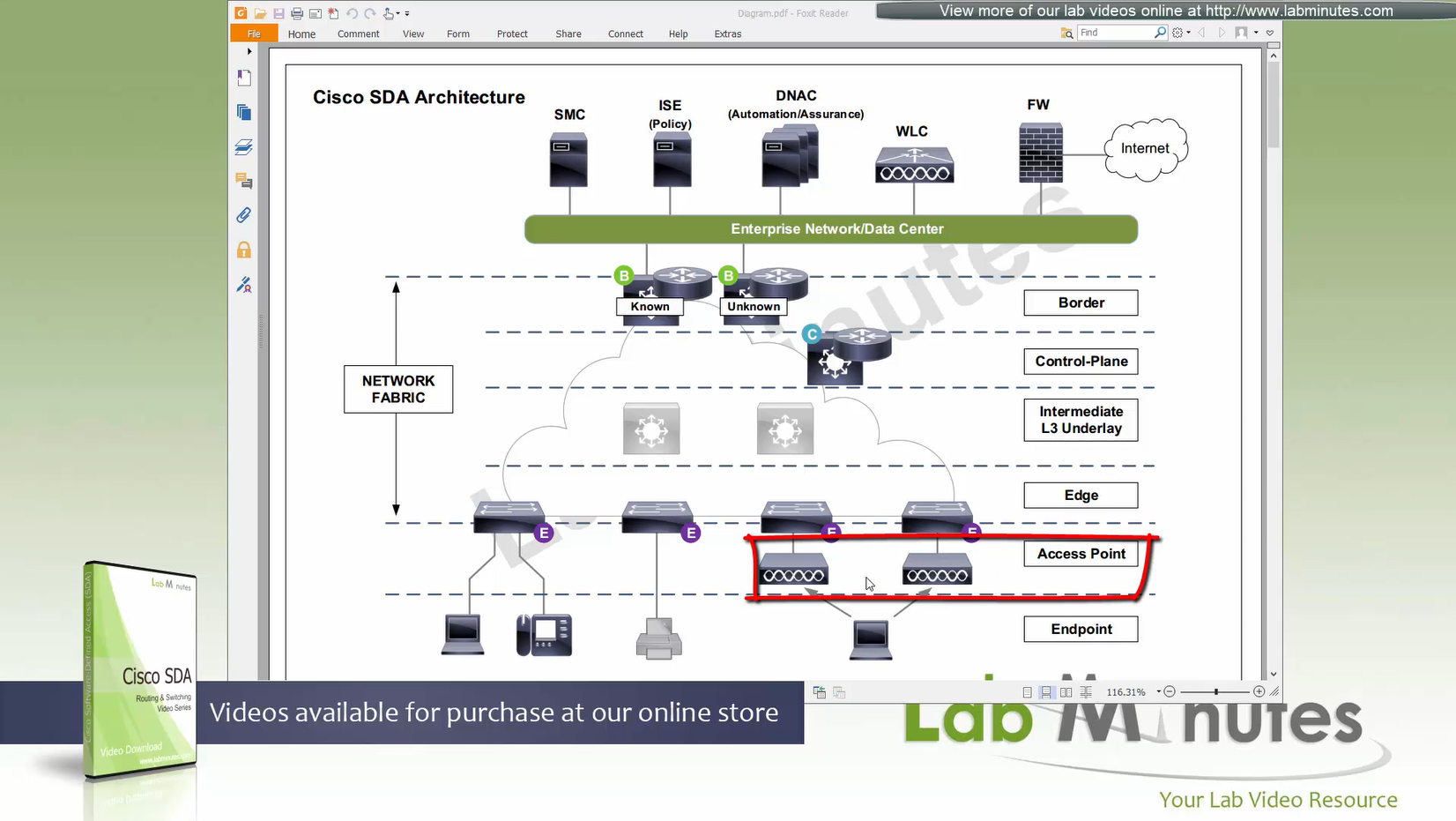
because Access points connect to edge nodes directly clients are connected like
Client <–Wireless–> AP <–VXLAN–> Edge node
DNAC
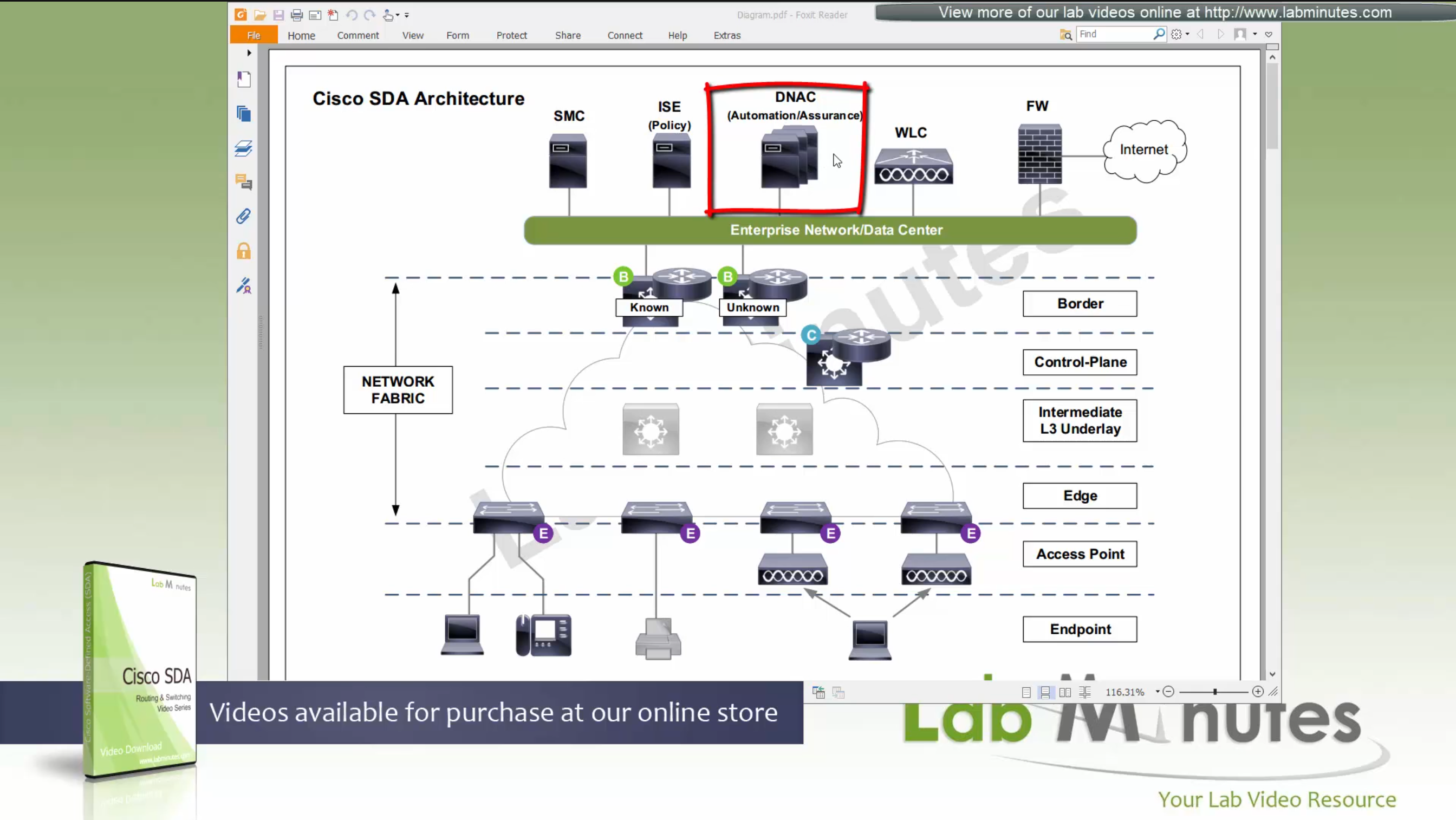
ISE maintains the security policy and contains Authentication / Authorization policy and also TrustSec related components
DNAC uses APIs to push configuration to ISE for SGT but ISE is separately managed
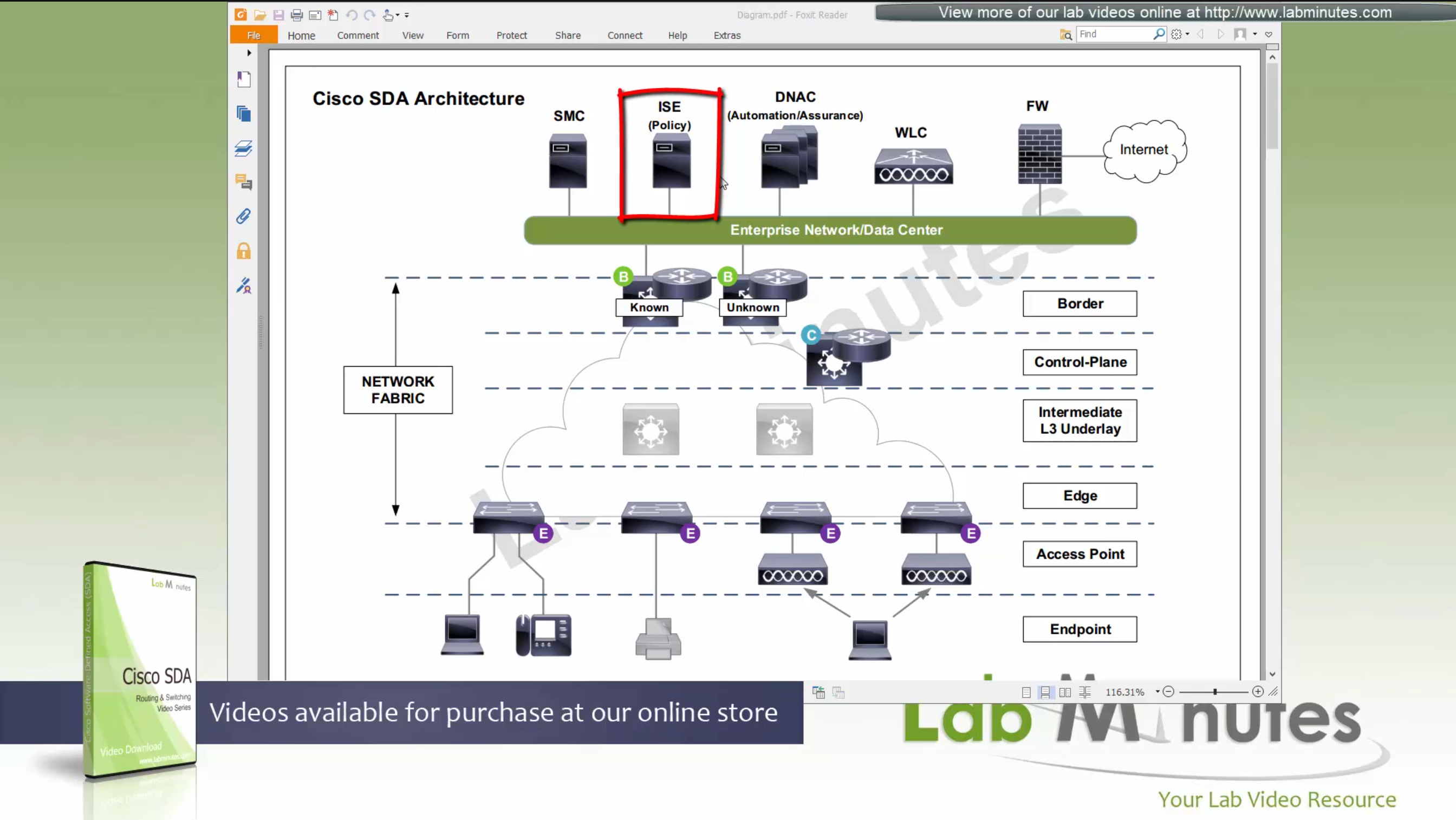
Management loosing network such as DNAC will keep the data forwarding and not cause outage
One thing to keep in mind is that we need to have high speed LAN like access between all fabric nodes and DNAC, that is why DNAC cannot be spanned across WAN, all Fabrics must have high speed access to DNAC
DNAC is available as C220-M4 which is same C series server as APIC for ACI
It is always recommended by Cisco to deploy DNAC in cluster of 3
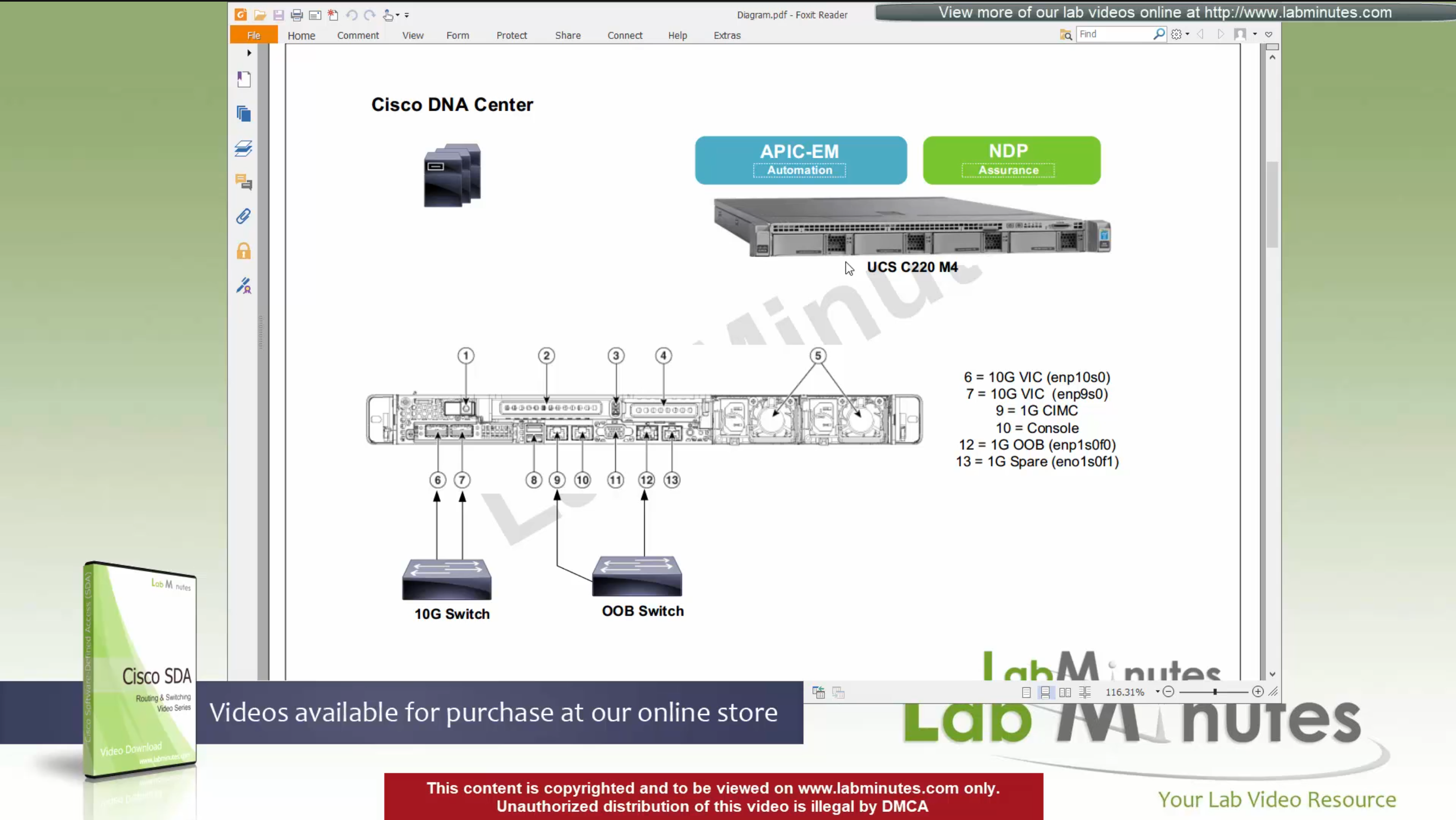
For connectivity DNAC has 2x (redundant) 10G VIC Cards – Data path for managing the fabric
for Management connections it is not mandatory to configure the OOB connection
Data port IP can be used for management unlike ACI, where GUI and SSH must strictly be done via OOB IP
CIMC interface – Server interface for KVM and firmware upgrades
Console interface – in case network connectivity is lost
(out of band) OOB Mgmt interface – optional for HTTP and SSH for DNAC but it is recommended so we have another path for accessing the GUI and SSH
There are 2 engines running on DNAC,
APIC-EM
NDP
There is 3rd engine called policy engine but it does not run on DNAC but on ISE
APIC-EM shares a lot of features with APIC and helps with Network topology discovery, software management and upgrades aspect etc
APIC-EM is also responsible for the network automation
NDP stands for Network Data Platform – NDP takes care of the, end to end network “monitoring”, “telemetry”, “assurance” and “data analytics”, This is like NPM of Solarwinds
NDP is more with analysis and alerting
while the APIC-EM is like NCM for pushing changes and making changes
In NDP Assurance comes from the fact that it goes one level deep and not just polls network devices for system stats and health but it also gets the Client’s connectivity monitored from client and their experience perspective
Client connection stats and connection health and client experience is one of the big things, and it is client connectivity that “assures” that network is working because clients are live and using the network, so instead of SLA on the box, client data traversing the network is a better testament that network is working or not
NDP also has “machine learning” elements
DNAC Assurance or NDP collects data from various sources, once data is received, Assurance engine does correlation and provide information
This is the list of devices that are supported, some devices have some features supported and others fully support all the features. This sheet can be found on google, Y and N in column have been added, older hardware possibly cannot support those features
Most devices support basic functionality offered by APIC-EM such as inventory, topology, Image Management, plug and play, easy QoS and so on.
These things are marked in green color, but when it comes to SDA (green column) we can see that only limited set of new devices are supported
We can see that very first switch that can do SDA is 3650 Copper
SDA deployment shows what is supported on which models based on the “node role such as edge node, border node, control nodes etc”,
“for example some cisco models can be the edge nodes only but not the border node or control node”.
So make sure that we order right kind of hardware before deployment.
If we are going for new hardware then Cat 9k will support most of the SDA features
If you are looking to “scale” for a lot “larger campus” then we can upgrade the “border or control nodes to routers which have bigger memory to deal with large number of routes which can get us bigger MAP server”
This list also includes routers, as routers are also supported in SDA for Border and control nodes
See how some devices can be edge and not border or control and then there are some devices which can be border and control but not the edge, that is why it is safe to go with 9300 and 9500 series Catalyst switches
3850 switches are supported for SDA but for small deployments
Similarly there are WLCs that are validated for SDA, be sure to check SDA hardware sheet
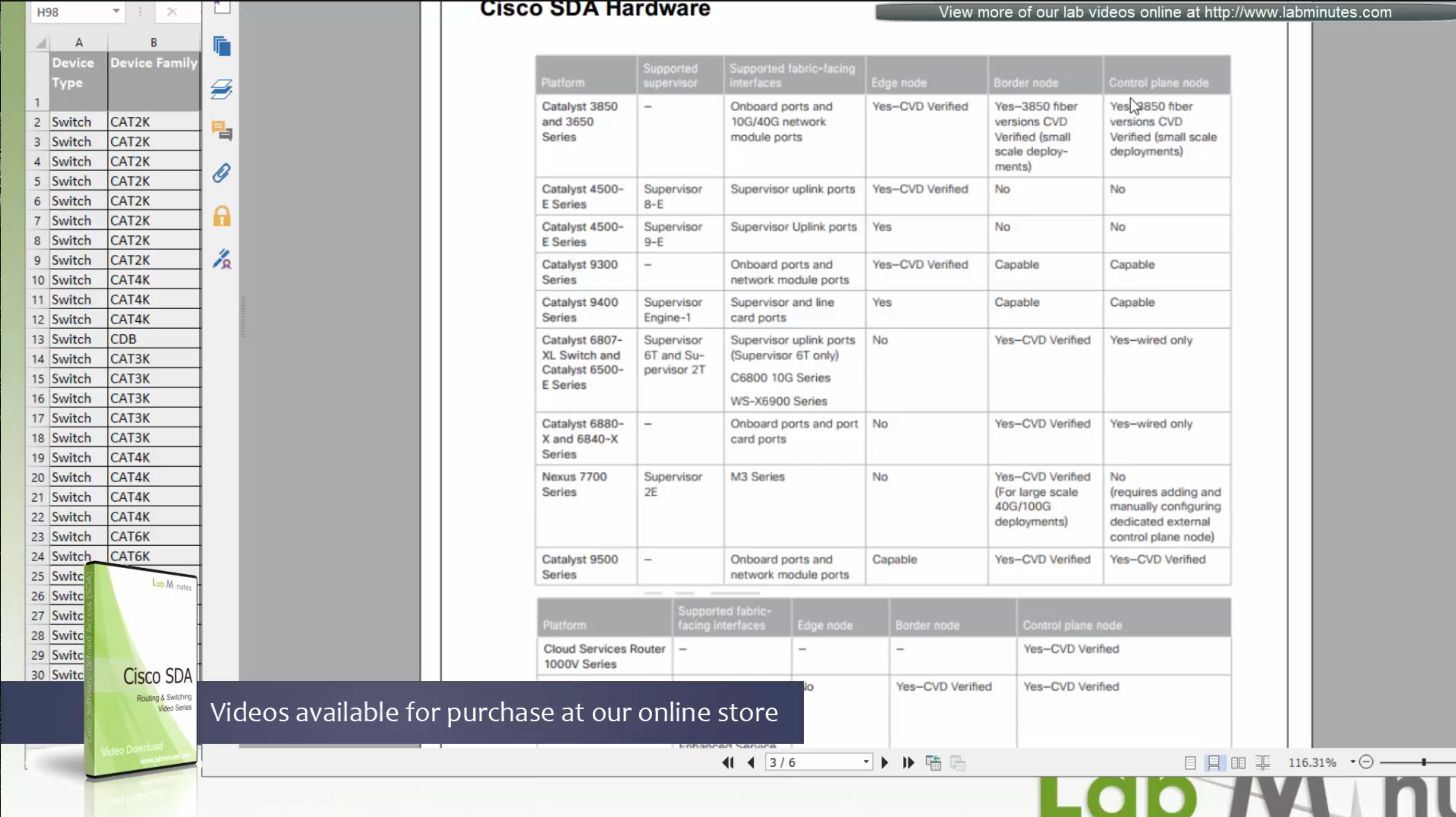
Always consult “ordering guide” for new deployments
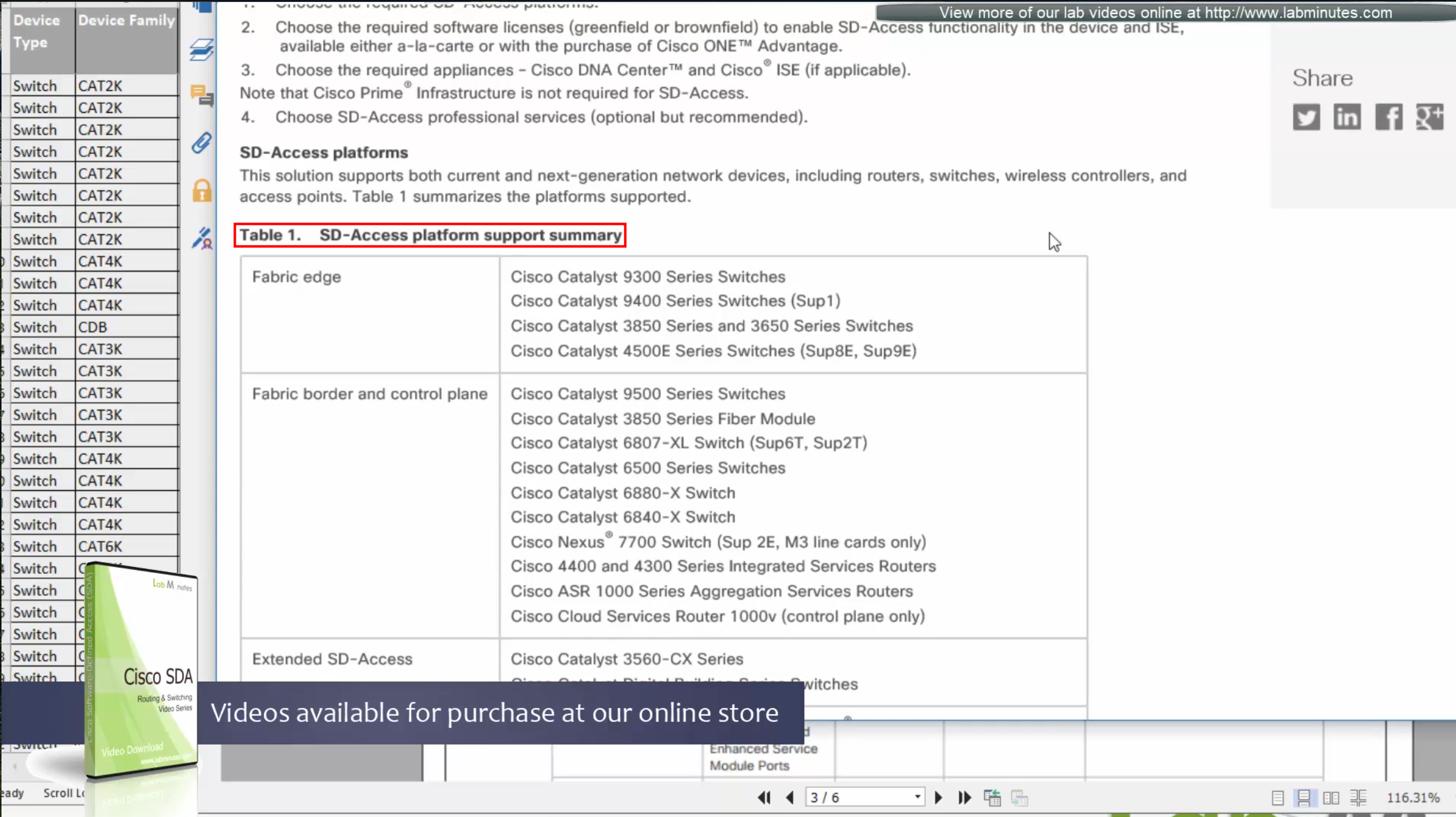
Fabric is consistent across the network and is not different unlike legacy network which can have different networks between different switches because of inconsistent configuration. Fabric on the other hand is consistent from L2 and L3 perspective.
All the underlay network is going to see is UDP packets


Fabric edge nodes tell the control plane about new endpoint by snooping the ARP response and DHCP offer packets (device tracking on edge), information told to control pane includes “MAC addresses”, “IP addresses”, “port connected to”, “Liveliness” (to see if host is there or not) and “VNI host belongs to” (VNI is equivalent of the VLAN in VXLAN world).
Edge node sends a “MAP register” message to control node
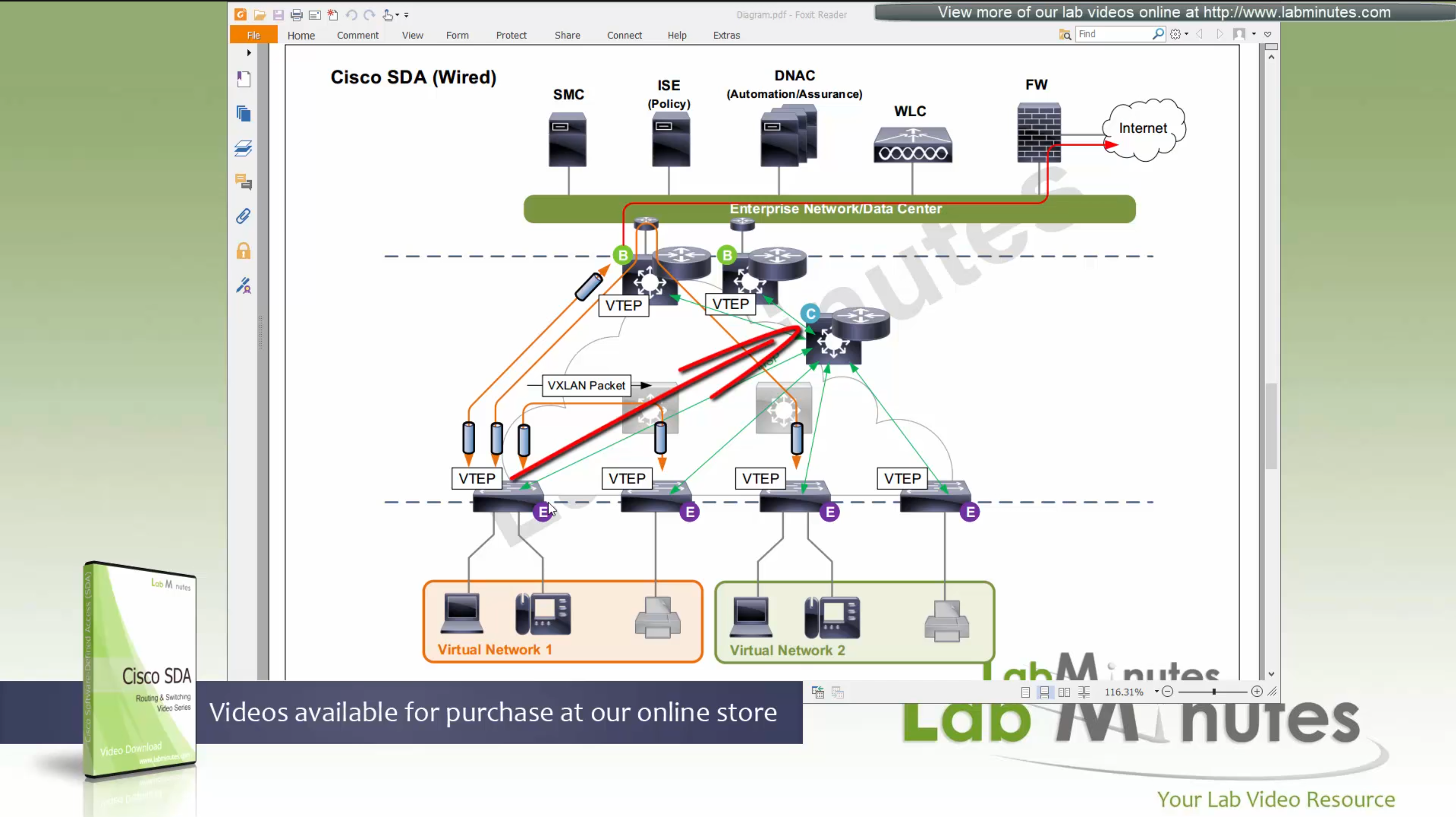
Control node creates an EID (Endpoint identifier) to RLOC (Routing locator) entry is created in database
VTEP and RLOC refers to same thing, the loopback IP address on the switch
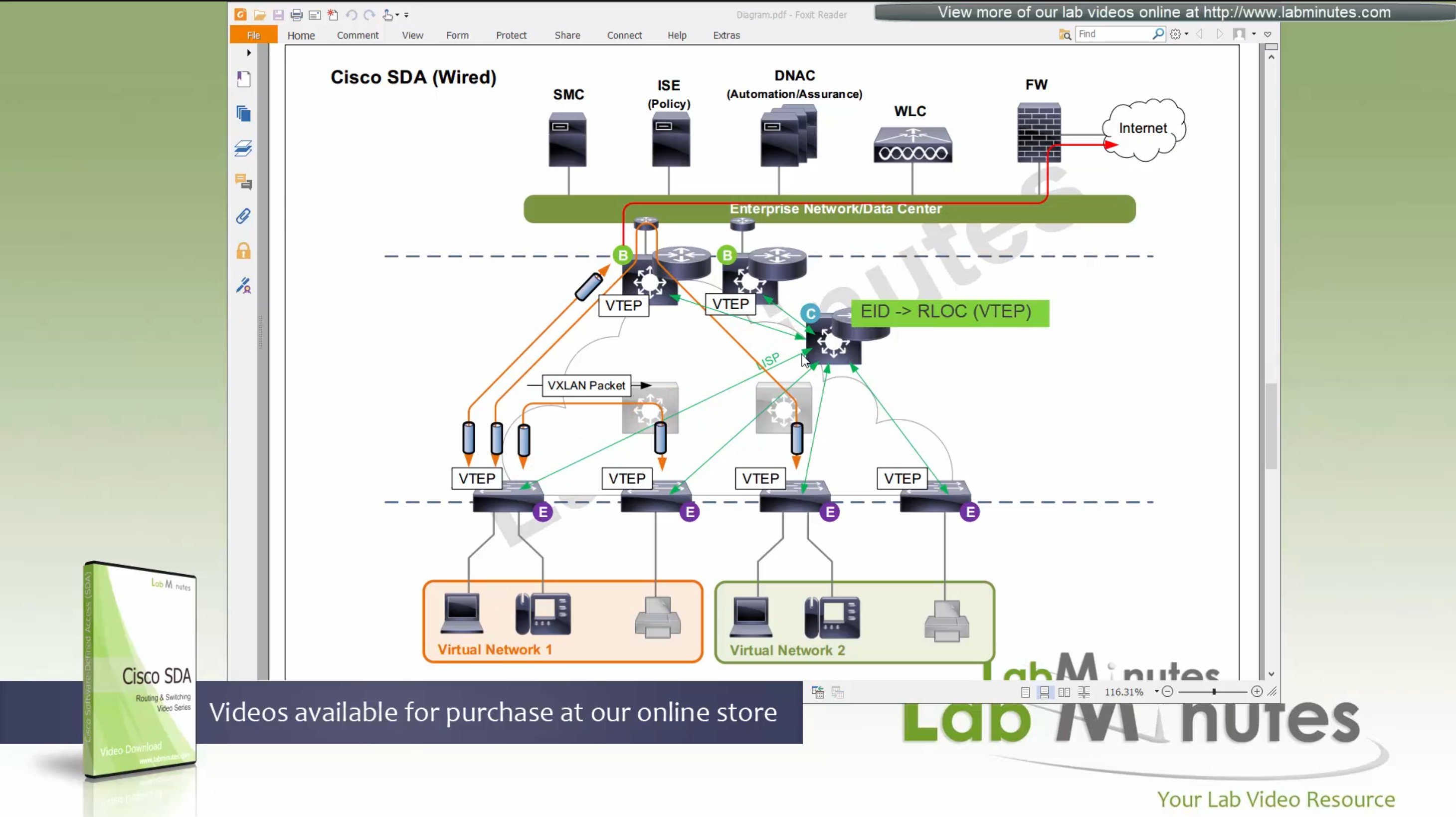
Border node does the same thing the edge nodes do with control node (if on same chassis, then it does that process internally), but instead of registering Endpoint IDs it has prefixes to deal with, prefixes it learns from Fusion for external networks (outside of fabric) as EIDs to Control node.

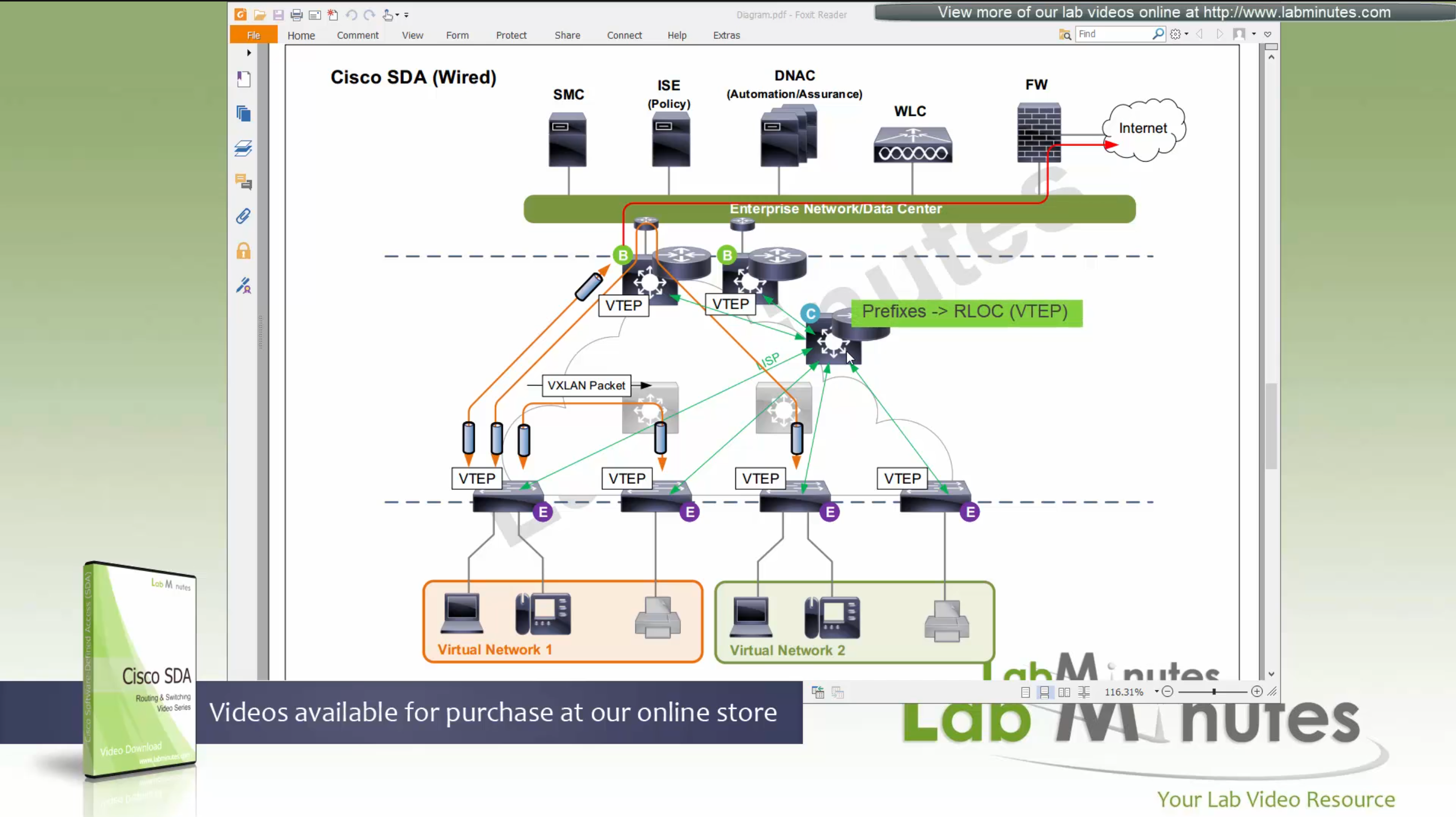
which means that control plane node not only maintains the EID but also the prefixes
border node needs to be redundant

Edge switches query the MAP server on control node
Similarly when border receives traffic destined to an EID in fabric (inbound)
or border receives traffic for networks outside of the fabric (outbound)
border node goes to control node and queries the MAP server on control node
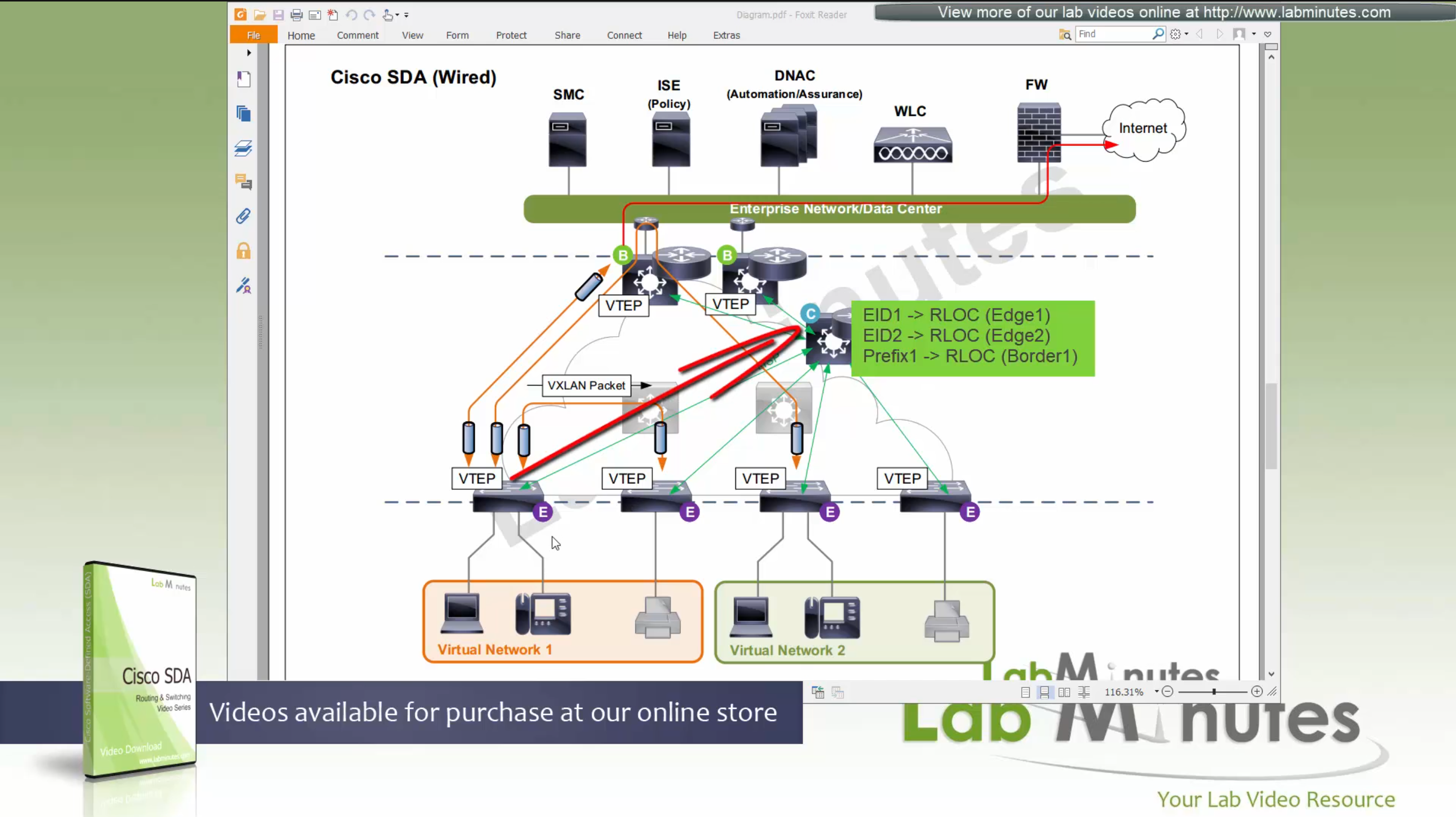
control plane node then responds with the RLOC,
Caching: border or edge node then caches in a local cache that RLOC entry for future use
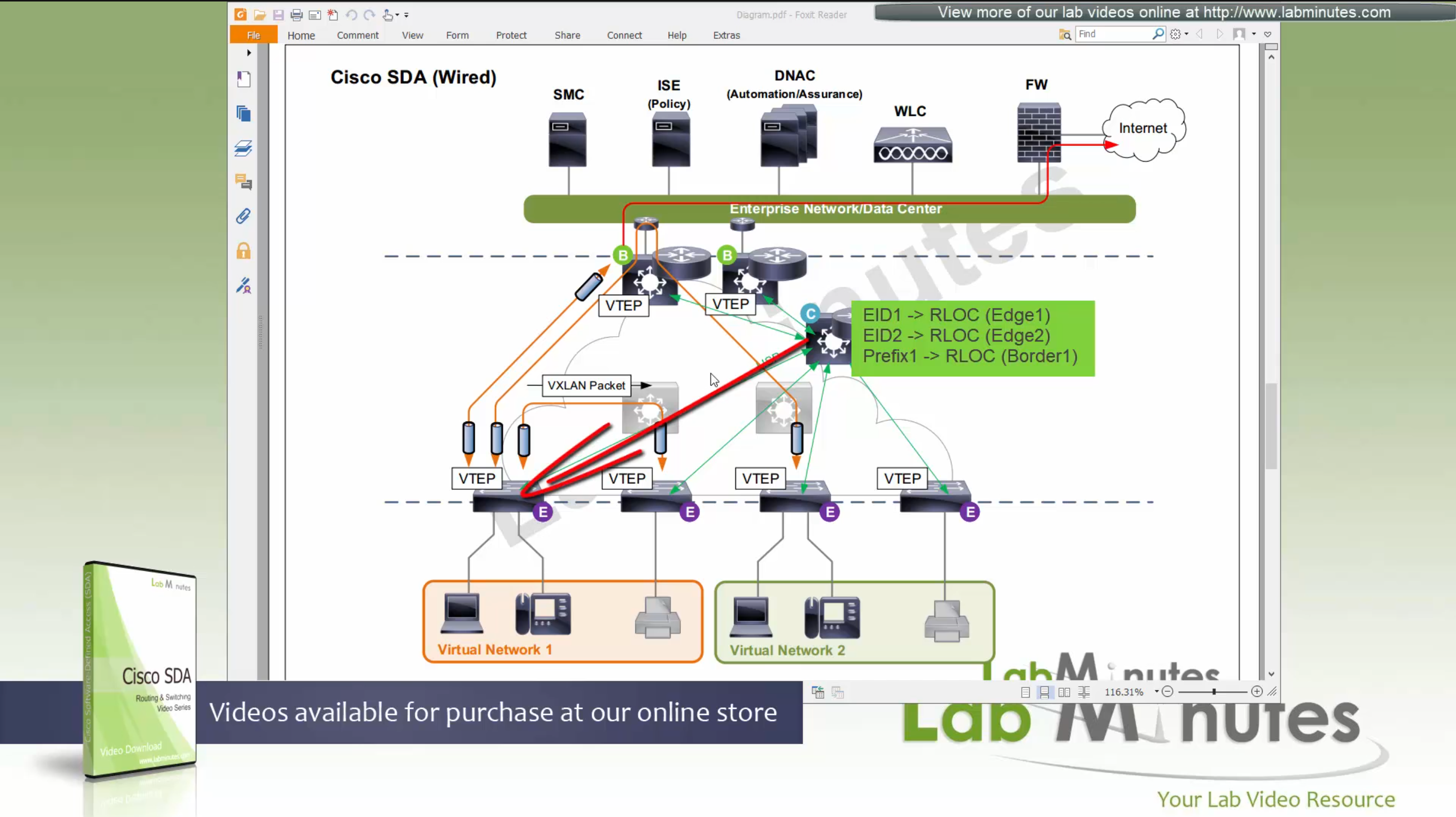
Edge node or border then makes VXLAN tunnel to that RLOC
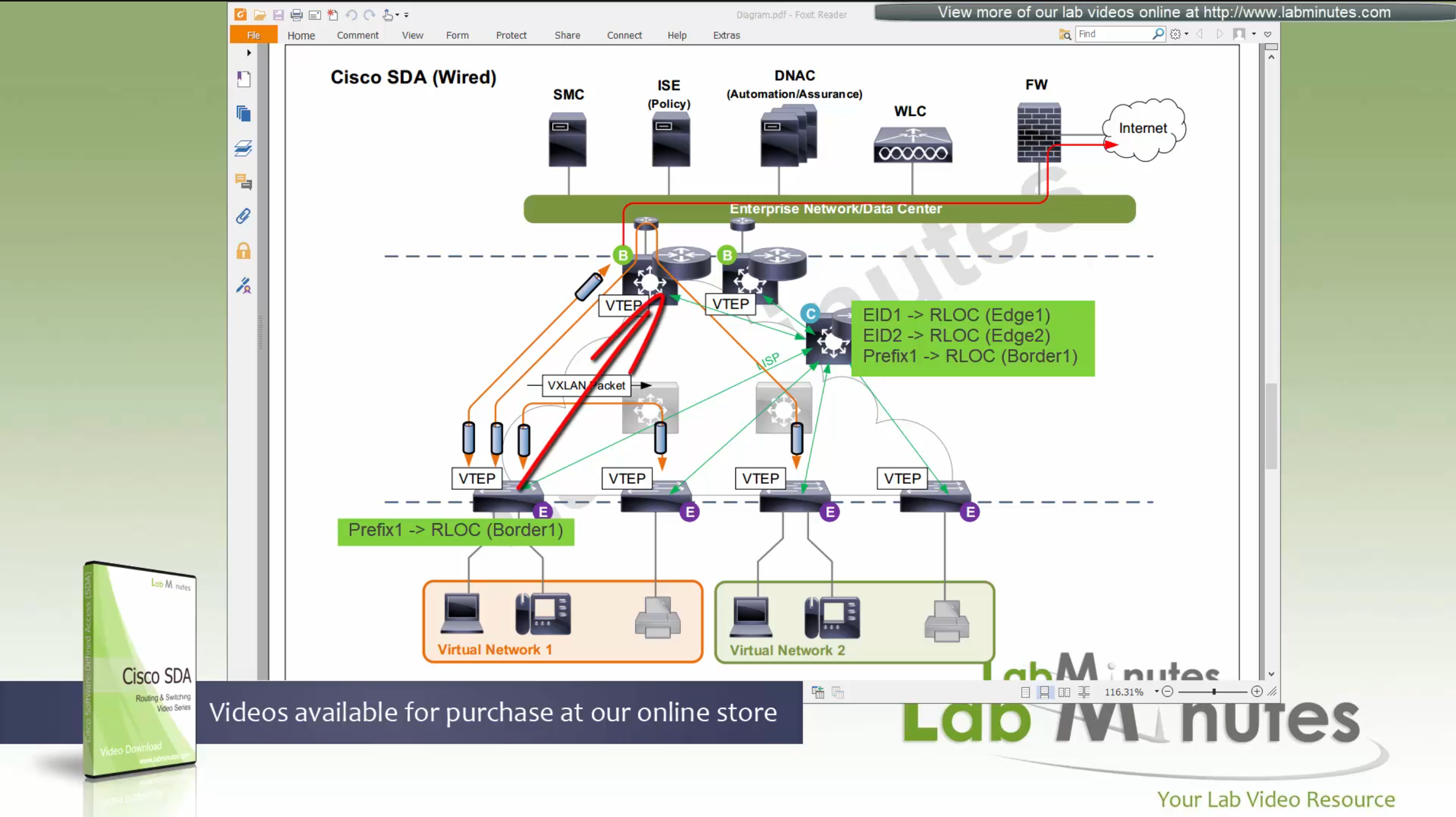
because edge and border receives and caches the RLOC entries on need to basis, it keeps their routing table or FIB small and this translates to scalability, that acts as a consulting table to route or switch over the fabric and not the routing table
Edge nodes also run something called Anycast gateway which makes SVI available on all the edge and border nodes
These SVIs also have same MAC addresses so when client roams from one node to another, it is seamless
despite presence of SVIs edge nodes always ask / consult control plane node and get the answer because these SVIs are available on edge nodes simply to offer seamless L3 gateway after roaming to new location
These SVI anycast gateways exist on both Border nodes and also on edge nodes
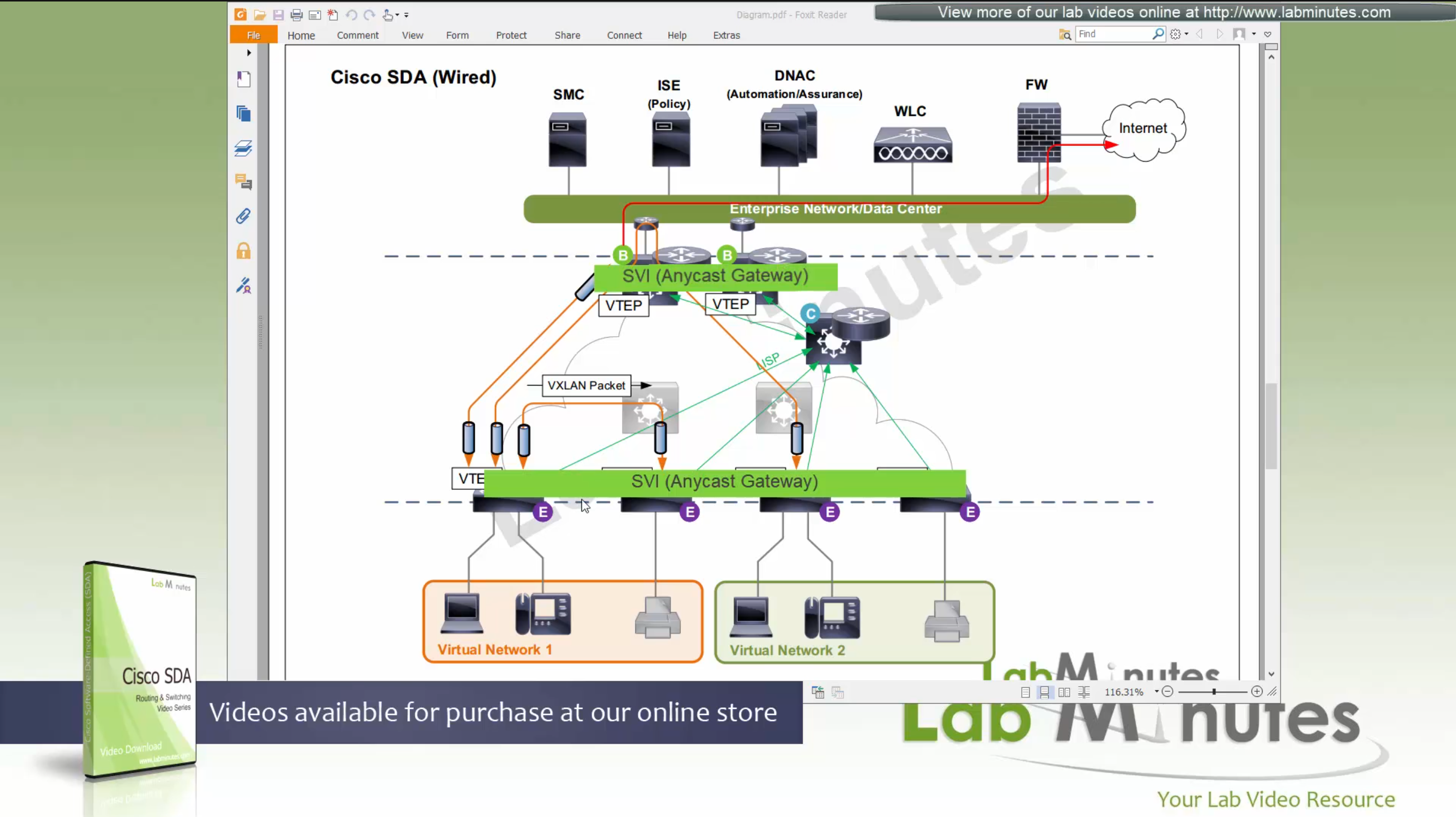
Here we have two different virtual networks or VRFs
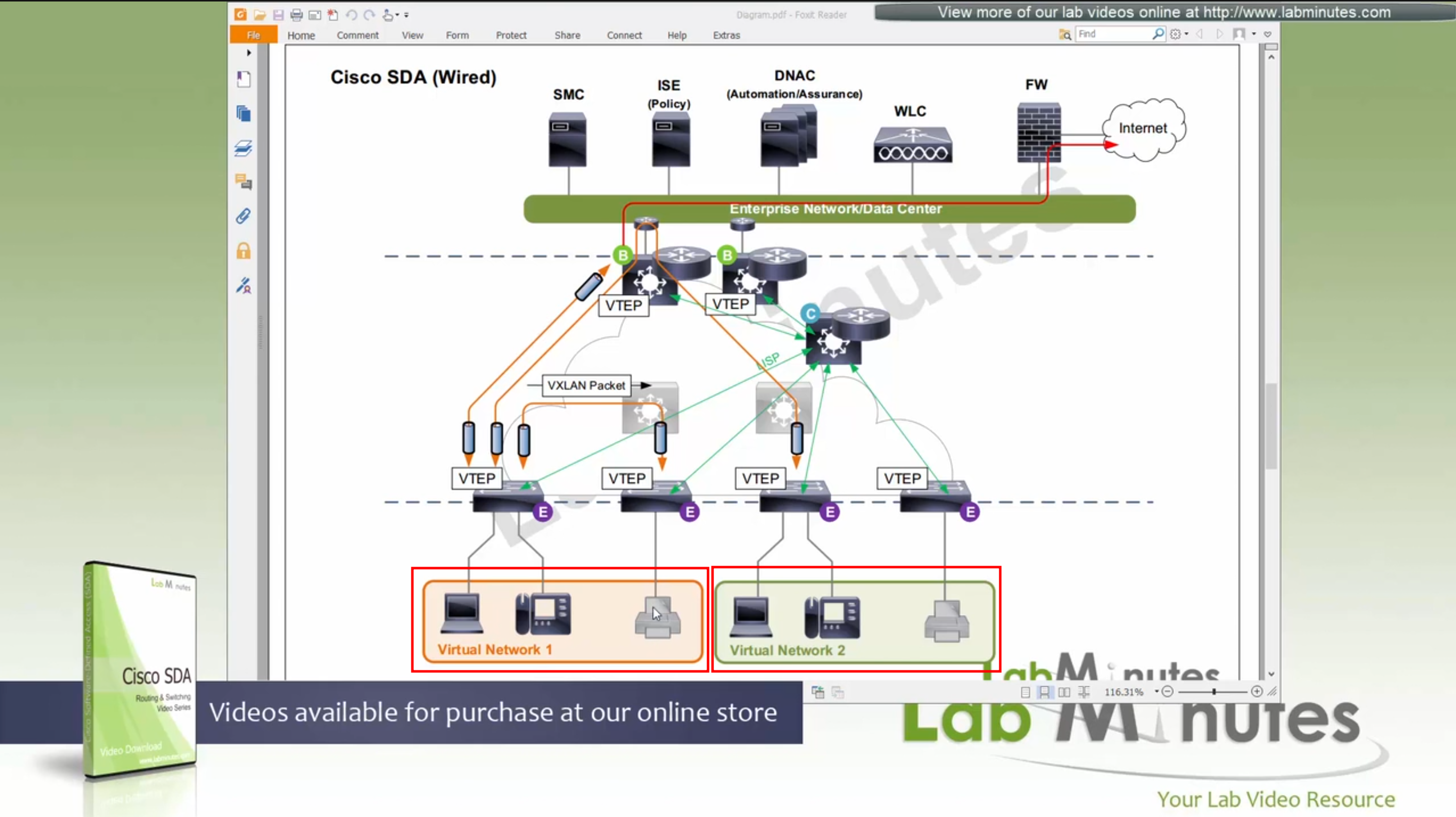
Scenario 1: Packet stays on same switch
In this scenario packet does not leave the switch and is switched from one port to another and that makes it fastest, if you have an ultra low latency requirement where even couple of milliseconds of latency such as 2 ms or latency of VXLAN packetization and encapsulation is not tolerable then place the hosts on same switch
Scenario 2: Packet stays within the Fabric, IntraVN (same VN) traffic
When PC needs to communicate to the printer, it speaks to control node (because printer is on another edge node) and obtains RLOC for that edge node where printer is attached,
it will create a vxlan packet with correct L2 VNI tag, and correct outer L3 RLOC destination IP address
and insert original IP packet into it as a payload and then send it out to the underlay to deliver.
Underlay will deliver
As seen in diagram, this VXLAN flow will not touch border node
As these VXLAN packets reach Intermediate Nodes, because they have loopbacks advertised in ISIS (shortest paths for loopbacks) VXLAN packets will be switched from “edge node to Intermediate node to edge node” Triangle: Edge <–> Intermediate <–> Edge
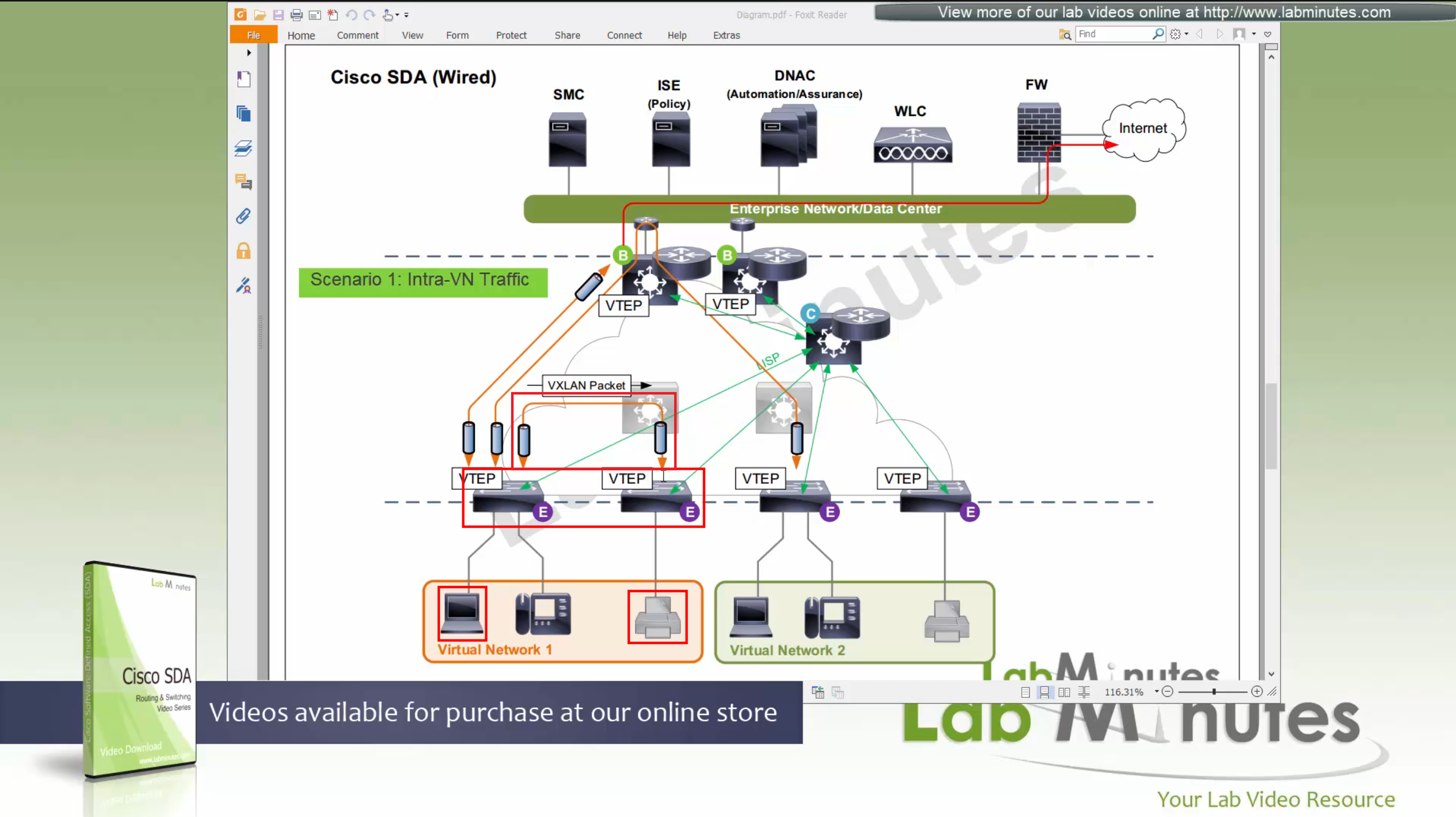
Scenario 3: Packet destined for “Known” external network outside the fabric.
Edge node inquires the control plane for “destination”, control plane returns the RLOC of the border node that registered the prefix and then edge sends the packet to border node,
it will create a vxlan packet with correct L2 VNI tag, and correct outer L3 RLOC destination IP address
and insert original IP packet into it as a carrier and its payload and then send it out to the underlay to deliver.
Underlay will deliver vxlan packets to the border node and border node will “decapsulate and deliver it out to the external network”
Packets will flow from edge node to intermediate node to border node and then fusion node to get to external networks
Edge <–> Intermediate <–> Border <–> Fusion <–> External destinations
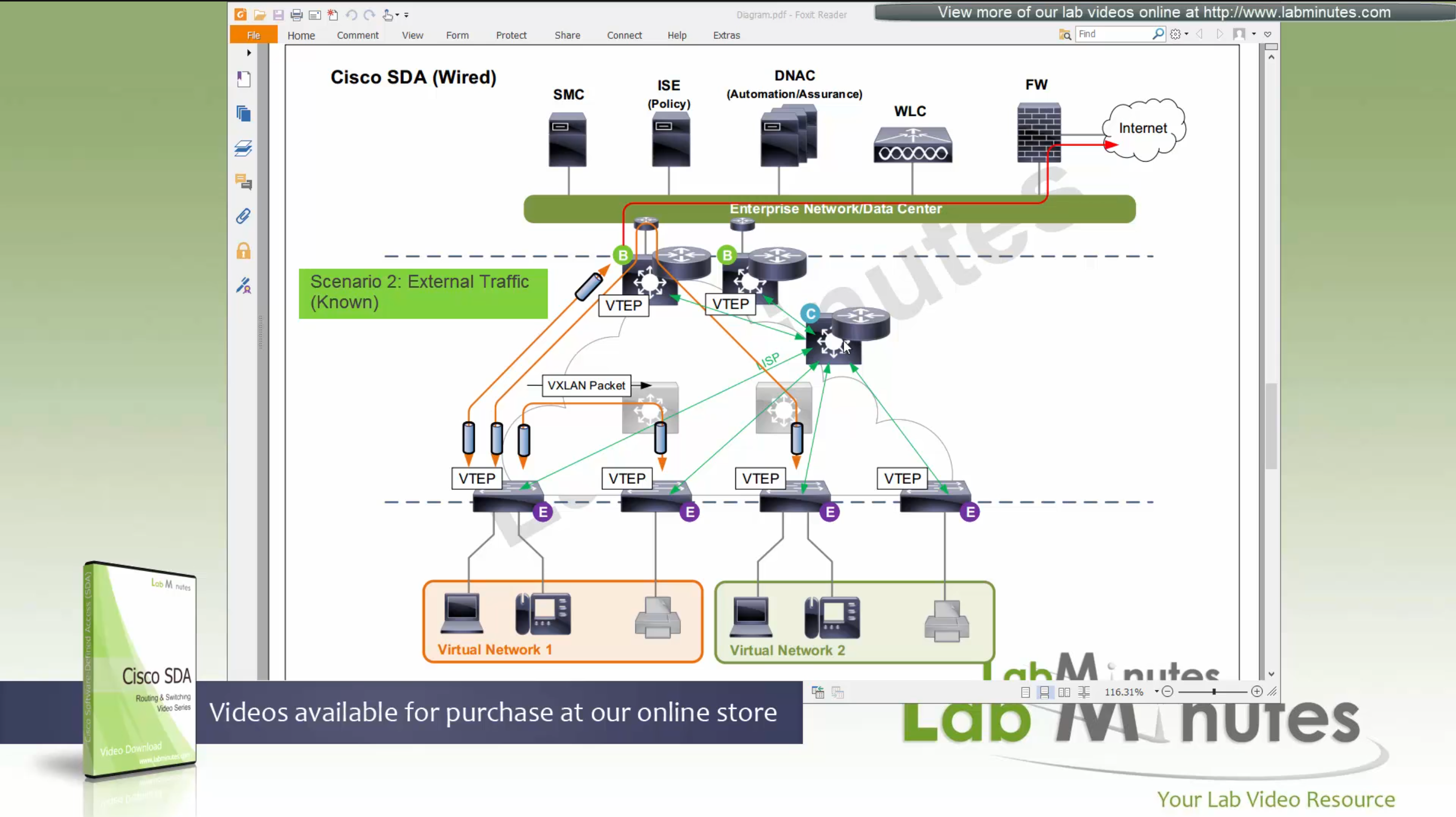
Scenario 4: Packet desitned for “Unknown” external network outside the fabric.
Edge node inquires the control plane for “destination”, control plane returns the RLOC of the “default” border node, in most networks Default Border Node and Known Border Node are the same device, then edge sends the packet to border node
it will create a vxlan packet with correct L2 VNI tag, and correct outer L3 RLOC destination IP address
and insert original IP packet into it as a carrier and its payload and then send it out to the underlay to deliver.
Underlay will deliver vxlan packets to the border node and border node will “decapsulate and deliver it out to the external network”
Packets will flow from edge node to intermediate node to border node and then fusion node to get to external networks

Scenario 5: Packet destined for another Virtual Network, InterVN (to another VN) traffic
This scenario applies when host in Virtual Network 1 needs to communicate with host inside Virtual Network 2 below, queries will still happen as in previous scenarios with control plane
Now this gets a bit trickier in these notes because this is an old video for an old release when SDA did not allow route leaking inside the Fabric, so that meant that packets will be routed all the way out of the fabric to the fusion router and routed back into the fabric, because border node cannot be routing “between” different Virtual Networks, and for this to work fusion router also needs one “transit” sub-interface per Virtual Network or VRF
Obviously this is not optimal as InterVN traffic will face more delays than IntraVN traffic and fusion router is also single point of failure
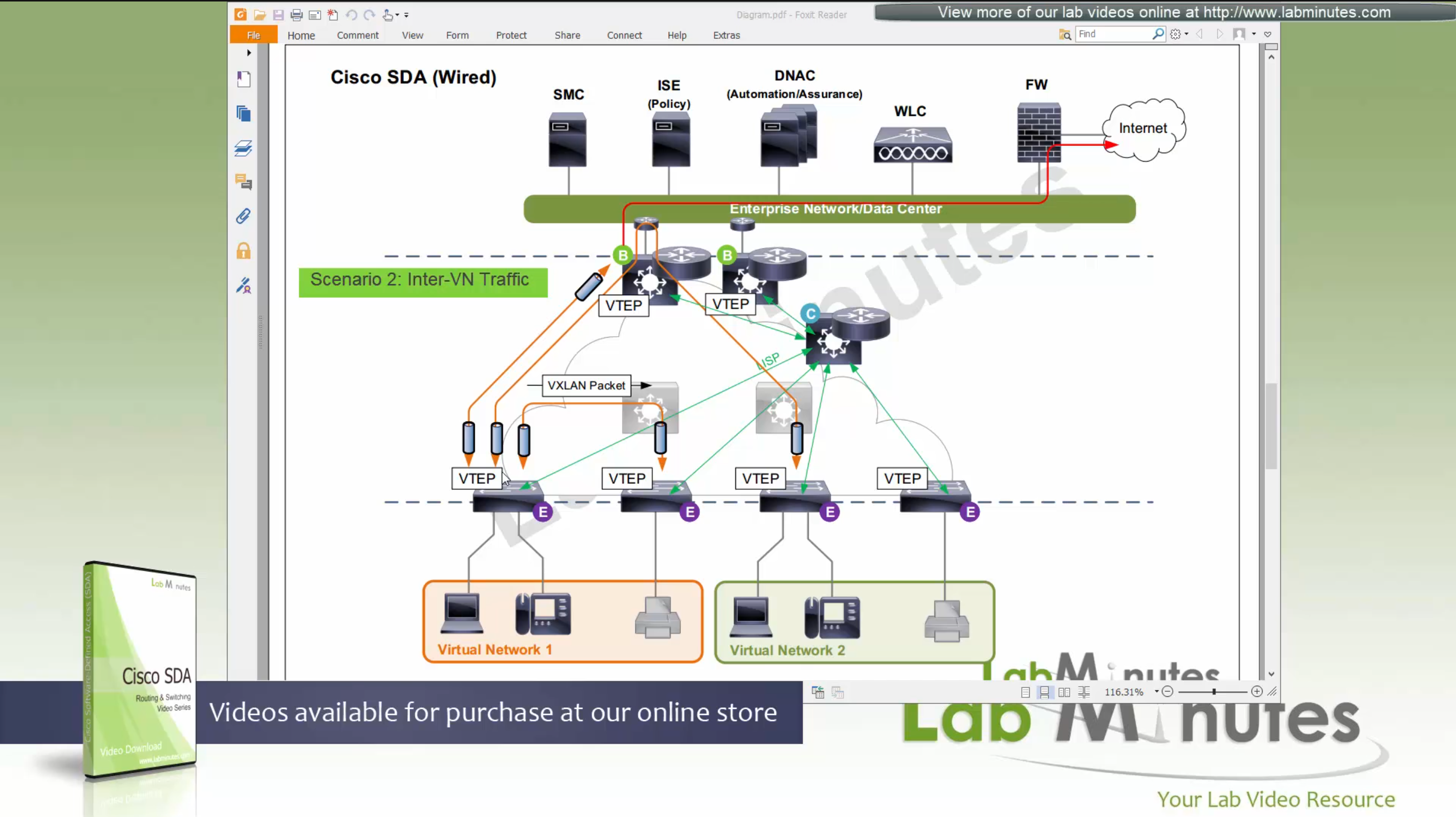
SDA wireless is next evolution from converged access mode and this is called “Fabric mode AP” and “Fabric mode WLC”, there are small differences now
WLC <—LISP session—> Control node
WLC speaks to control node using LISP session just like edge node and border node
WLC sends register EID (of wireless client) to control plane,
Control plane node has full view of the network including the EIDs from wired and EIDs from wireless as well
AP <—VXLAN Locally Switches Data—> Edge node
AP <—CAPWAP control connection only—> WLC
Second difference is that AP still maintains the CAPWAP to WLC but it is only for CAPWAP control connection, data is locally switched to the edge node over the mini VXLAN tunnel.
Data sent by Fabric mode AP to edge switches using VXLAN tunnel
this VXLAN tunnel between Fabric mode AP and edge is only between AP and edge that are directly connected, it does not extend from AP to remote edge switches
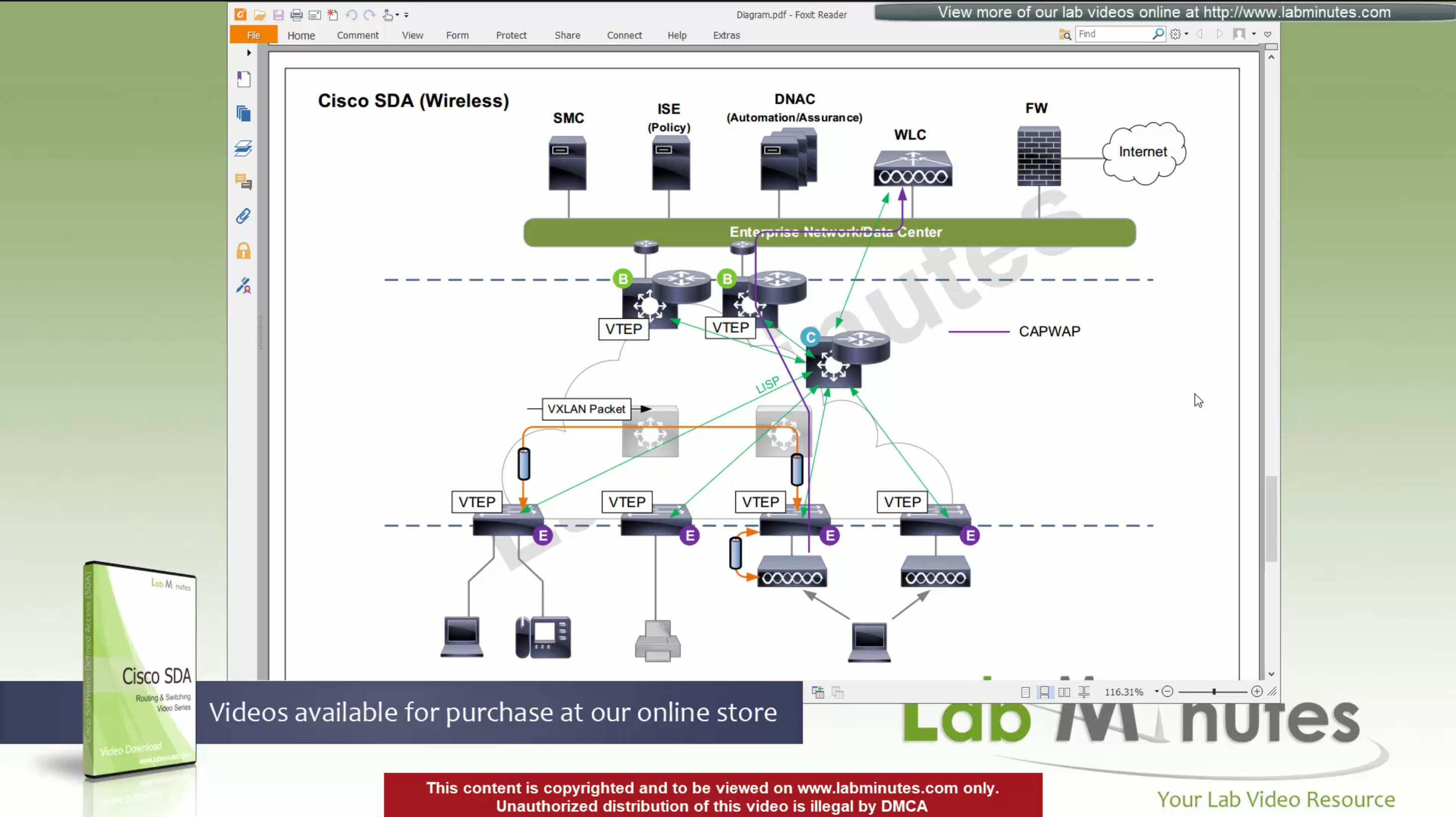
Client will associate and authenticate with the SSID, obtain IP address

“WLC will do MAP register with control plane node” and tell control plane node about the client as EID and which AP it belongs to (just like it does same for switchport)
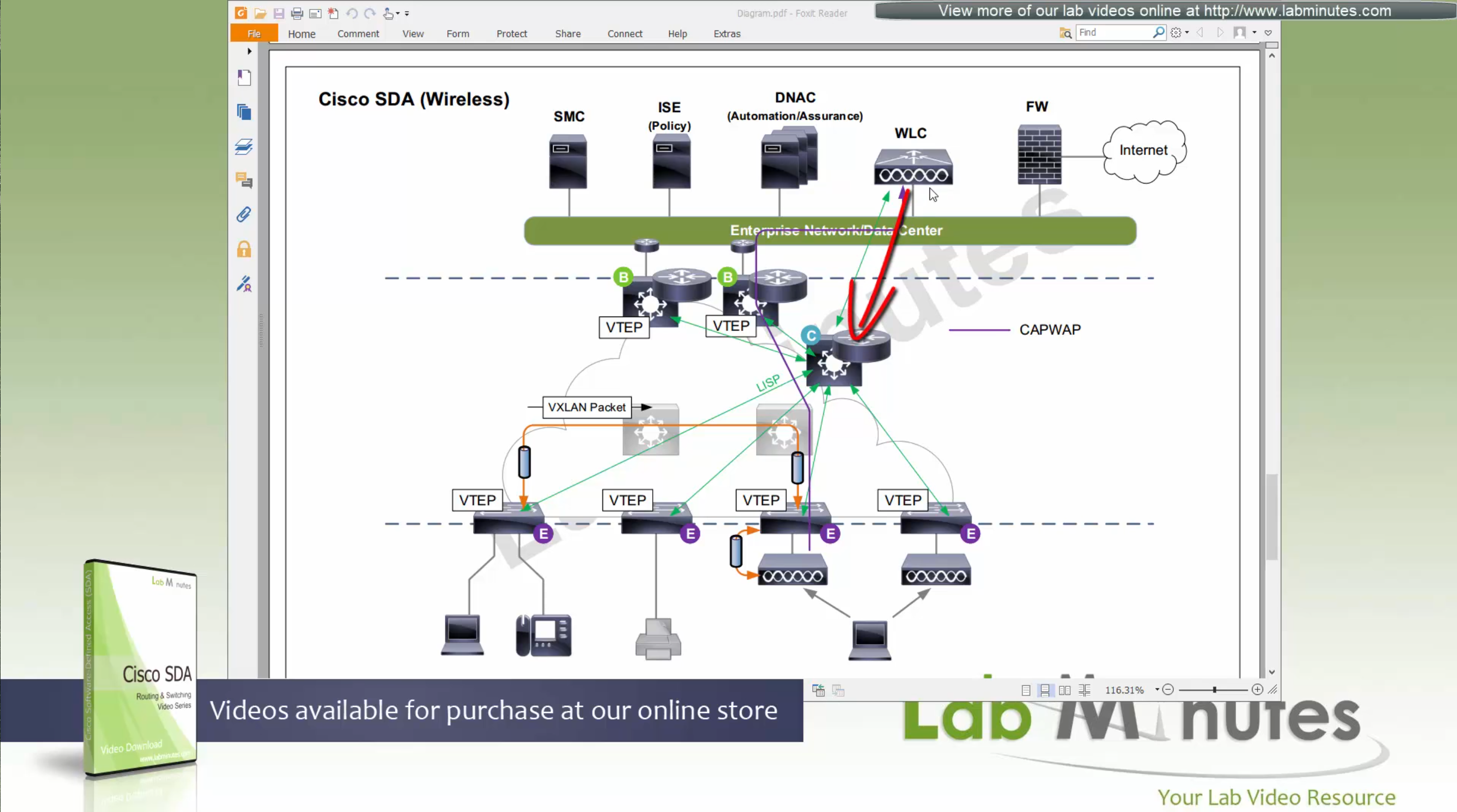
When wired client needs to communicate with the wireless client

edge node of the wired client will obtains the RLOC from control plane and make tunnel to the edge switch where wireless client’s AP is connected
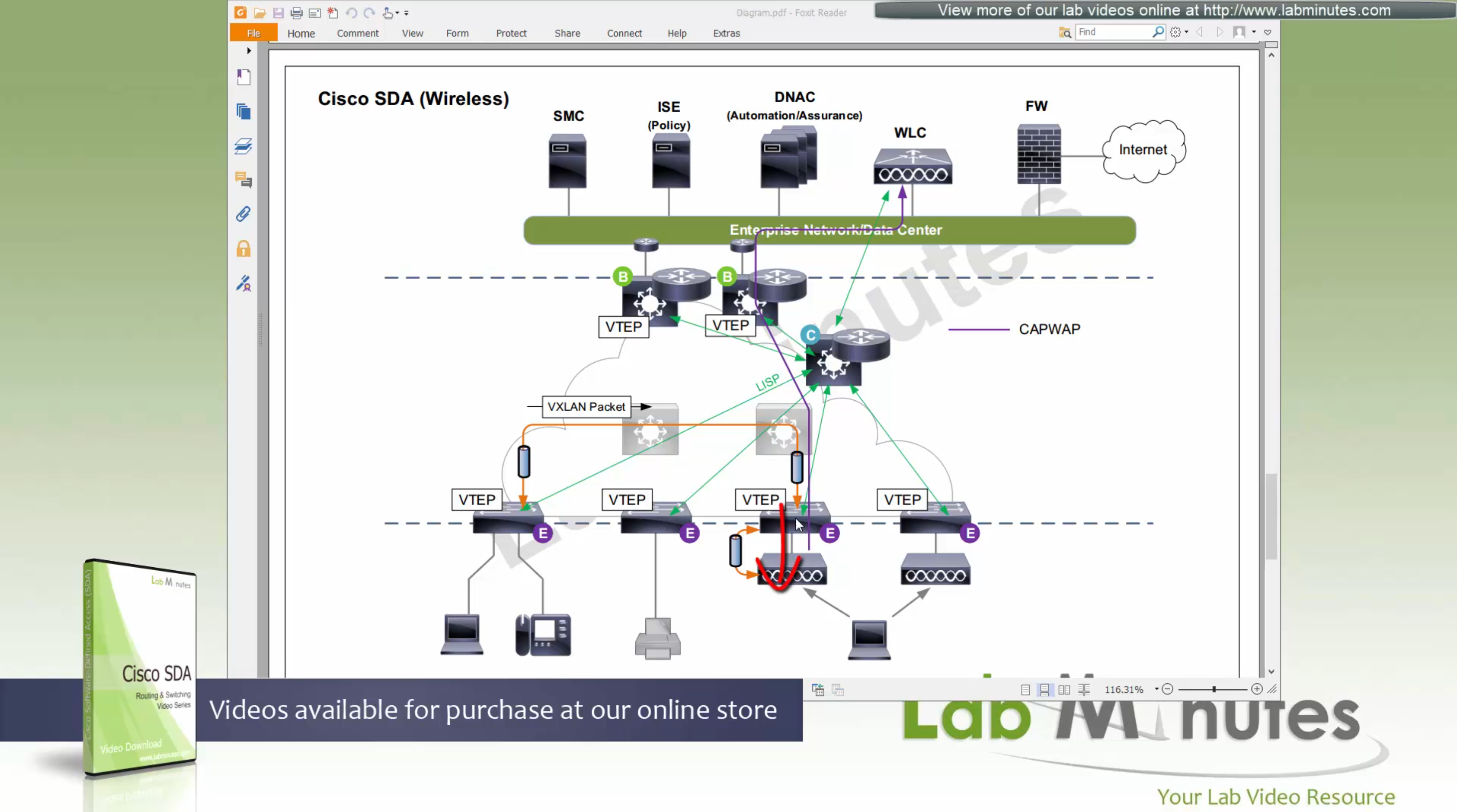
once edge node de-encapsulates the VXLAN tunnel, it checks and sees that mac address of the wireless client is behind that mini VXLAN tunnel, so it will re-encapsulate the traffic and send that to AP and vice versa in reverse
The reason for AP to VXLAN is so that AP can inform the switch of the correct VNI the client belongs to, this is the point or mechanism that keeps consistency from the wired world for VNI, making wireless clients seem like just like wired clients policy and monitoring wise, SGT are tagged in overlay and SGT tags are inside the tunnel and not outside on the VXLAN packets themselves
and when user roams from one AP on one edge switch to another AP on another edge switch, WLC will be informed about the roam by the roamed to and from APs, WLC will inform the control plane also and control plane will update the entry’s RLOC to be the new edge switch whose new AP client has roamed to
While in Fabric, WLC and APs can still be connected to the Fabric but operate in “Legacy mode” which is also called “over the top” setup, in which data from AP is sent in CAPWAP (Data tunnel) to WLC and WLC switches the traffic out
There is also a low latency requirement of 20ms between the WLC and AP so keep in mind that APs have to stay somewhat close to the controller in the campus setup
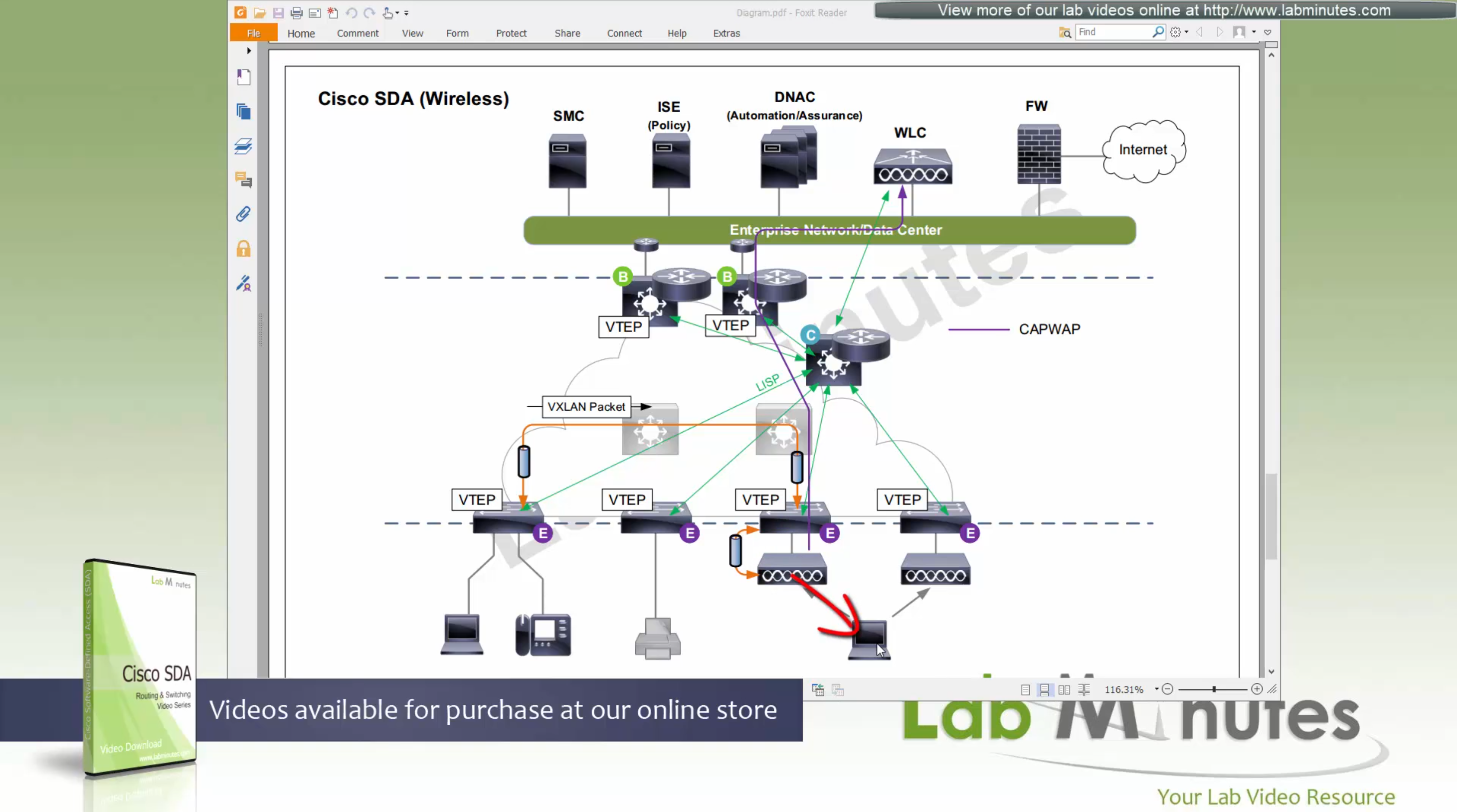
With Cat 9k we have following options for licensing
DNA Essential gives most of the feature set of the APIC-EM
while DNA Advantage gives most of the features in Assurance and NDP + SDA
SDA is only available with DNA Advantage license
Network Essentials and Network Advantage are for IOS-XE and Network Advantage is like IP services license (like it used to be in older IOS)
Cisco offers a license called One Advantage that offers DNA + ISE + Stealthwatch all in one license

Right after installation of DNAC and first GUI login we need to quickly download the packages or software apps which are GBAC Group Based Acccess Control ( SGT / SXP / ISE ) and also SDA package to enable SDA in DNAC. Cisco does not readily ship the DNAC with ova or iso, SDA and a lot of other modules need to be downloaded using below very specific settings


Group Based Access Control is not there and needs to be downloaded

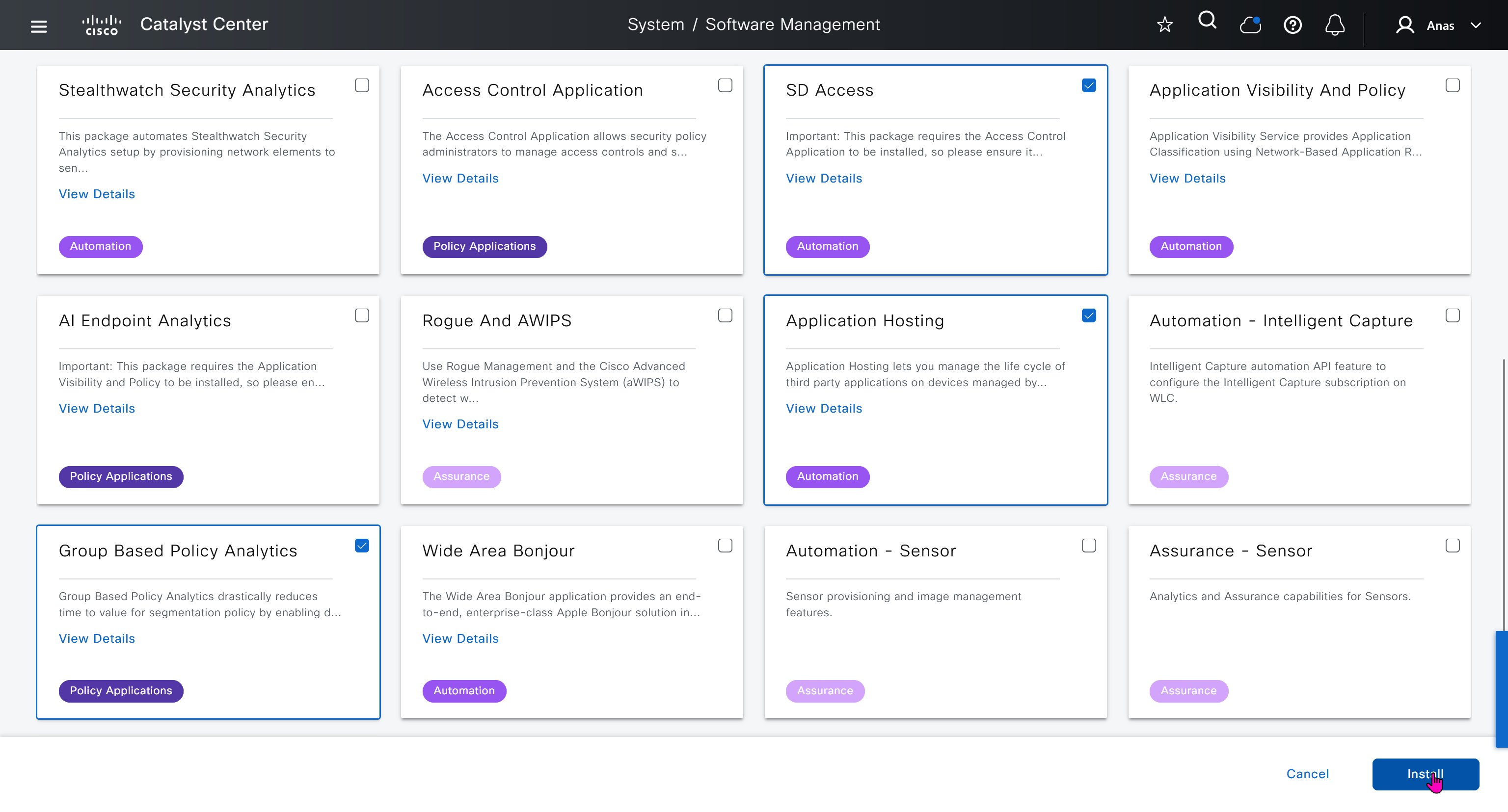

Installation kept failing at download stage

I had to remove the VM as there was something wrong and when new dnac was installed, one thing I did is I added the company’s cco information here but not in the smart licensing, dont add to the smart licensing section instead add at the beginning on first GUI login

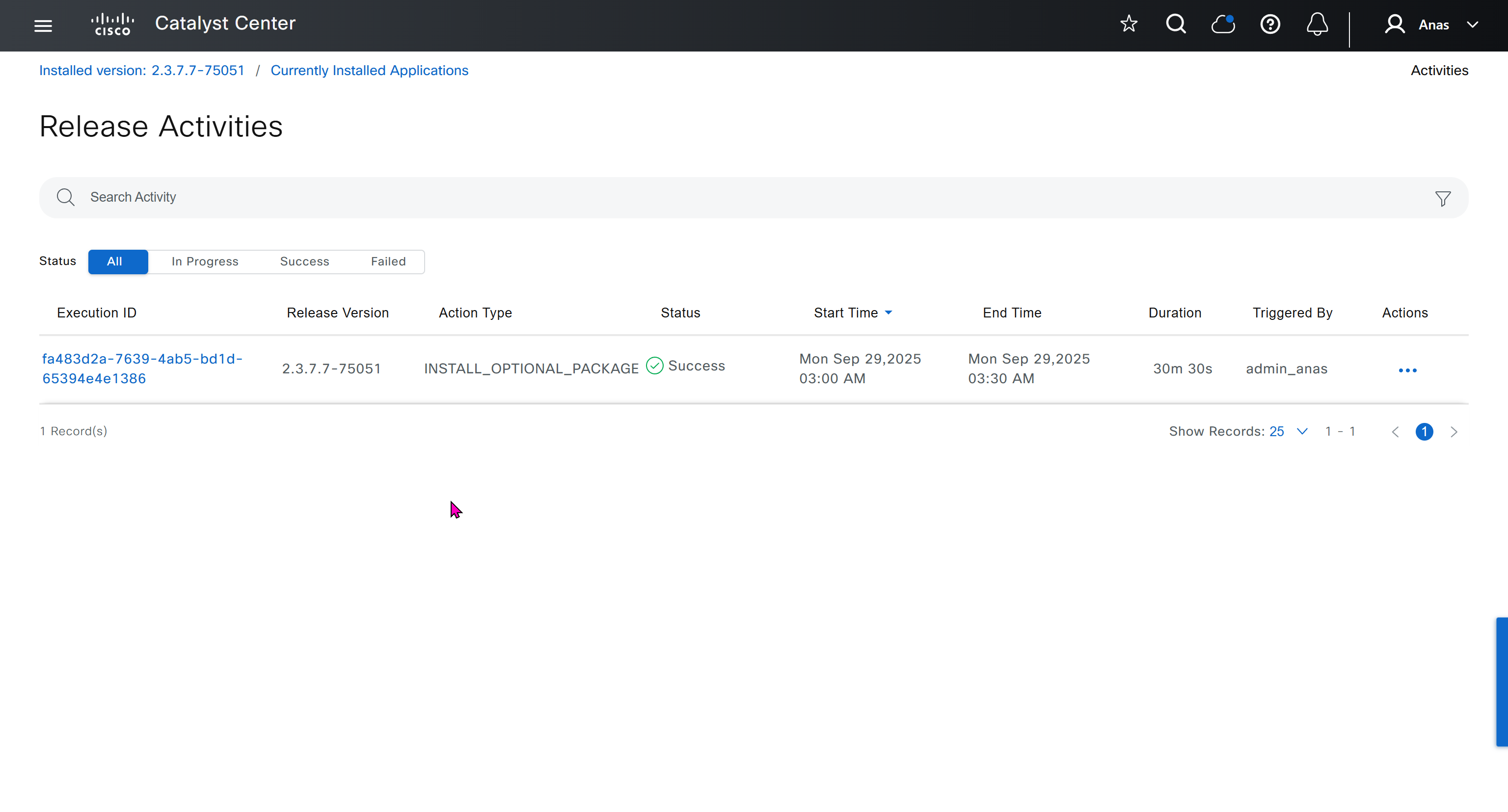
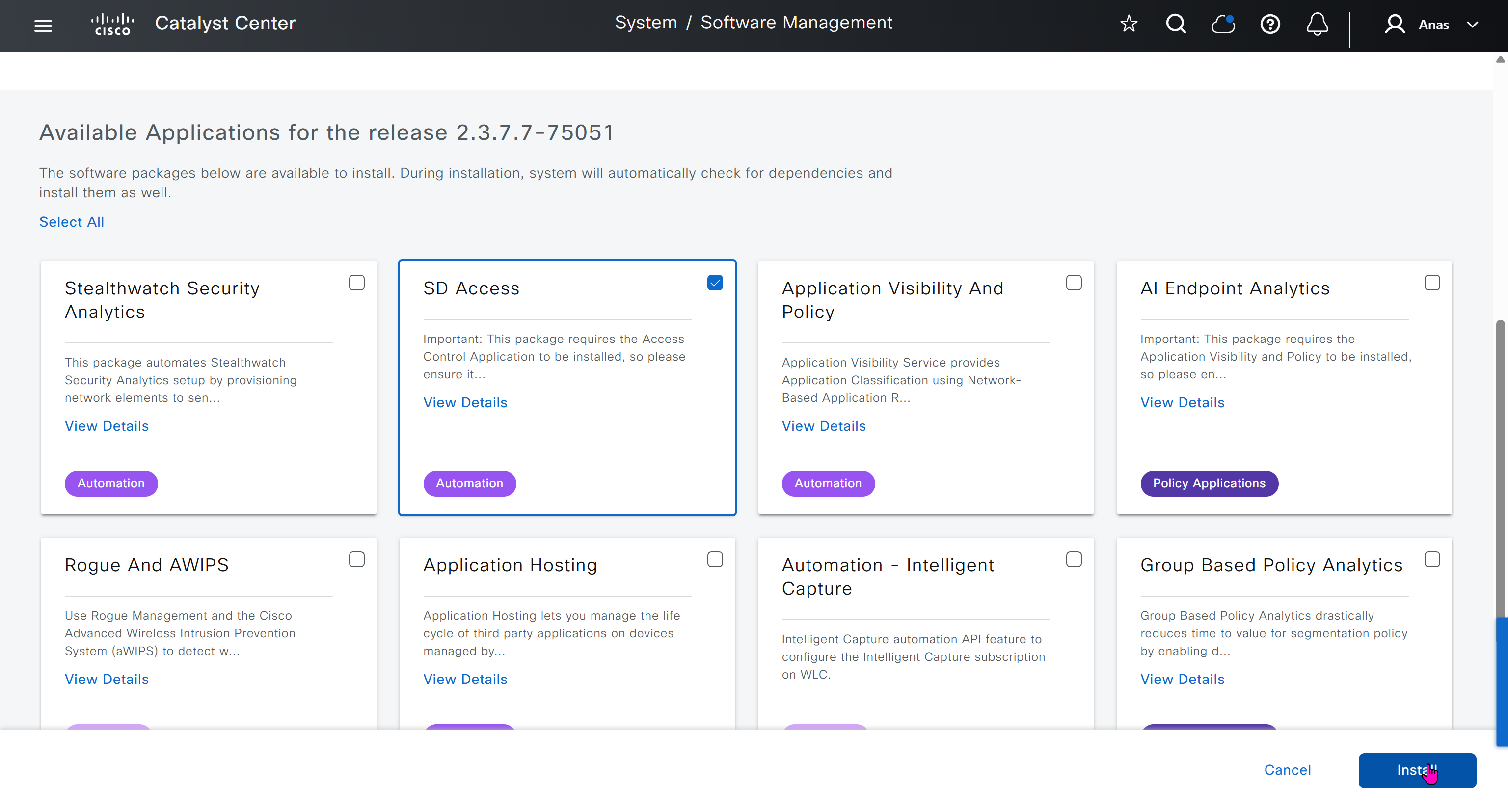
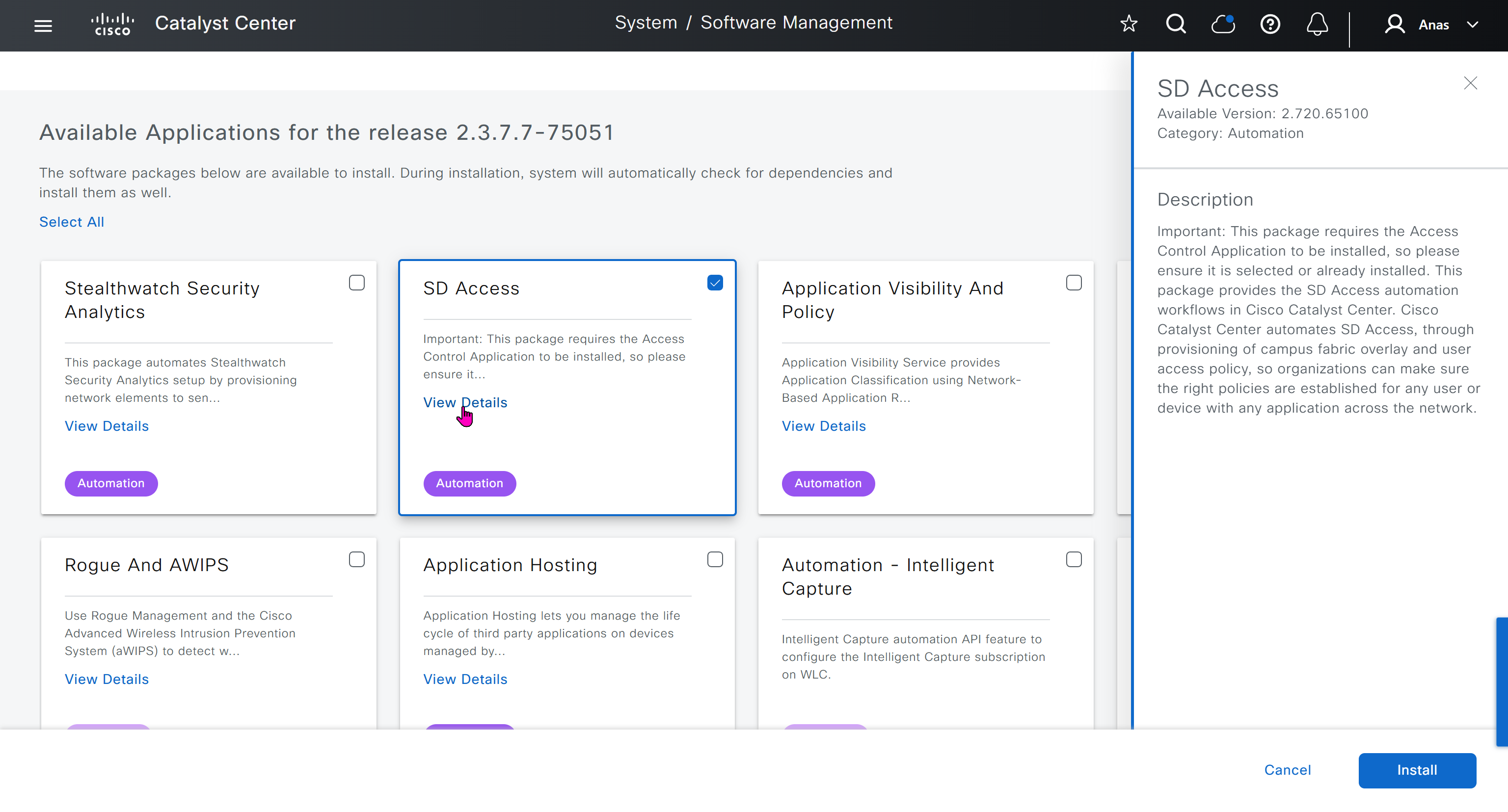
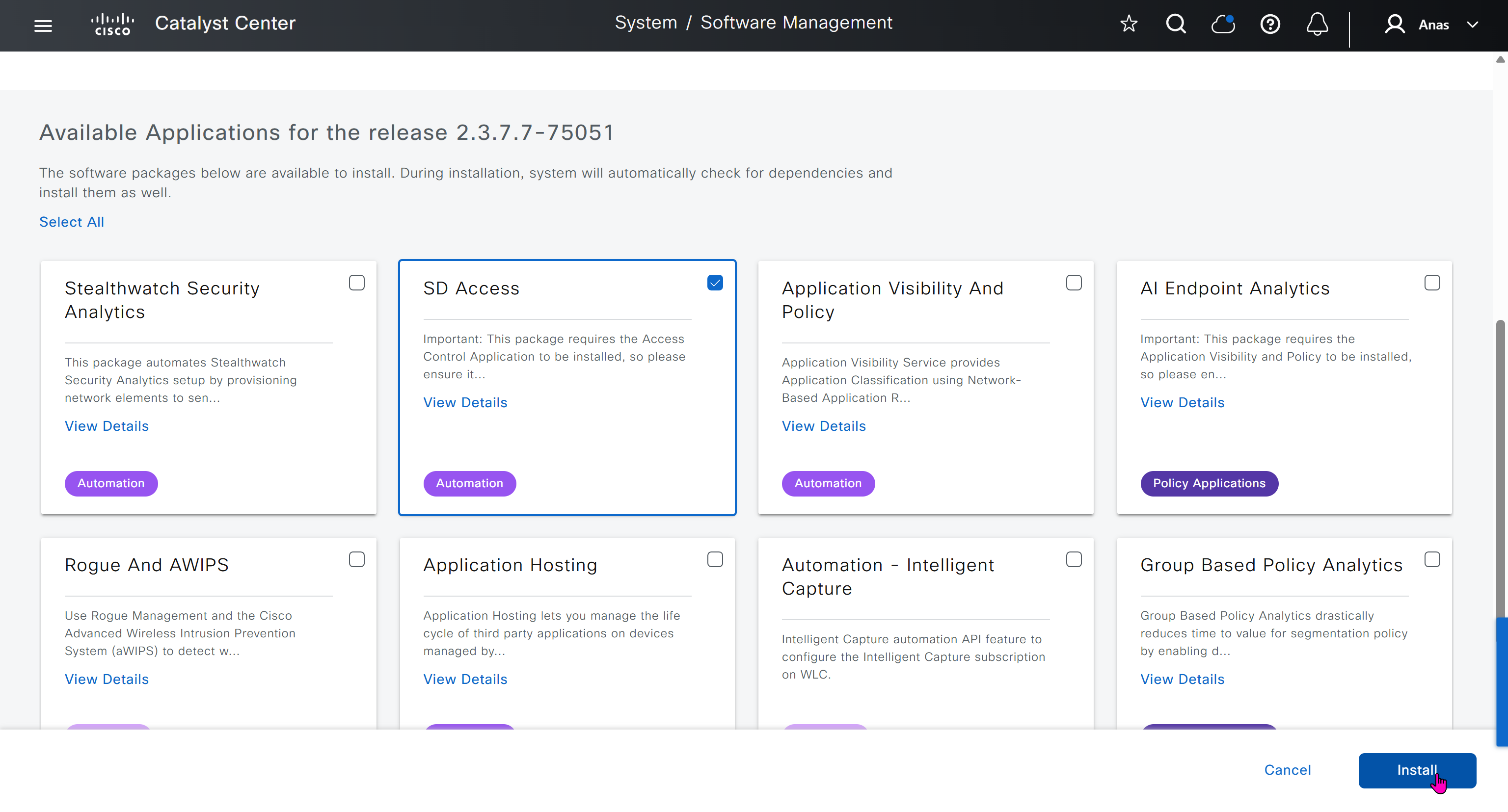
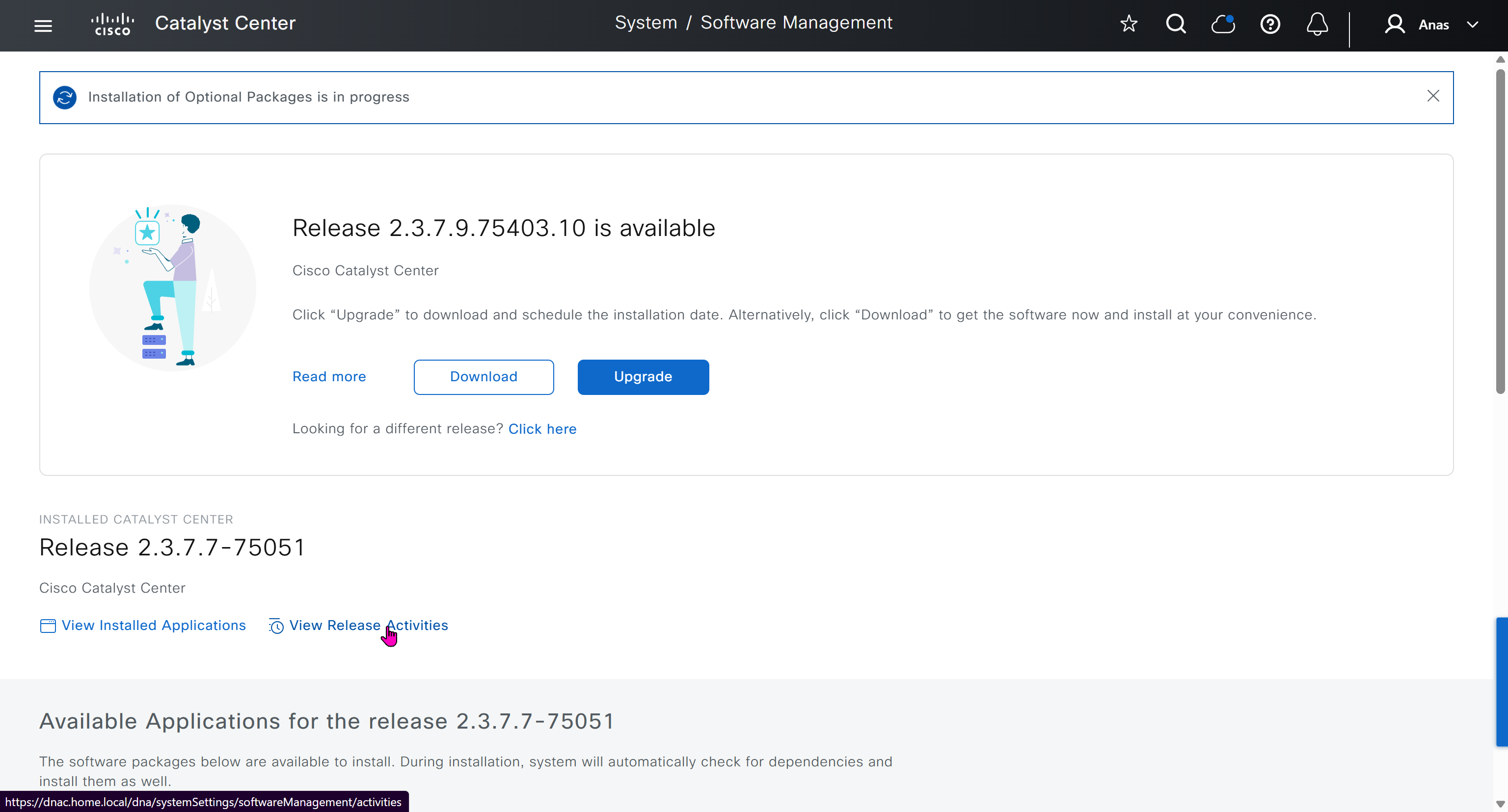

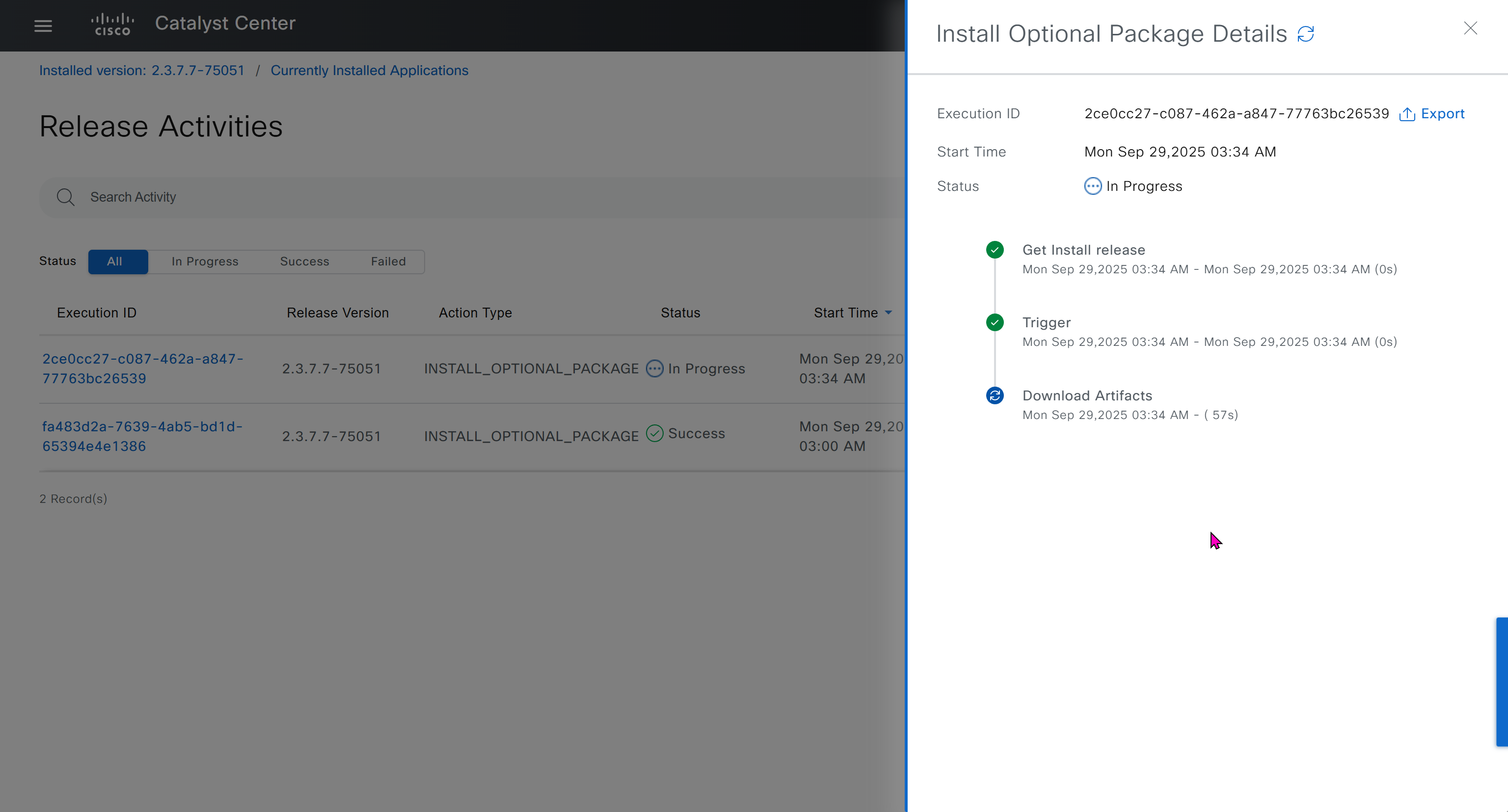
Finally it installed well
now Group Based Access Control GBAC is showing in menu now

We will take a look at installing certificate as ISE needs to be integrated, and for that we need to take information from default certificate’s information, common name is the name that we provided during the initial installation of DNAC

If we look at subject alternative names we can see a lot of SAN entries, these SAN entries contain IP addresses as well and one of those IP addresses will be of the VIP in case we have multiple DNAC appliances

Enhanced Key Usage: Server Authentication, Client Authentication as this is used for ISE PX Grid integration

We will have to install the OpenSSL for Windows
cd C:\Program Files\OpenSSL-Win64\binopenssl req -new -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout dnac.key -out dnac.csr -subj "/C=UK/ST=GB/L=London/O=home.local/OU=IT/CN=dnac.home.local" -addext "subjectAltName=DNS:dnac.home.local,DNS:dnac01.home.local,DNS:dnac02.home.local,DNS:dnac03.home.local,DNS:dragonfly-kong-frontend,DNS:dragonfly-kong-frontend.maglev-ingress,DNS:localhost,DNS:pnpserver.dnac.home.local,DNS:pnpntpserver.dnac.home.local,DNS:dragonfly-kong-frontend.maglev-ingress.svc,DNS:dragonfly-kong-frontend.maglev-ingress.svc.cluster,DNS:dragonfly-kong-frontend.maglev-ingress.svc.cluster.local,IP:10.21.1.2,IP:169.254.6.66,IP:172.16.25.2,IP:127.0.0.1,IP:::1"openssl req -noout -text -in dnac.cerWe have added those lines
Make sure that Data and OOB IP addresses are added including all Data and OOB IP addresses from clusters too
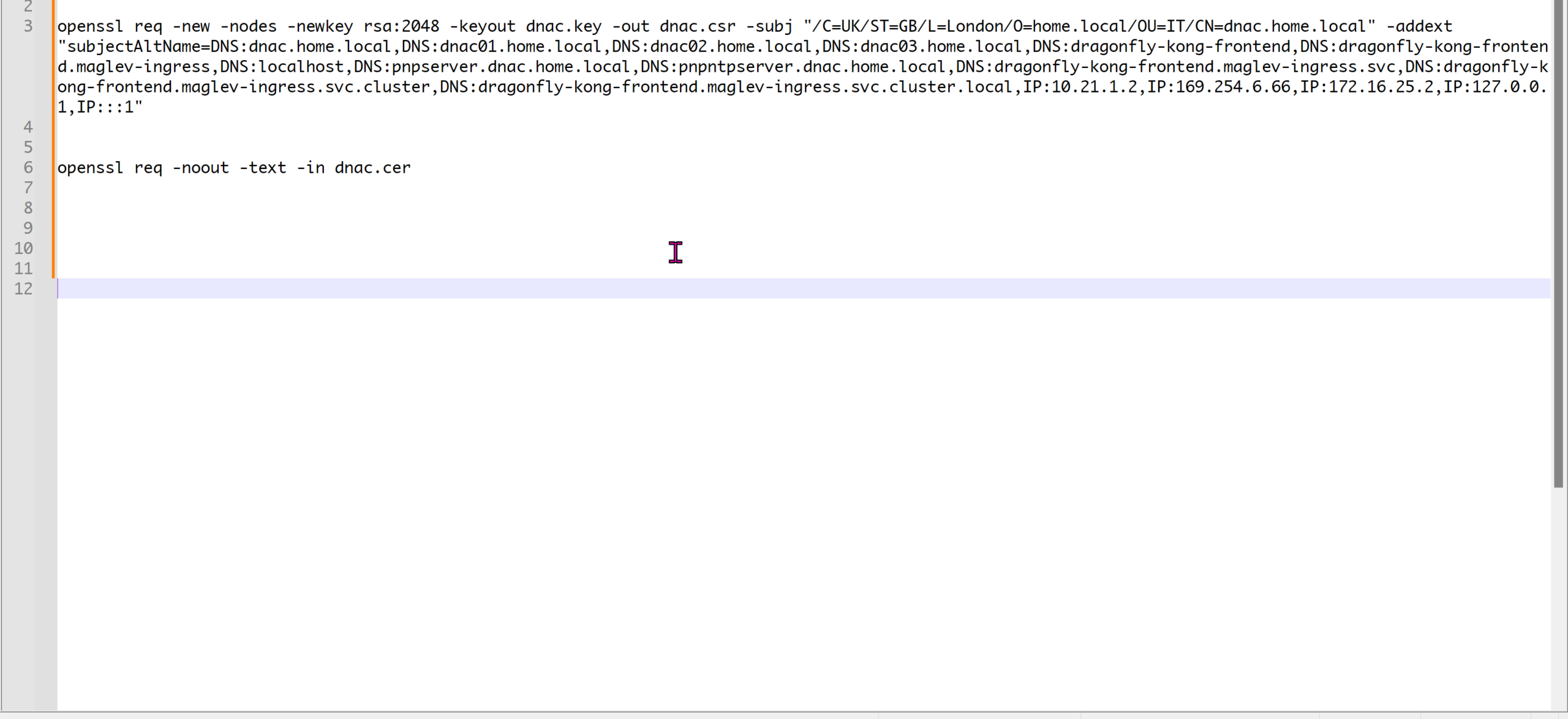


This Web Server EKU as Extended Key Usage has Client Authentication
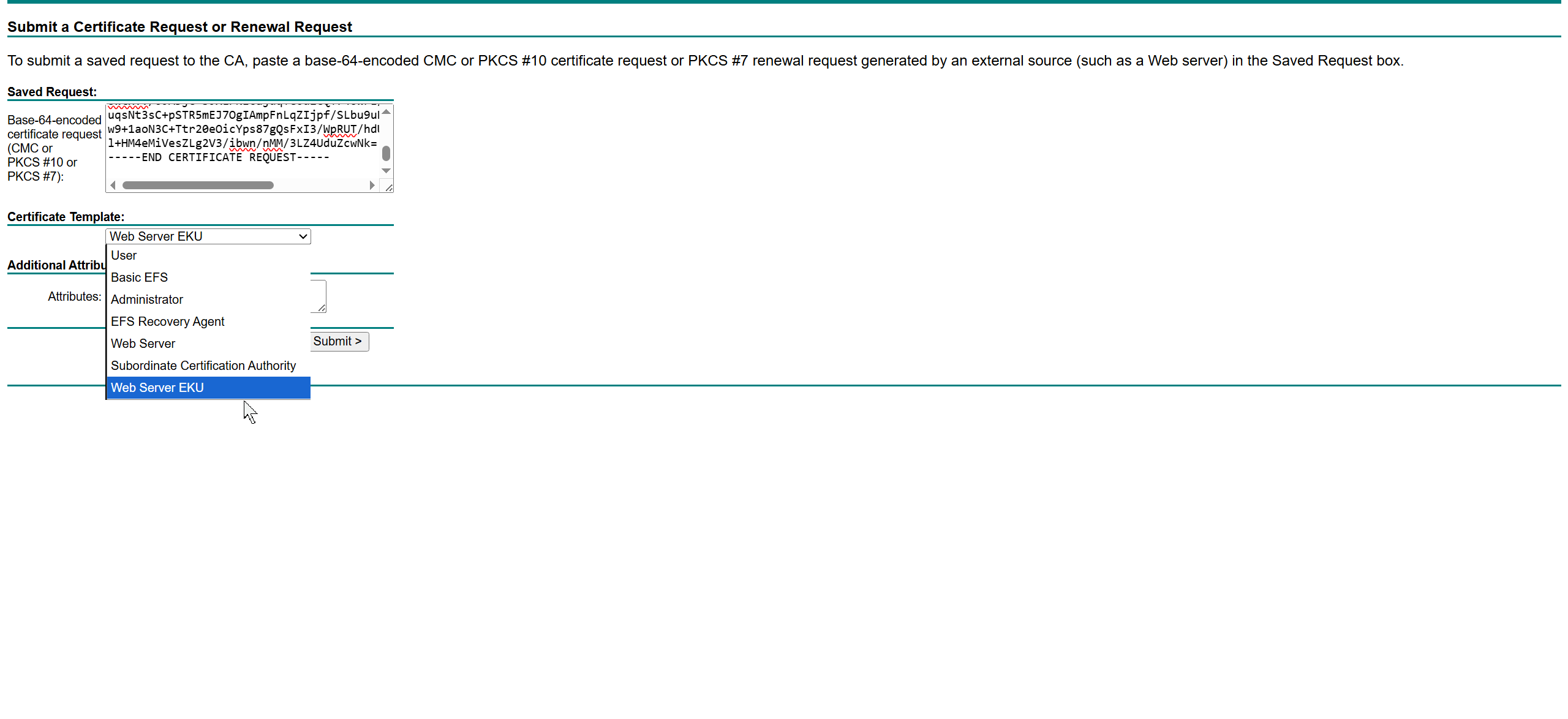

We will append the root ca certificate (because identity cert comes first) in this notepad file and combine it for DNAC, in case you have any intermediate CA certificates then add them as well in the middle of identity and root ca certificate


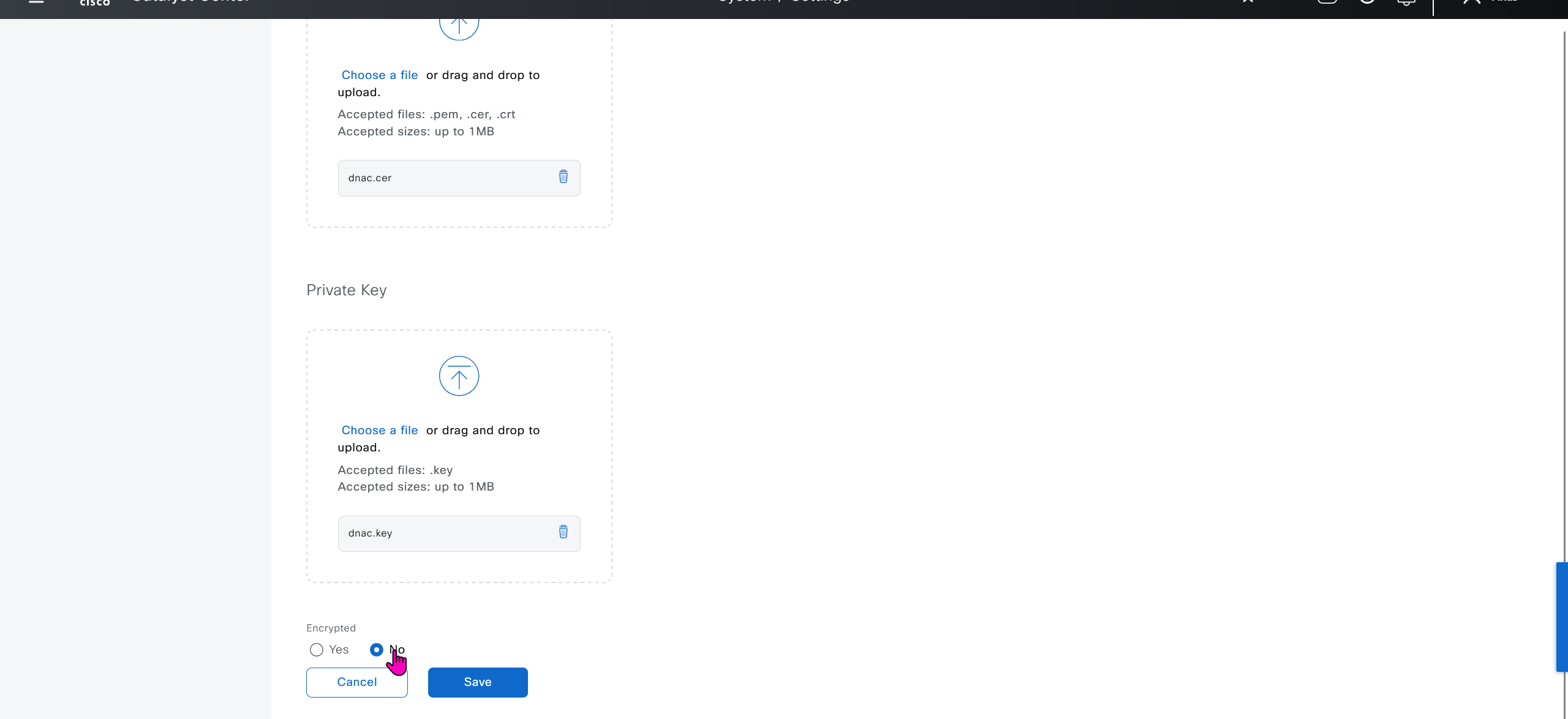





DNAC also issues certificates to devices which get added to it, and by default DNAC acts as the internal root ca but we can add our enterprise root ca or windows root ca too and this decision should be made right at the beginning before adding devices in DNAC or SDA fabric but once enterprise root ca is added we cannot convert this setting back to internal CA, usually we leave DNAC as the root ca for those devices

We can control the period for certificate’s validity
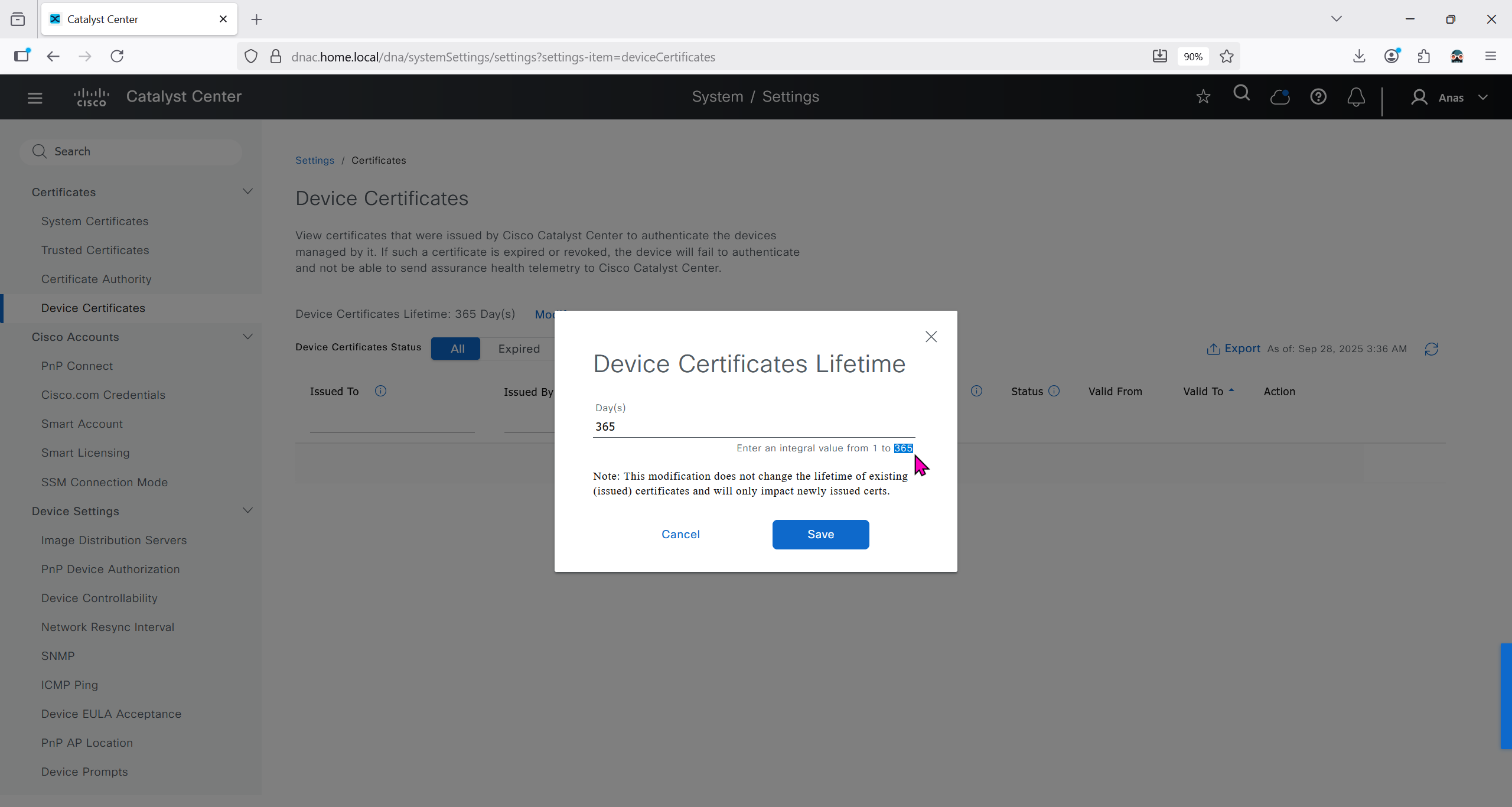
We will just click on option to enable SubCA mode but will not enable it just to see the message from DNAC
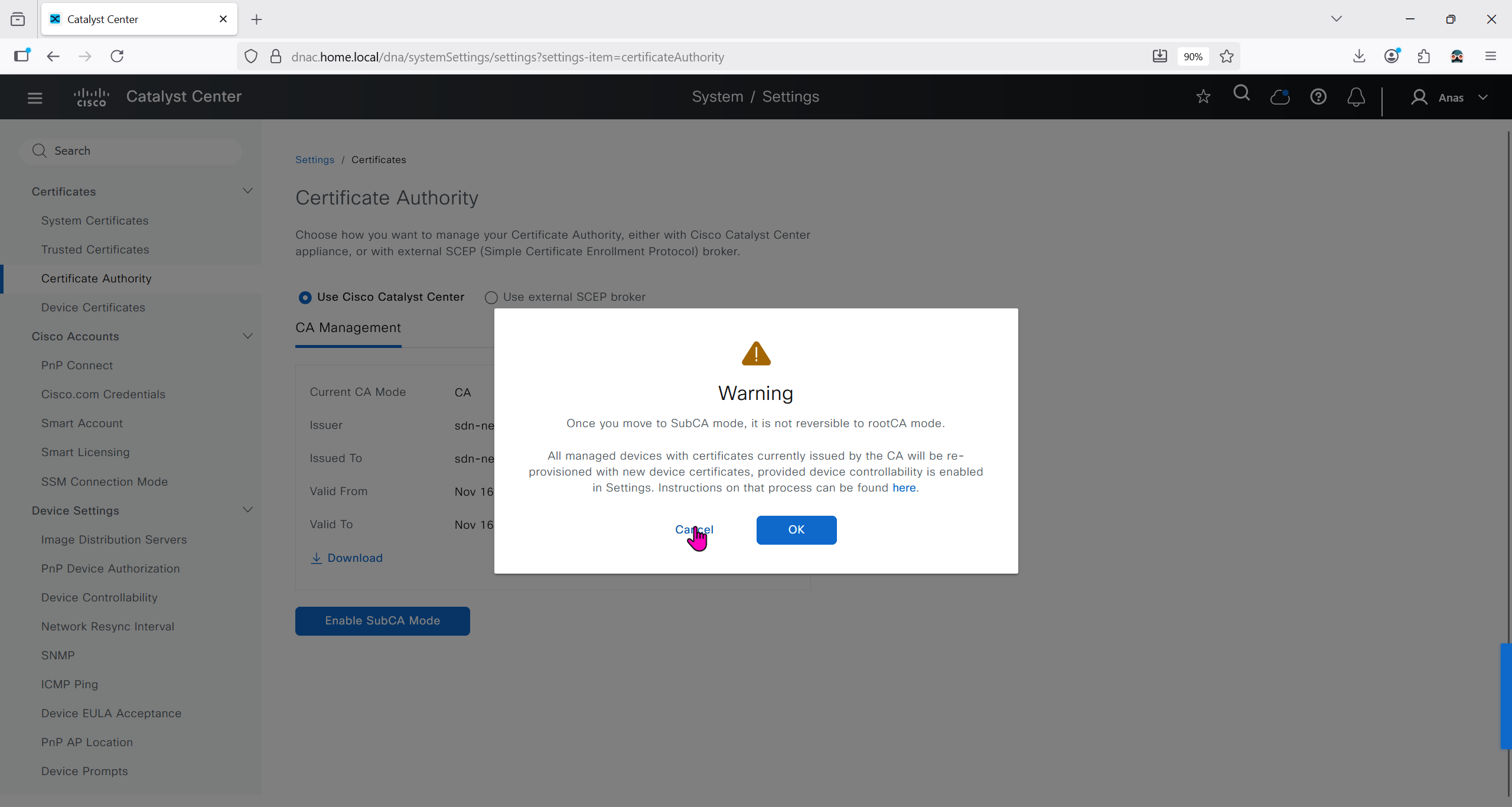
But if we were to enable it then following will be the steps
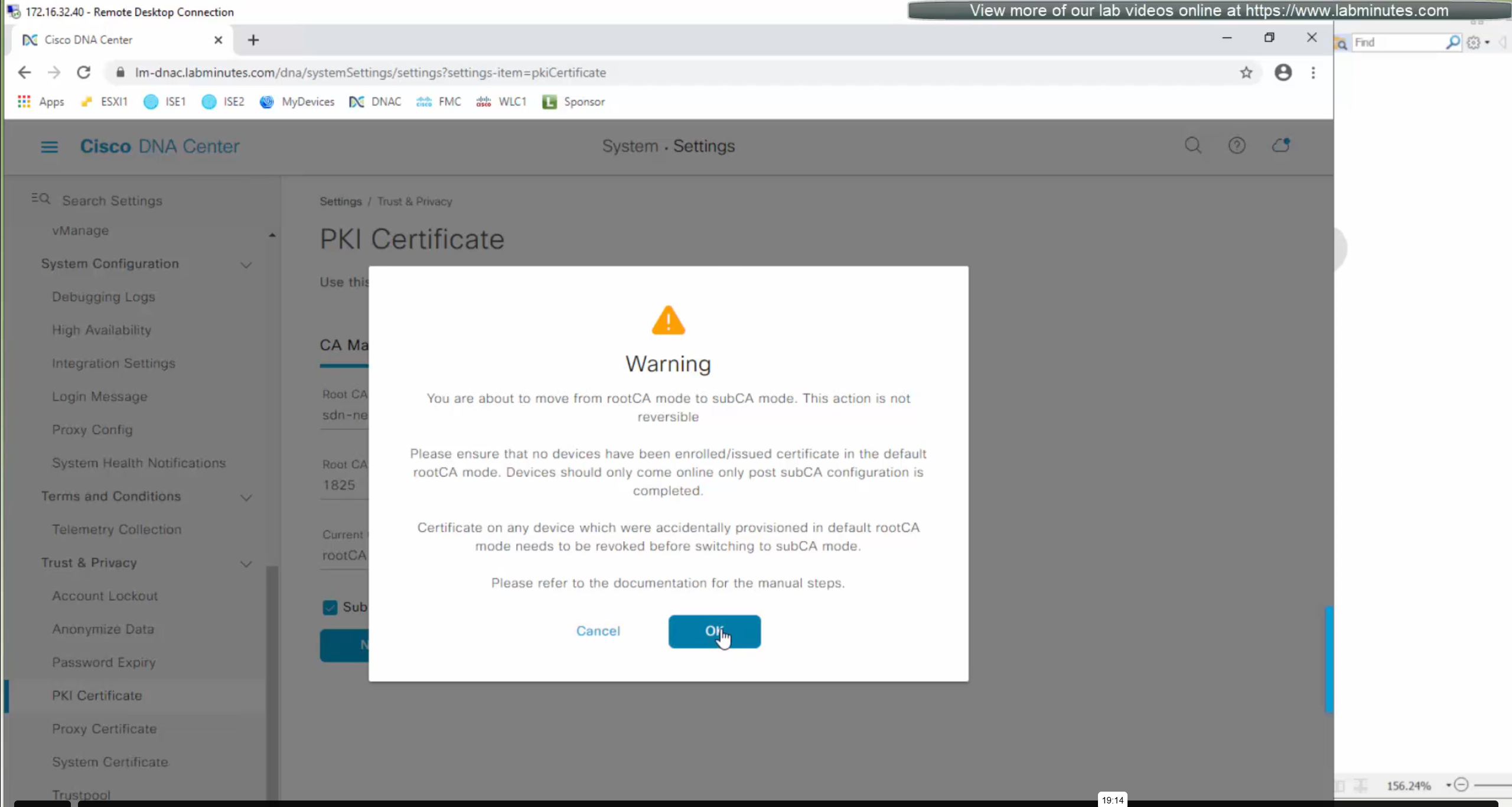
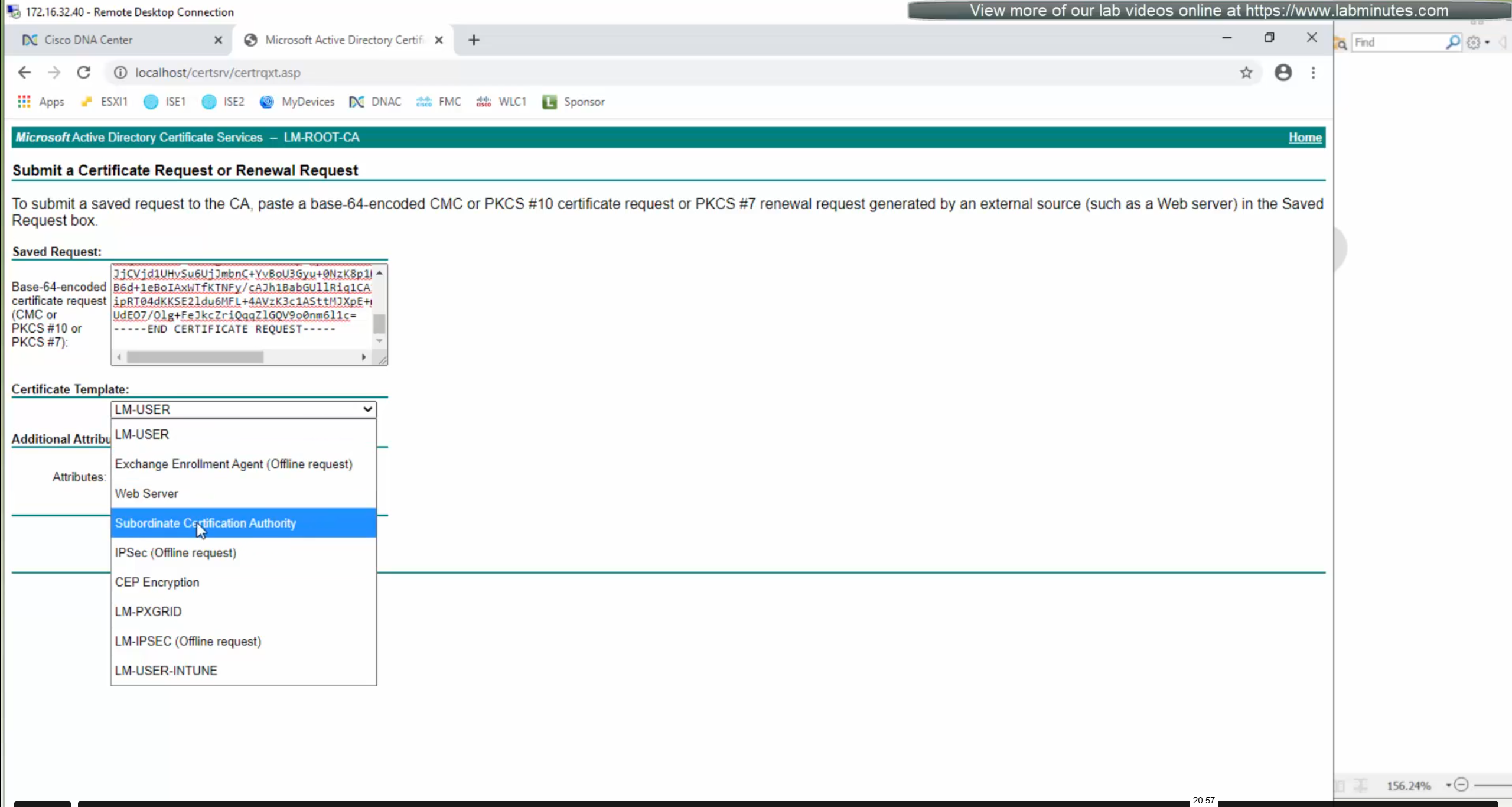
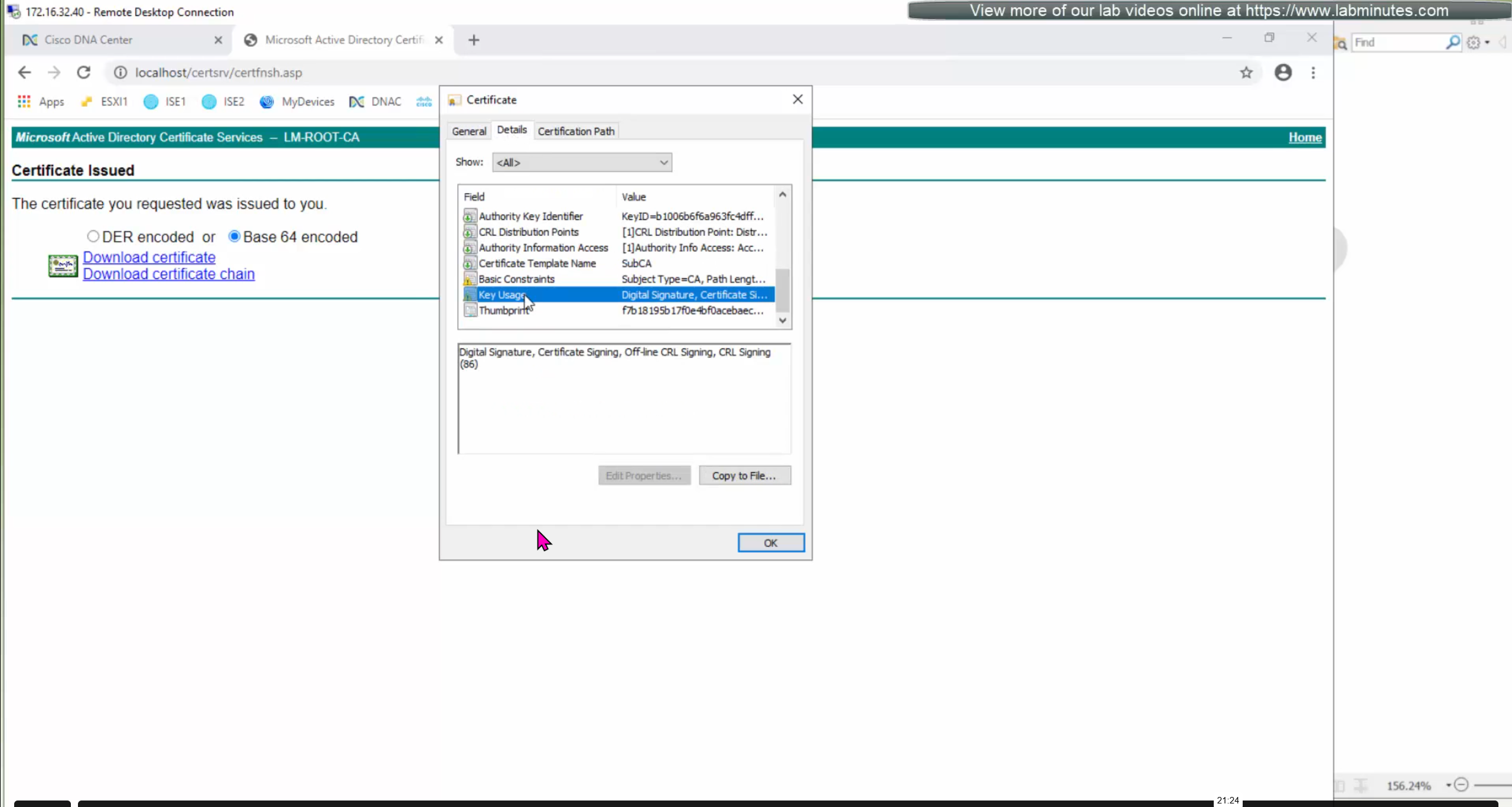





ISE is part of the SDA architecture by using RADIUS (Policy Server with mab and dot1x), TACACS and PXGrid
We need to have dot1x and mab authentication and
authorization configured in ISE
It used to be that ISE should not have TrustSec configuration configured, as config from DNAC will overwrite the existing config
But now if there is configuration conflict between ISE and DNAC then ISE configuration will take higher precedence
After integration, DNAC continues to poll ISE in order to keep trustsec configuration in sync
Integration between DNAC and ISE is very version specific so make sure you check documentation to see which version of ISE will integrate with which version of DNAC
Make sure that DNAC can reach ISE on ssh, and it is very important that GUI and CLI credentials are same
Also make sure that our ISE certificate has SAN entries for ISE IP and FQDN in ISE certificate


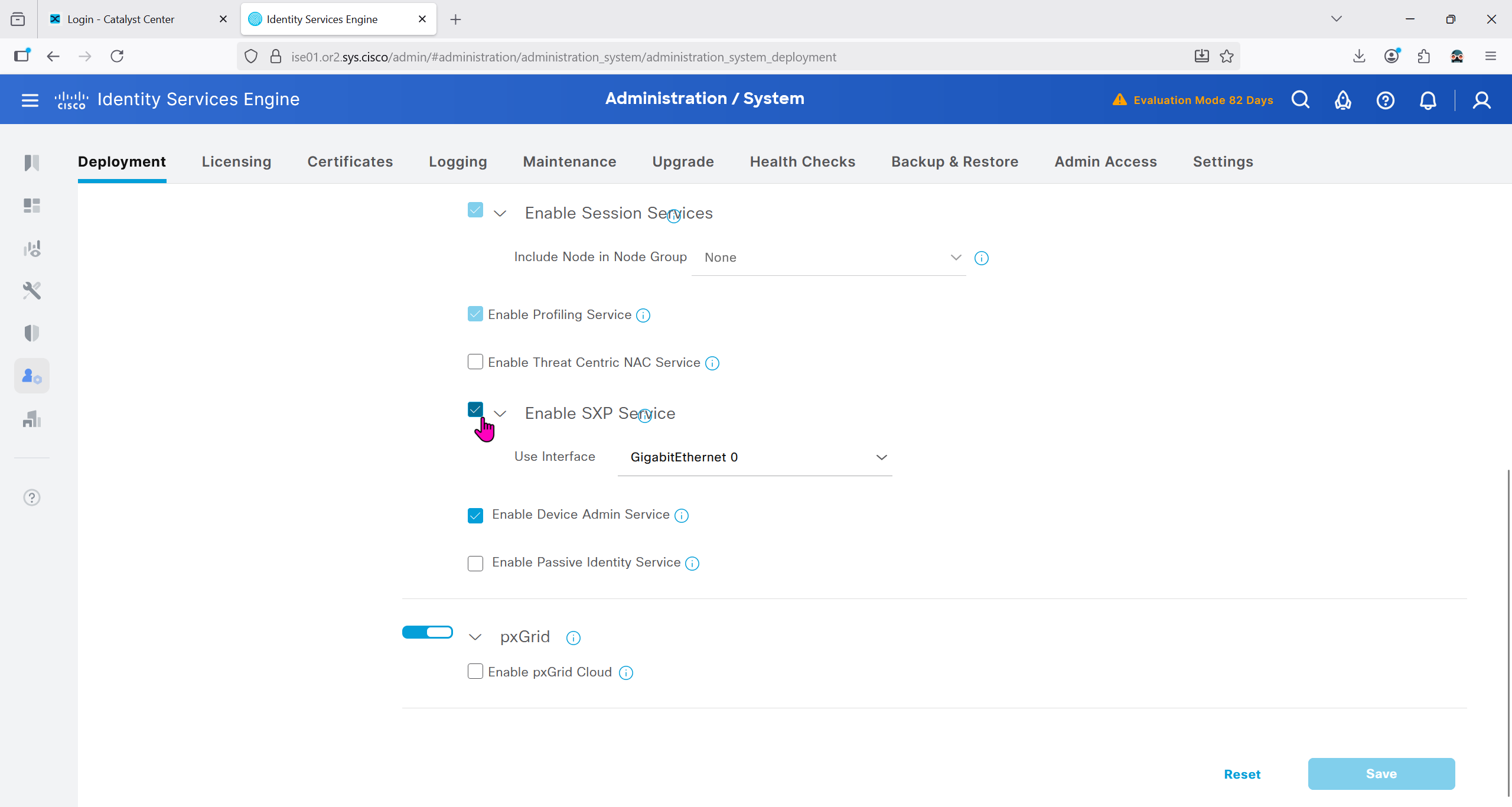
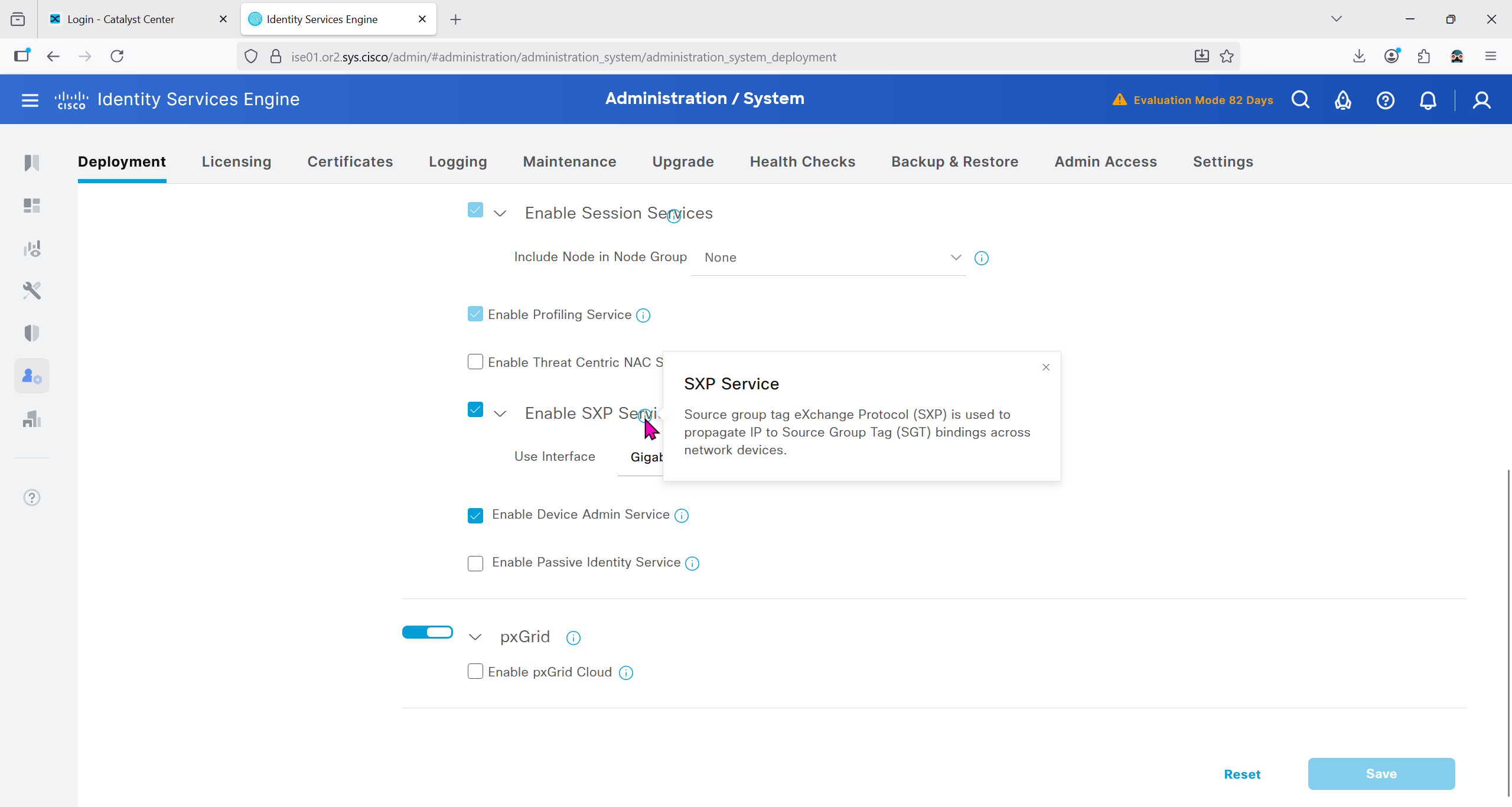


Make sure that when DNAC’s cert is presented it is trusted by ISE

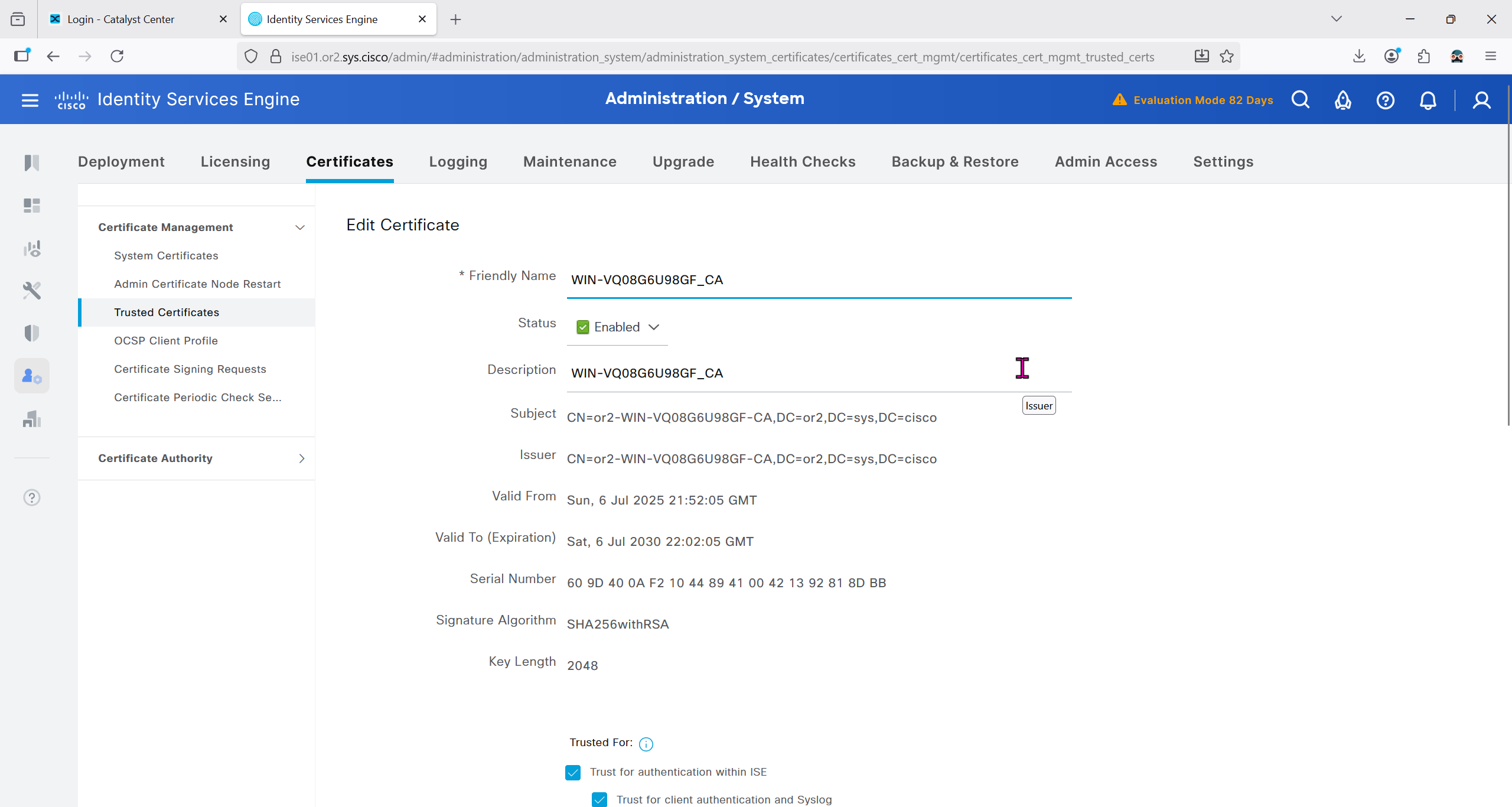
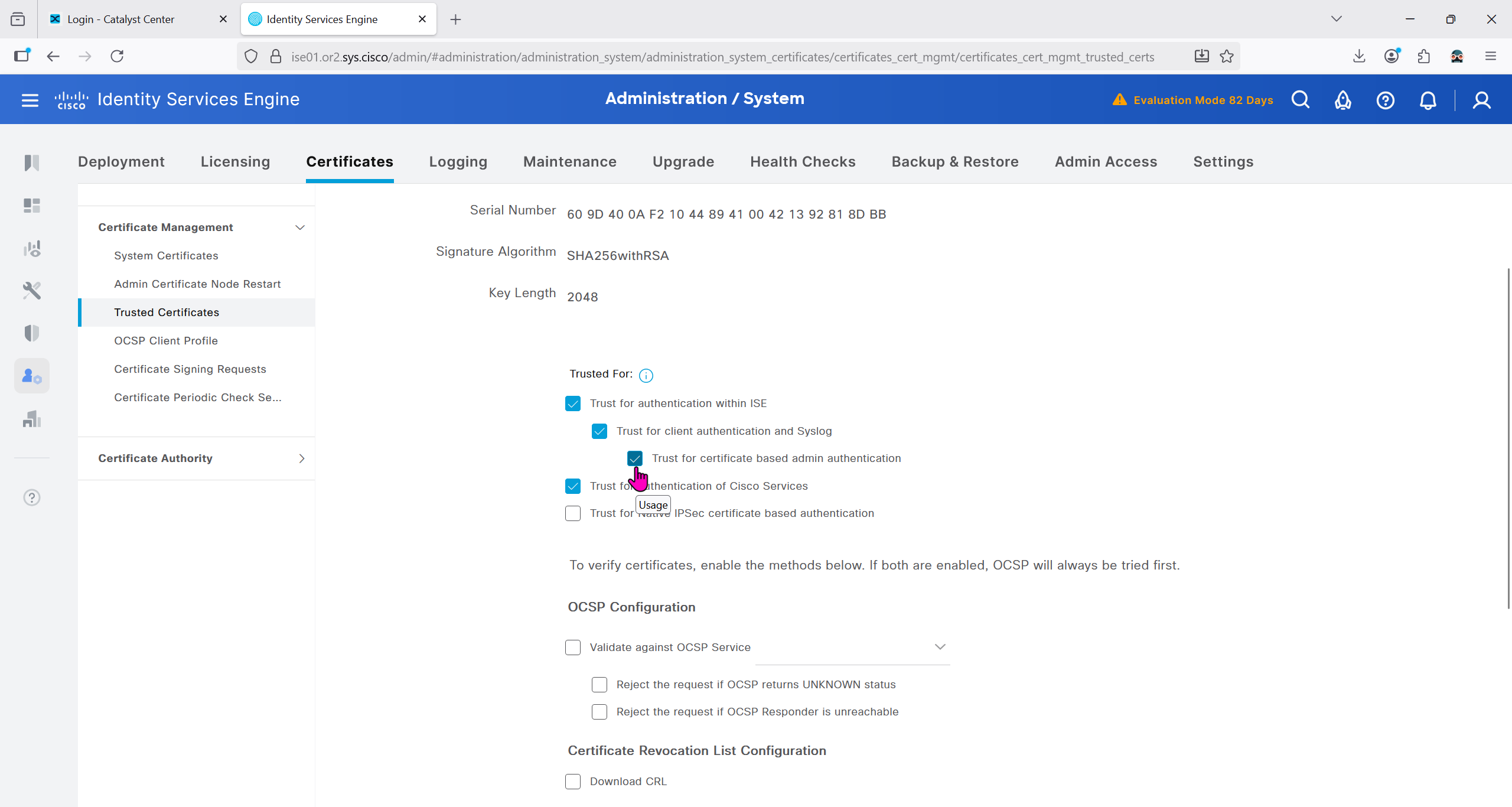
Because DNAC uses API to communicate with ISE, ERS needs to be enabled


Make sure PXgrid service is running
Currently in Client management we do not have any PXgrid clients yet
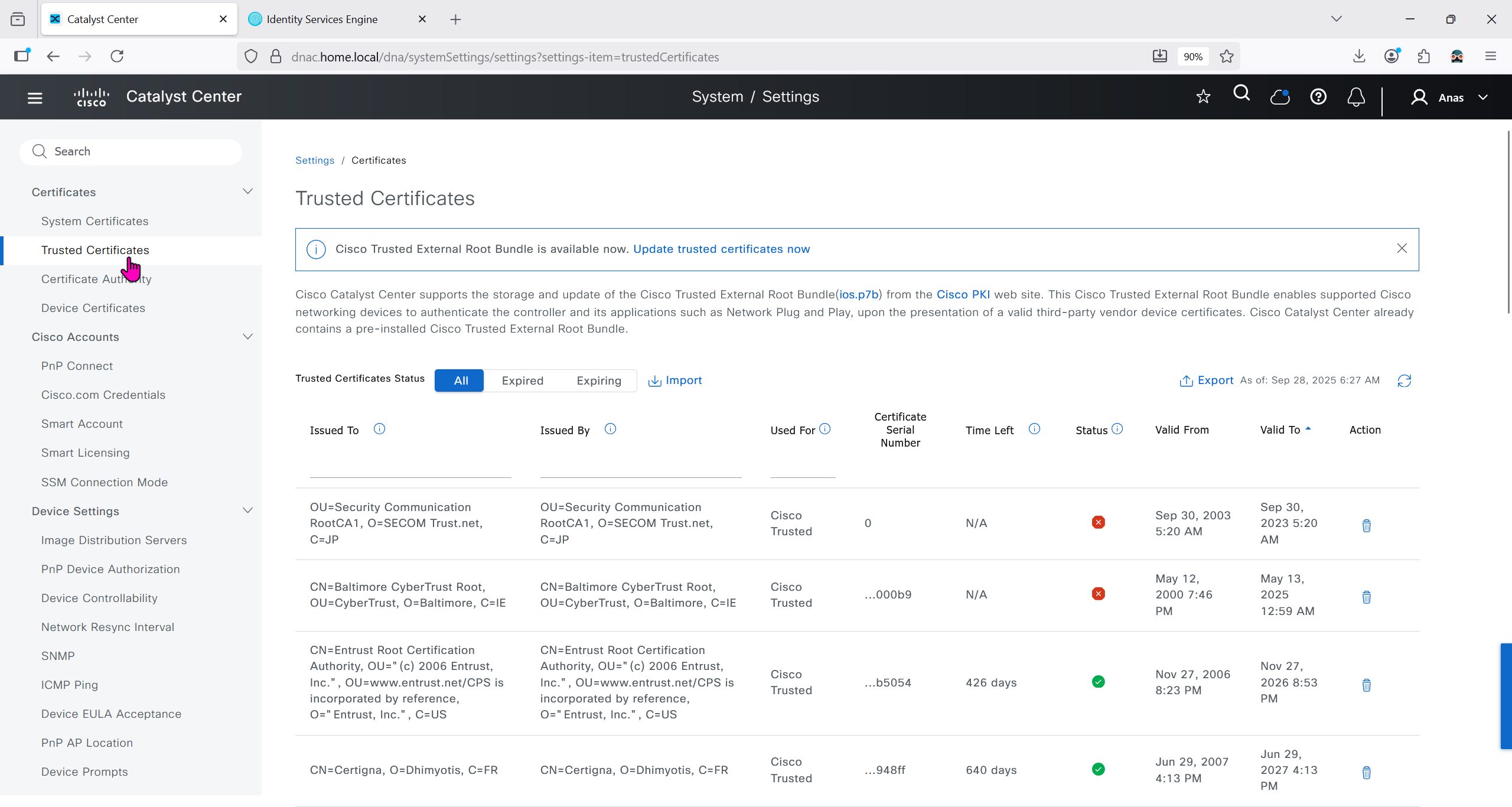
We will import the root ca cert in dnac so it can trust the certificate presented by ISE

Make sure dnac can reach ise 172.16.32.12

Add ISE server 172.16.32.12 and this shared secret is the secret that will be used on catalyst devices which are added to dnac
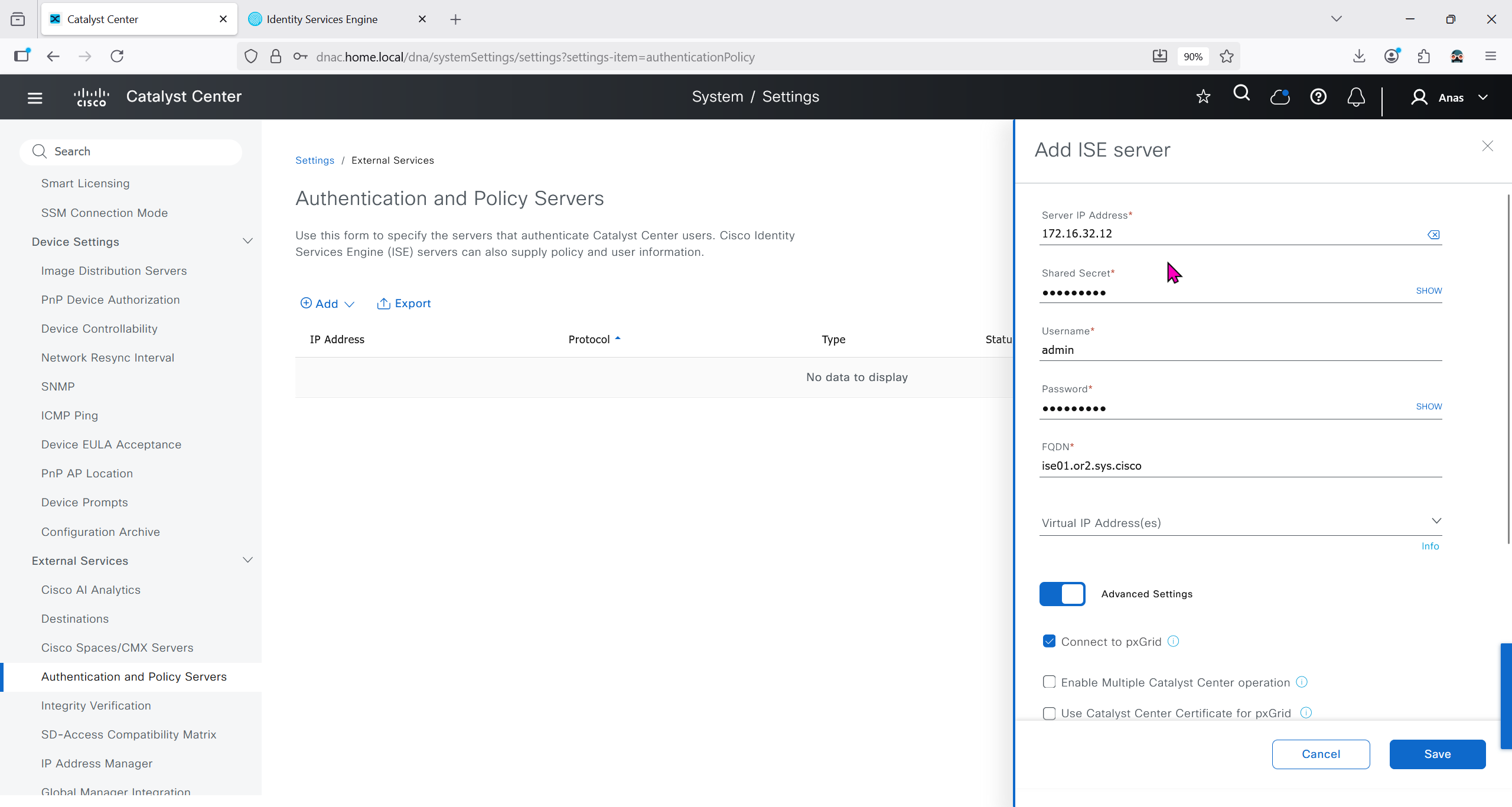
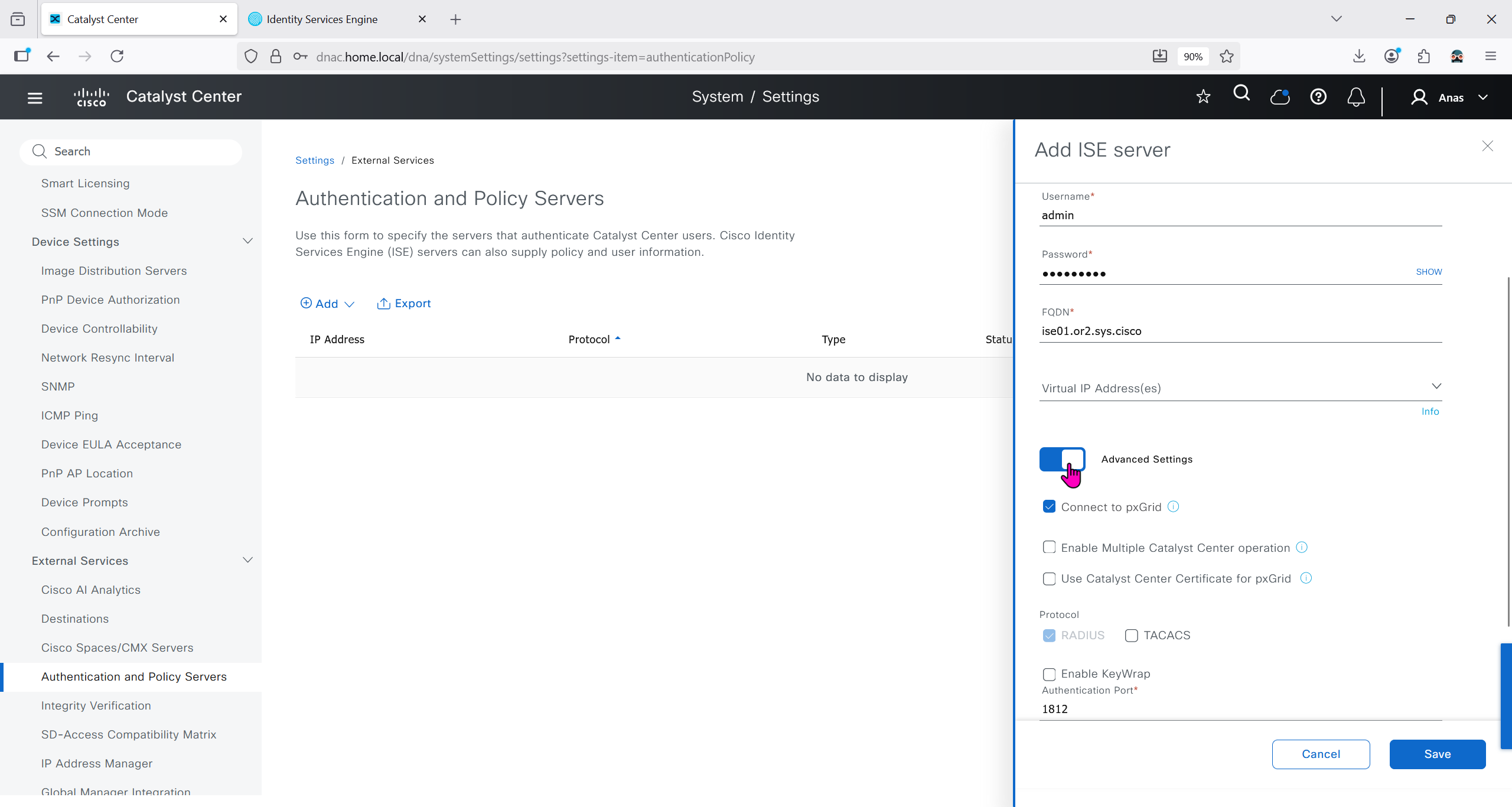
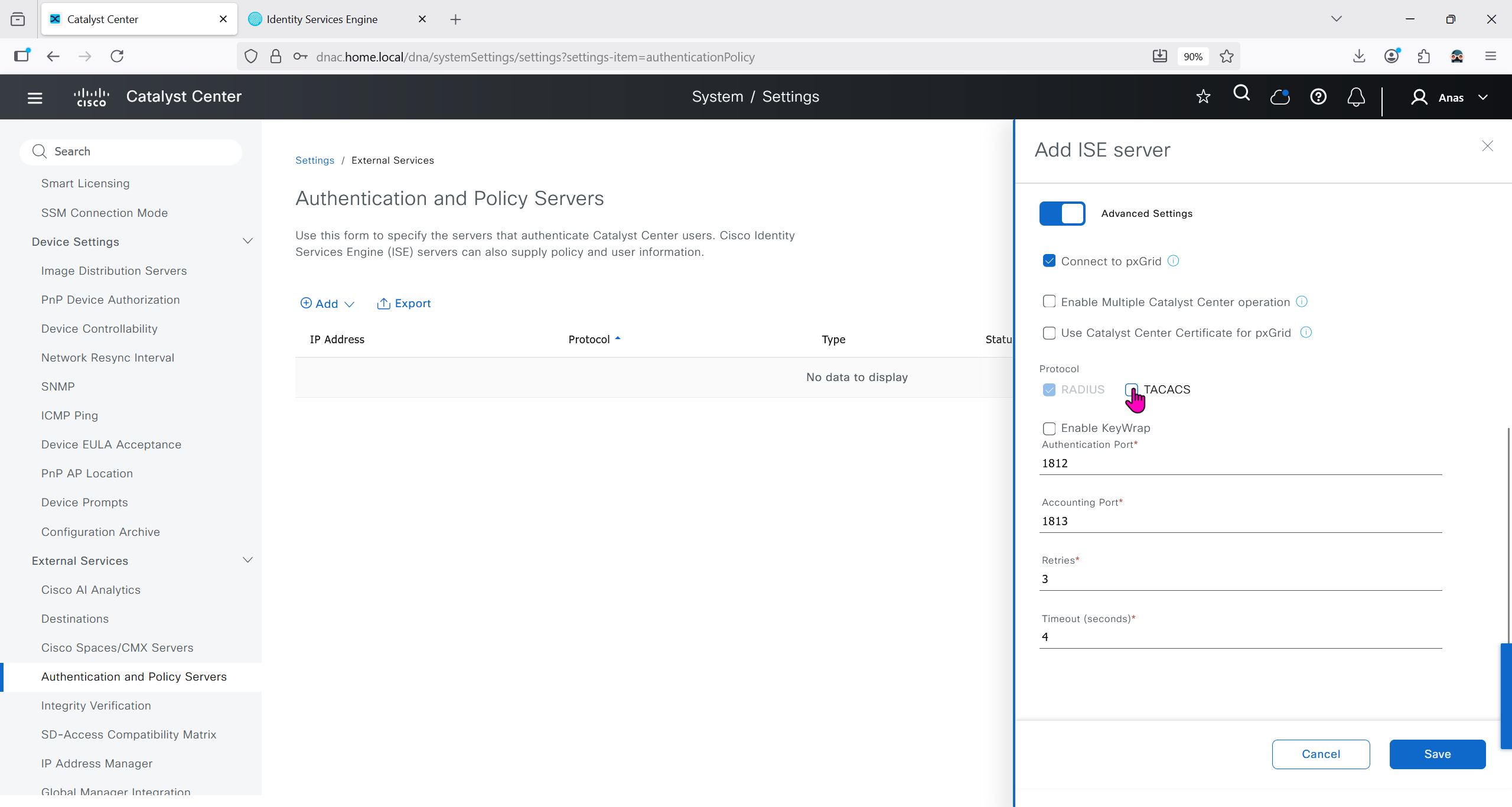
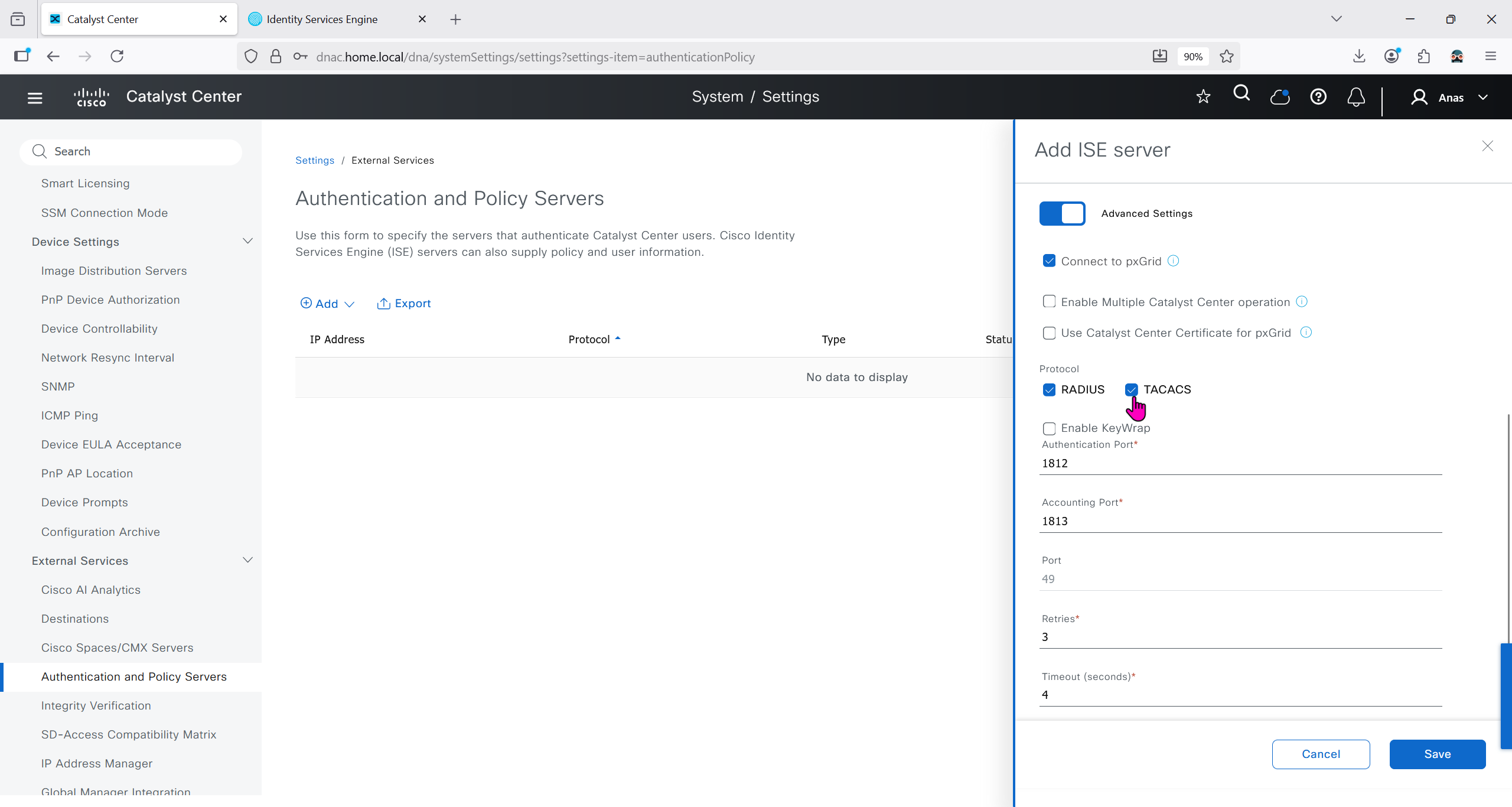

It should say IN PROGRESS and then it should move on to ACTIVE
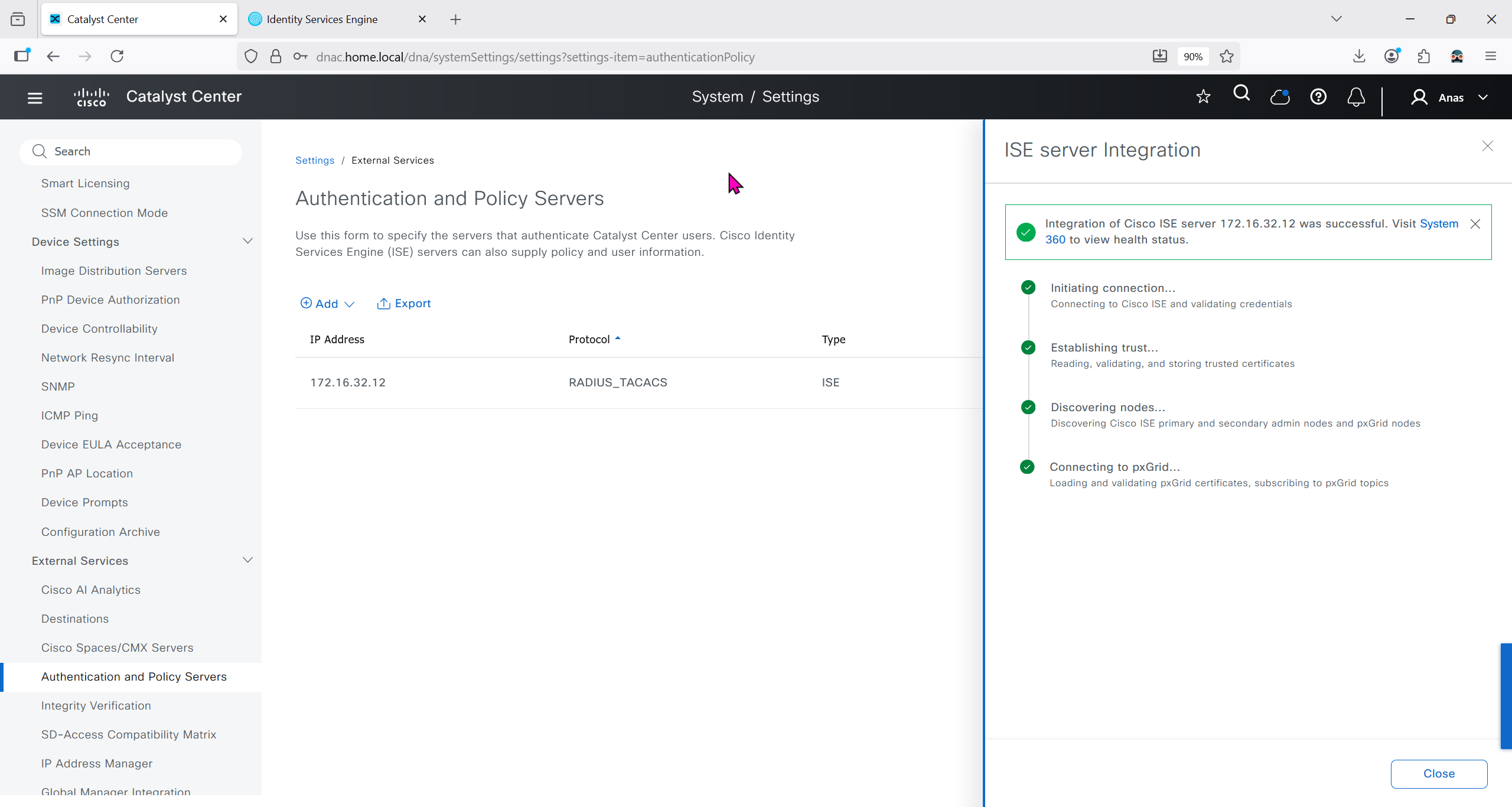
In ISE we will check Administration > pxgrid > summary for 1 client that is dnac

in pxgrid > client management, if dnac is showing pending then approve it

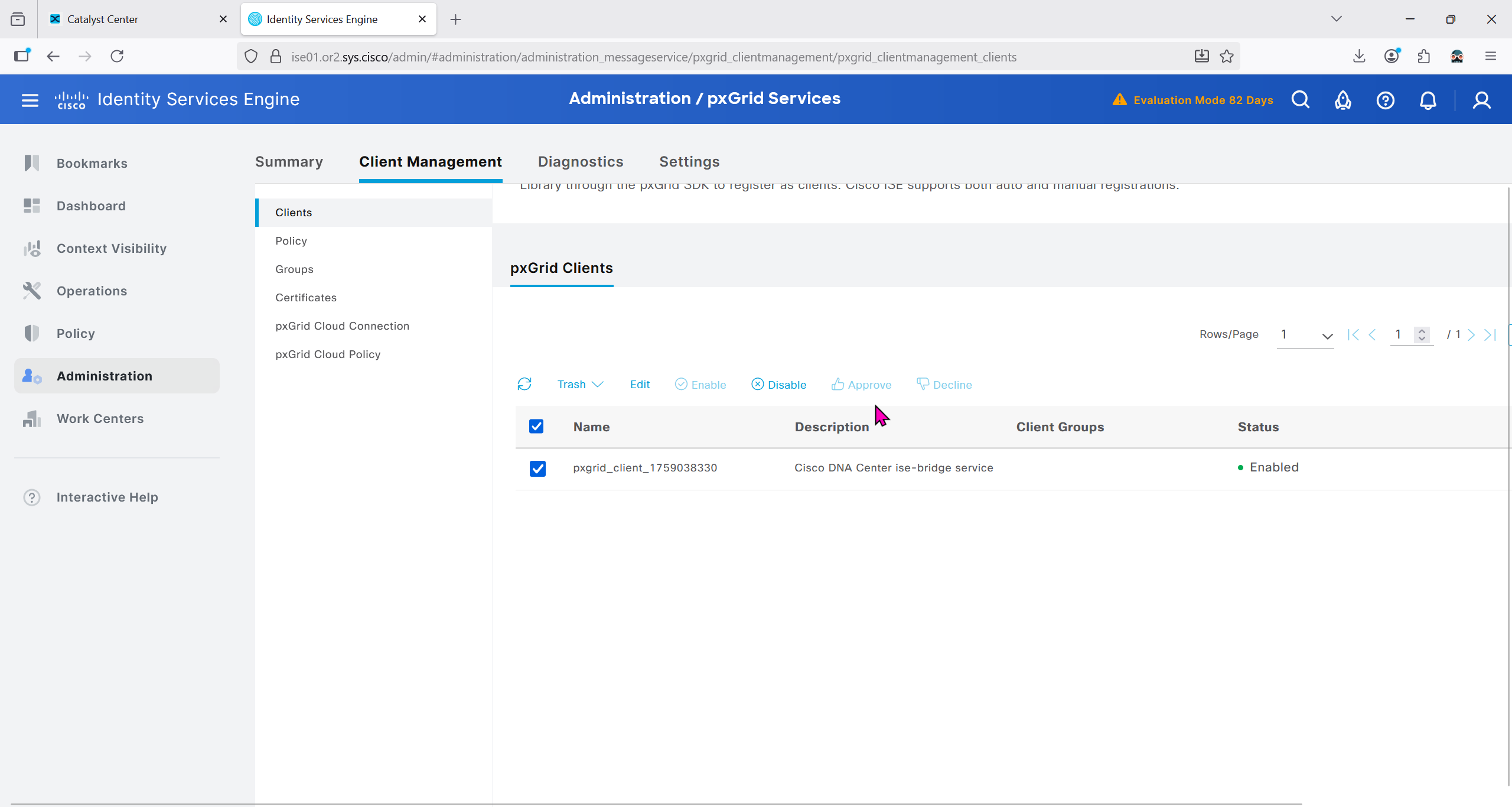
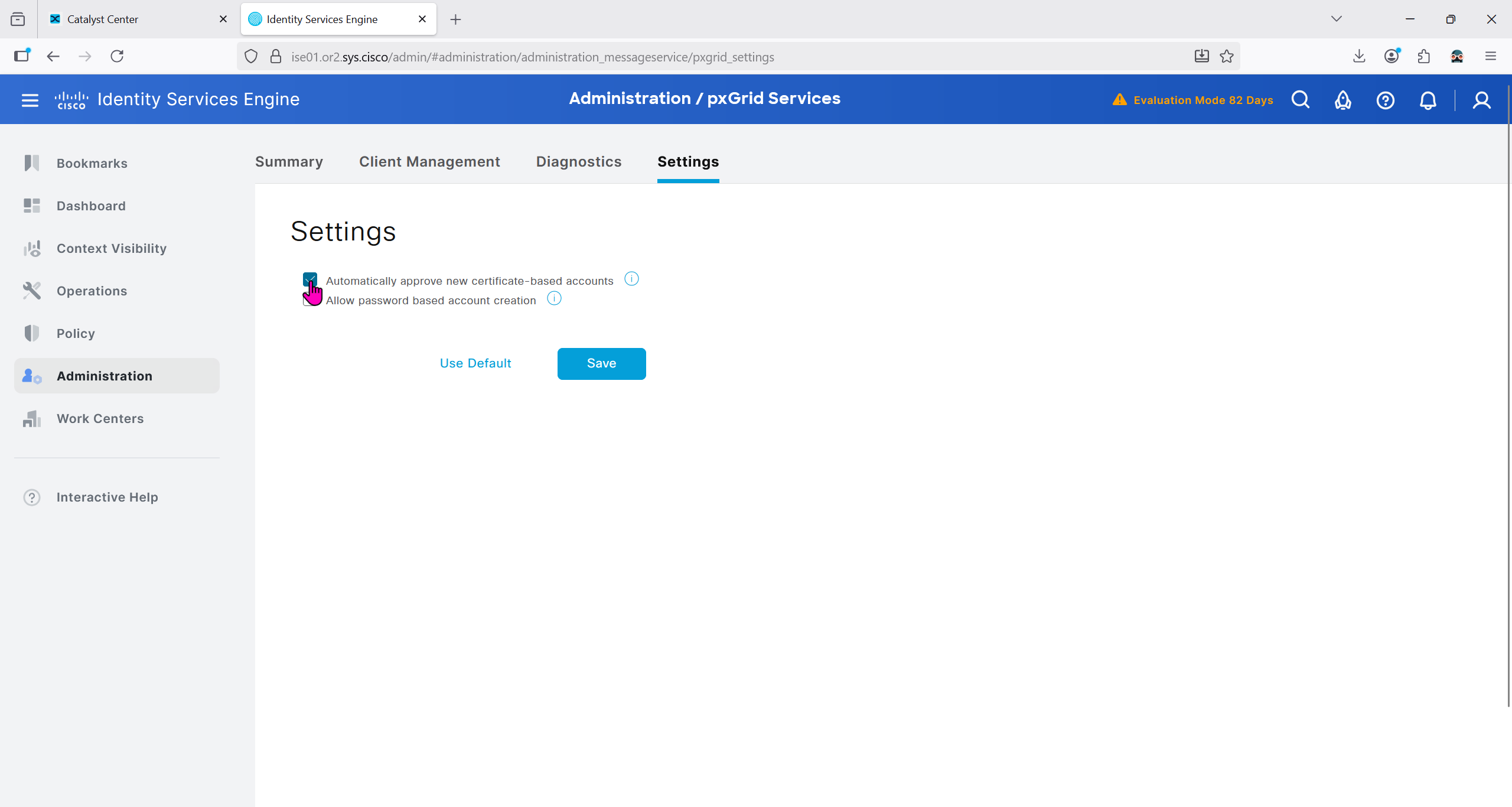



We should have installed Group based policy analytics, which we will do now

This message basically says to config sync between DNAC and ISE and use DNAC as the administration point for GBAC policy
In order to begin using Catalyst Center as the administration point for Group-Based Access Control, Catalyst Center must migrate policy data from the Cisco Identity Services Engine (ISE):
Any policy features in Cisco ISE that are currently not supported in Catalyst Center will not be migrated, you will have a chance to review the migration rule after click on "Start migration"
Any policy information in Catalyst Center not already exist in Cisco ISE will be copied to Cisco ISE to ensure the 2 sources are in syncOnce the data migration is initiated, you cannot use Group-Based Access Control in Catalyst Center until the operation is complete.
Start migration
After policy data migration has completed, if you prefer to manage Group-Based Access Control in Cisco Identity Services Engine, you can select that option under “Group-Based Access Control Configuration”.
We need to click on Start migration, Backup is recommended because this is a 2 way sync and configuration in ISE will also change if there is pre existing config in DNAC
After migration DNAC has become the policy administration point and all changes should be made in ISE
“Migration is complete. Catalyst Center will be the policy administration point, and screens of Security Groups, Access Contracts and Policies in Cisco Identity Services Engine will be read-only. You can review the policy migration log, and/or change the administration mode in Group-Based Access Control Configurations”
All these security groups have been downloaded into DNAC and any future configuration changes you make in DNAC will be reflected in ISE
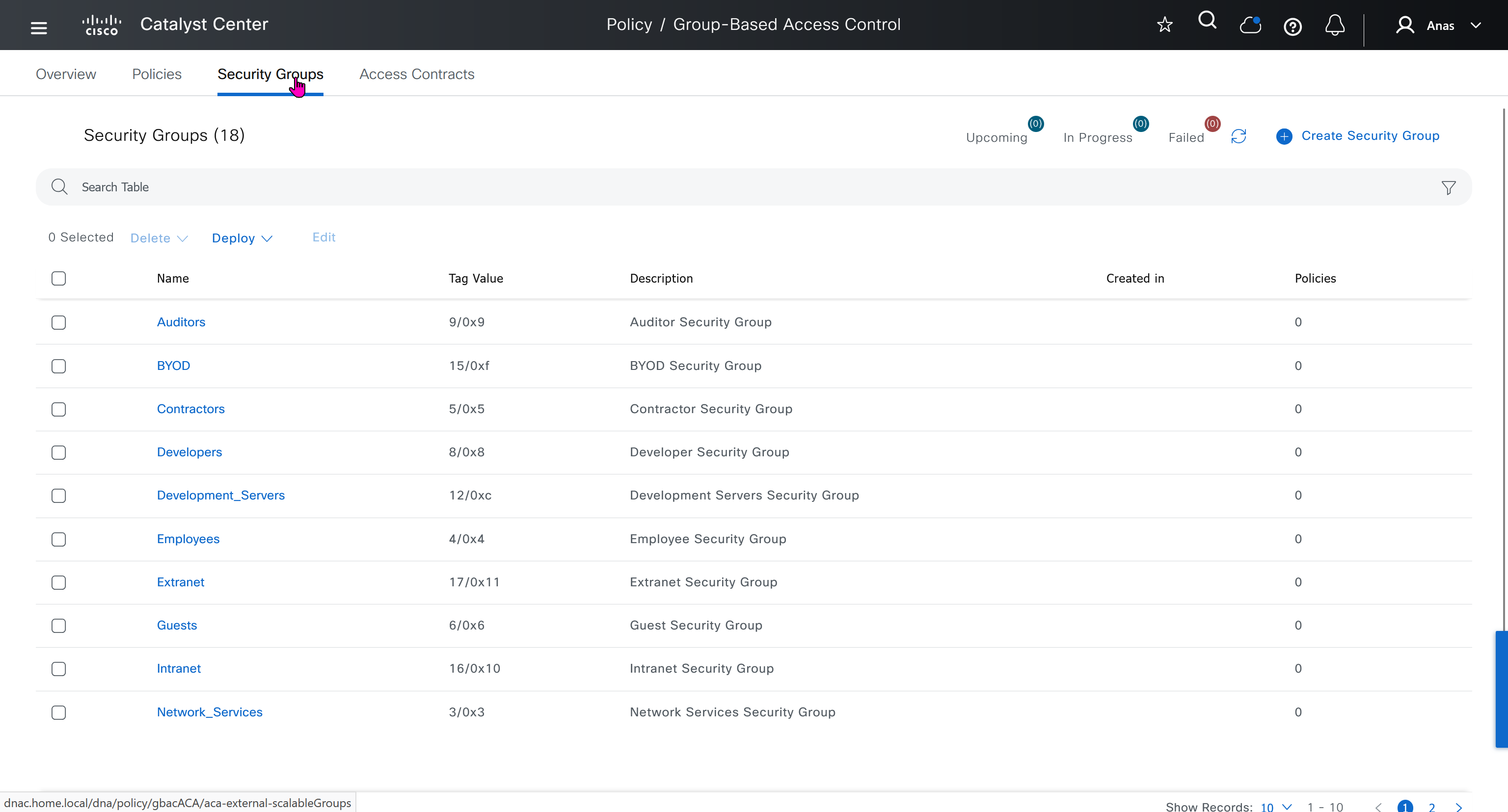


next post
SDA Deployment
SDA LISP Roles
ITR – Ingress Tunnel Router – devices which accepts traffic from the client and looks at transmitting to the destination.
ETR – Egress Tunnel Router – device which transmits traffic to the client, this is where destination client is attached.
These above roles of LISP would be on Fabric Edge node.
Example of Ping (I am omitting the full lookup against Map Resolver and RLOC etc):
Client A —> Switch A (ITR) —> Switch B (ETR) —> Client B
Reply:
Client A <— Switch A (ETR) <— Switch B (ITR) <— Client B
If a node has both roles ITR and ETR, that Fabric Edge switch is referenced as xTR
(P – Proxy) PITR and PETR would be the Border node which communicates with destinations outside the fabric, Similarly to the last example, one border node can have both roles and can be referenced as PxTR.
Traffic example: Client A —> Switch A (ITR) — Border A (PITR) —> Server A
Reply: Client A <— Switch A (ETR) <— Border A (PETR) <— Server A
ESXI and VCenter Deployment
-: Z840 :-
Upgrade BIOS
Factory Reset BIOS
set controller mode to AHCI from RAID
enable Intel VTd under System Security section
-: ESXI DEPLOYMENT :-
VMware-VMvisor-Installer-7.0.0-15843807.x86_64
ESXi 7.0 keys
JJ2WR-25L9P-H71A8-6J20P-C0K3F
ESXI01.home.local
192.168.0.10
root
C0mplex30-
-: VCENTER DEPLOYMENT :-
Create following entries in host file
192.168.0.10 esxi01.home.local <<<<
192.168.0.11 vcenter.home.local <<<< This is checked from local machine when running VCSA setup to install vcenter, this check is different from vcenter A and PTR record lookup by installer, that is why DNS server on Windows server 2016 is needed
Bring up a winserver 2016 instance in eveng metal and configure DNS server on it
VMware-VCSA-all-7.0.0-16386292.iso
vCenter 7 keys
406DK-FWHEH-075K8-XAC06-0JH08
VCENTER.home.local
192.168.0.11
root
C0mplex30-
administrator@vsphere.local
C0mplex30-
Import vcenter Certificates in Installation station
Because we are deploying appliance through VA launcher script, we need to import certificates of vcenter into local computer trusted root certificate’s store, go to https://vCenter_FQDN/certs/download.zip, download ZIP and extract all the certs and import them



Windows Server DNS deployment

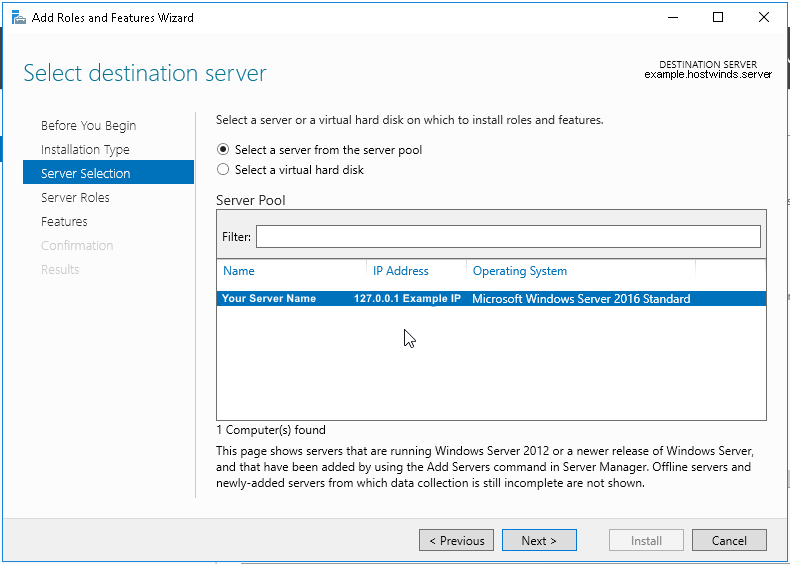
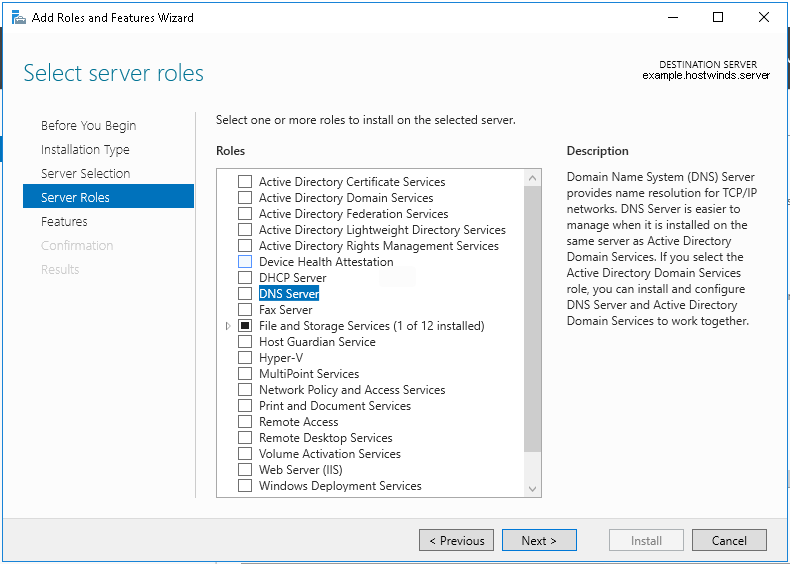
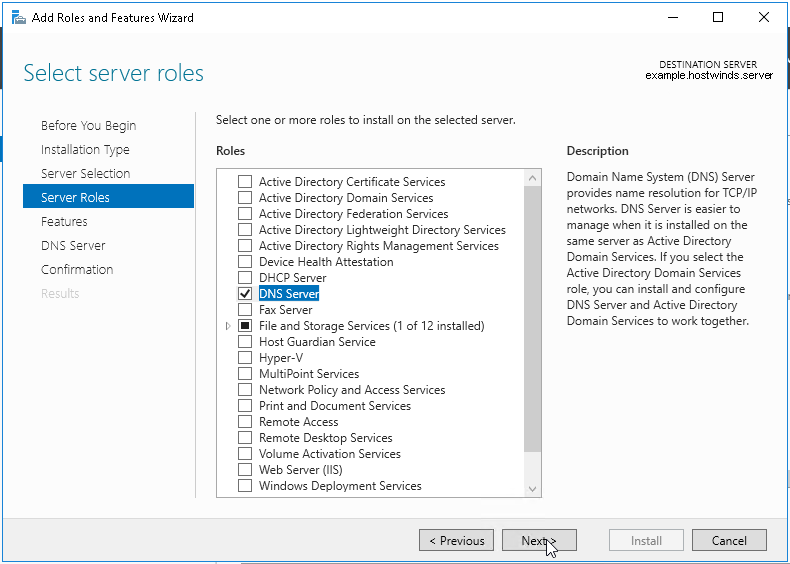
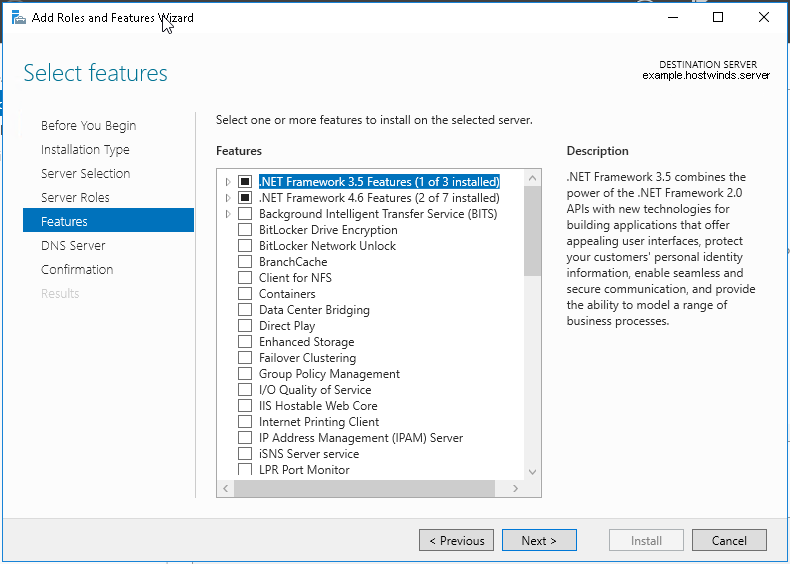

configure forward zone
configure reverse zone
create A record
vcenter.home.local 192.168.0.11
dnac.home.local 10.21.1.2
Windows 10 and VYOS deployment
Windows 10 VM
Create Windows 10 VM for VYOS deployment validation and internet access check
2 vCPUs
5GB RAM
25GB disk
admin/Test123
Pet name
dnac
City born in
dnac
City parents met
dnac
Assign only 192.168.0.200/24 and do not assign gateway 192.168.0.1
Disable IPv6 on the Windows VM interface
connect VM’s interface in vcenter
Go to Network folder and join the network
Share Downloads folder
copy wub and debloater to downloads folder
once all done then put network interface in DHCP again
VYOS deployment
2 CPUs
RAM 2 GB
4 GB Disk
! Install open-vm-tools on VY OS gateway
vyos@vy-gateway:~$ sudo vim /etc/apt/sources.list
! press esc to make sure we are in normal mode
! press i to go in insert mode
! enter first line
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main contrib
! press escape
! enter ":wq"
vyos@vy-gateway:~$ sudo cat /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye main contrib
! Update failed because of no DNS resolution
vyos@vy-gateway:~$ sudo apt update
Ign:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease
Ign:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease
Ign:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease
Err:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease
System error resolving 'deb.debian.org:http' - getaddrinfo (16: Device or resource busy)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
All packages are up to date.
W: Failed to fetch http://deb.debian.org/debian/dists/bullseye/InRelease System error resolving 'deb.debian.org:http' - getaddrinfo (16: Device or resource busy)
W: Some index files failed to download. They have been ignored, or old ones used instead.
vyos@vy-gateway:~$ sudo bash
root@vy-gateway:/home/vyos# sudo bash -c 'cat > /etc/resolv.conf <<EOF
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 1.1.1.1
EOF'
root@vy-gateway:/home/vyos# cat /etc/resolv.conf
nameserver 8.8.8.8
nameserver 1.1.1.1
root@vy-gateway:/home/vyos# apt update
Get:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye InRelease [75.1 kB]
Get:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 Packages [8,066 kB]
Get:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main Translation-en [6,235 kB]
Get:4 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/contrib amd64 Packages [50.4 kB]
Get:5 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/contrib Translation-en [46.9 kB]
Fetched 14.5 MB in 4s (4,084 kB/s)
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
8 packages can be upgraded. Run 'apt list --upgradable' to see them.
! install should work now
root@vy-gateway:/home/vyos# apt install -y open-vm-tools
Reading package lists... Done
Building dependency tree... Done
Reading state information... Done
The following additional packages will be installed:
libdrm-common libdrm2 libmspack0 libssl1.1 libxmlsec1 libxmlsec1-openssl
libxslt1.1
Suggested packages:
open-vm-tools-desktop cloud-init
Recommended packages:
zerofree
The following NEW packages will be installed:
libdrm-common libdrm2 libmspack0 libssl1.1 libxmlsec1 libxmlsec1-openssl
libxslt1.1 open-vm-tools
0 upgraded, 8 newly installed, 0 to remove and 8 not upgraded.
Need to get 2,793 kB of archives.
After this operation, 8,598 kB of additional disk space will be used.
Get:1 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 libdrm-common all 2.4.104-1 [14.9 kB]
Get:2 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 libdrm2 amd64 2.4.104-1 [41.5 kB]
Get:3 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 libmspack0 amd64 0.10.1-2 [50.3 kB]
Get:4 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 libssl1.1 amd64 1.1.1w-0+deb11u1 [1,566 kB]
Get:5 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 libxslt1.1 amd64 1.1.34-4+deb11u1 [240 kB]
Get:6 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 libxmlsec1 amd64 1.2.31-1 [149 kB]
Get:7 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 libxmlsec1-openssl amd64 1.2.31-1 [100.0 kB]
Get:8 http://deb.debian.org/debian bullseye/main amd64 open-vm-tools amd64 2:11.2.5-2+deb11u3 [632 kB]
Fetched 2,793 kB in 0s (10.4 MB/s)
Preconfiguring packages ...
Selecting previously unselected package libdrm-common.
(Reading database ... 84389 files and directories currently installed.)
Preparing to unpack .../0-libdrm-common_2.4.104-1_all.deb ...
Unpacking libdrm-common (2.4.104-1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libdrm2:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../1-libdrm2_2.4.104-1_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libdrm2:amd64 (2.4.104-1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libmspack0:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../2-libmspack0_0.10.1-2_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libmspack0:amd64 (0.10.1-2) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libssl1.1:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../3-libssl1.1_1.1.1w-0+deb11u1_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libssl1.1:amd64 (1.1.1w-0+deb11u1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libxslt1.1:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../4-libxslt1.1_1.1.34-4+deb11u1_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libxslt1.1:amd64 (1.1.34-4+deb11u1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libxmlsec1:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../5-libxmlsec1_1.2.31-1_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libxmlsec1:amd64 (1.2.31-1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package libxmlsec1-openssl:amd64.
Preparing to unpack .../6-libxmlsec1-openssl_1.2.31-1_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking libxmlsec1-openssl:amd64 (1.2.31-1) ...
Selecting previously unselected package open-vm-tools.
Preparing to unpack .../7-open-vm-tools_2%3a11.2.5-2+deb11u3_amd64.deb ...
Unpacking open-vm-tools (2:11.2.5-2+deb11u3) ...
Setting up libssl1.1:amd64 (1.1.1w-0+deb11u1) ...
Setting up libmspack0:amd64 (0.10.1-2) ...
Setting up libxslt1.1:amd64 (1.1.34-4+deb11u1) ...
Setting up libxmlsec1:amd64 (1.2.31-1) ...
Setting up libdrm-common (2.4.104-1) ...
Setting up libxmlsec1-openssl:amd64 (1.2.31-1) ...
Setting up libdrm2:amd64 (2.4.104-1) ...
Setting up open-vm-tools (2:11.2.5-2+deb11u3) ...
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/vmtoolsd.service → /lib/systemd/system/open-vm-tools.service.
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/open-vm-tools.service → /lib/systemd/system/open-vm-tools.service.
Created symlink /etc/systemd/system/open-vm-tools.service.requires/vgauth.service → /lib/systemd/system/vgauth.service.
Processing triggers for libc-bin (2.36-9+deb12u10) ...
localepurge: Disk space freed: 0 KiB in /usr/share/locale
localepurge: Disk space freed: 0 KiB in /usr/share/man
localepurge: Disk space freed: 0 KiB in /usr/share/aptitude
localepurge: Disk space freed: 0 KiB in /usr/share/vim/vim90/lang
Total disk space freed by localepurge: 0 KiB
root@vy-gateway:/home/vyos#vyos/C0mplex30
Install from live image
install image
show configuration
show configuration commands
configure
set interfaces ethernet eth0 address '192.168.0.12/24'
set interfaces ethernet eth0 description 'home'
set interfaces ethernet eth1 address '172.16.25.1/24'
set interfaces ethernet eth1 description 'mgmt'
set interfaces ethernet eth2 address '10.21.1.1/24'
set interfaces ethernet eth2 description 'data'
show interface ethernet
show interface ethernet eth0
show interface ethernet eth0 physical
set protocols static route 0.0.0.0/0 next-hop 192.168.0.1 distance '1'
set service ssh port '22'
set system host-name 'vy-gateway'
commit
save vcenter
edit host and create a new standard switch and call it mgmt
edit host and create a new standard switch and call it data
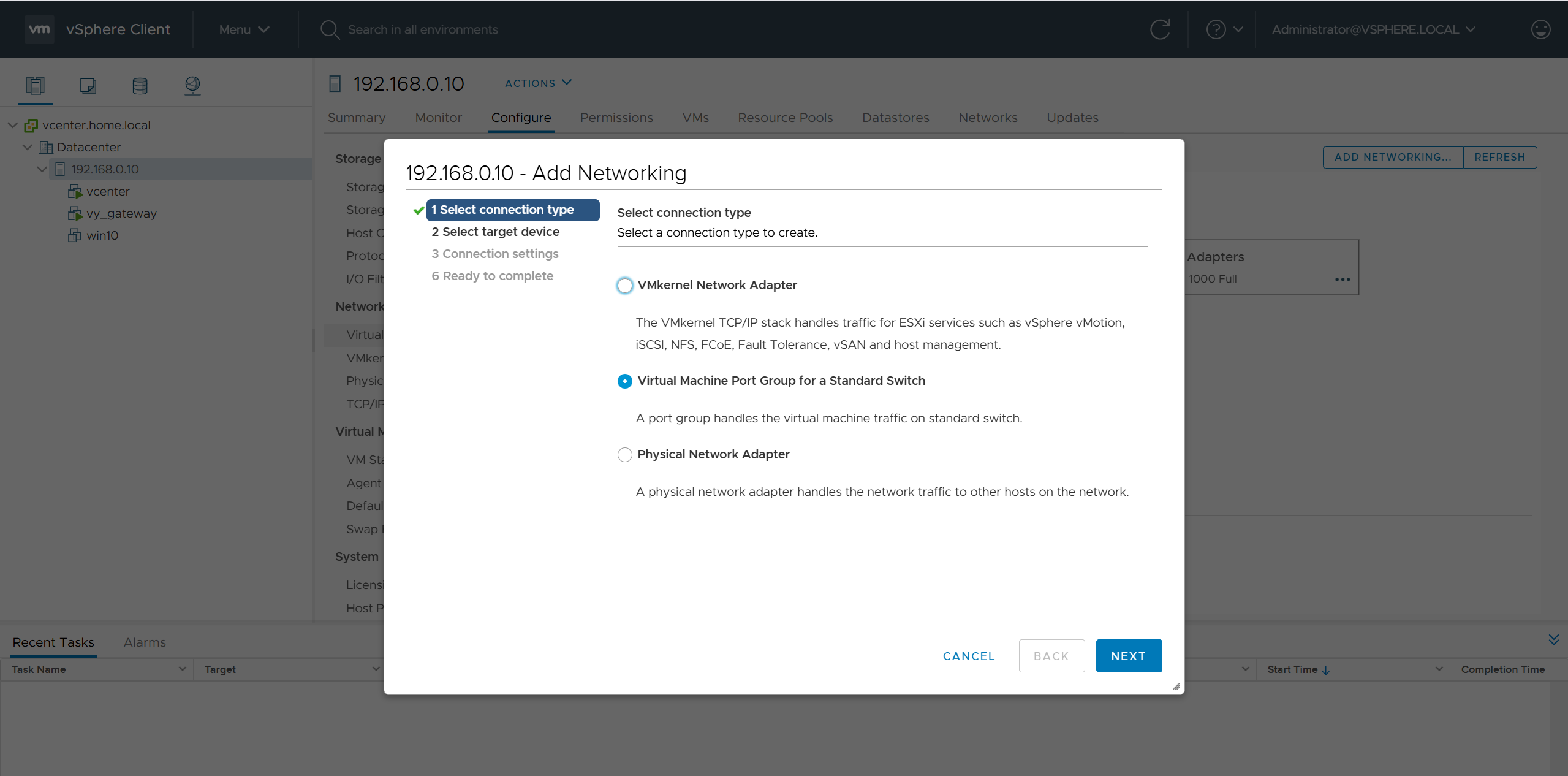
add 2nd interface for vy-gateway into mgmt
add 3rd interface for vy-gateway into data

home router
Add routes for networks 10.21.1.0/24 and 172.16.25.0/24

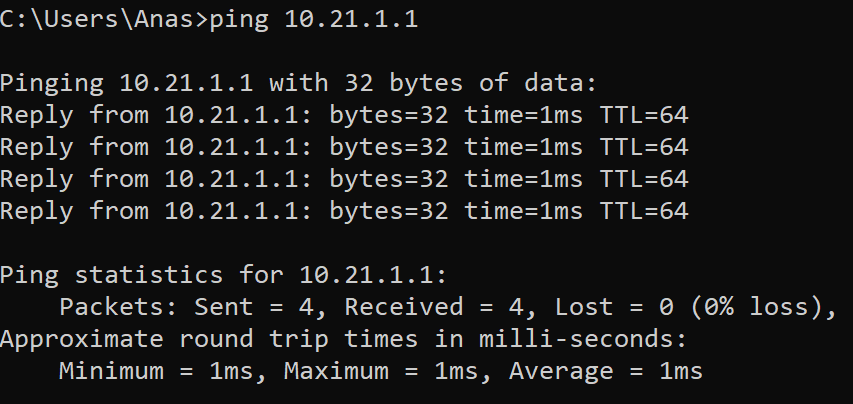
vyos routing is reachable
Cisco Catalyst Center 2.3.7.x on ESXi Deployment – Part 1
Virtual Machine Minimum Requirements
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Virtualization platform and hypervisor | VMware vSphere (which includes ESXi and vCenter Server) 7.0.x or later, including all patches. |
| Processors | Intel Xeon Scalable server processor (Cascade Lake or newer) or AMD EPYC Gen2 with 2.1 GHz or better clock speed.32 vCPUs with 64-GHz reservation must be dedicated to the VM. |
| Memory | 256-GB DRAM with 256-GB reservation must be dedicated to the VM. |
| Storage | 3-TB solid-state drive (SSD).If you plan to create backups of your virtual appliance, also reserve additional datastore space. For information, see “Backup Server Requirements” in the Cisco Catalyst Center on ESXi Administrator Guide. |
| I/O Bandwidth | 180 MB/sec. |
| Input/output operations per second (IOPS) rate | 2000-2500, with less than 5 ms of I/O completion latency. |
| Latency | Catalyst Center on ESXi to network device connectivity: 200 ms. |
Scale numbers are different
for example maximum number of devices supported in non-fabric deployment is 1000 and maximum number of devices in fabric deployment is 2000, for more info
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/cloud-systems-management/network-automation-and-management/catalyst-center/catalyst-center-va/esxi/2-3-7/deployment-guide/b_cisco_catalyst_center_237x_on_esxi_deployment_guide.html
Cisco Catalyst Assurance uses near real-time streaming analytics, which requires heavy resource usage. When operating Catalyst Center on ESXi close to maximum scale, this functionality may be impacted by uncontrolled external events, such as host resource oversubscriptions and edge use cases that result in a resource usage spike. A number of things can indicate that these events are taking place, such as slow performance, data processing gaps, high I/O latency, and a CPU readiness percentage that’s higher than normal.
Catalyst Center VM can be deployed using Catalyst Center VA Launcher
Import the IdenTrust Certificate Chain
The Catalyst Center on ESXi OVA file is signed with an IdenTrust CA certificate, which is not included in VMware’s default truststore. As a result, the Deploy OVF Template wizard’s Review details page will indicate that you are using an invalid certificate while completing the wizard. You can prevent this by importing the IdenTrust certificate chain to the host or cluster on which you want to deploy the OVA file.

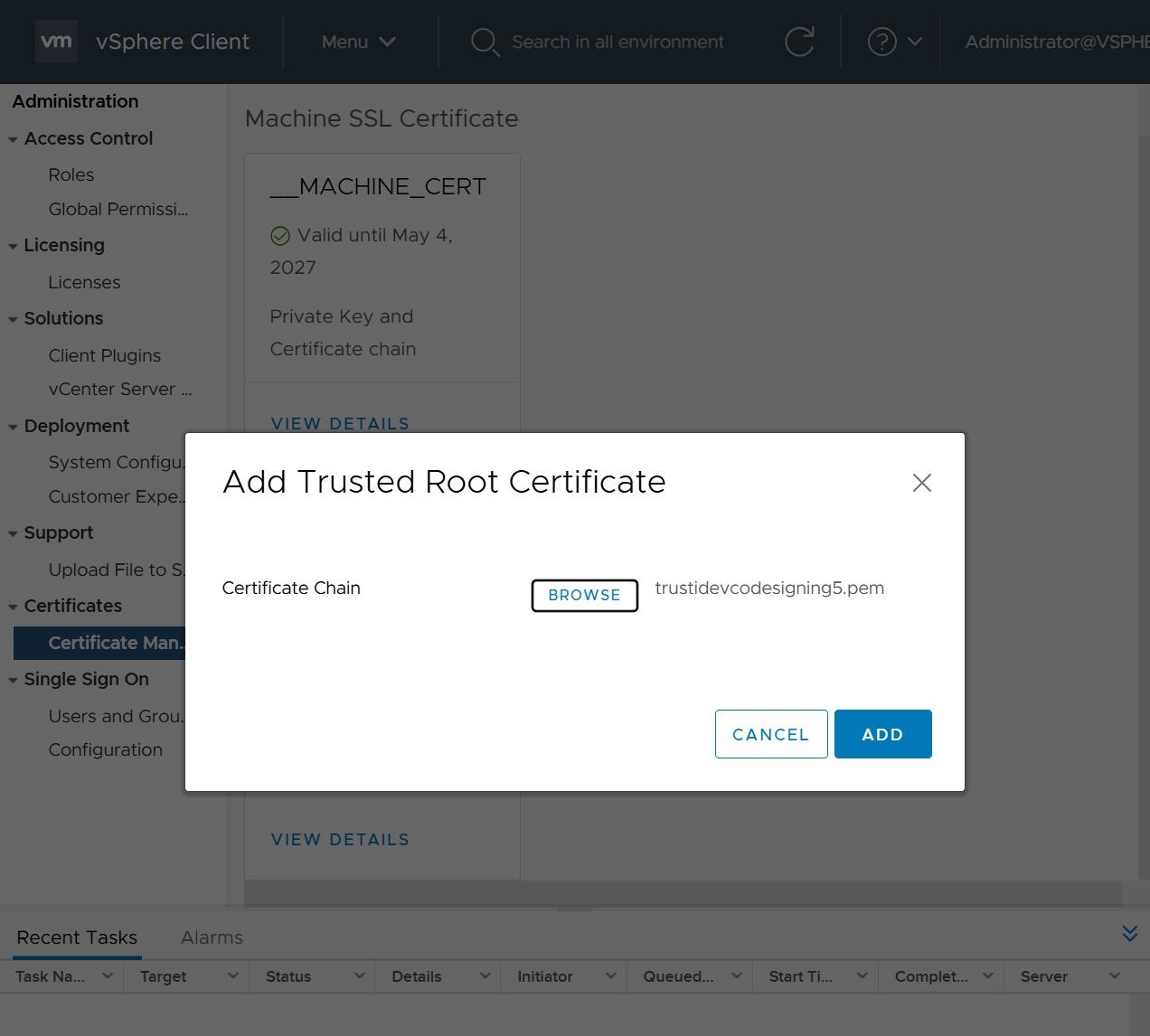
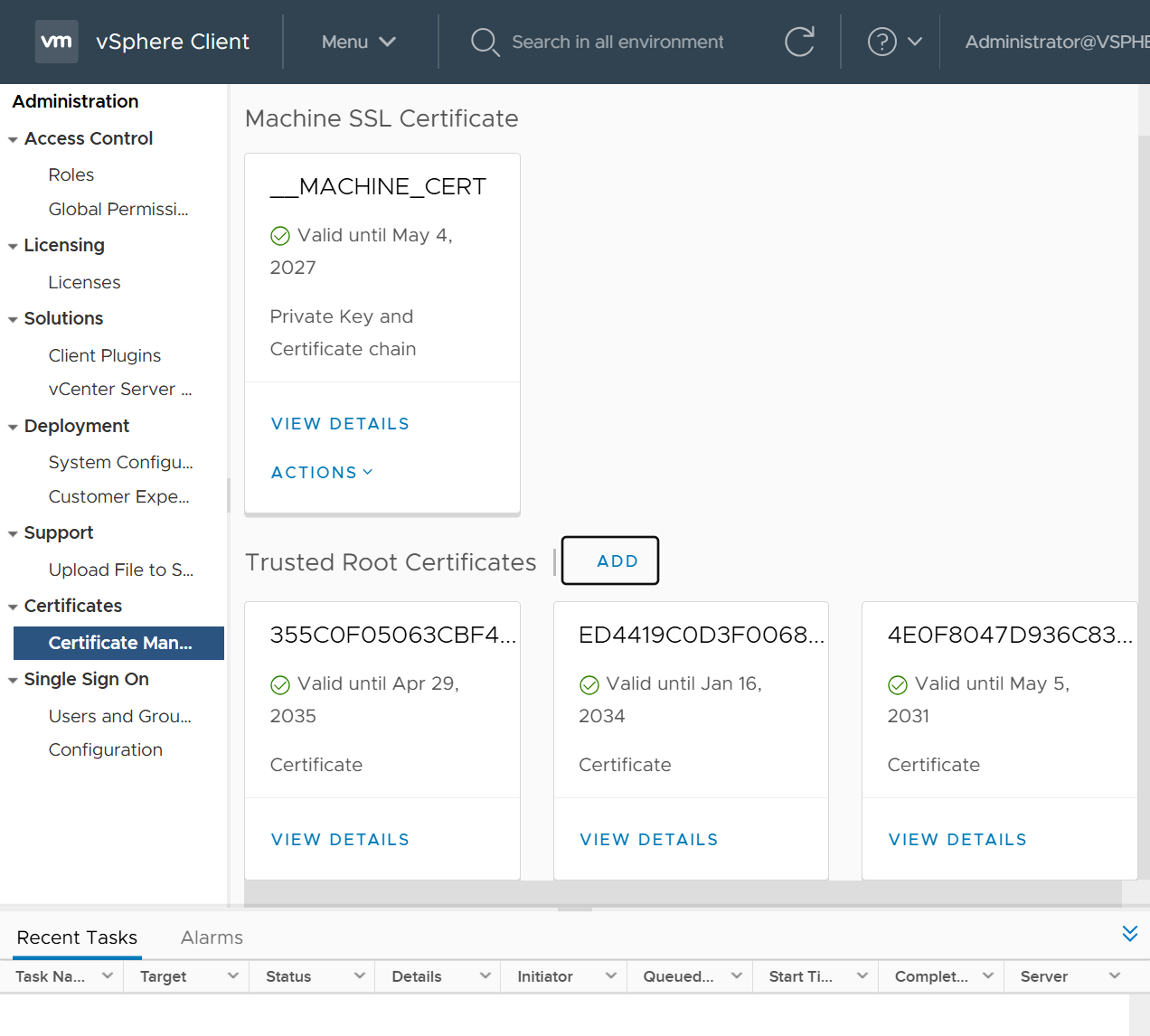
Cat center requires access to following URLs during install
| In order to… | …Catalyst Center on ESXi must access these URLs and FQDNs |
|---|---|
| Download updates to the system and application package software; submit user feedback to the product team. | Recommended: *.ciscoconnectdna.com:4431Customers who want to avoid wildcards can specify these URLs instead:https://www.ciscoconnectdna.comhttps://cdn.ciscoconnectdna.comhttps://registry.ciscoconnectdna.comhttps://registry-cdn.ciscoconnectdna.com |
| Catalyst Center on ESXi update package. | https://*.ciscoconnectdna.com/**.cloudfront.net*.tesseractcloud.com |
| Smart Account and SWIM software downloads. | https://apx.cisco.comhttps://cloudsso.cisco.com/as/token.oauth2https://*.cisco.com/*https://download-ssc.cisco.com/ |
| Authenticate with the cloud domain. | https://dnaservices.cisco.com |
| Integrate with ThousandEyes. | *.awsglobalaccelerator.comapi.thousandeyes.com |
| Manage Cisco Enterprise Network Function Virtualization Infrastructure Software (NFVIS) devices. | *.amazonaws.com |
| Collect product telemetry. | https://data.pendo.io |
| Allow API calls to enable access to Cisco CX Cloud Success Tracks. Otherwise, the enhancements made to extended configuration-based scanning for the Security Advisories, Bug Identifier, and EOX features that Machine Reasoning Engine (MRE) supports will not operate as expected. | https://api-cx.cisco.com |
| Integrate with Webex. | http://analytics.webexapis.comhttps://webexapis.com |
| User feedback. | https://dnacenter.uservoice.com |
| Integrate with Cisco Meraki. | Recommended: *.meraki.com:443Customers who want to avoid wildcards can specify these URLs instead:dashboard.meraki.com:443api.meraki.com:443n63.meraki.com:443 |
| Check SSL/TLS certificate revocation status using OCSP/CRL. | http://validation.identrust.com/crl/hydrantidcao1.crlhttp://commercial.ocsp.identrust.comNote These URLs should be reachable both directly and through the proxy server that’s configured for Catalyst Center. |
| Allow Cisco authorized specialists to collect troubleshooting data when Catalyst Center on ESXi Remote Support functionality is enabled. | wss://prod.radkit-cloud.cisco.com:443 |
| Integrate with cisco.com and Cisco Smart Licensing. | *.cisco.com:443Customers who want to avoid wildcards can specify these URLs instead:software.cisco.comcloudsso.cisco.comcloudsso1.cisco.comcloudsso2.cisco.comapiconsole.cisco.comapi.cisco.comapx.cisco.comsso.cisco.comapmx-prod1-vip.cisco.comapmx-prod2-vip.cisco.comtools.cisco.comtools1.cisco.comtools2.cisco.comsmartreceiver.cisco.com |
| Connect to the Network-Based Application Recognition (NBAR) cloud. | prod.sdavc-cloud-api.com:443 |
| Render accurate information in site and location maps. | www.mapbox.com*.tiles.mapbox.com/* :443. For a proxy, the destination is *.tiles.mapbox.com/* |
| For Cisco AI Network Analytics data collection, configure your network or HTTP proxy to allow outbound HTTPS (TCP 443) access to the cloud hosts. | https://api.use1.prd.kairos.ciscolabs.com (US East Region)https://api.euc1.prd.kairos.ciscolabs.com (EU Central Region) |
| Access a menu of interactive help flows that let you complete specific tasks from the GUI. | https://ec.walkme.com |
| Access the licensing service. | https://swapi.cisco.com |
| Integrate with Cisco Spaces. | https://dnaspaces.iohttps://dnaspaces.euhttps://ciscospaces.sg |
ciscoconnectdna.com is a cisco domain
Windows server NTP server
https://www.domat-int.com/en/how-to-configure-a-local-ntp-server
https://docs.litmus.io/litmusedge/product-features/system/network/configure-dns-ntp-servers/configure-local-ntp-server
Configure the Windows Time Service
In the File Explorer, navigate to: Control Panel\System and Security\Administrative Tools
Double-click Services. This same task can be completed by entering services.msc in the Windows Run dialog (Windows Key + R).
In the Services list, right-click on Windows Time and click Stop.
Note: The Windows Time service may already be stopped. In this case, skip this step and go to the next step to Update the Windows Registry
Update the Windows Registry to Create a Local NTP Service
Launch Windows Run (Windows Key + R).
Enter regedit and click OK.
Navigate to the registry key: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Parameters
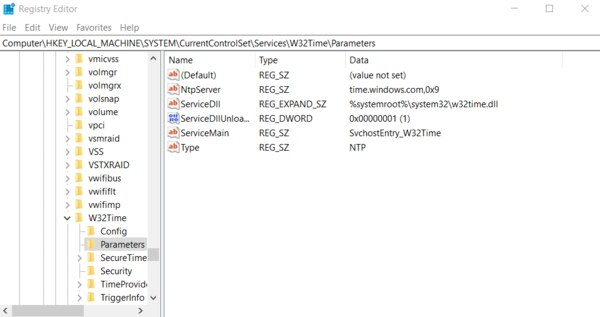
If you do not see LocalNTP REG_DWORD in the list, create it using the following steps.
Right-click in the Registry Editor, select New, select DWORD and enter LocalNTP (note that this name is case sensitive).
Double-click LocalNTP, change the Value data to 1, select a Base of Hexadecimal , and click OK.
Do not close the Registry Editor because it is used in the following steps.
Update the Windows Registry to Configure the Time Provider
Navigate to the registry key: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\TimeProviders
Select NtpServer, double-click Enabled, change the Value Data to 1, select a Base of Hexadecimal and click OK.
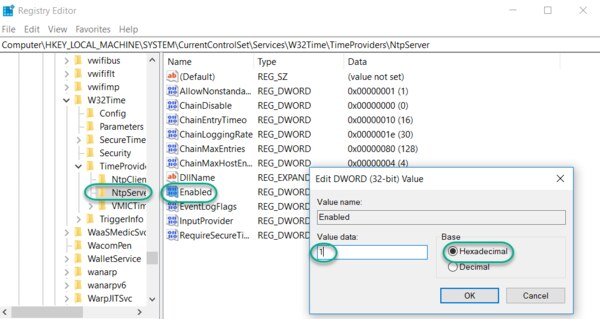
Do not close the Registry Editor because it is used in the following steps.
Update the Windows Registry to Configure the Announce Flags
Navigate to the registry key: Computer\HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\W32Time\Config
Double-click AnnounceFlags, change the Value data to 5, select a Base of Hexadecimal, and click OK.
Close the Registry Editor.
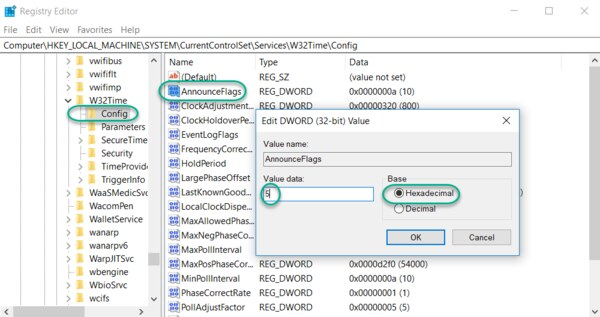
Start the Local Windows NTP Time Service
In the File Explorer, navigate to: Control Panel\System and Security\Administrative Tools
Double-click Services.
In the Services list, right-click on Windows Time and configure the following settings:
Startup type: Automatic
Service Status: Start
OK
Finally, enable UDP port 123 on the Windows firewall for incoming connections.
In Search find Firewall in Windows Defender…
Go to Incoming rules
In the right column, select New rule…
Select the rule Port
Enter UDP port 123 and click Next
Select Allow connection and click Next
Select all domains
Enter the rule name, e.g. Local NTP server, and click Finish.
The local NTP Time Server configuration is now complete. You now can synchronize the time of other computers and devices on your local network.
To test the server functionality from another PC (e.g. a service notebook) use for example the NTP Server Test Tool:
https://www.ntp-time-server.com/ntp-software/ntp-server-tool.html

DNAC deployment

C:\\Users\\Anas\\Downloads\\CatC-SW-2.3.7.7-VA.ova
Add 2 backslashes for OVA path to escape it
vcenter.home.local
administrator@vsphere.local
C0mplex30-
C:\\Users\\Anas\\Desktop\\CatC-SW-2.3.7.7-VA.ova
dnac
thick
2
data
mgmt
10.21.1.2
255.255.255.0
10.21.1.1
Mgmt interface:
172.16.25.2
255.255.255.0
DNS
172.16.32.11
NTP
172.16.32.11
dnac.home.local
maglev
C0mplex30



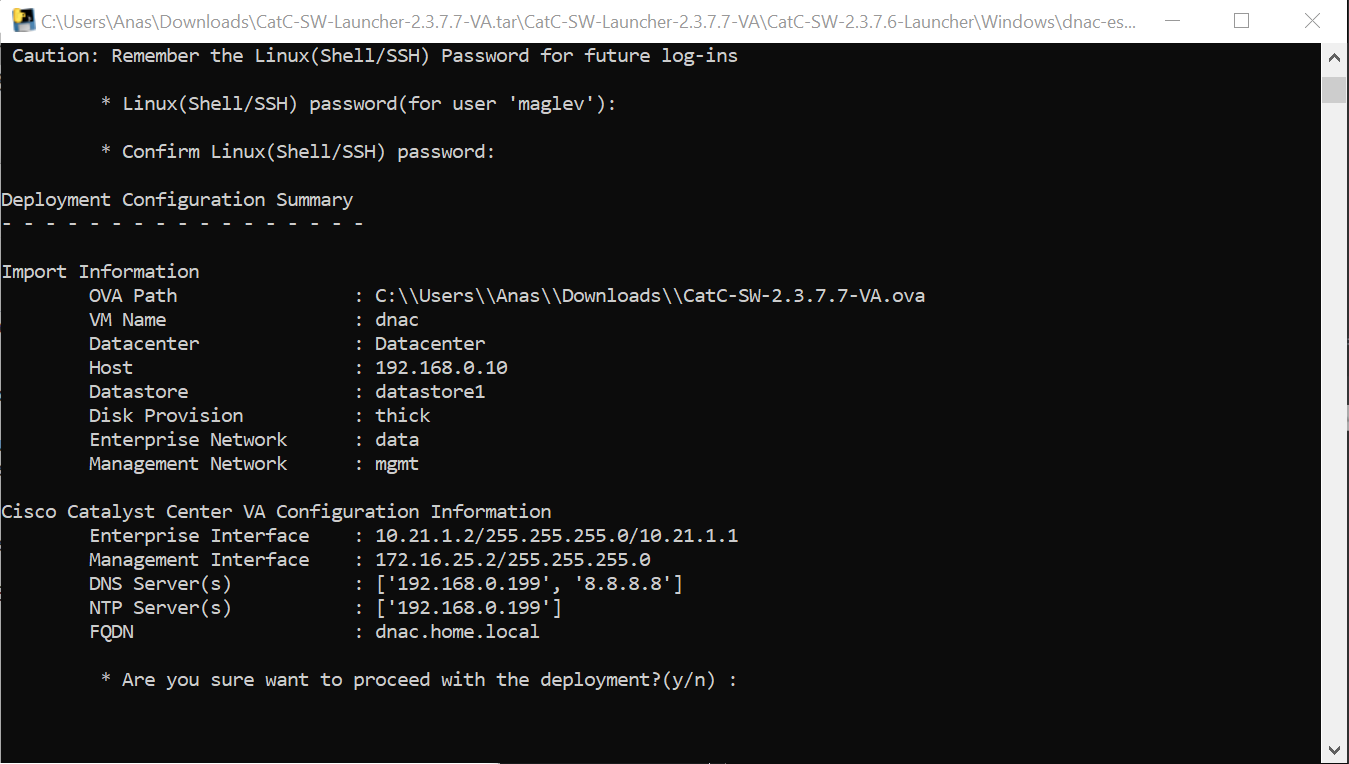




maglev will load containers

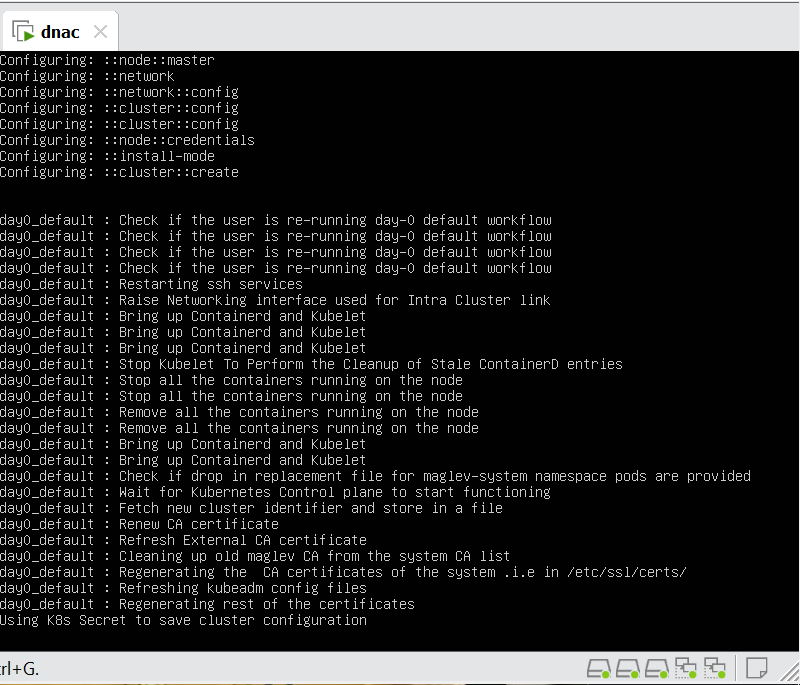
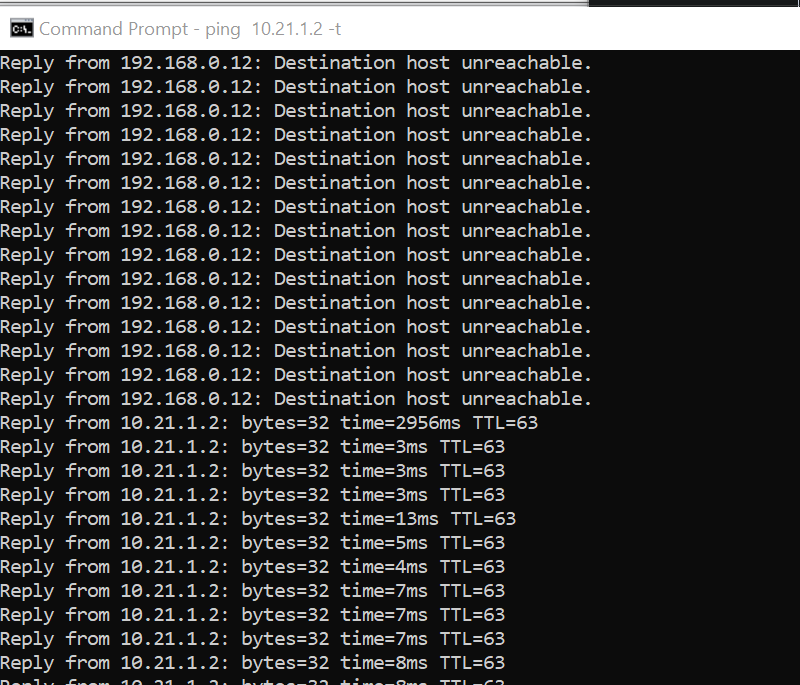

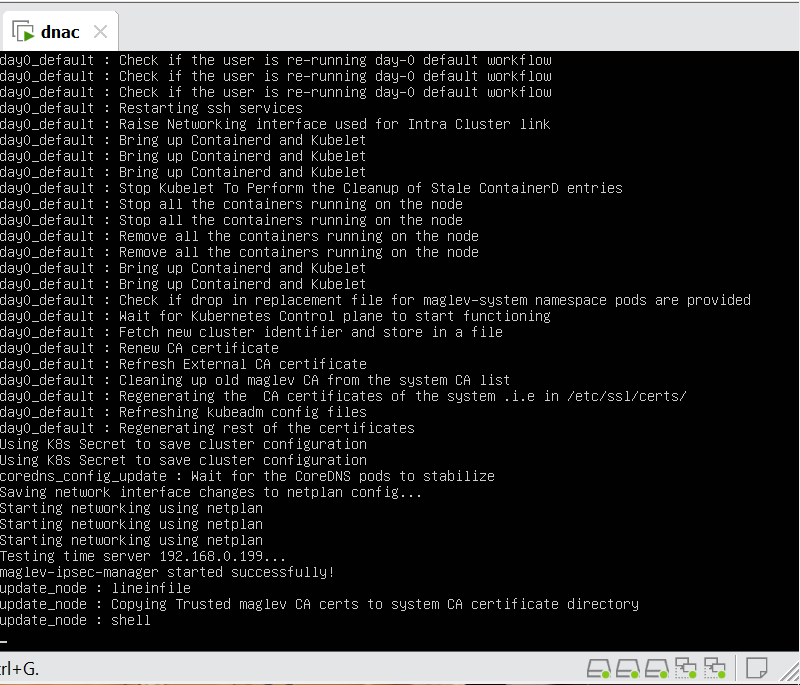
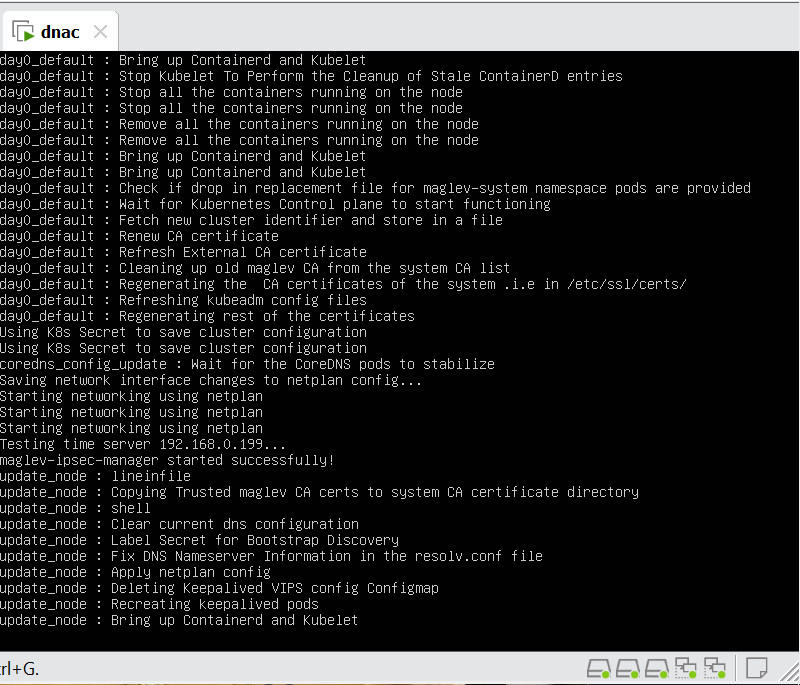
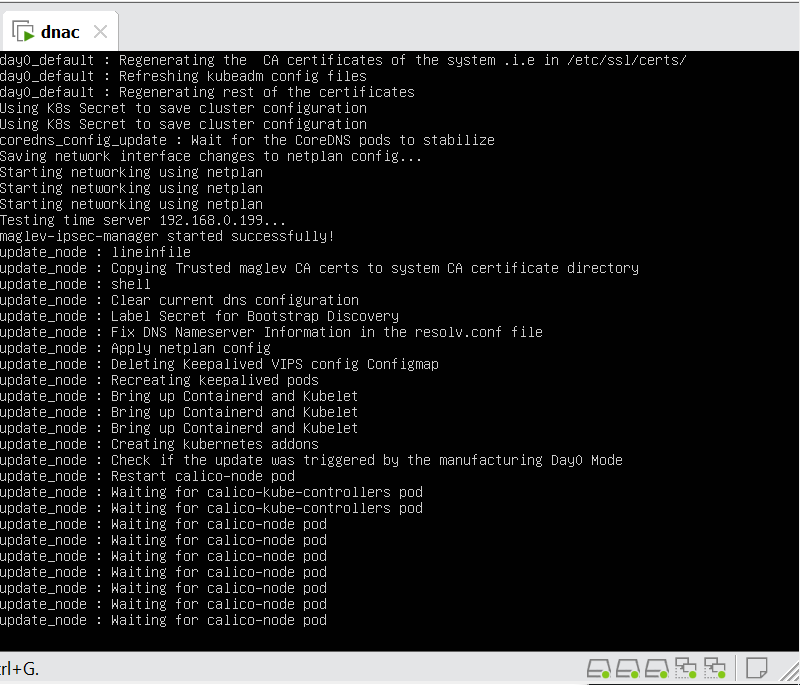
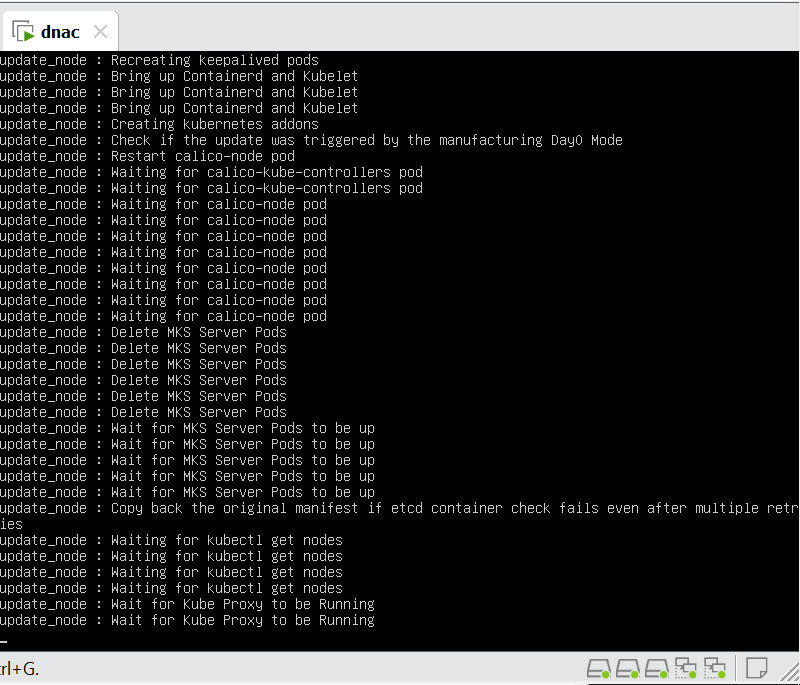
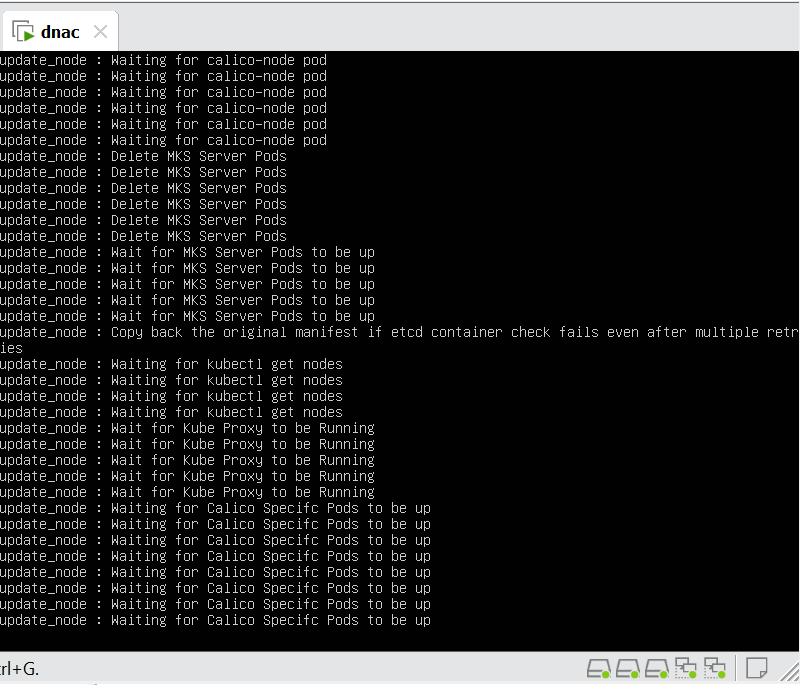
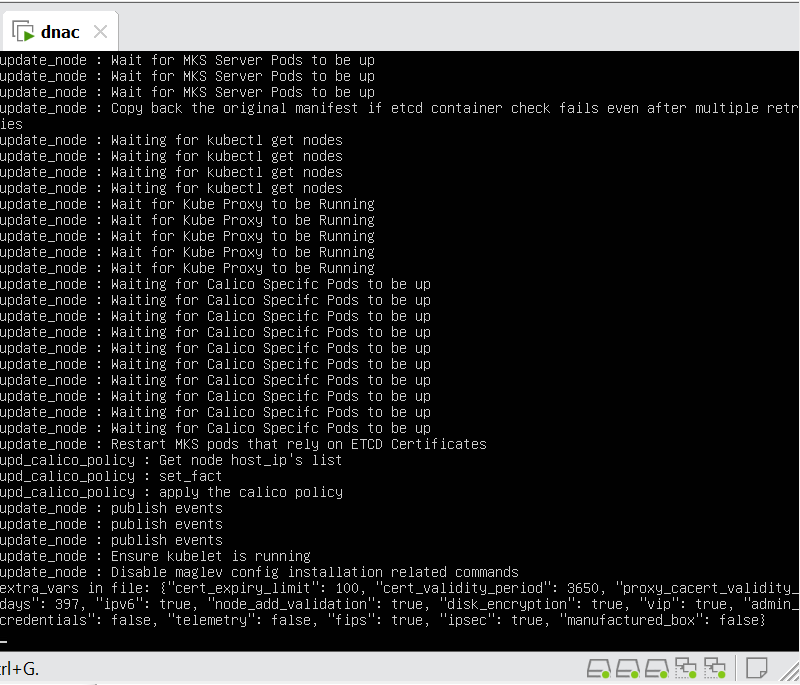

wait 30 mins before GUI shows up
In case unable to login
Login to CLI as maglev on VM’s console and reset password for admin
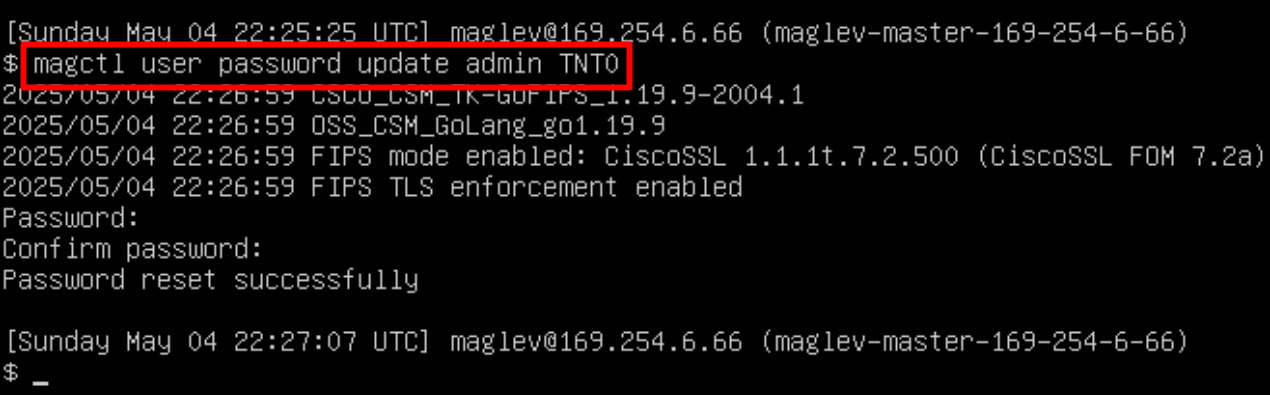
Logins
Default GUI login admin/maglev1@3
Login to create account admin_anas/C0mplex30
SSH login on port 2222 maglev/C0mplex30
DNAC VM Console login maglev/C0mplex30
Initial Login

provide user here that will be super admin such as admin_anas
provide your cco in email and not personal email
admin_anas/C0mplex30
provide company’s CCO details here that has contract and active cco – this is very important otherwise packages will not work




With new build make sure DNAC has internet access, go ahead and download the applications packages which are needed for SGT and SDA, Cisco has divided these features into applications or packages and with fresh install / build download these packages
- Download these packages
- Turn off the VM
- Take Snapshot with exact date and time
- Turn off time syncing of VM with ESXI
- ESXI add NTP server same as Windows Server
- Windows Server move back time on server when it is time to restore the VM
- When restore cut off internet access to DNAC

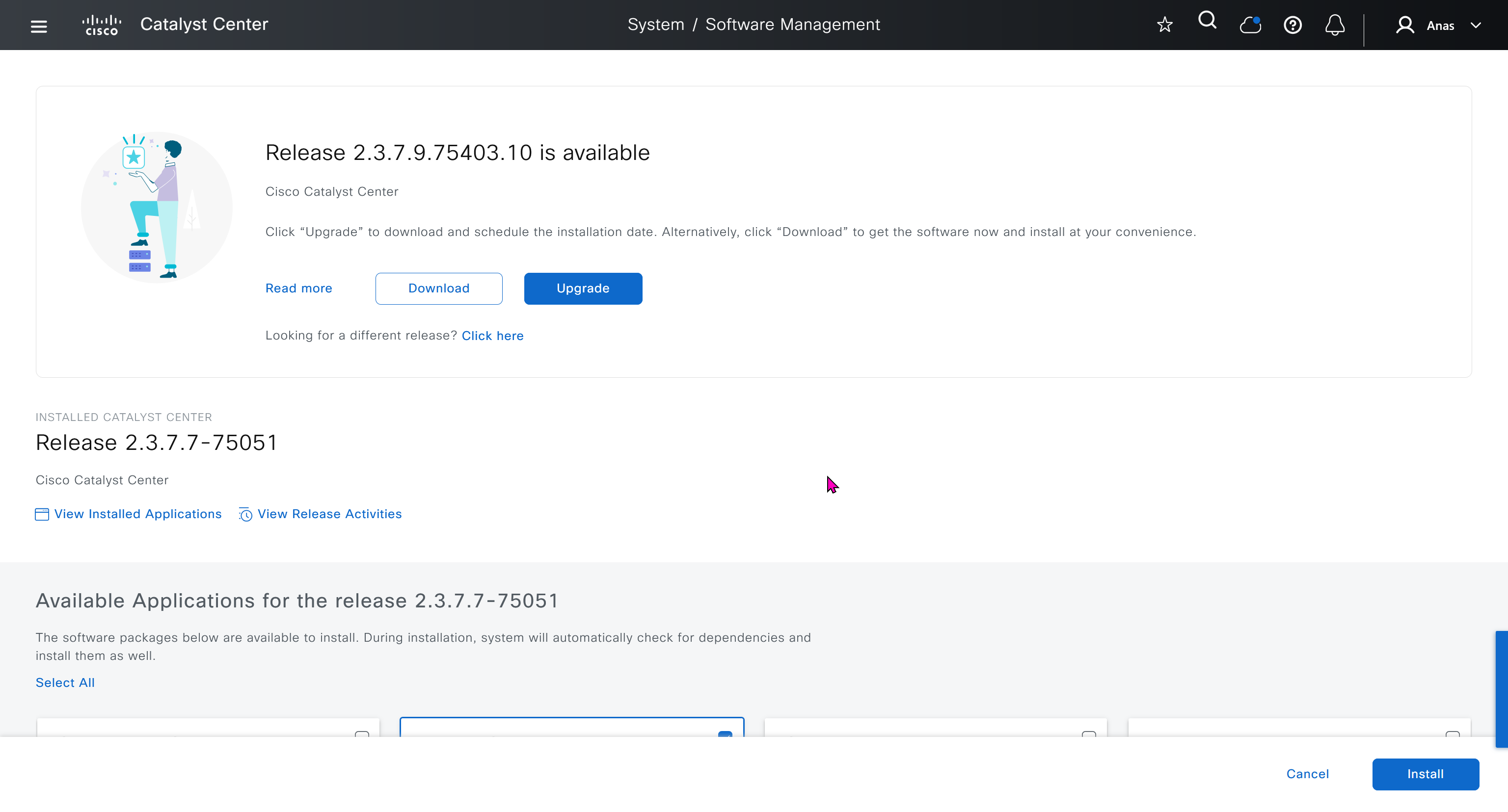
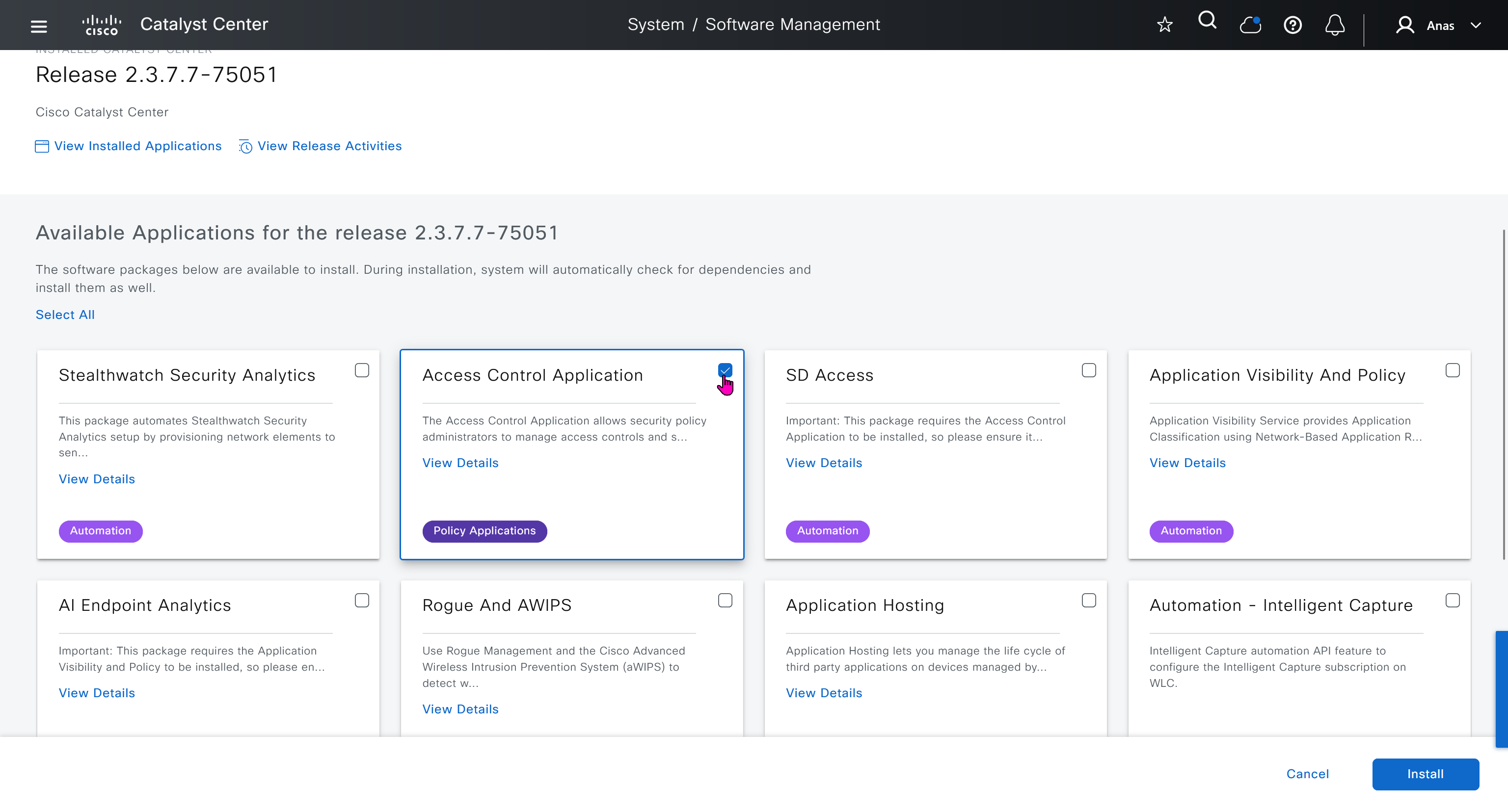
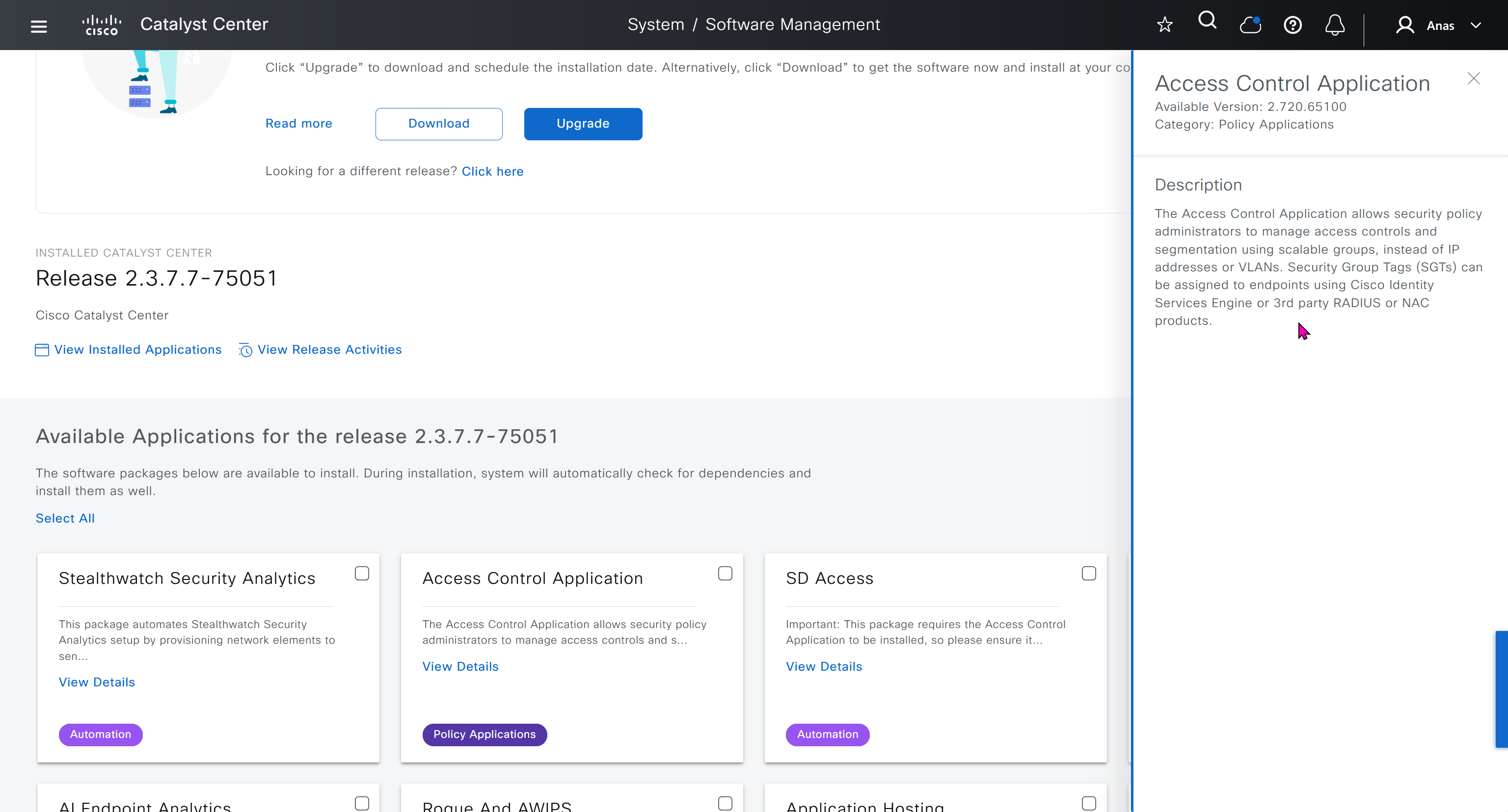
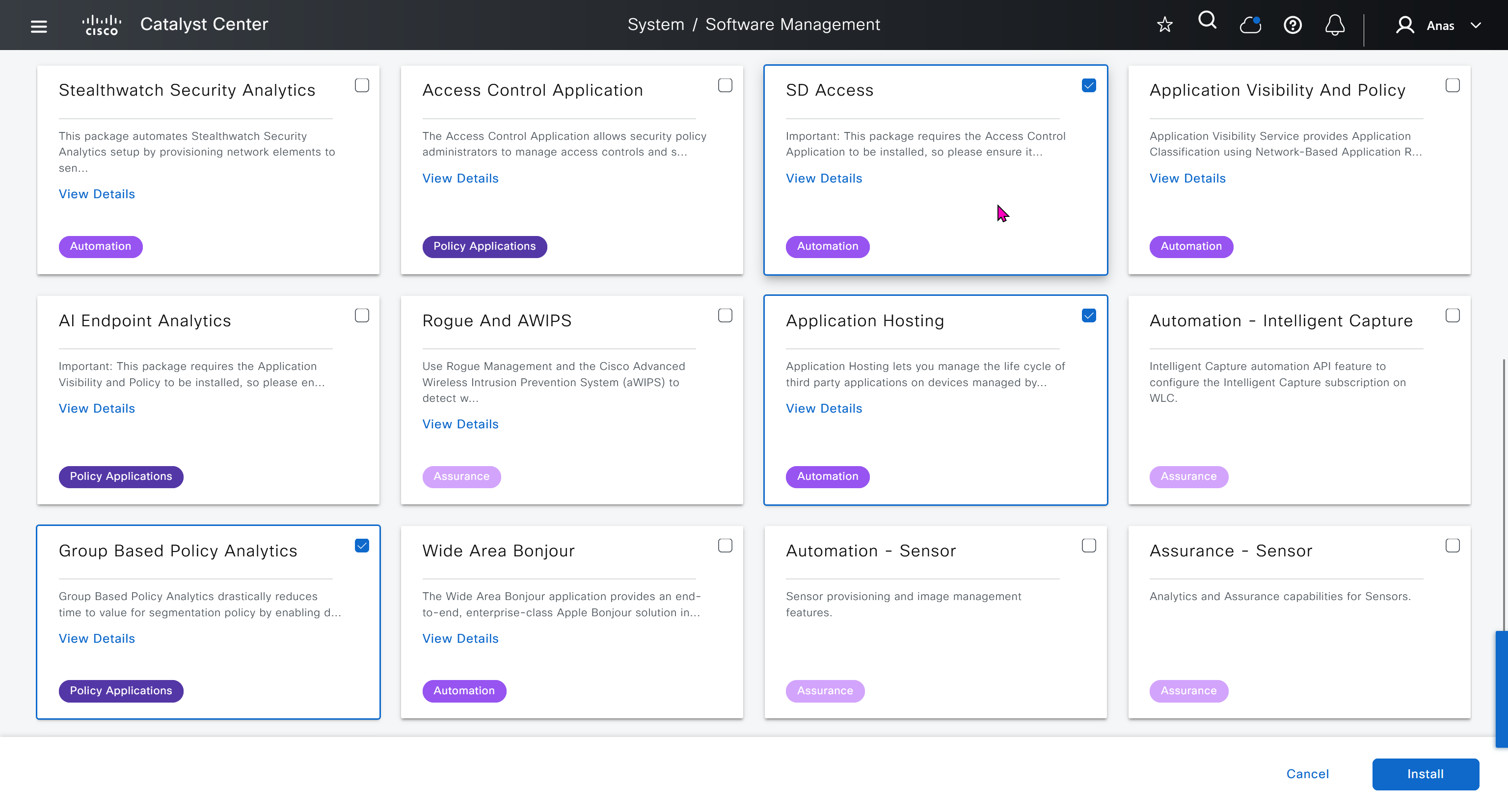




Here do not use personal email instead use email from company’s cco

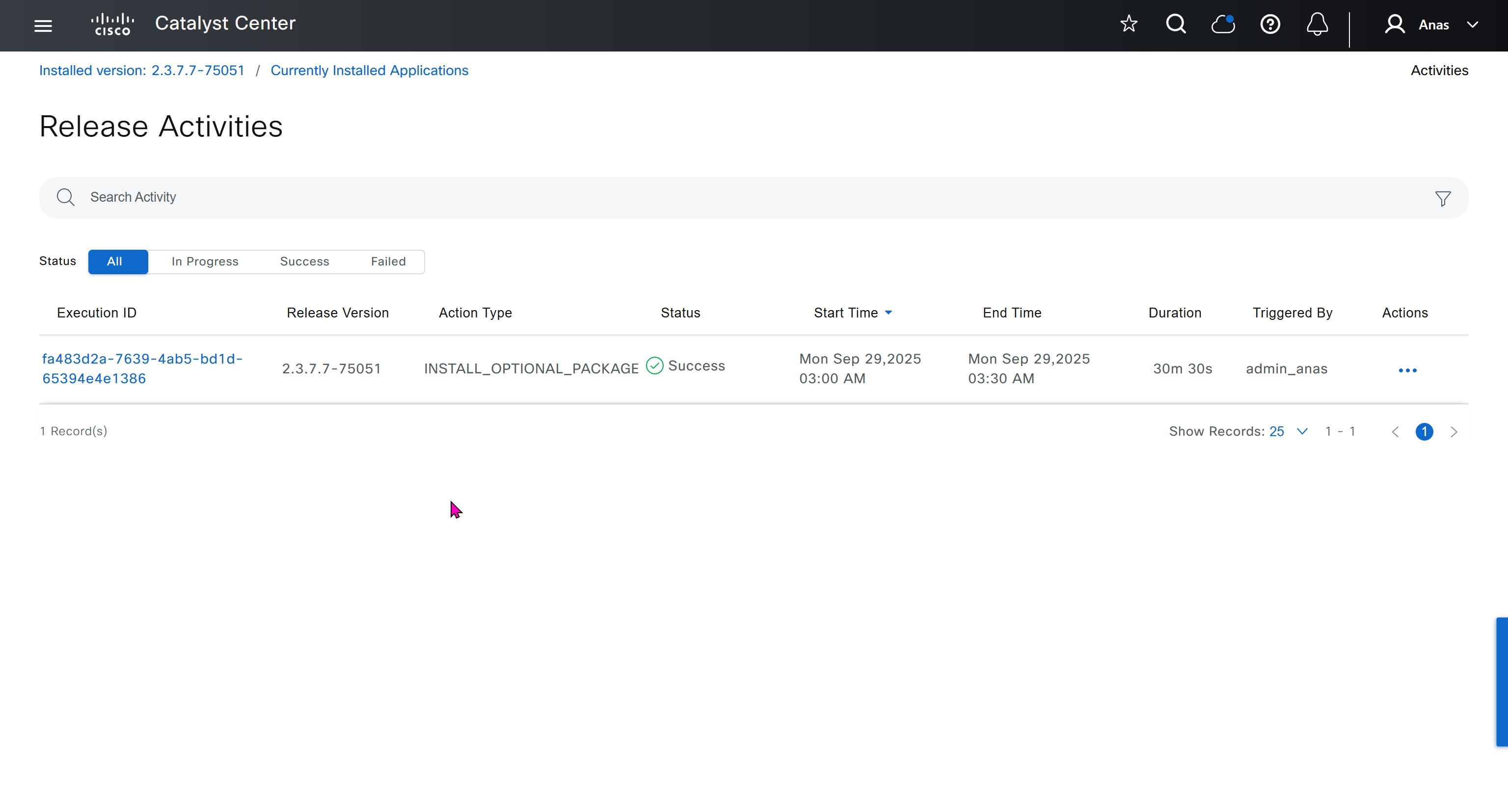
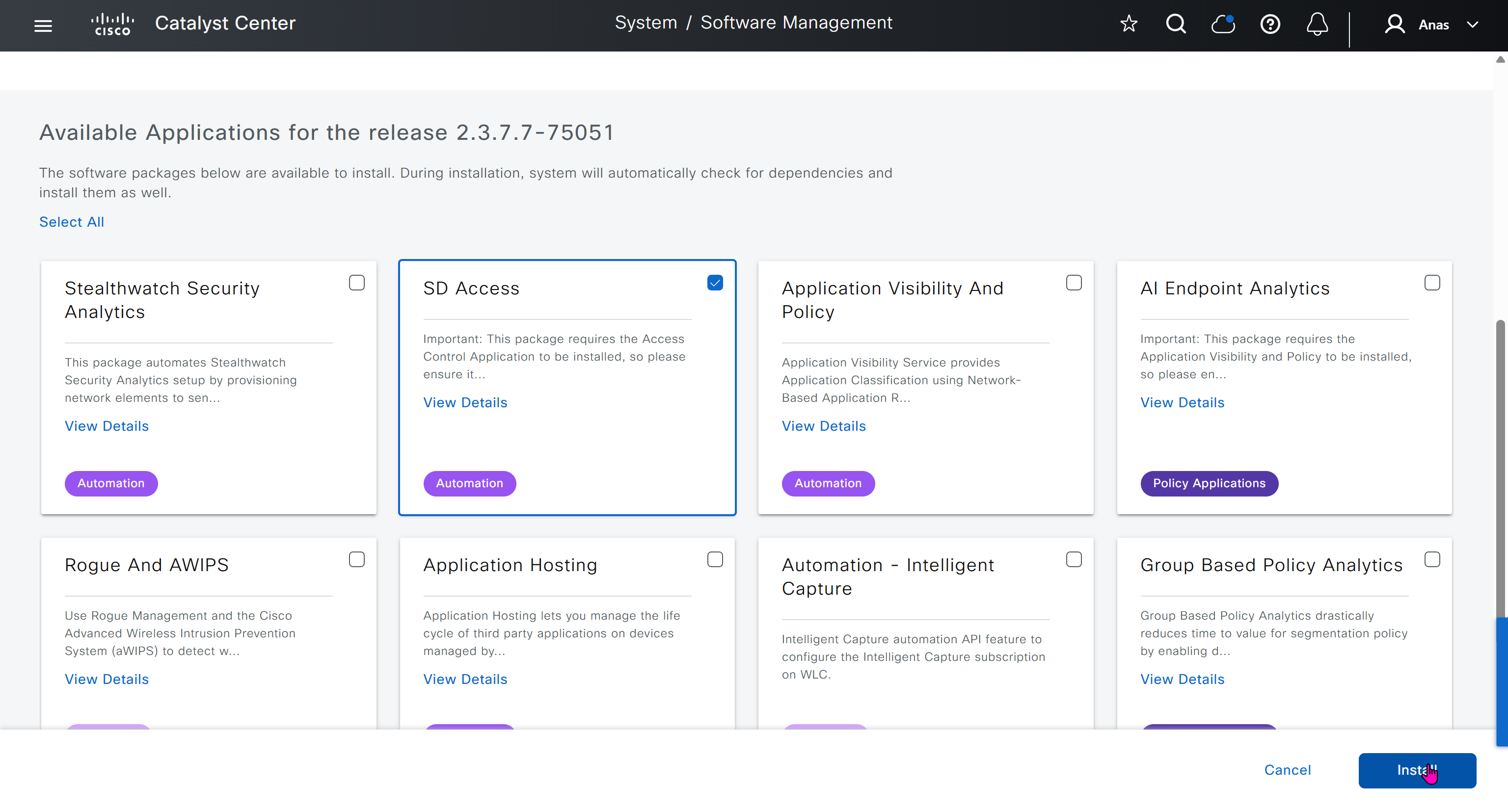
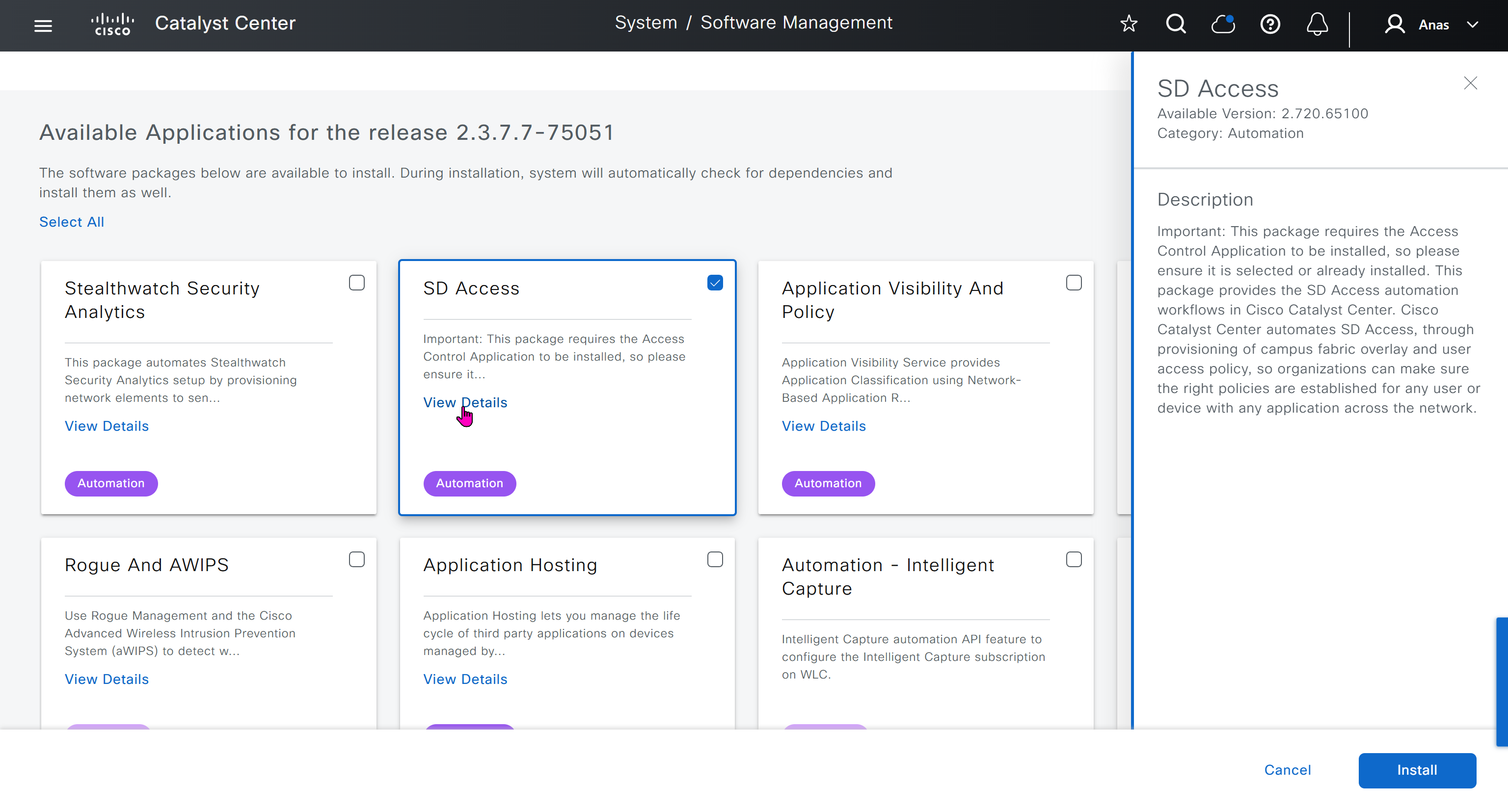
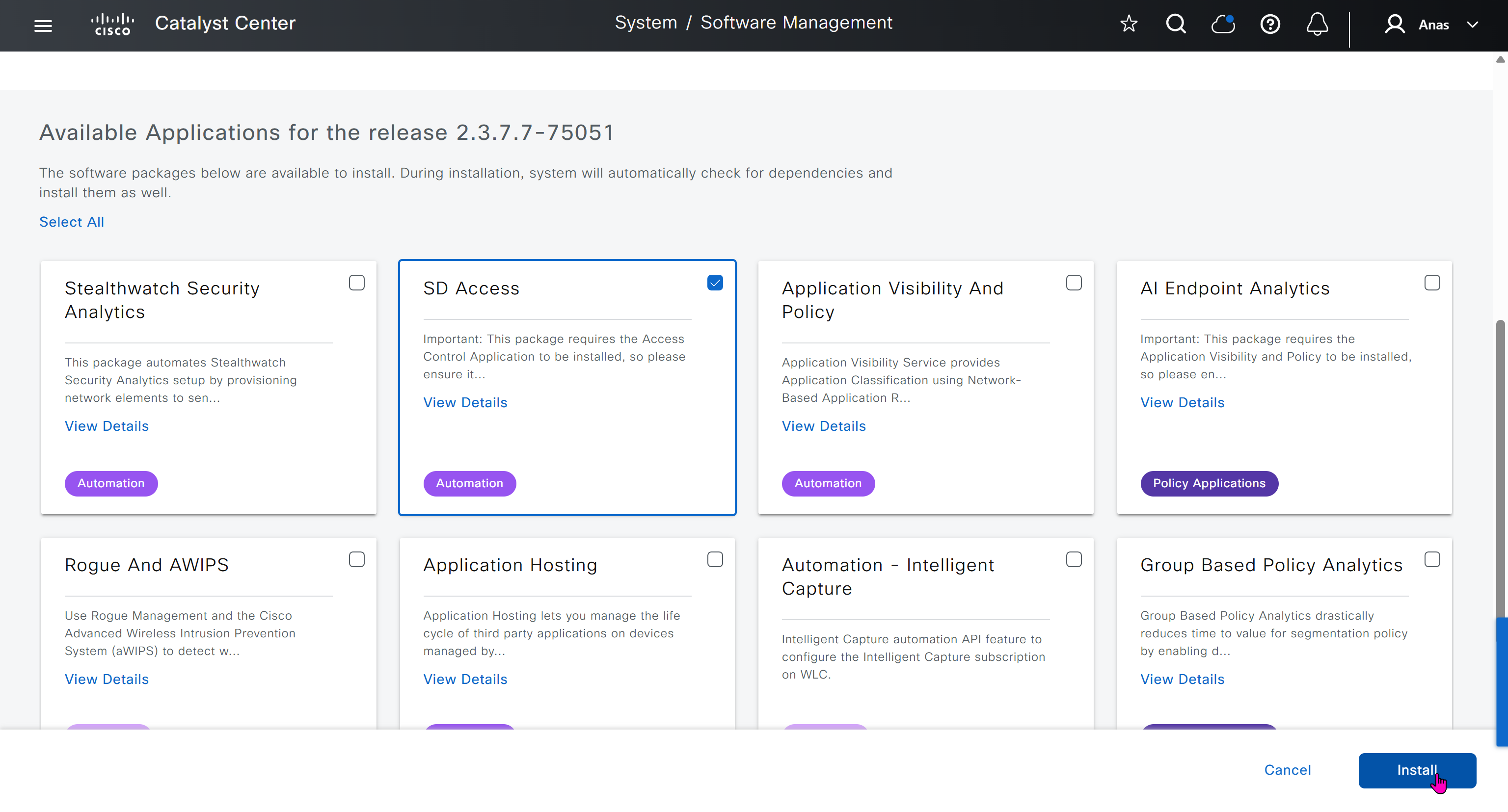

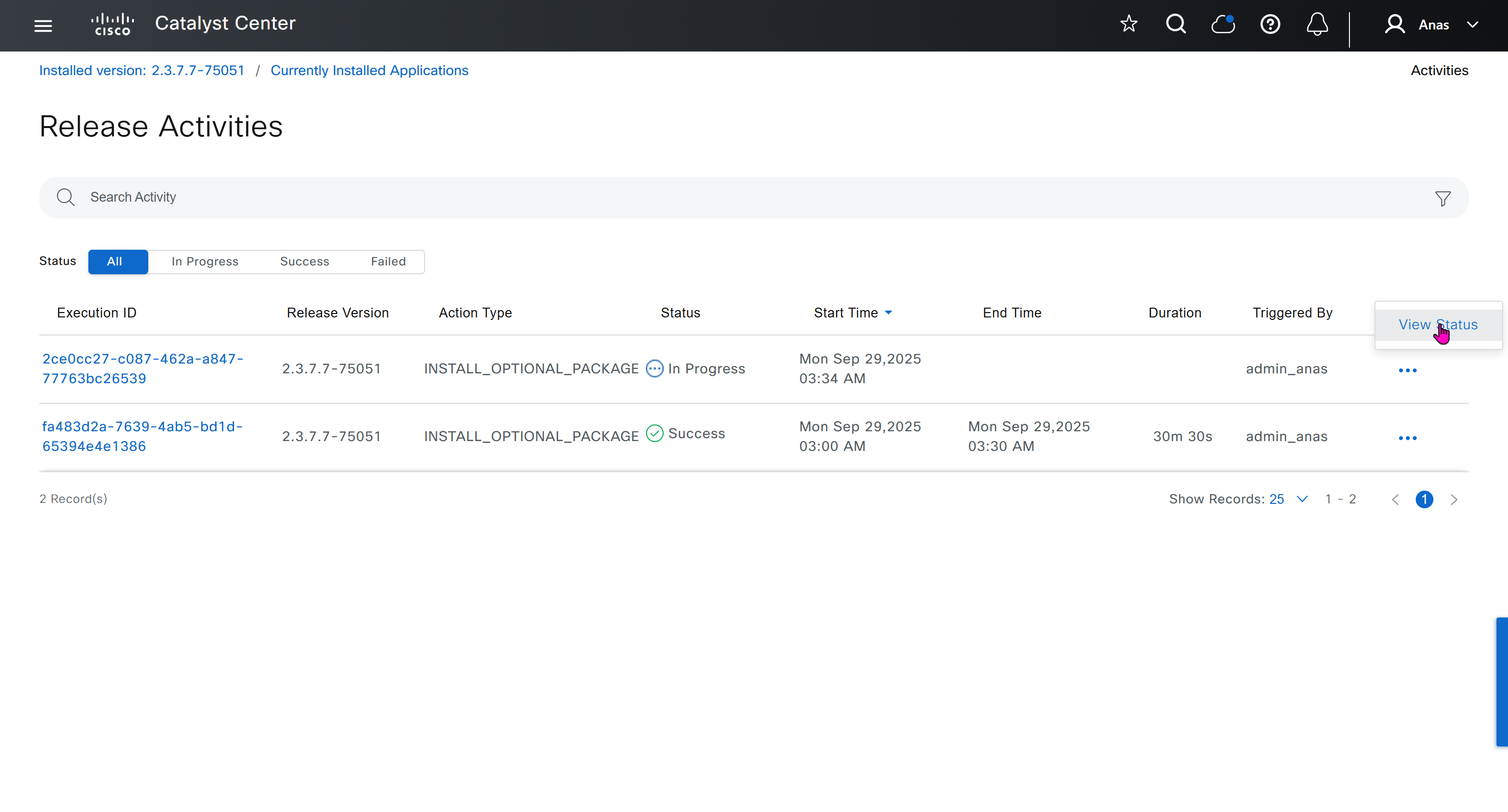
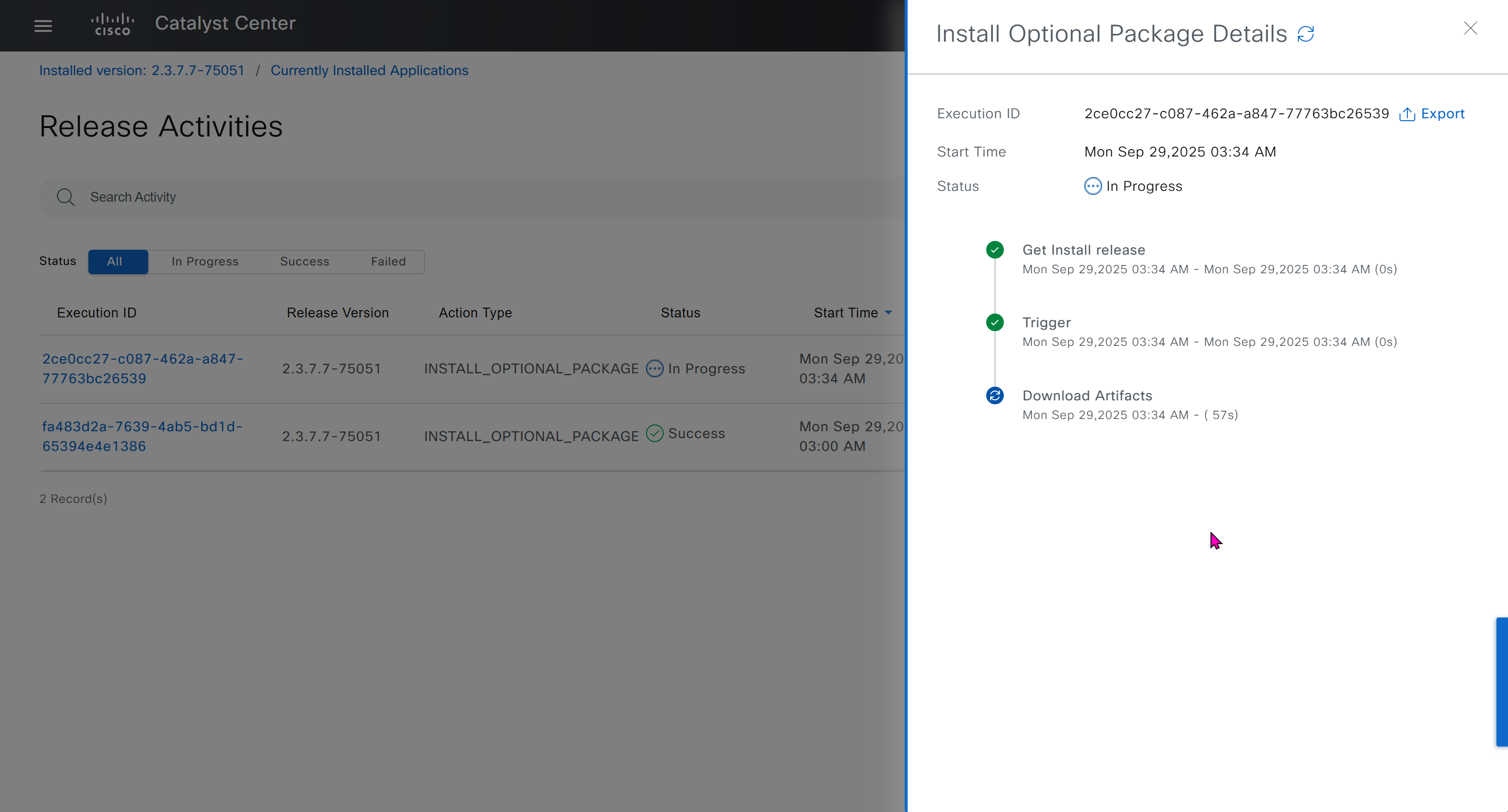

on next deployment also download below modules also
Sensor Assurance
AI Endpoint Analytics
Application Visibility and Policy (EasyQoS)
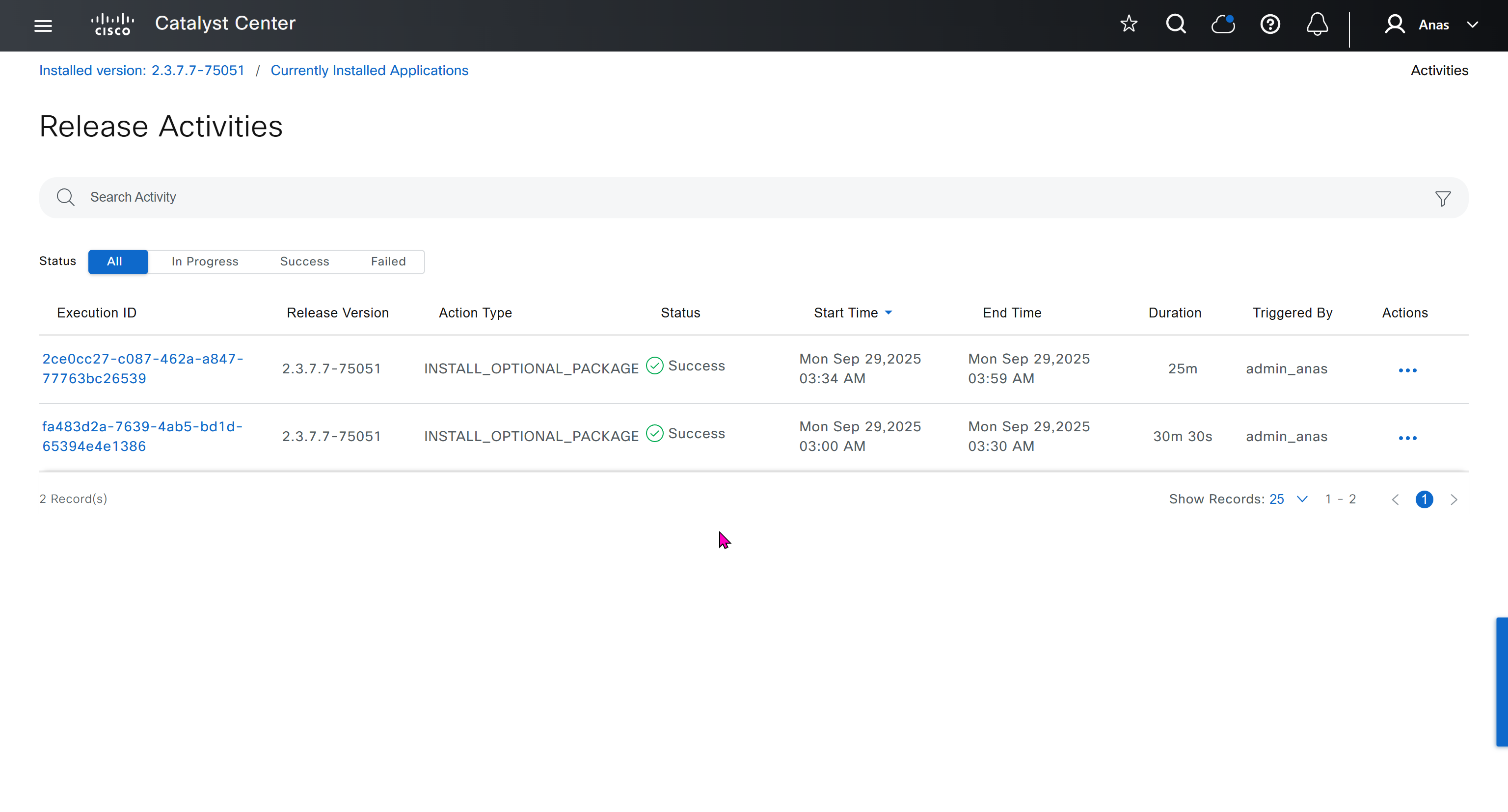
Only after these steps, add certificate to DNAC
Further configuration and ISE integration
Graceful shutdown DNAC
! Cat center shutdown
$ shutdown
! VYOS shutdown
sudo bash
shutdown -h now
! vcenter shutdown
Gracefully shutdown from esxiSDA Links
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/cloud-systems-management/network-automation-and-management/catalyst-center/catalyst-center-va/esxi/2-3-7/deployment-guide/b_cisco_catalyst_center_237x_on_esxi_deployment_guide.html#configure-a-virtual-appliance-using-the-interactive-cc-va-launcher
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/SD-Access-Distributed-Campus-Deployment-Guide-2019JUL.html
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/sda-fabric-deploy-2019oct.pdf
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/cisco-sda-design-guide.html
https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/CVD-Software-Defined-Access-Segmentation-Design-Guide-2018MAY.pdf